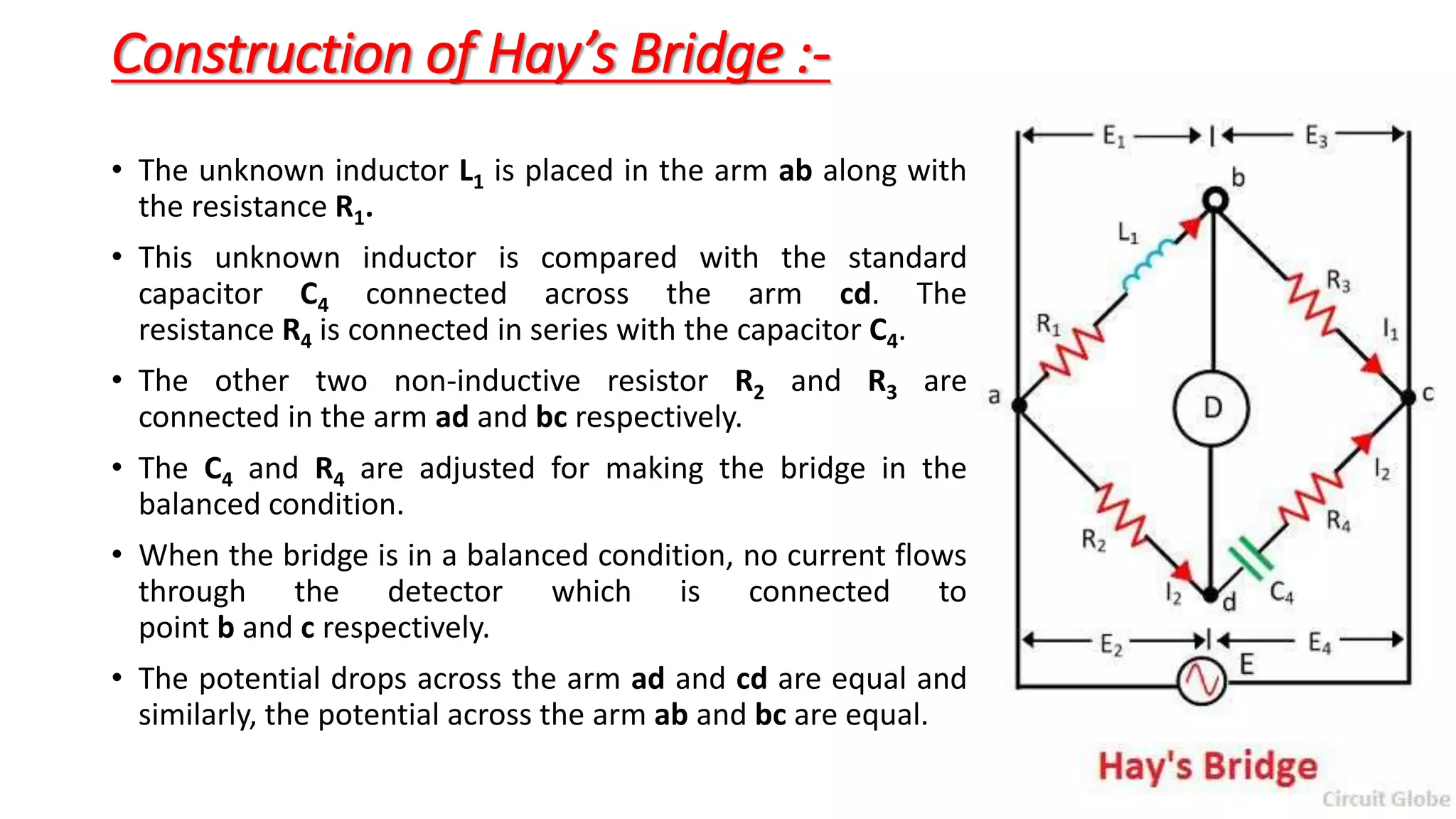
