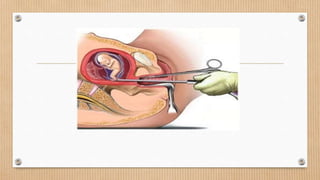
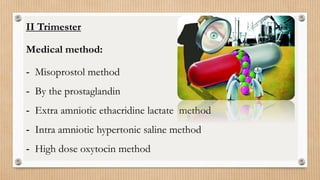
The lesson plan focuses on medical termination of pregnancy (MTP) by outlining its objectives, legal framework, procedures, and complications. It covers the definition and implications of MTP in nursing practice, legal requirements for abortion in India, and various methods employed for termination. By the end of the seminar, students will gain a comprehensive understanding of MTP and its application in clinical settings.