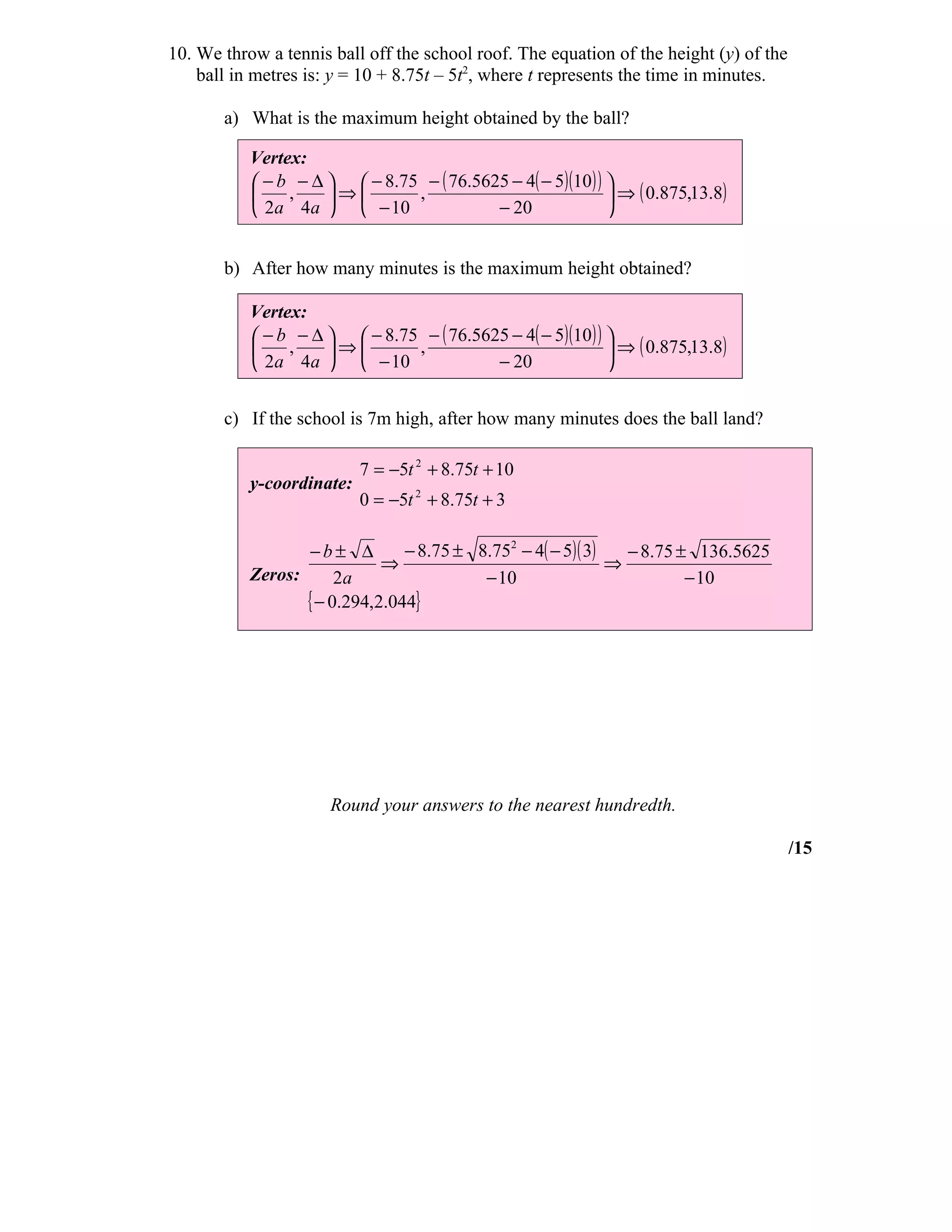
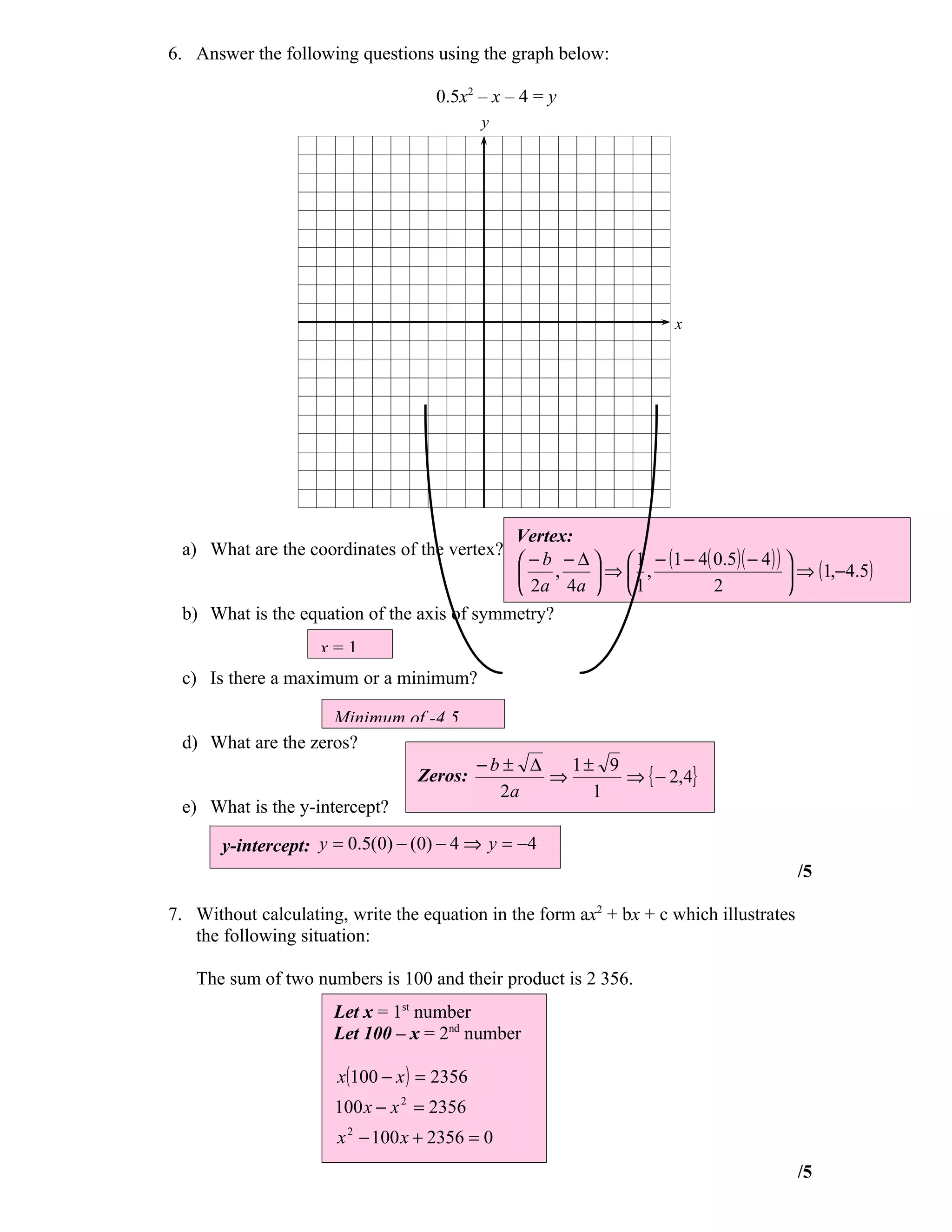
This document contains the answer key for a math test on quadratic functions. It includes:
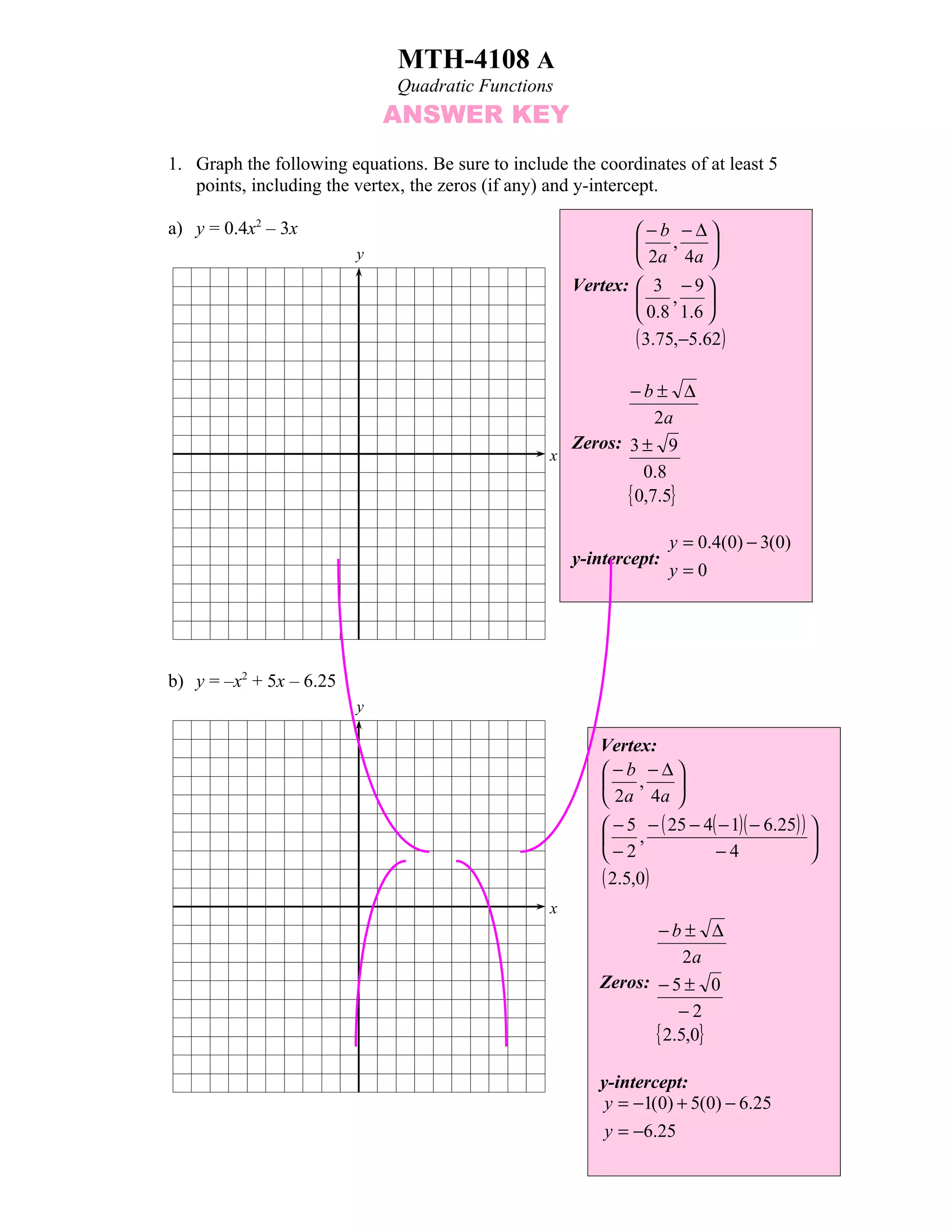
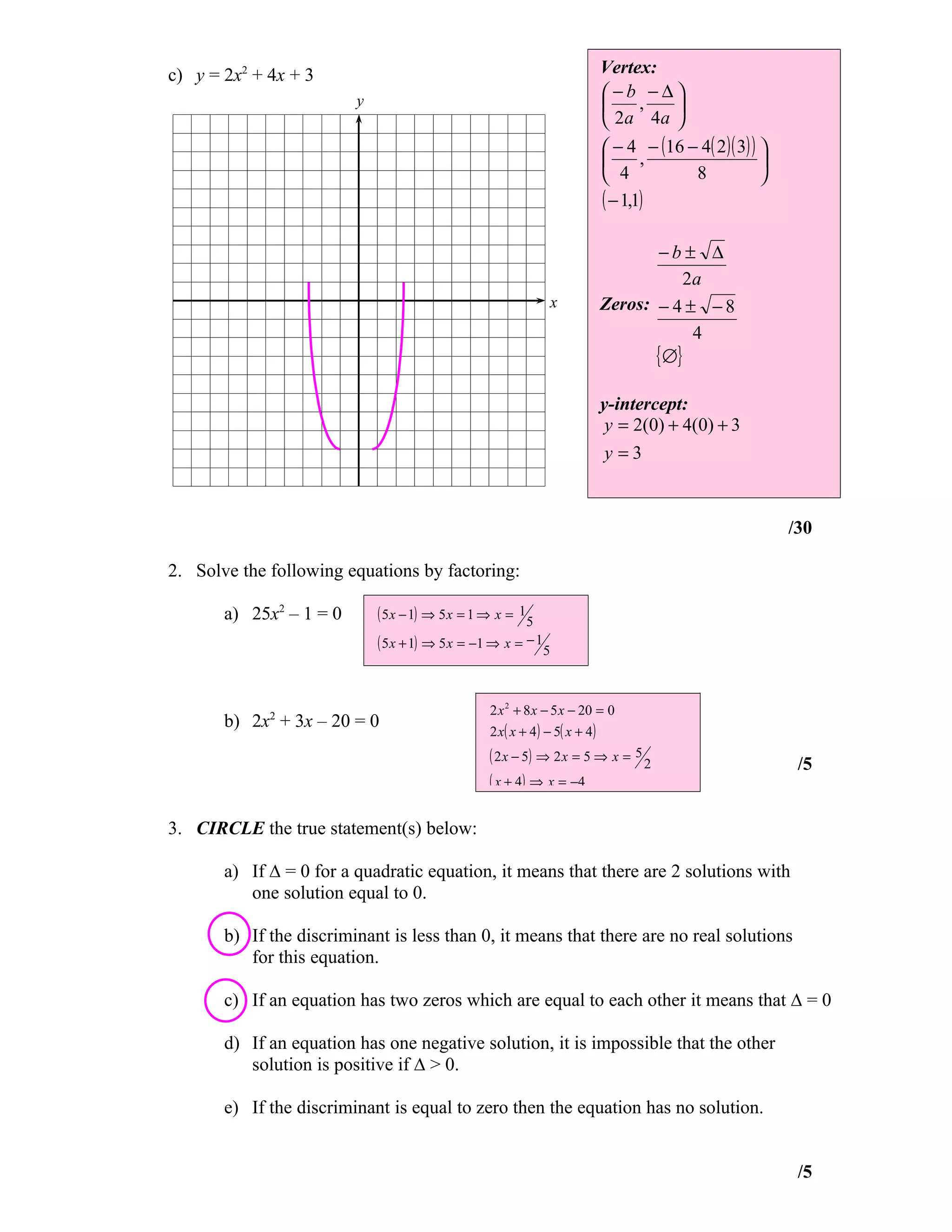
1) Graphing quadratic equations and finding vertices, zeros, and y-intercepts.
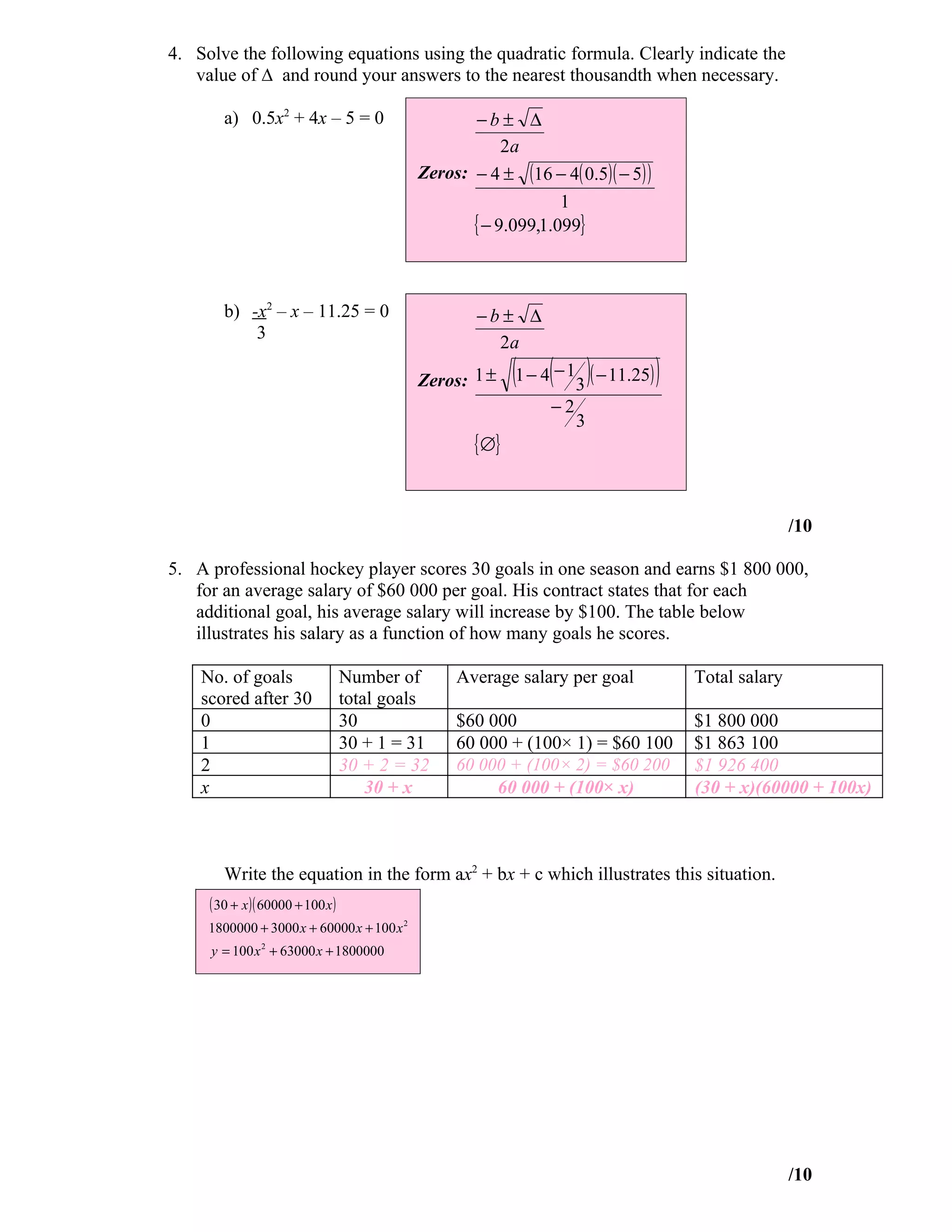
