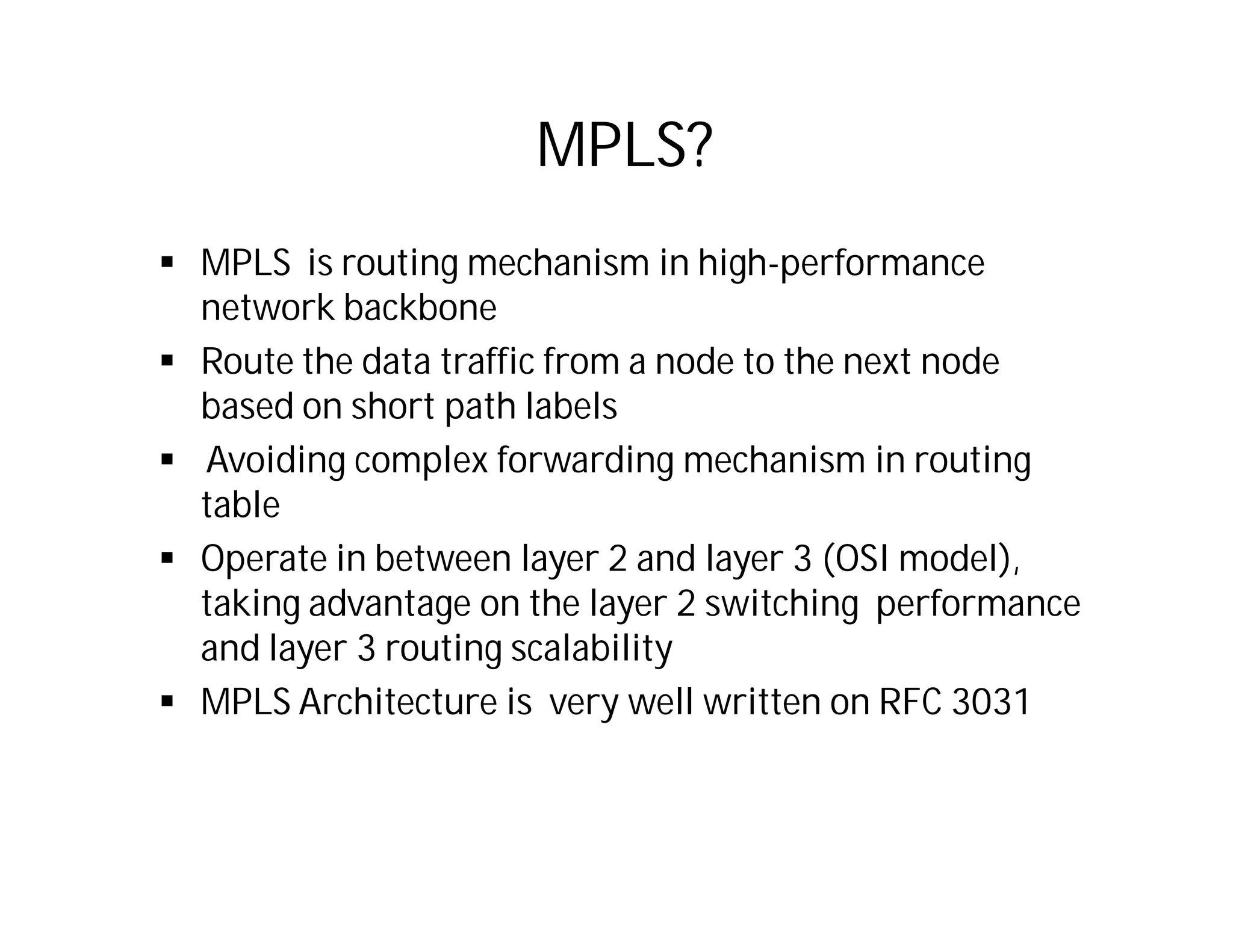
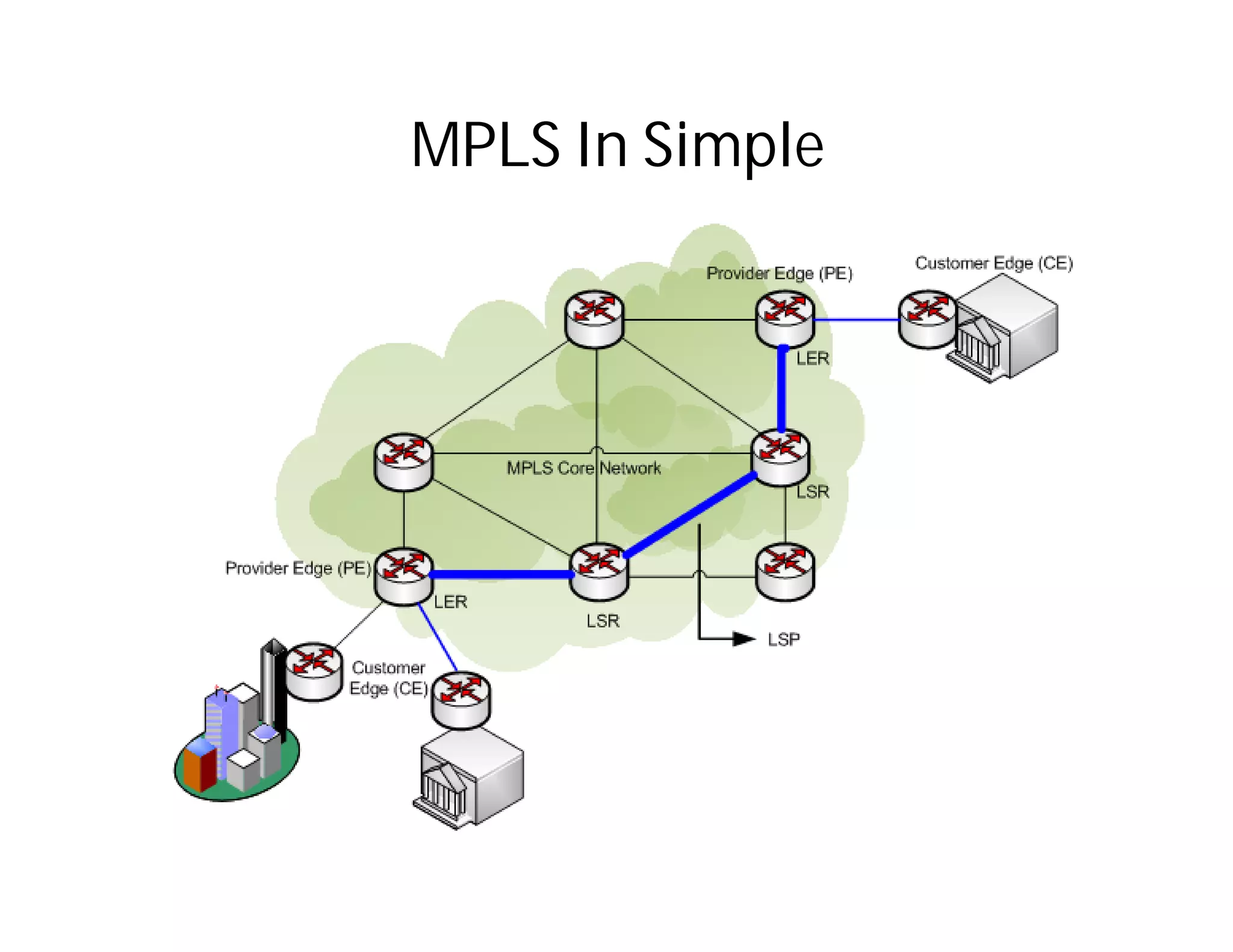
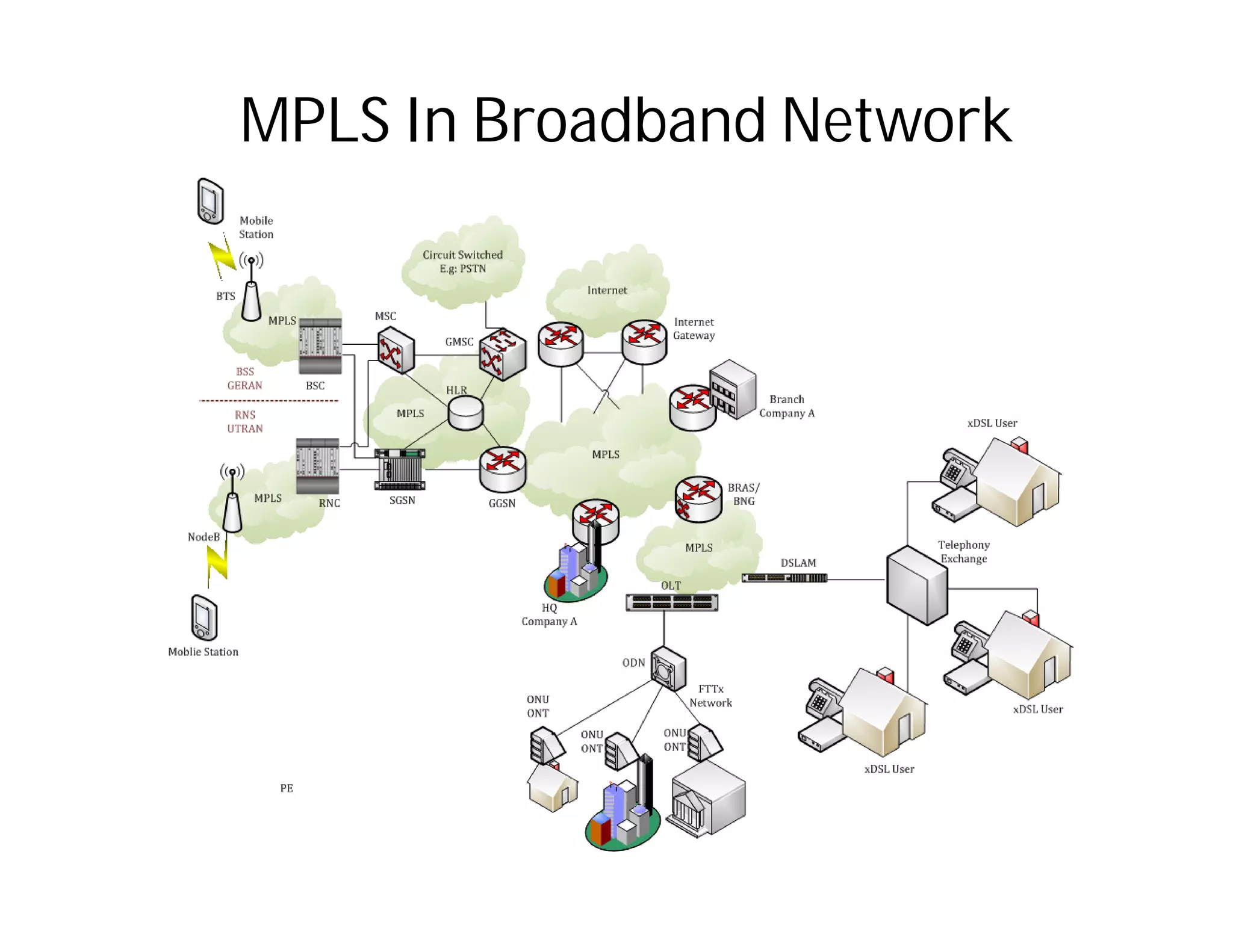
