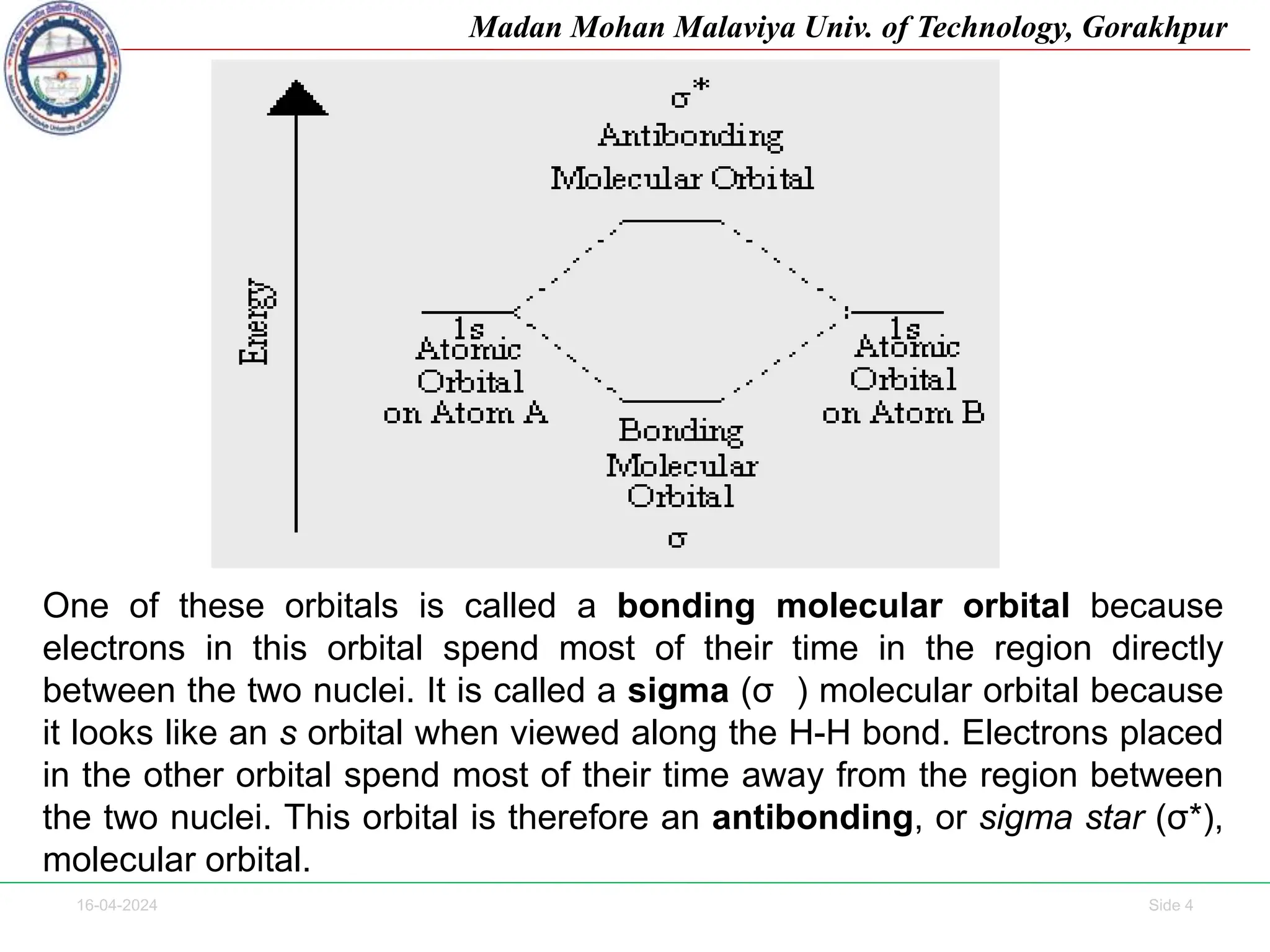
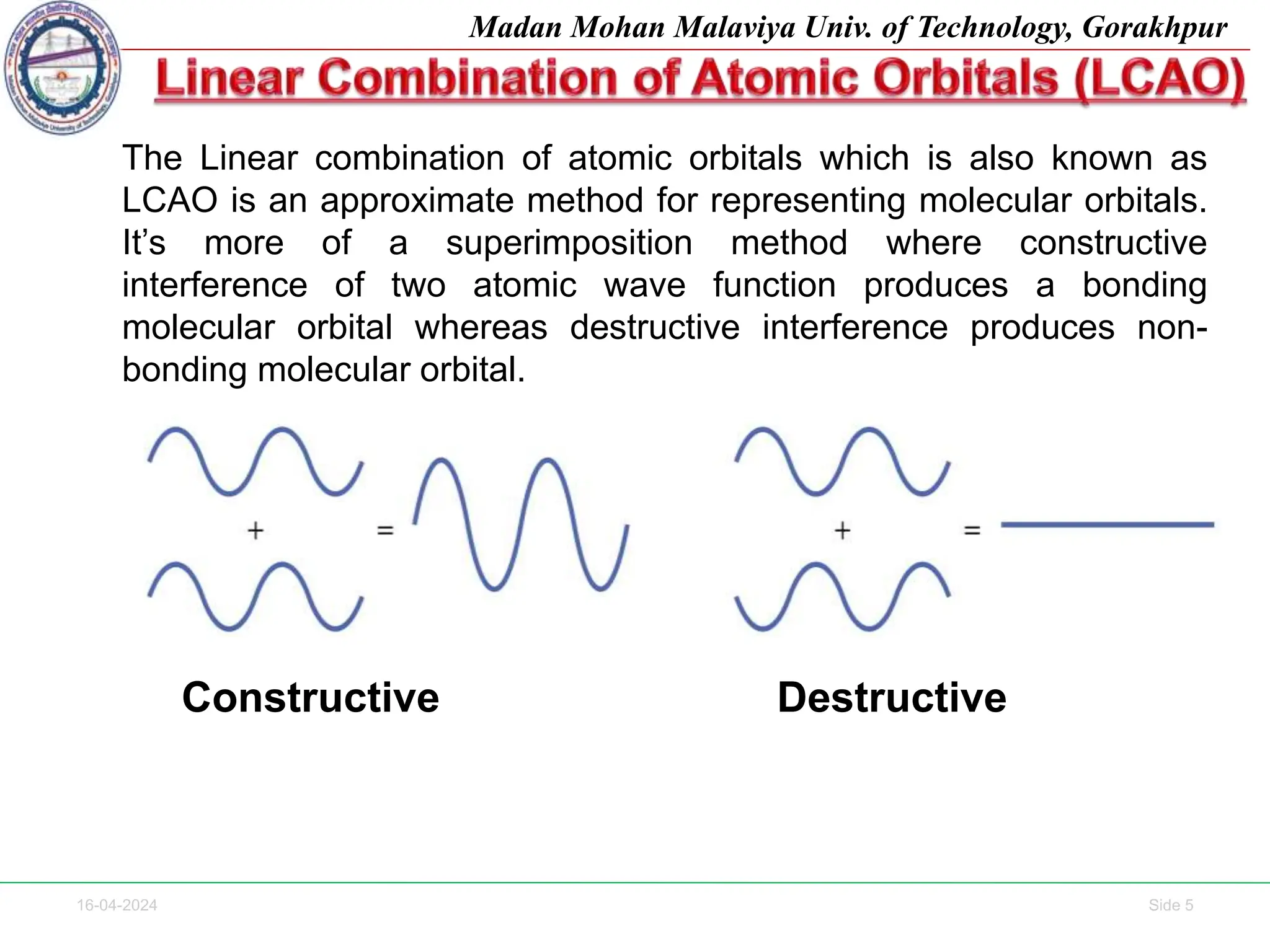
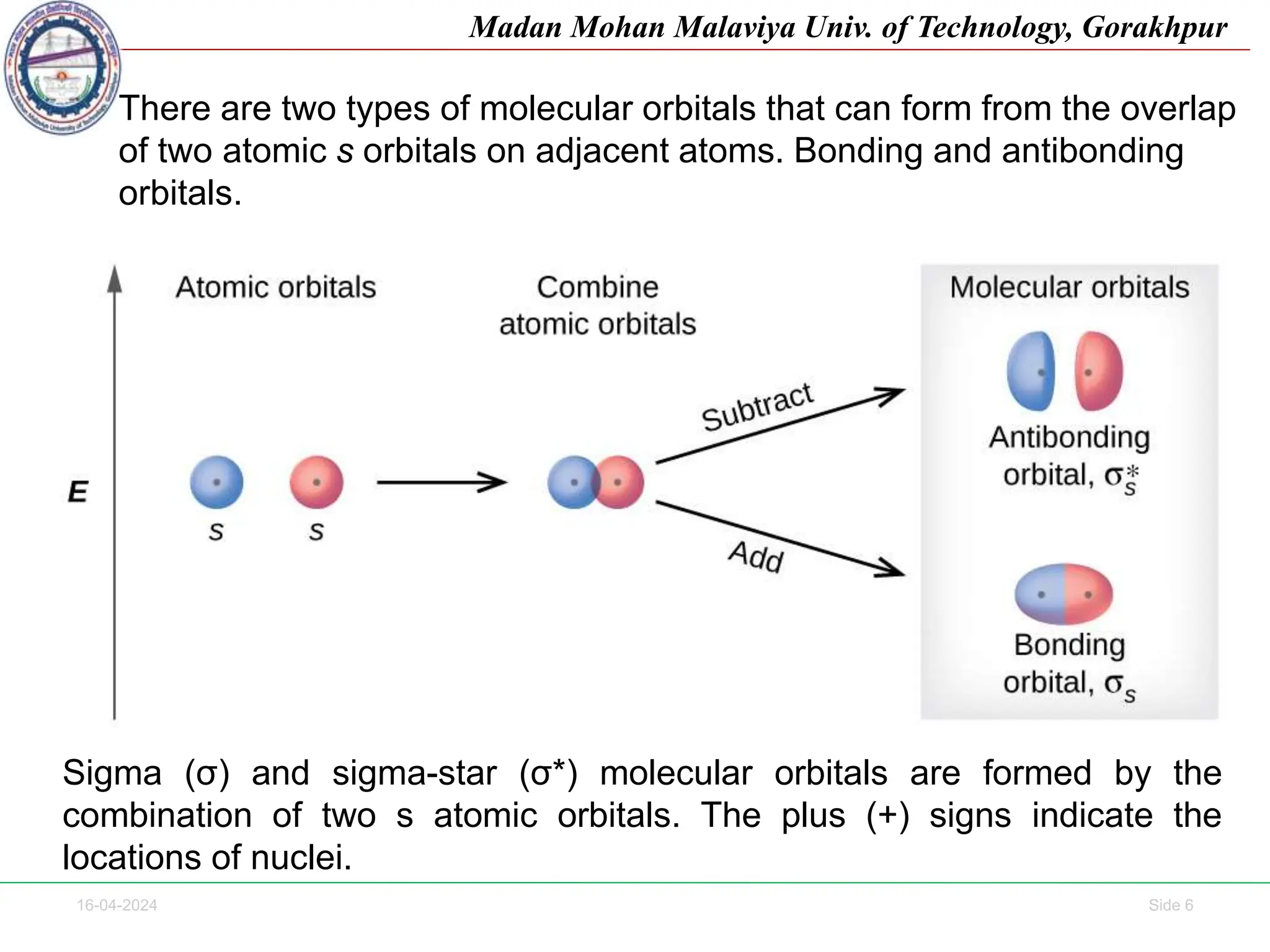
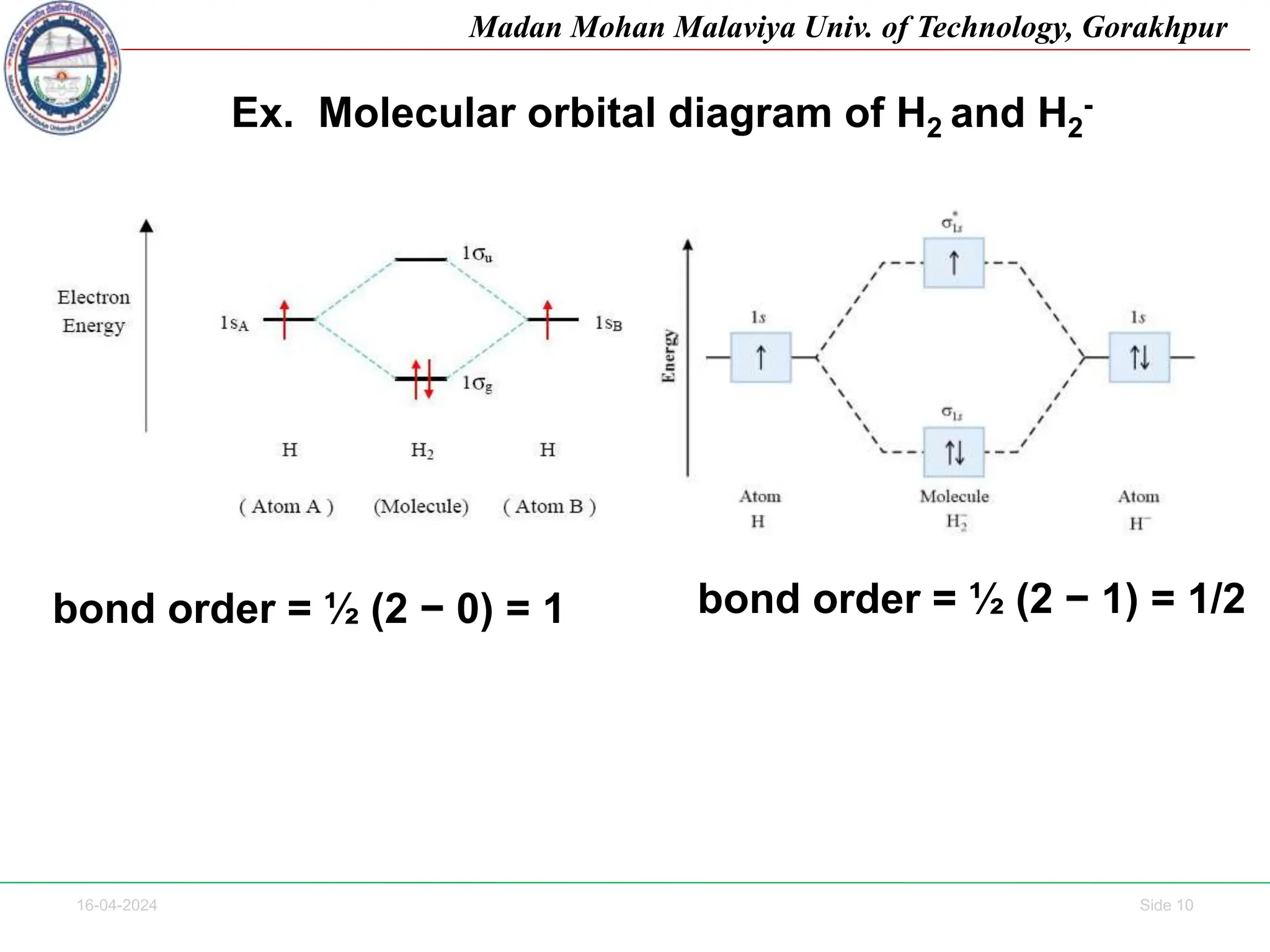
