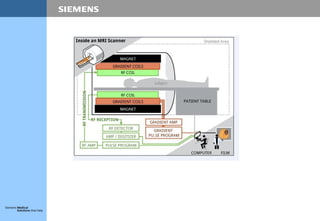
When performing an MRI scan, a patient is placed inside a cylinder containing a strong magnet. Radio waves are introduced, causing the body's atoms to resonate and emit signals. A computer translates these signals into a two-dimensional image. MRI uses magnets to align the spin of hydrogen nuclei in the body. Radio pulses cause the spins to resonate, and the emitted signals are detected to form an image. MRI magnets can be permanent, resistive, or superconductive depending on the required field strength.