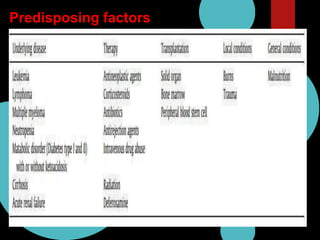
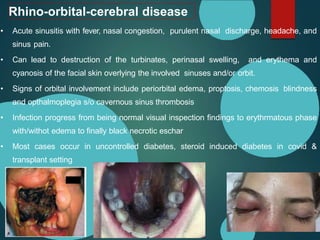
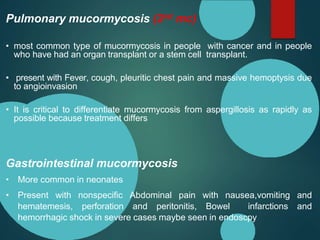
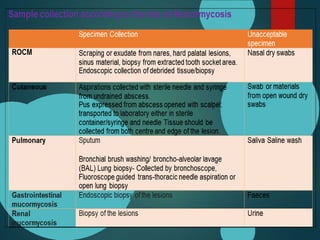
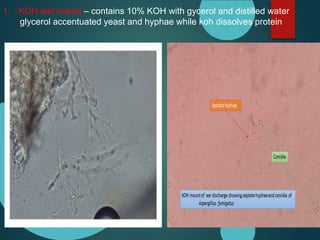
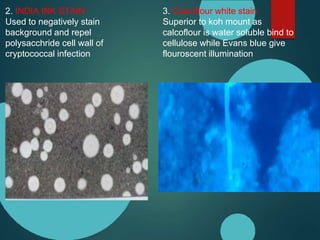
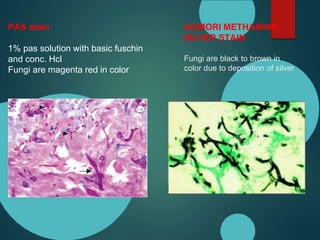
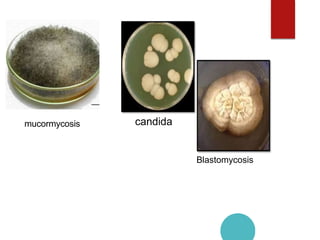
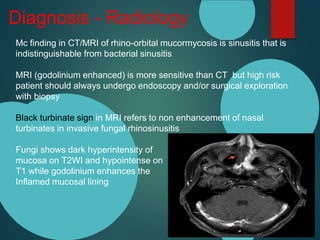
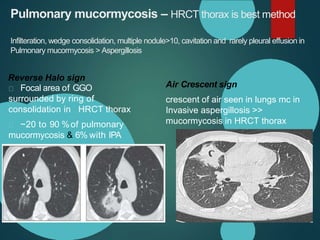
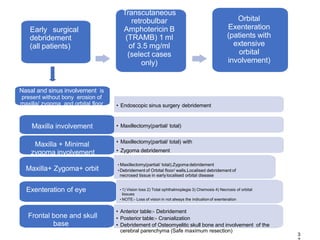
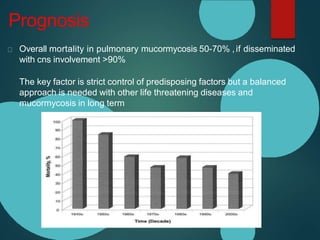
Mucormycosis is caused by fungi of the order Mucorales. It is an opportunistic infection seen in immunocompromised patients. The rhino-orbito-cerebral form presents as sinusitis that can invade the orbit and brain. Pulmonary mucormycosis is the second most common type seen in cancer and transplant patients. Diagnosis requires tissue biopsy demonstrating wide, ribbon-like hyphae. Treatment involves antifungal therapy with amphotericin B and surgical debridement of infected tissues. Prognosis depends on early diagnosis and treatment.