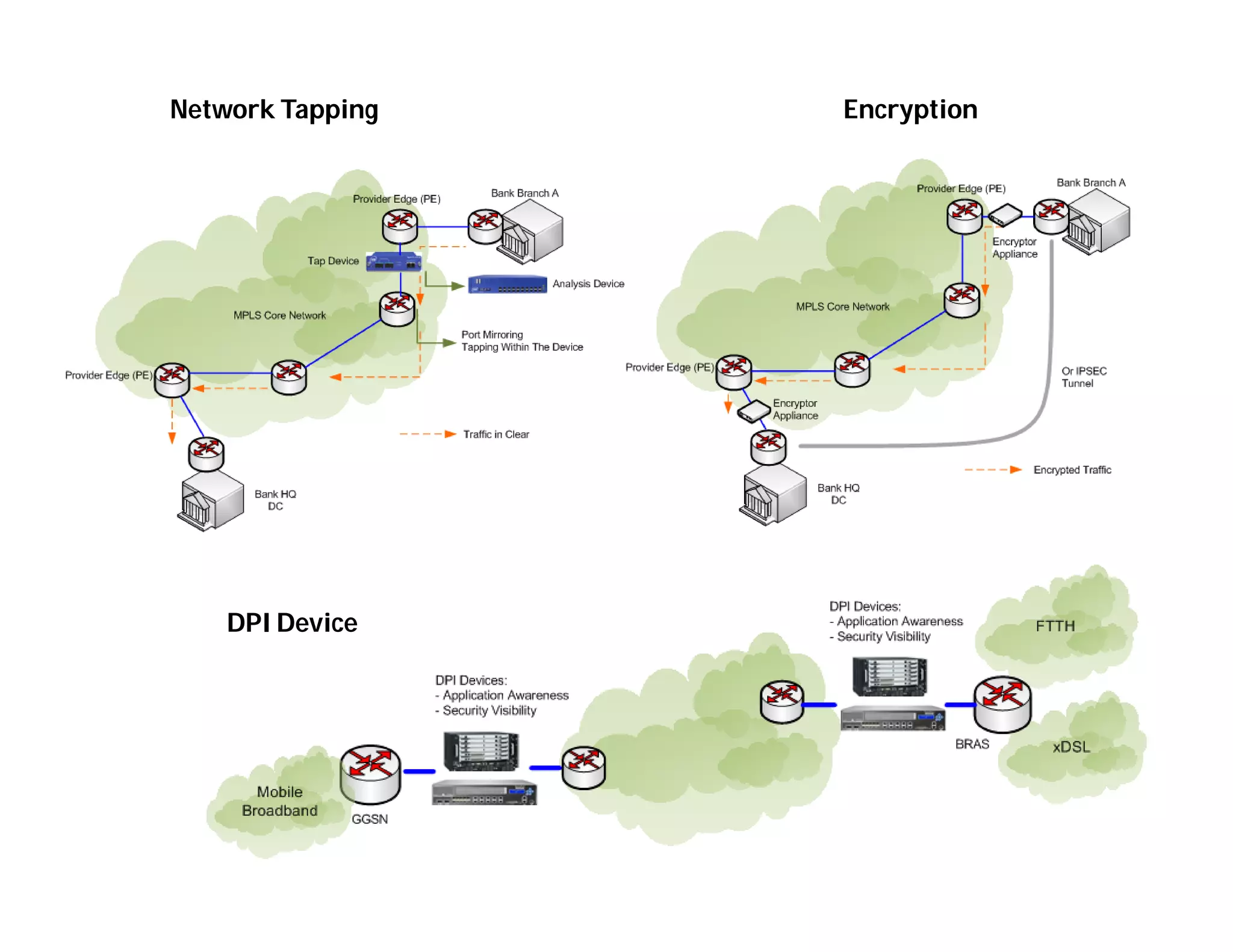
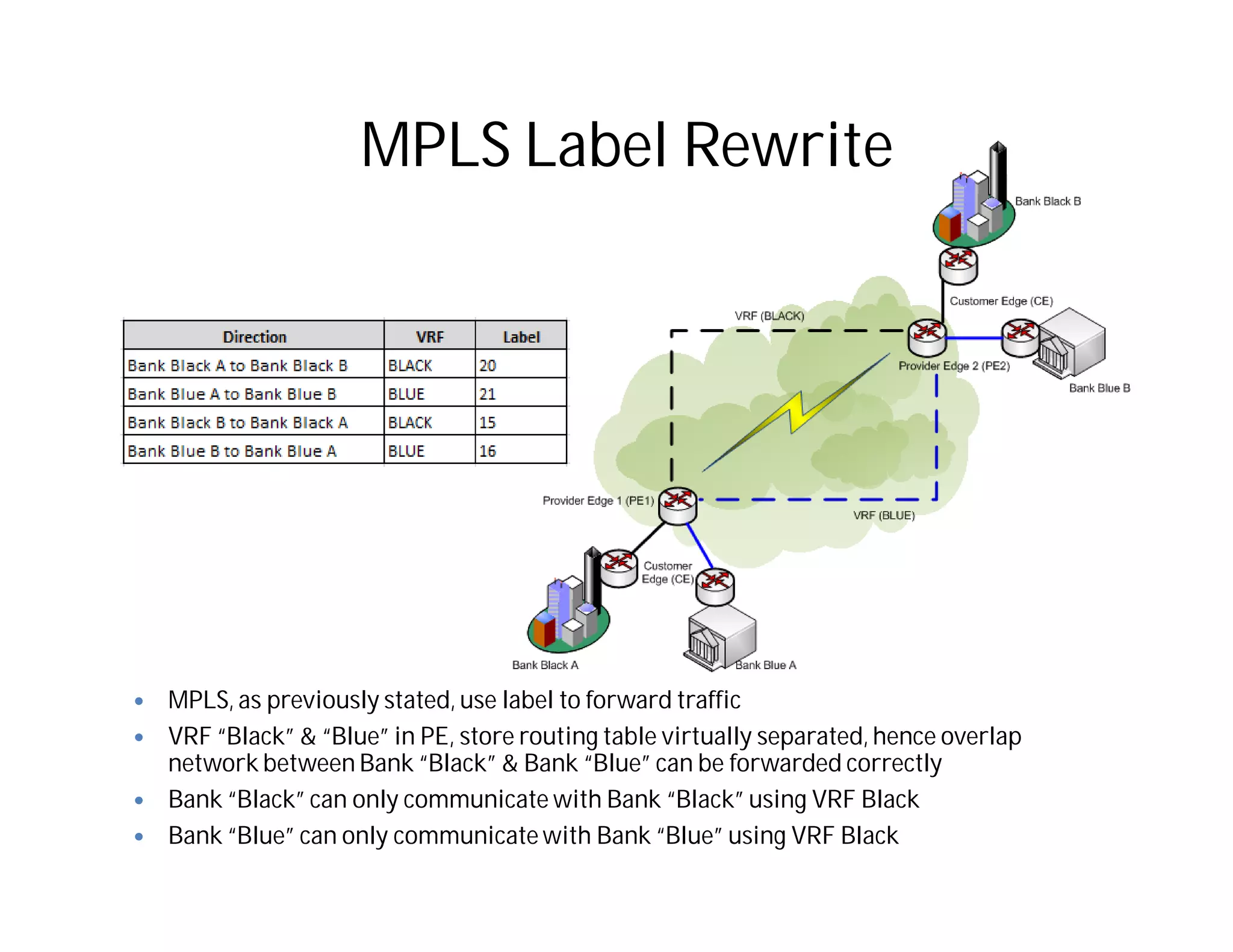
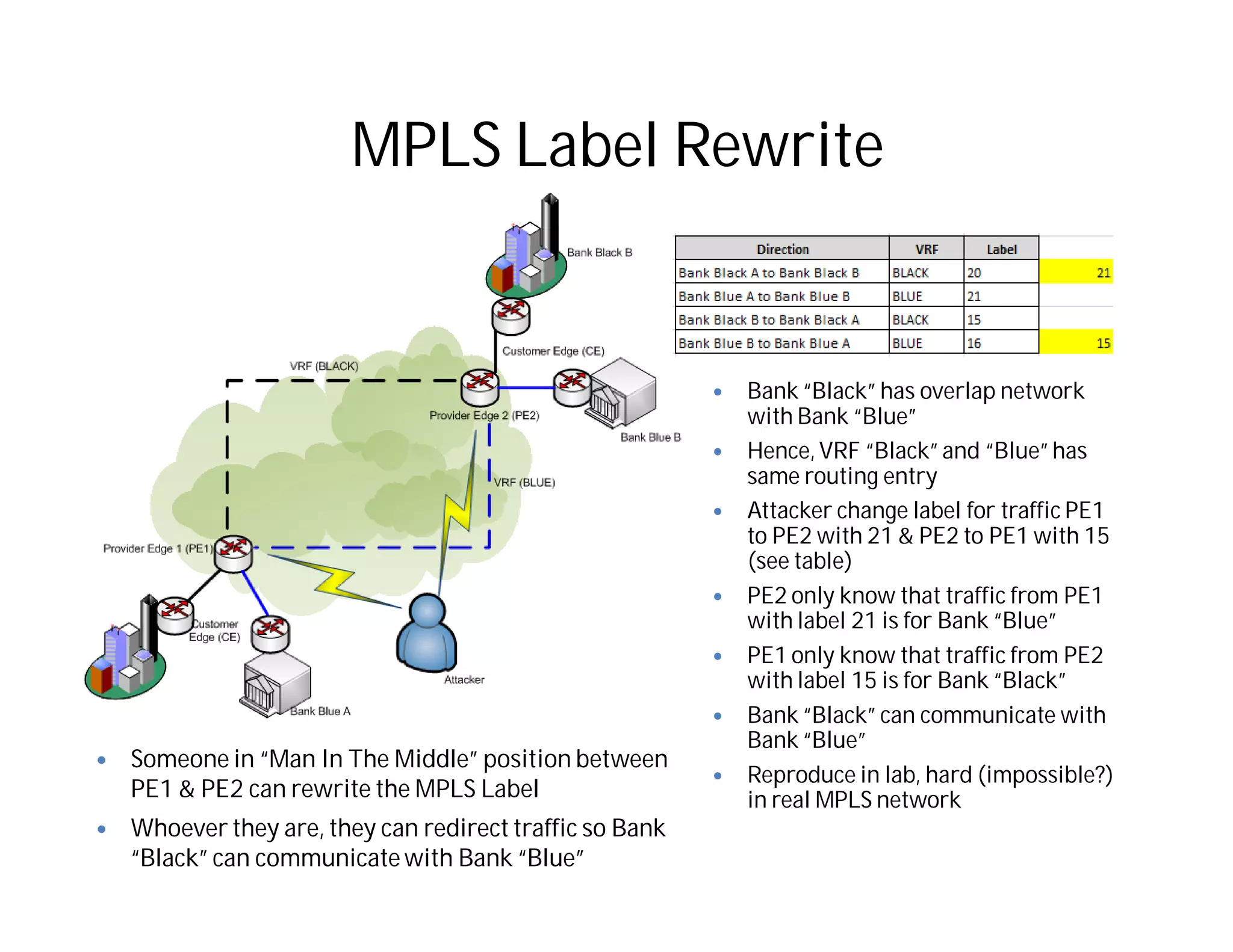