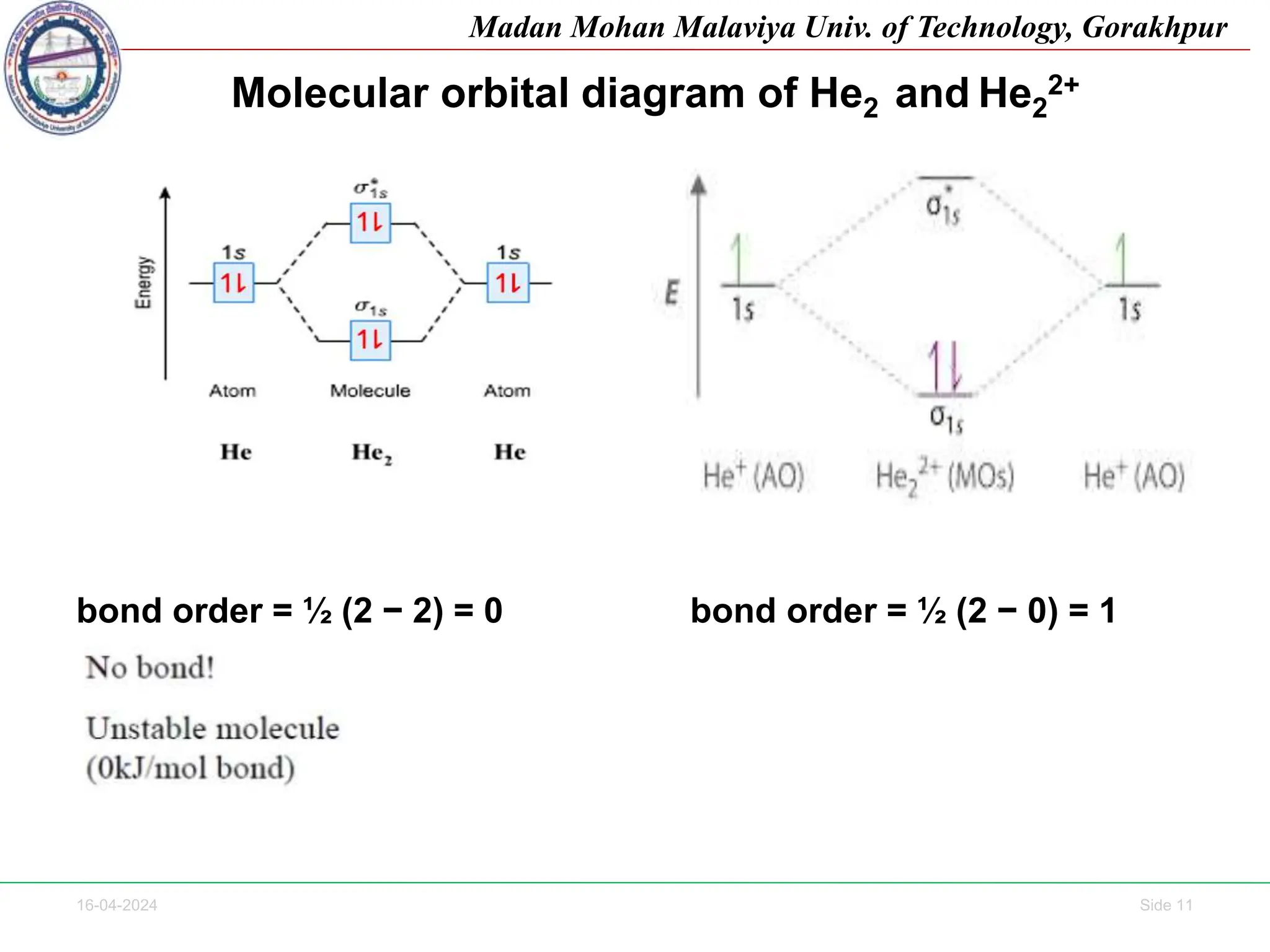
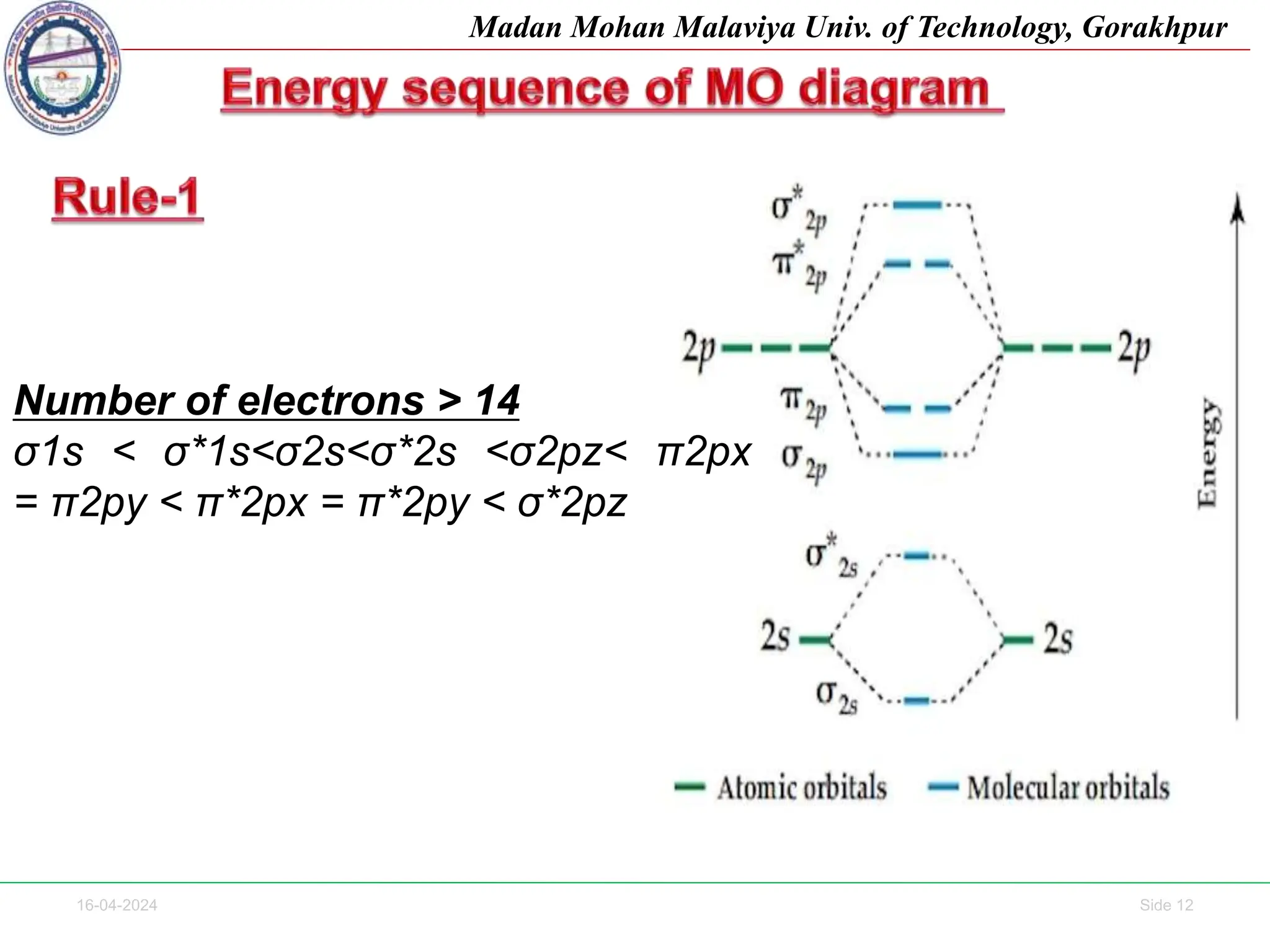
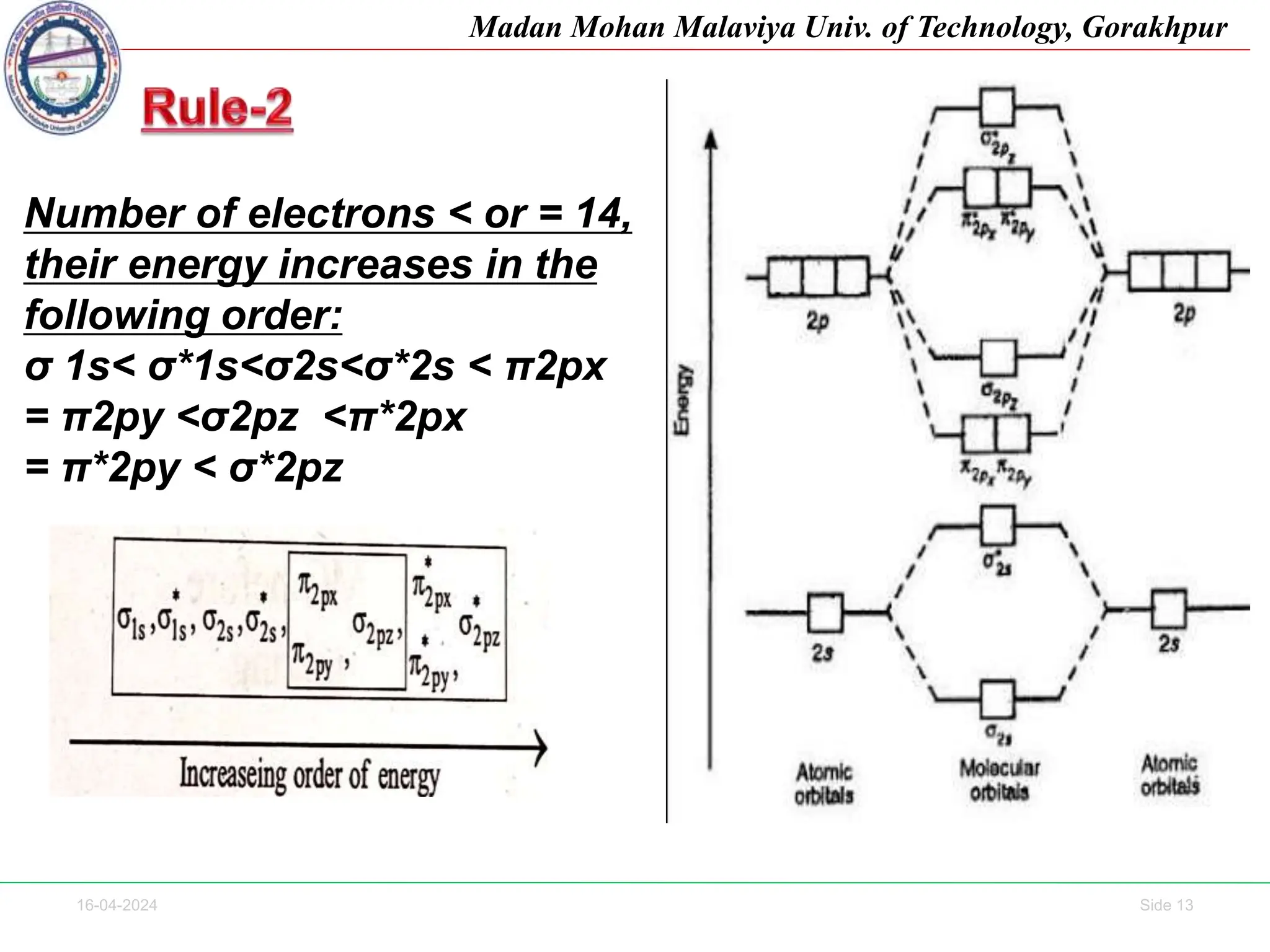
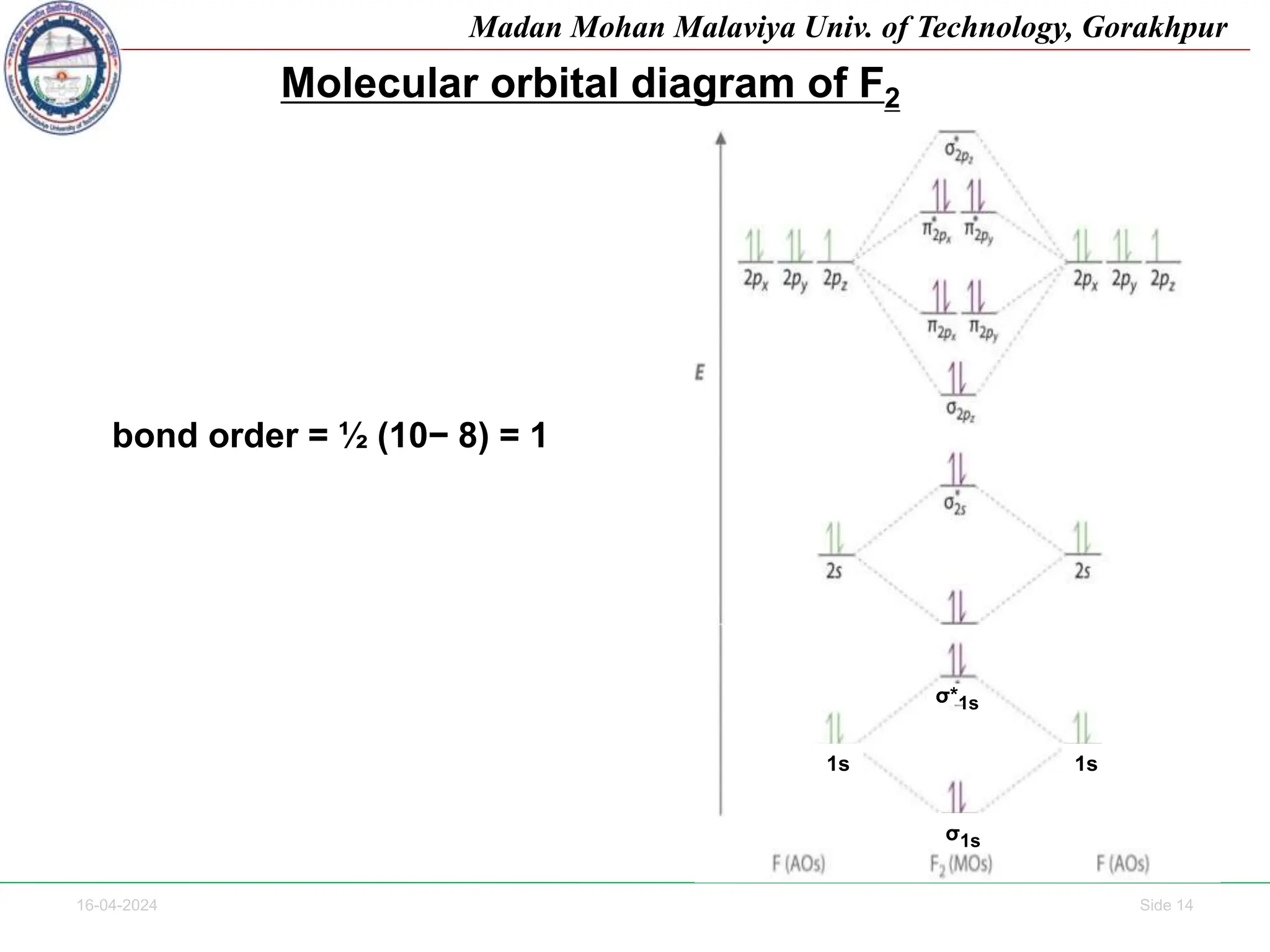
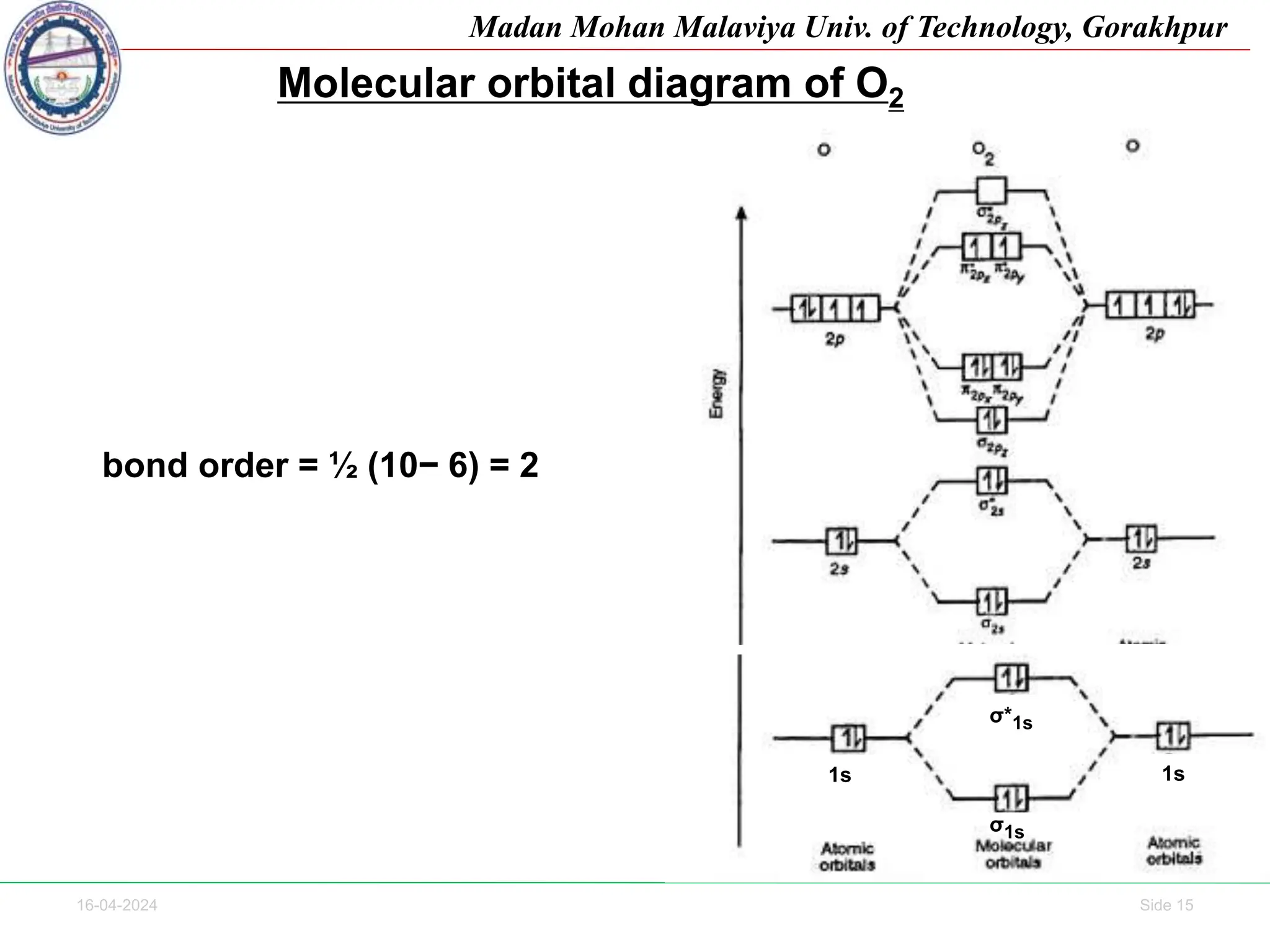
