The document discusses various theories of motivation including:
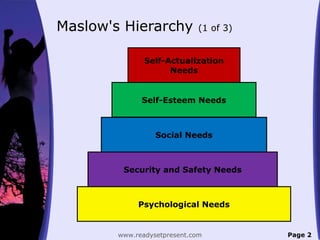
- Maslow's hierarchy of needs which identifies physiological, safety, social, esteem, and self-actualization needs.
- McGregor's Theory X which suggests that people dislike work and must be coerced to perform.
- Achievement motivation theory which states that internal and external factors influence people's need for achievement.
- Hackman and Oldham's job characteristics model which identifies five core job dimensions that influence motivation.