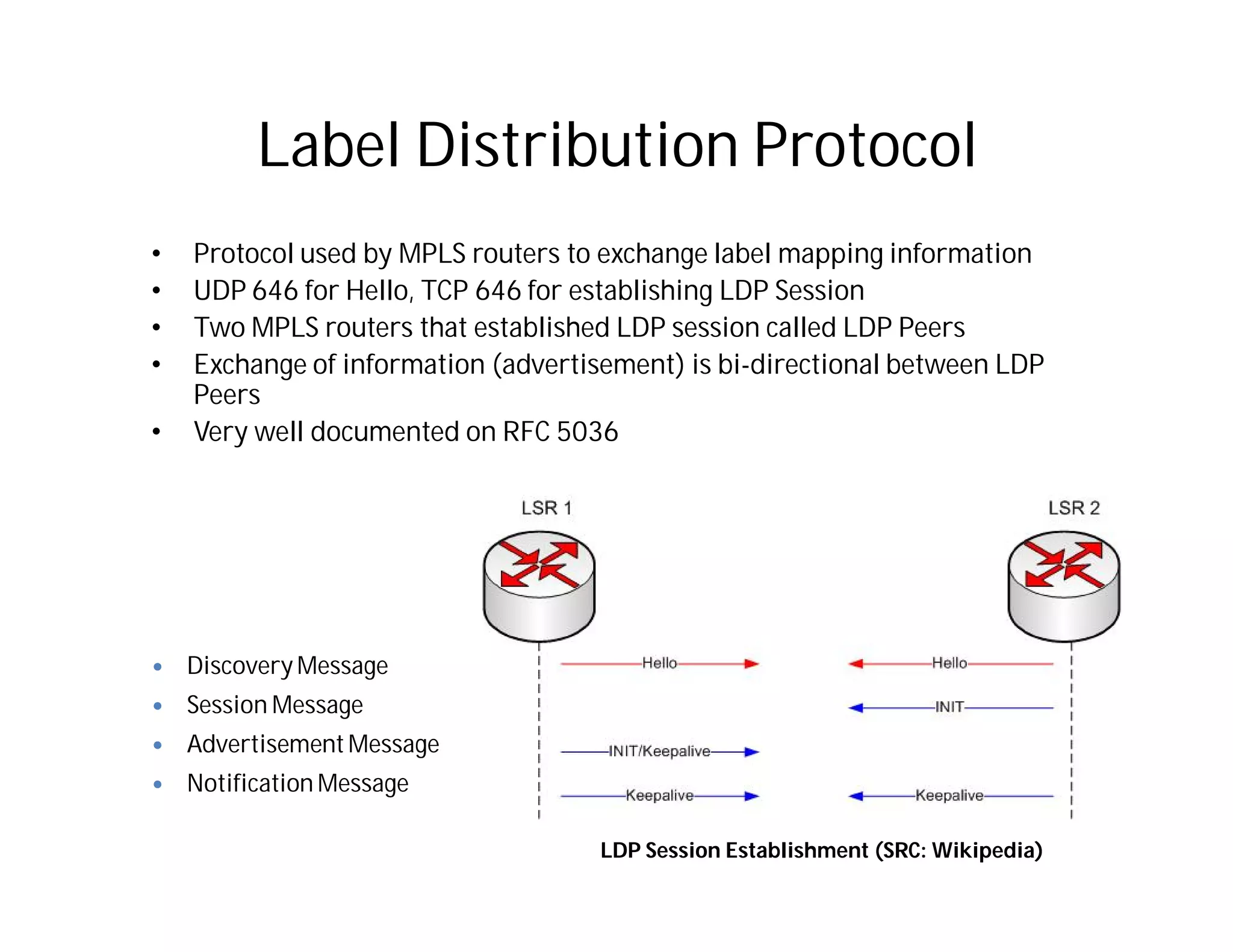
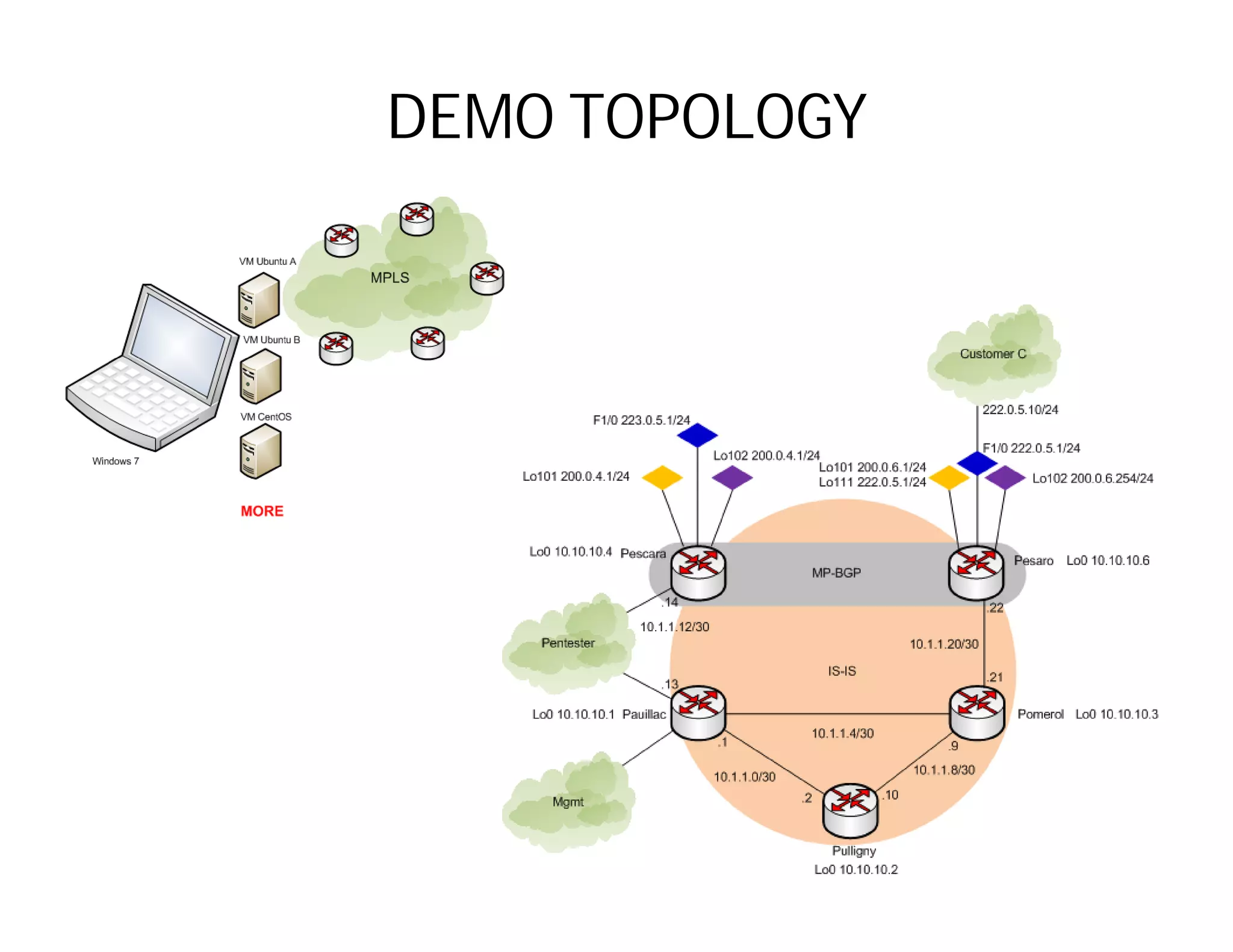
This document discusses potential security issues related to MPLS networks. It begins by defining some MPLS terminology like Label Distribution Protocol, Label Switched Path, and Label Switching Router. It then explores ideas like an attacker rewriting MPLS labels to redirect traffic or injecting spoofed messages into the Label Distribution Protocol to manipulate label mappings. However, the document notes that actually exploiting these issues against a real telecom backbone would be very difficult or impossible due to network controls and monitoring. The goal is to raise awareness of security considerations for MPLS rather than enable real attacks.