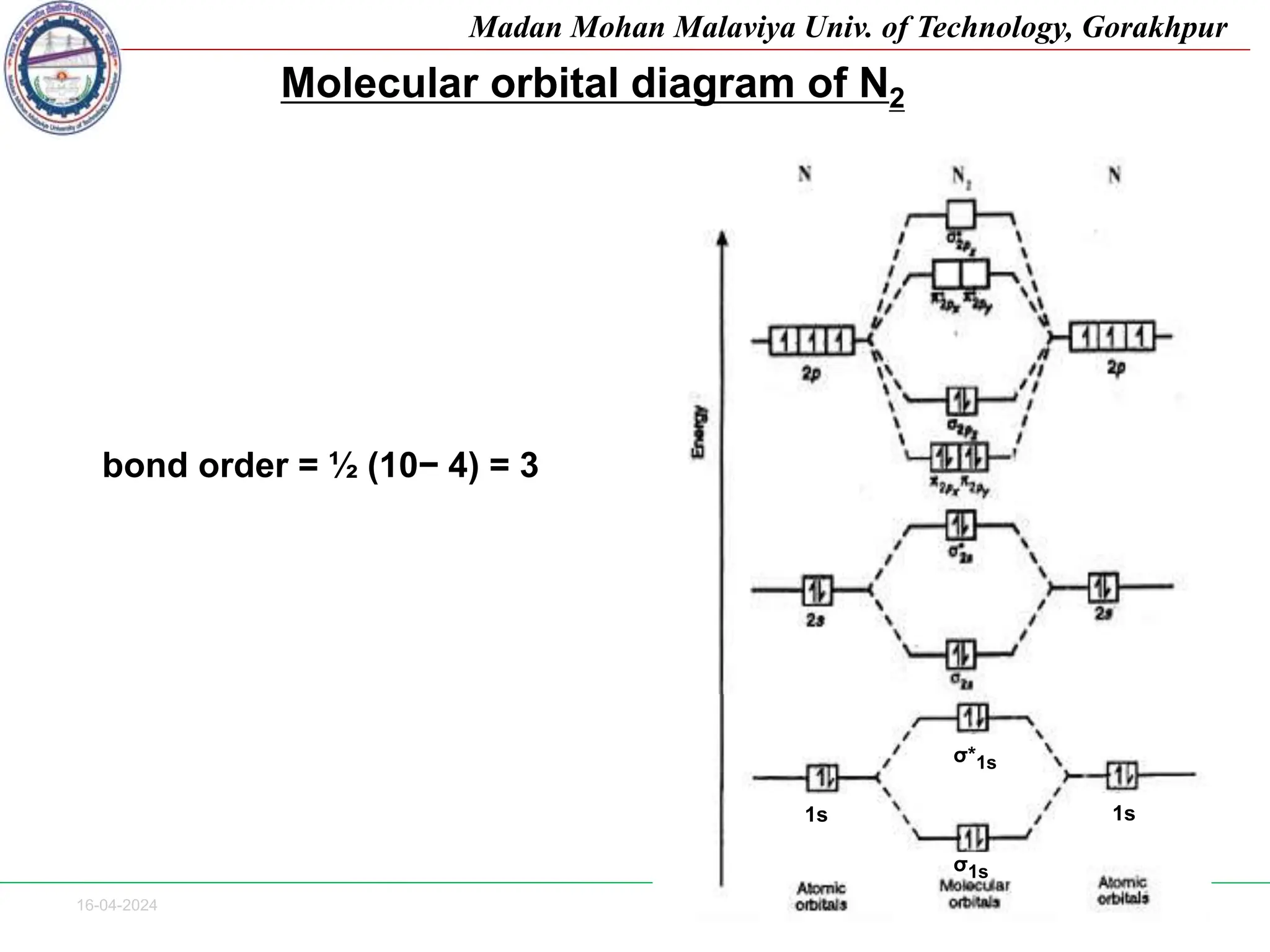
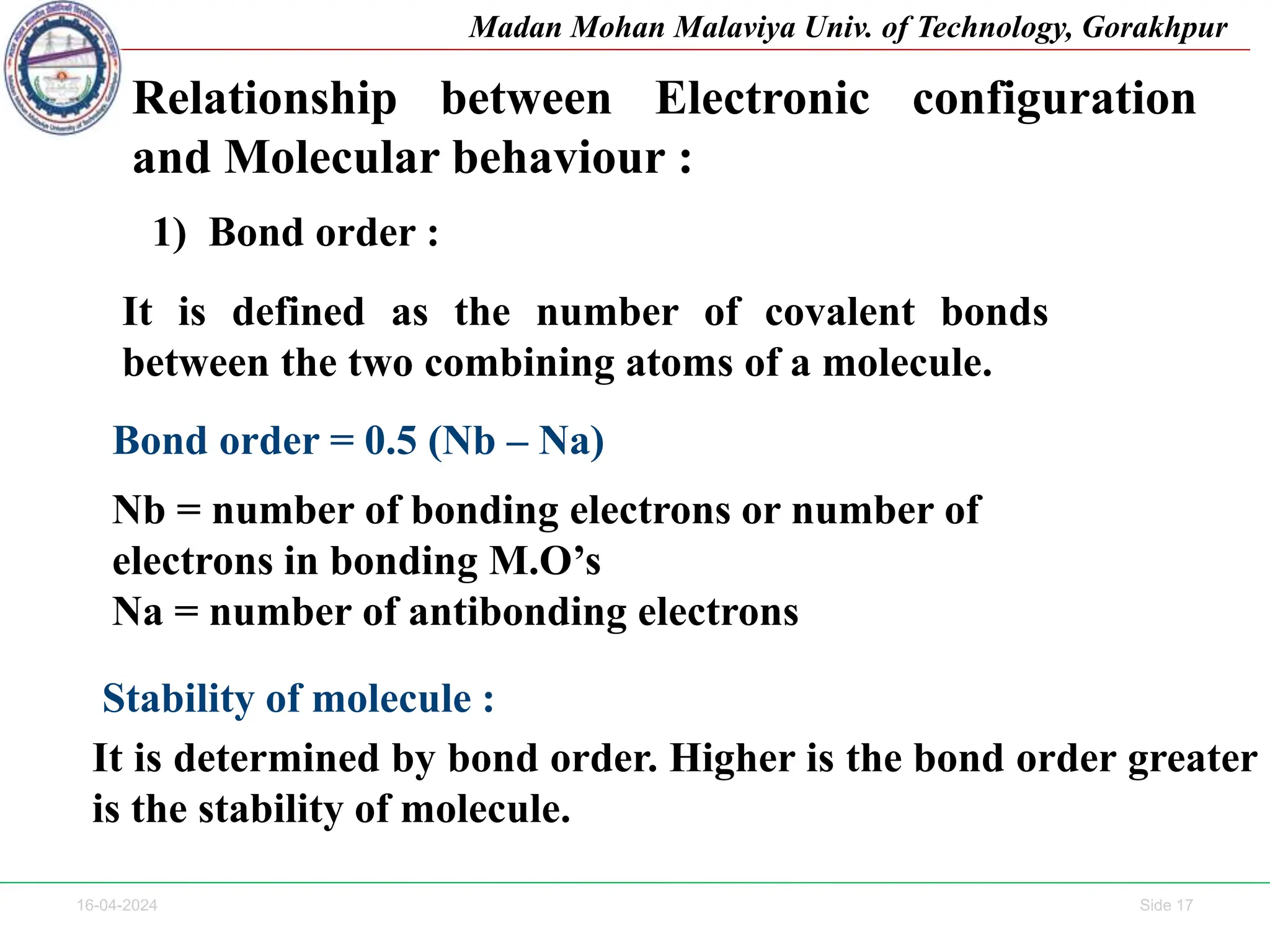
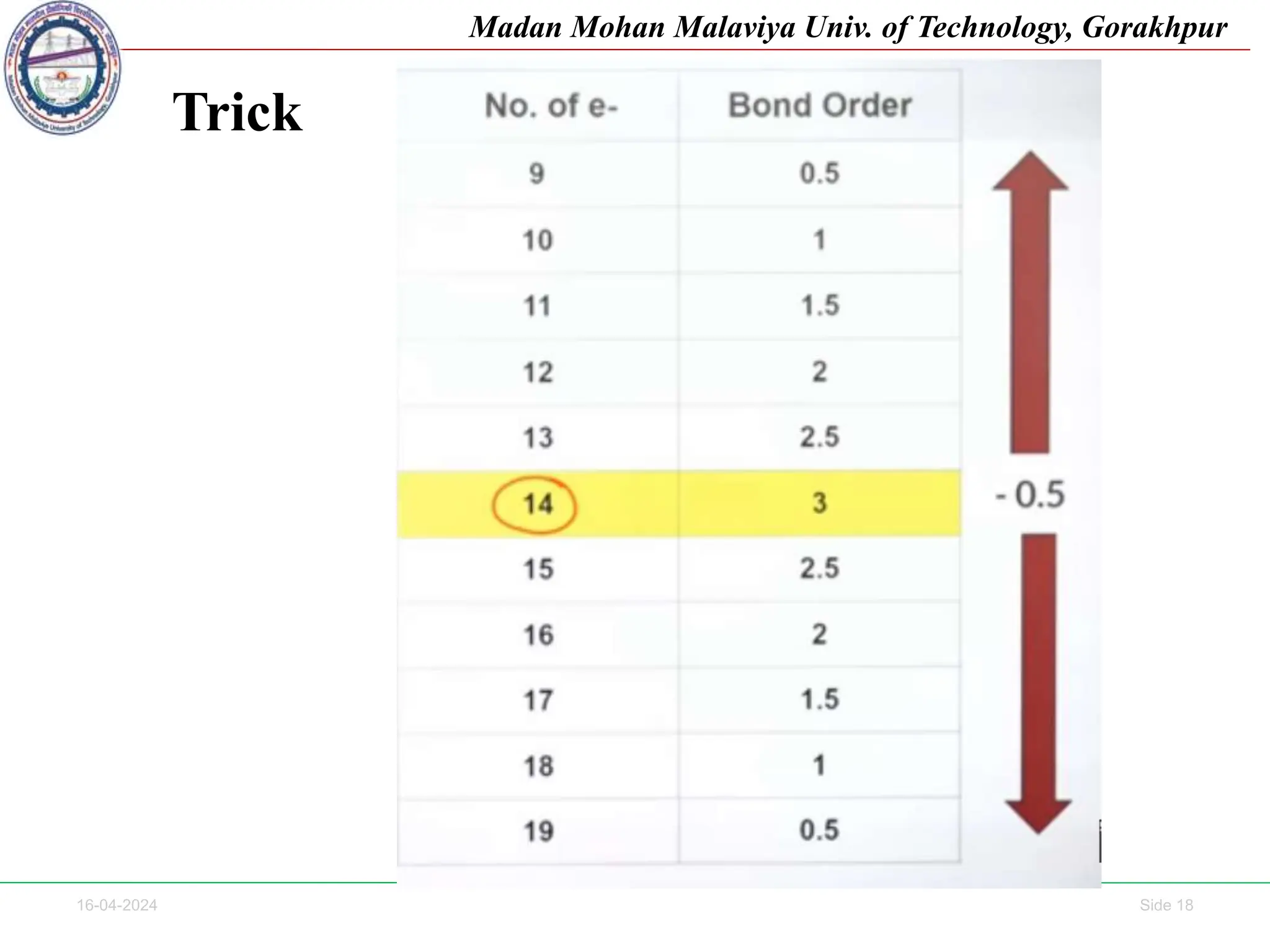
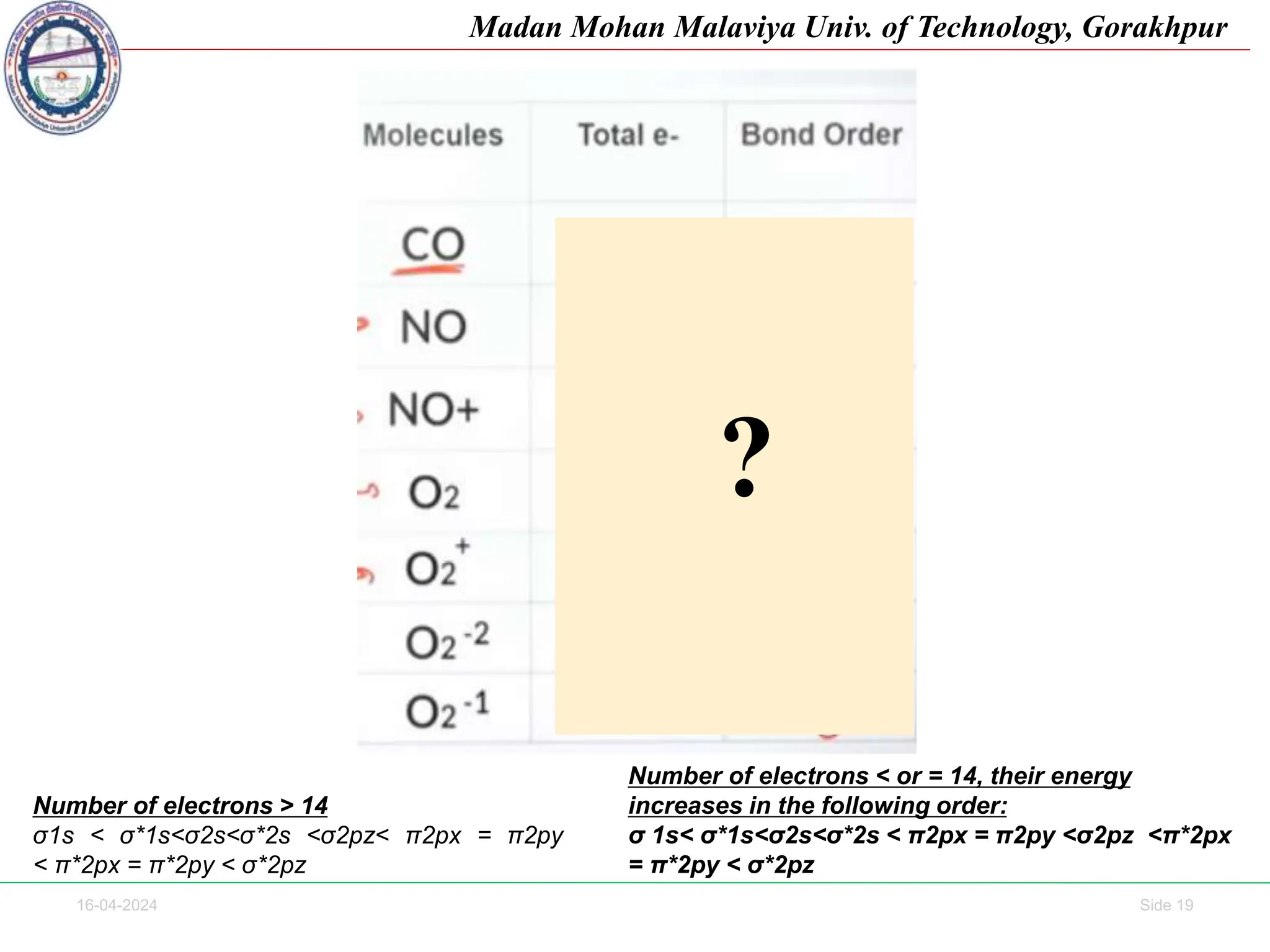
