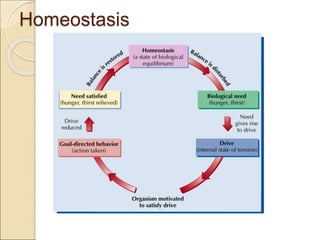
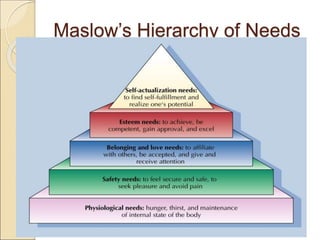
Motivation refers to factors that activate, maintain, and direct behavior towards a goal. The document discusses several general theories of motivation including instincts, drive reduction theory, homeostasis, arousal theory, cognitive approaches, and incentives approaches. It also describes Maslow's hierarchy of needs model which arranges human motivation needs in a pyramid with basic physiological and safety needs at the bottom and self-actualization at the top. Maslow's theory is that lower level needs must be satisfied before higher level needs.