2) Solving quadratic equations by factoring.
3) Using the quadratic formula to solve equations.
4) Questions about salaries as a function of goals scored, the areas of trapezoids, and the maximum height of a tennis ball thrown in the air.
![8. The small base of a trapezoid measures double the height. The large base
measures 3 metres more than the small base and the area of the trapezoid is equal
to 123.75 metres squared. What are the measurements of the small base, large
base and height of this trapezoid?
Let x = height
Let 2x = small base
Let 2x + 3 = large base
x[ 2 x + ( 2 x + 3) ]
= 123.75 −b± ∆
2
2a
x[ 4 x + 3]
= 123.75 − 3 ± 9 − 4( 4 )( − 247.5)
2
Zeros: 8
4 x 2 + 3 x 123.75
= − 3 ± 3969
2 1
4 x + 3 x = 247.5
2 8
{ − 8.25,7.5}
4 x 2 + 3 x − 247.5 = 0
/5
9. A sports store sells a certain number of bicycles at the regular price and receives
$17 500 profit. The following week the bikes go on sale for $150 less each
bicycle, and the store sells 15 more bicycles for the same total profit as the
previous week. What is the regular price of one bicycle?
Let x = price of one bicycle
17500 17500
+ 15 = −b± ∆
x x − 150
17500 + 15 x 17500 2a
=
x x − 150 150 ± 22500 − 4(1)( − 175000 )
17500 x − 2625000 + 15 x 2 − 2250 x = 17500 x Zeros: 2
150 ± 850
15 x 2 − 2250 x − 2625000 = 0
2
{ − 350,500}
x 2 − 150 x − 175000 = 0
/10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mth-4108-1aans-120306133634-phpapp01/75/Mth-4108-1-a-ans-5-2048.jpg)