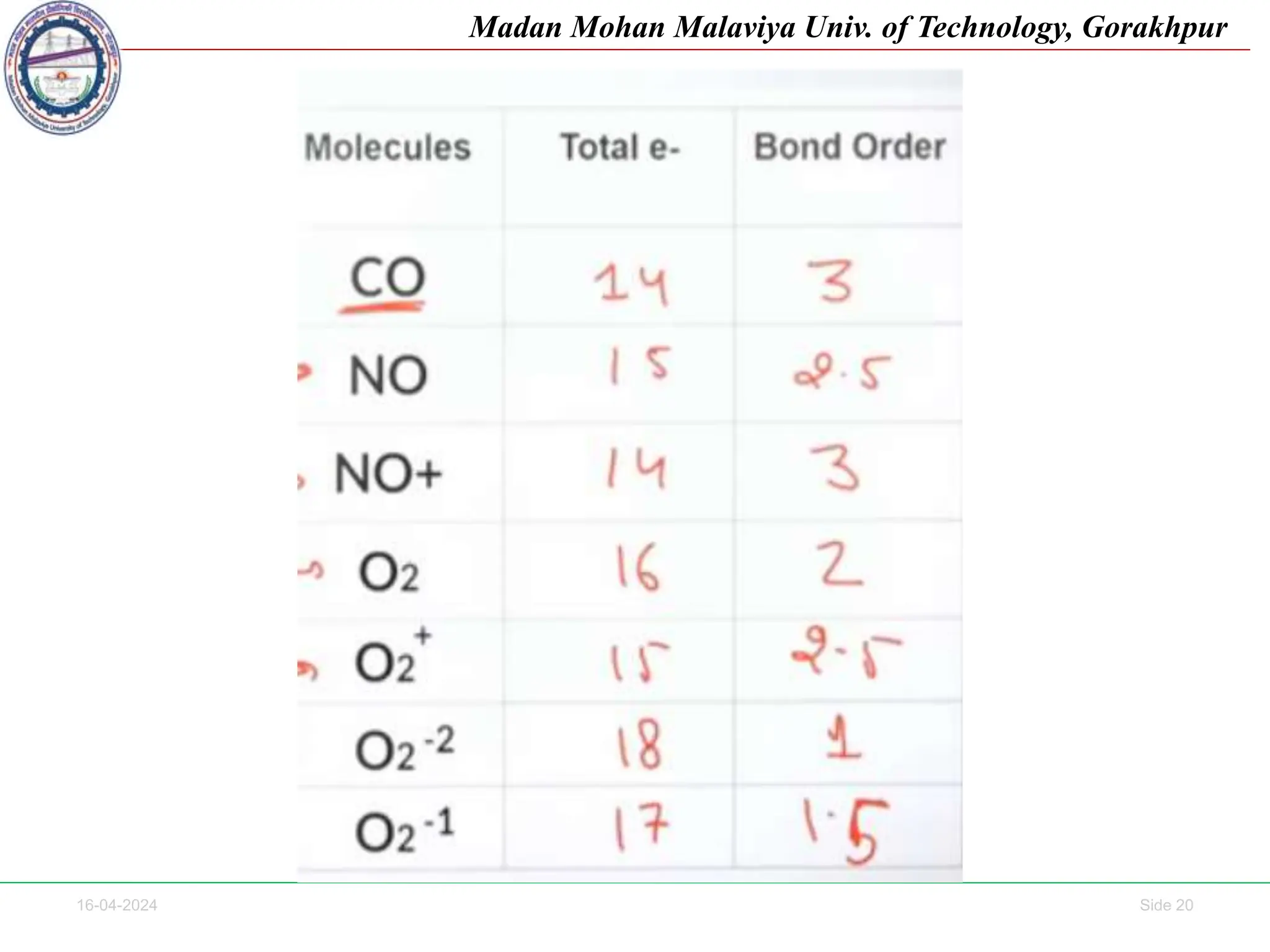
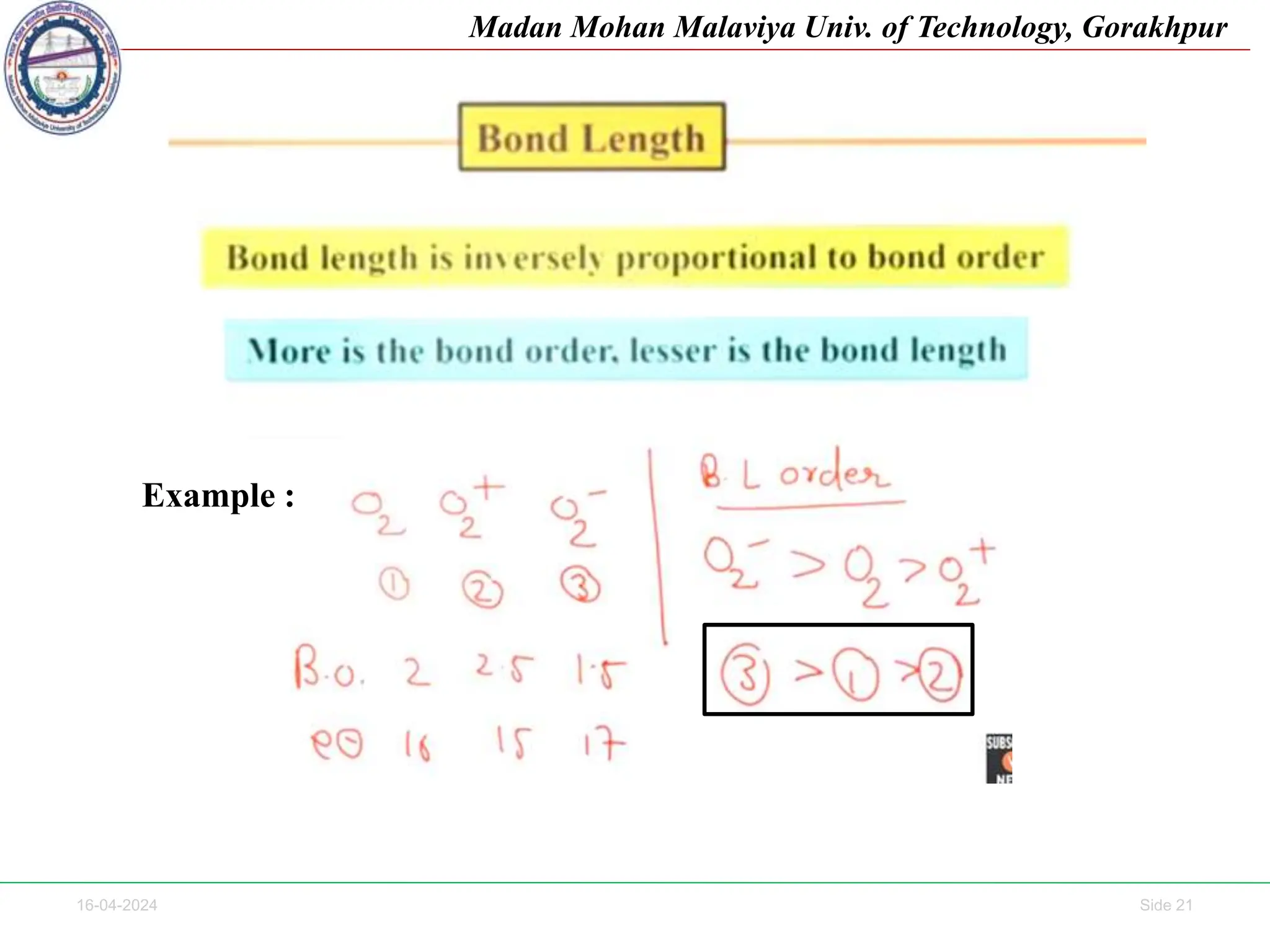
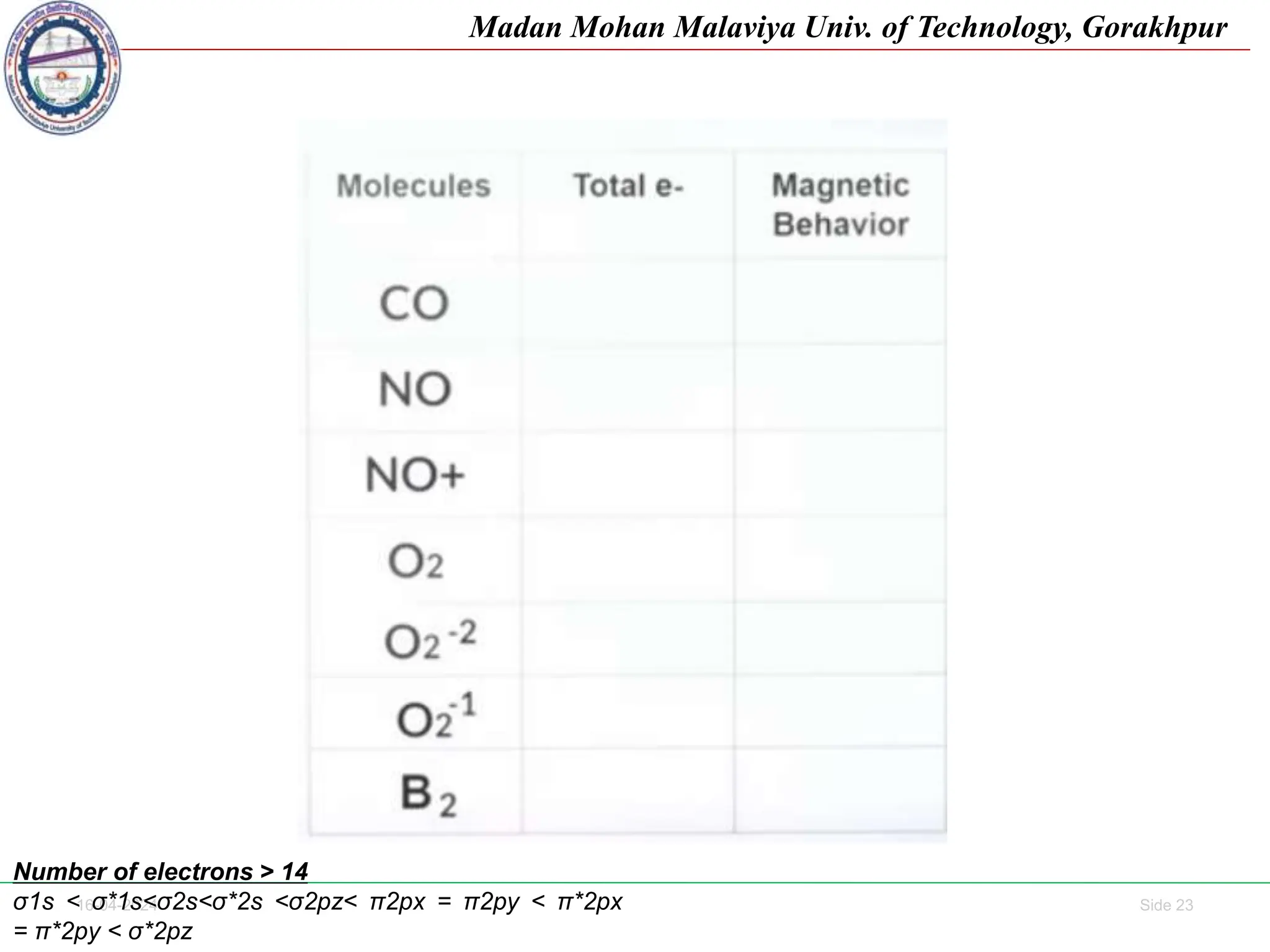
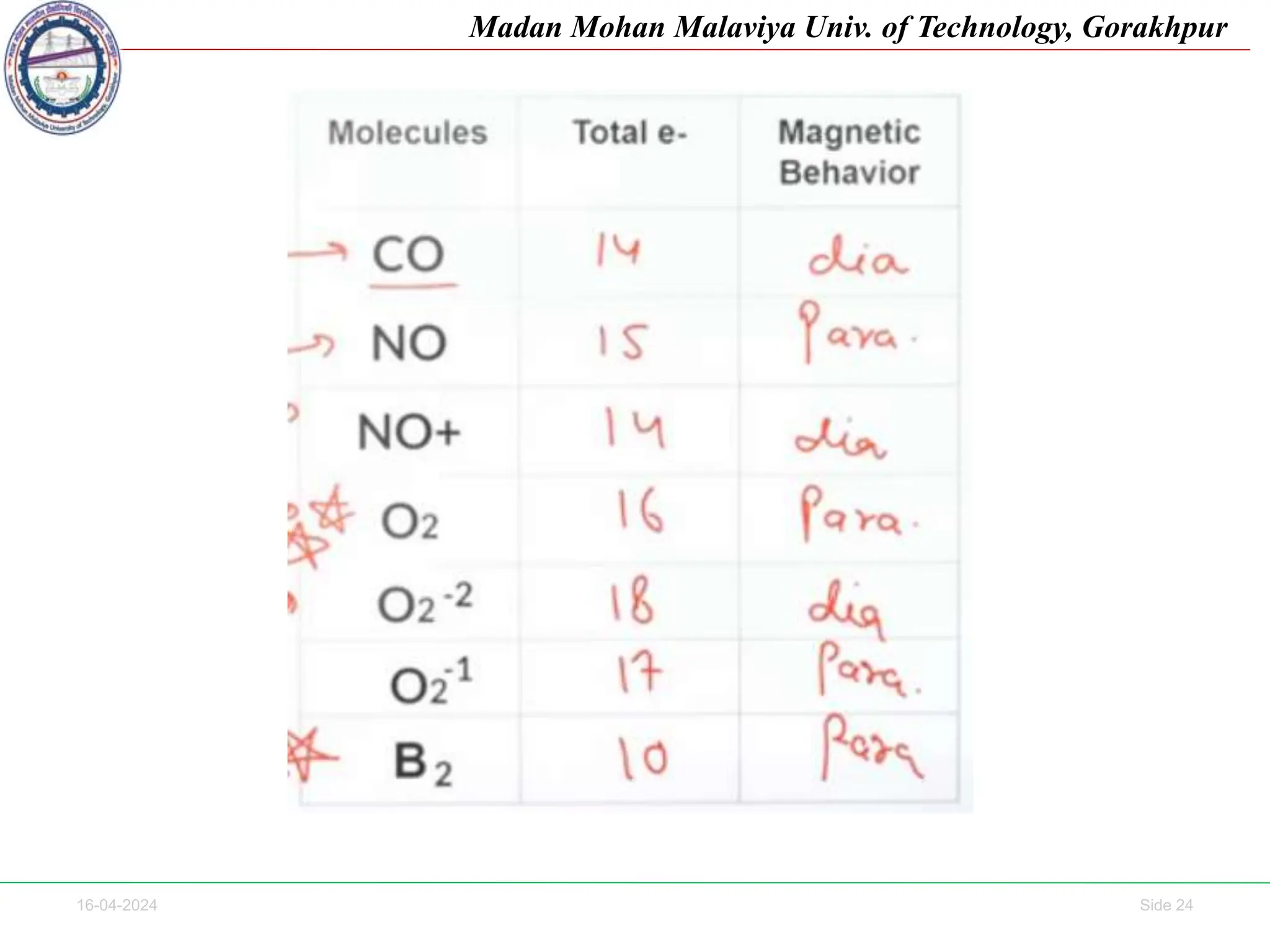
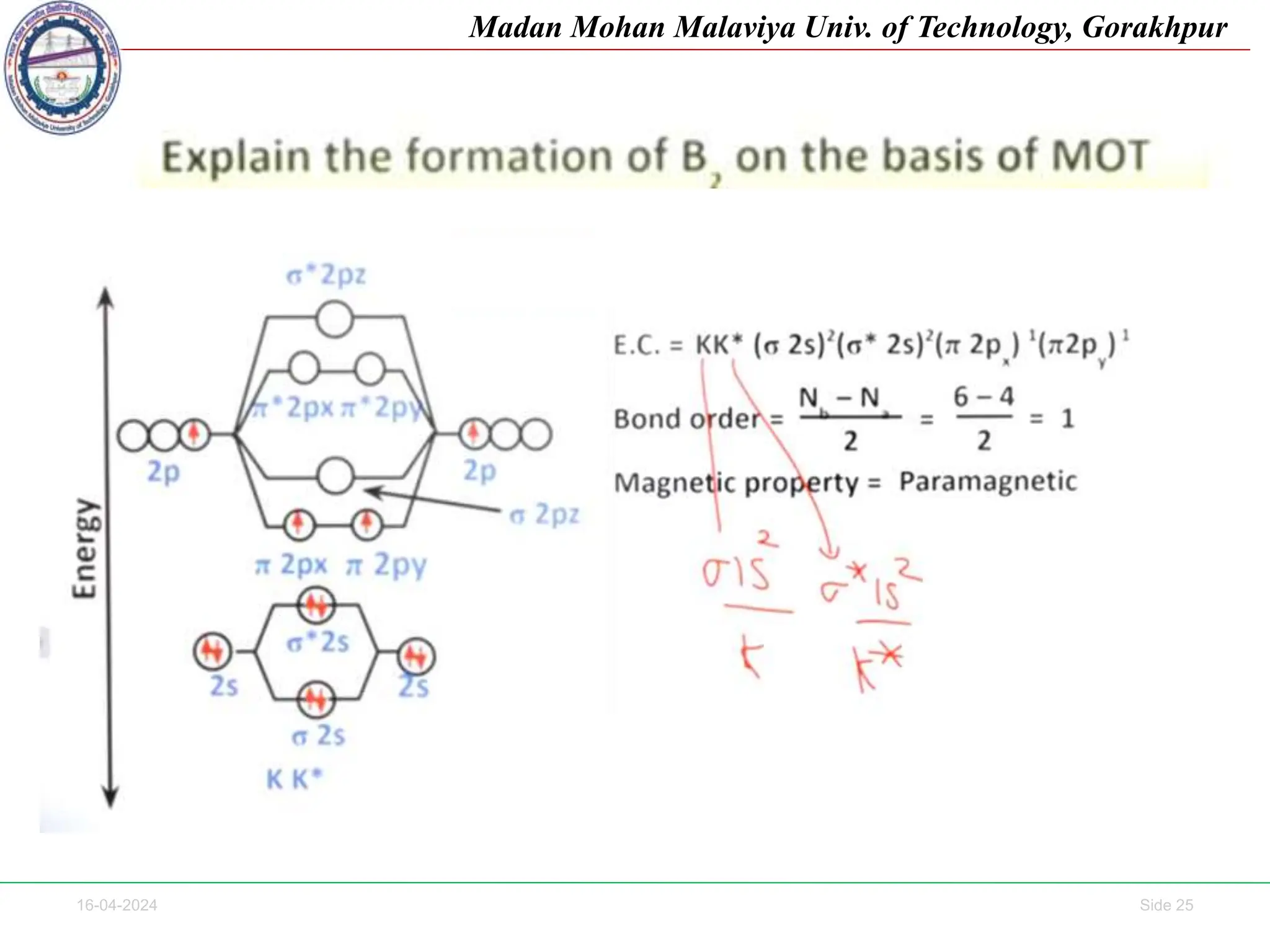
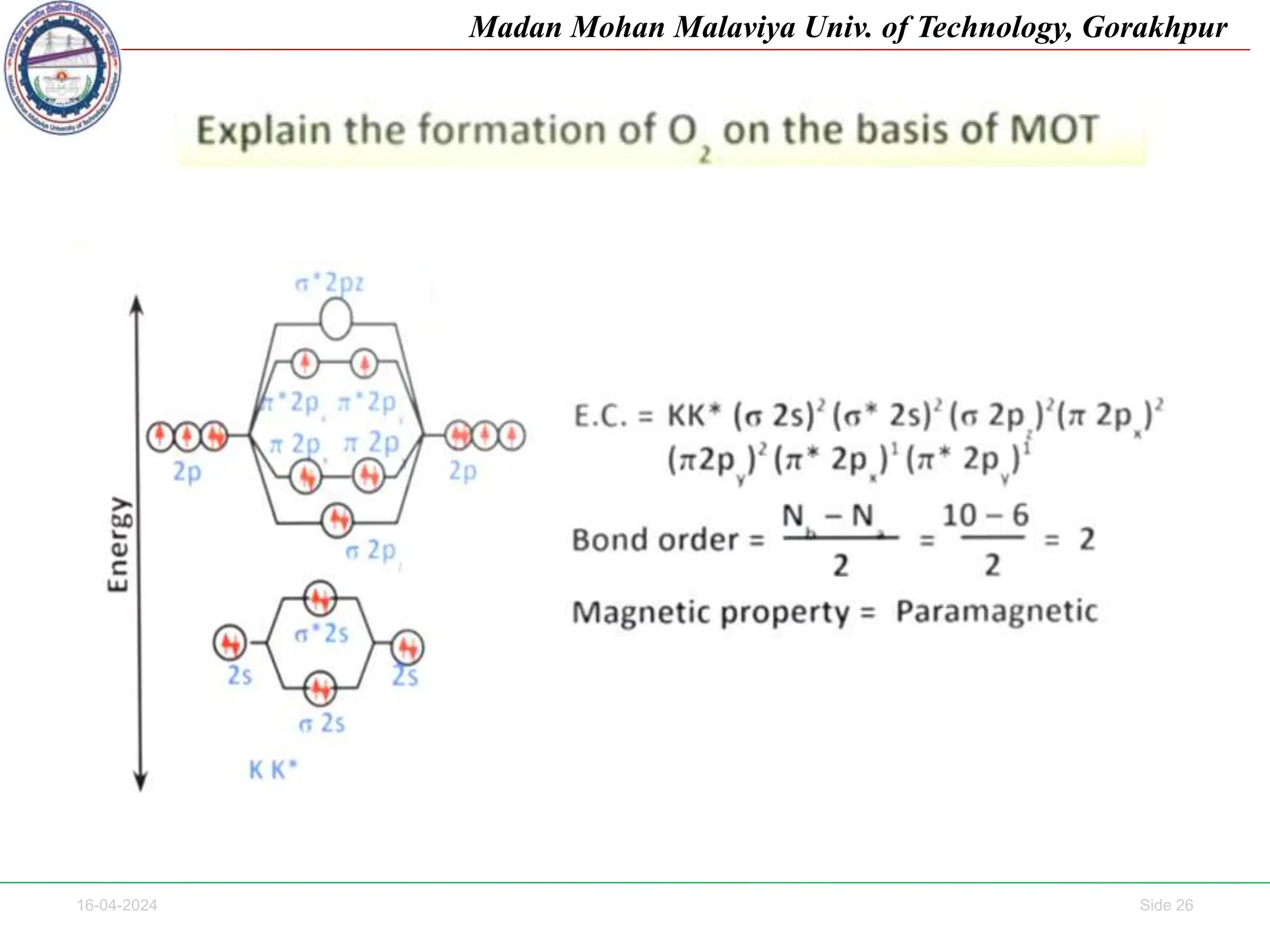
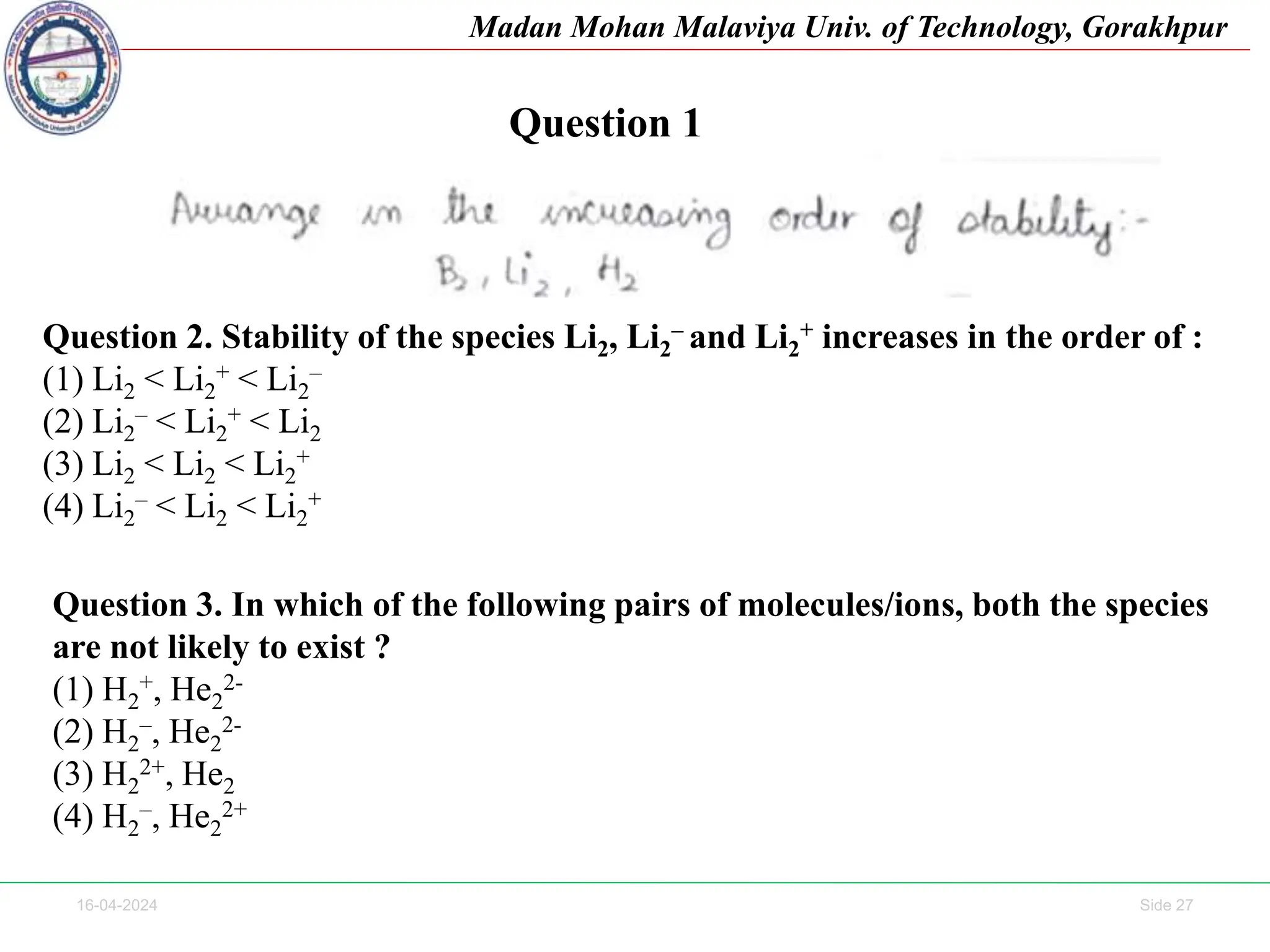
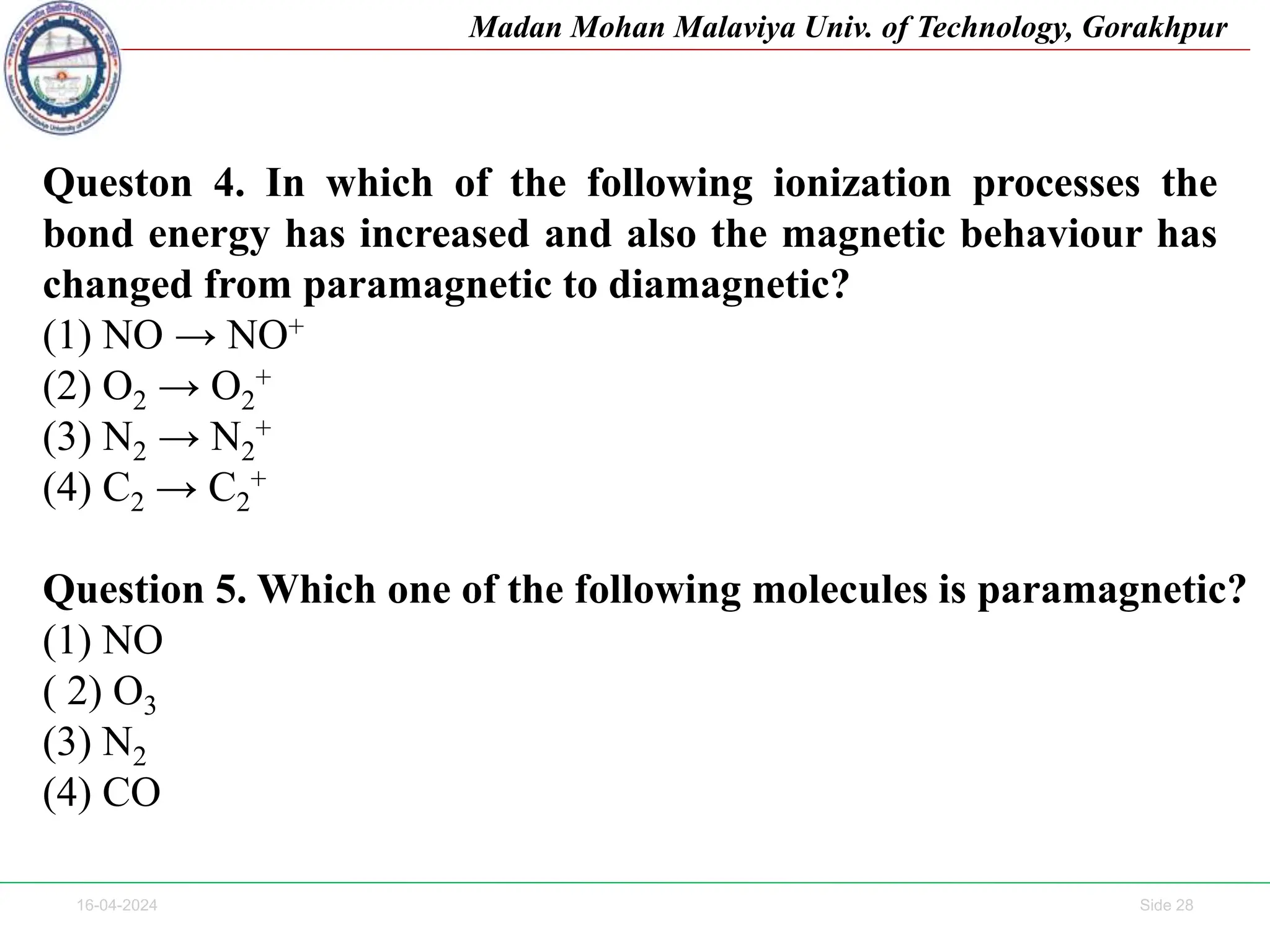
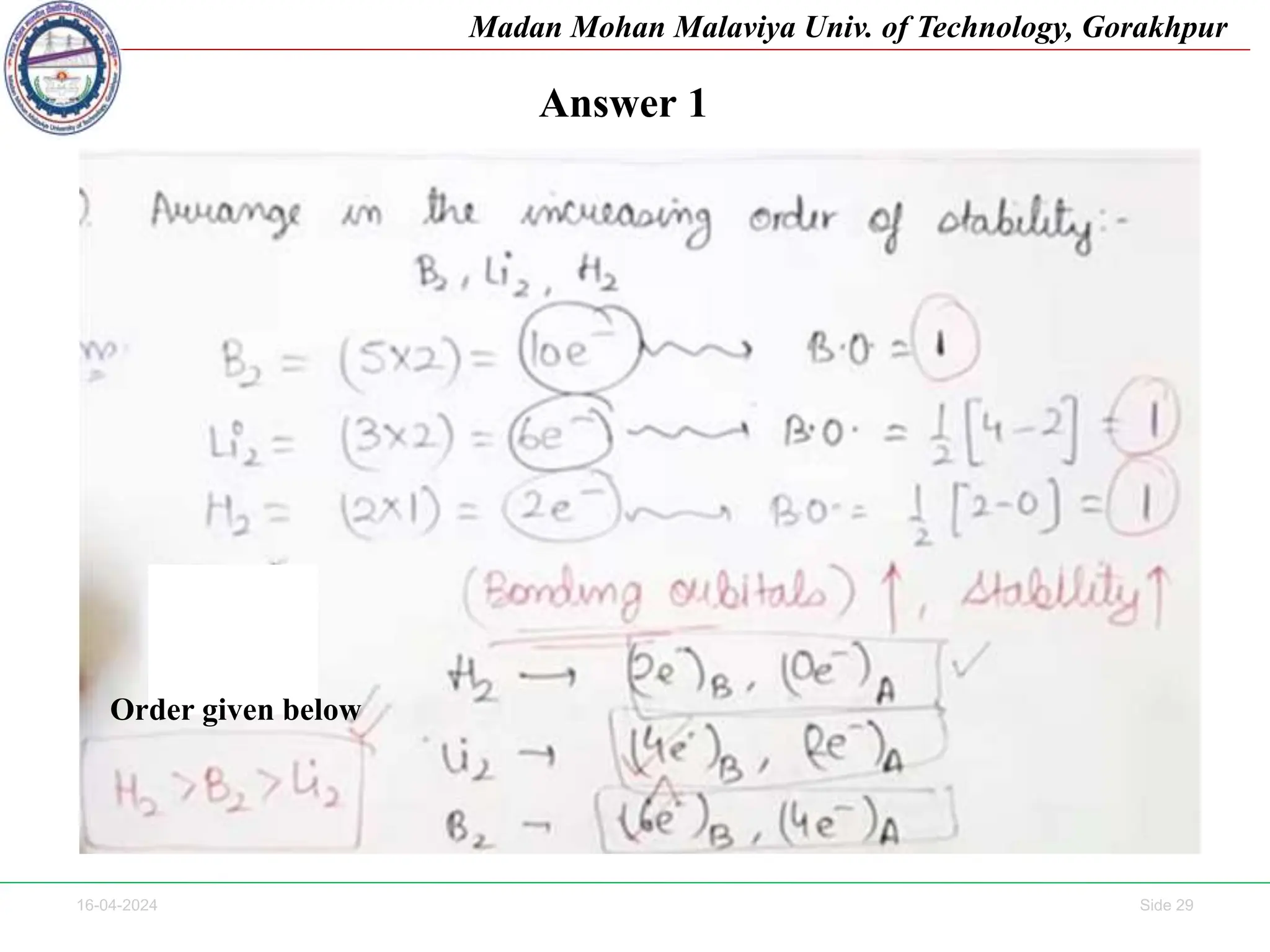
The document contains lecture notes on molecular orbital theory from Madan Mohan Malaviya University of Technology, Gorakhpur. It discusses the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) approximation, molecular orbital diagrams of diatomic molecules, bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals. It also addresses bond order, stability of molecules, and magnetic properties based on molecular electronic configurations. Several examples of molecular orbital diagrams and related concepts are provided.