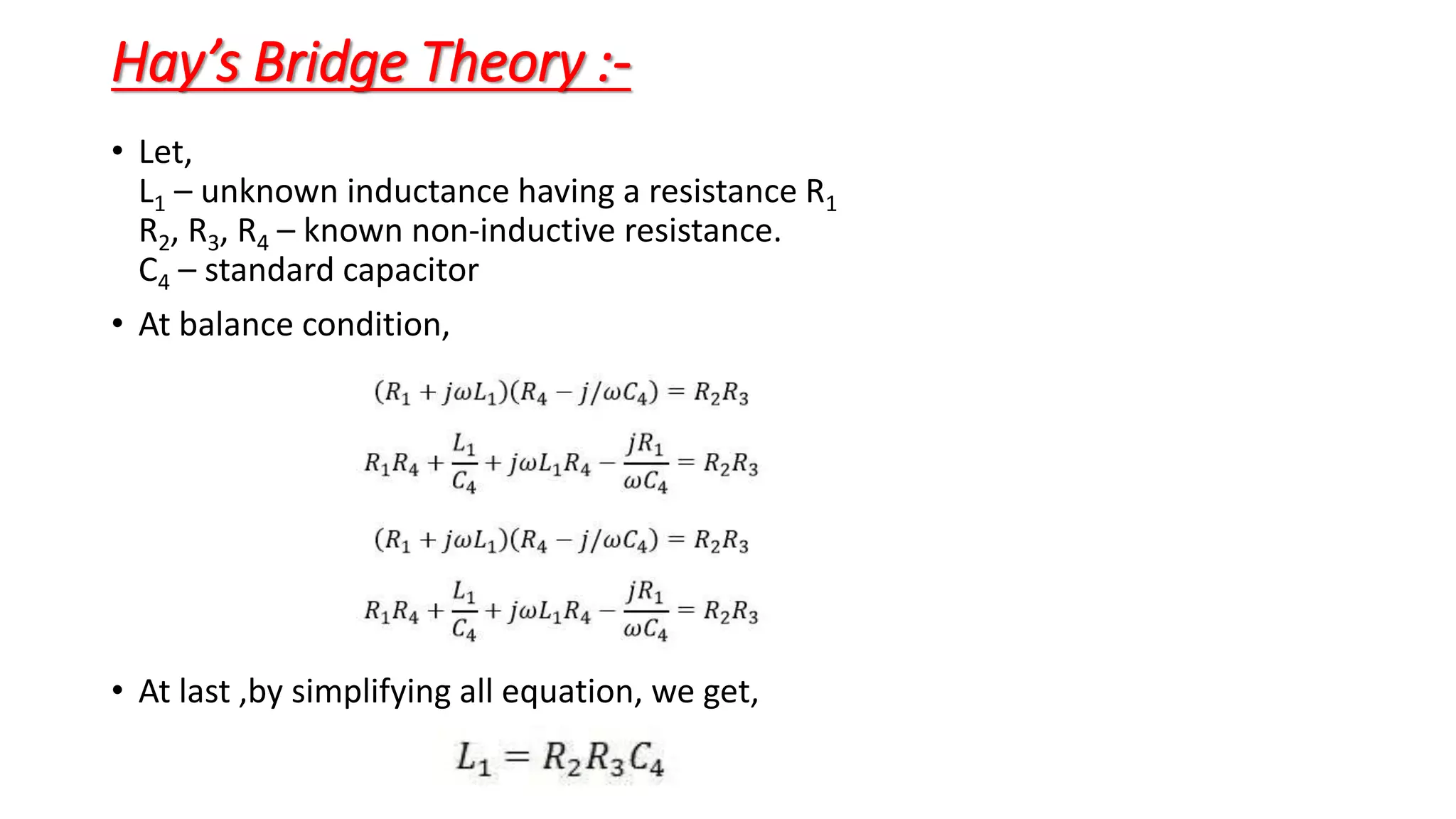
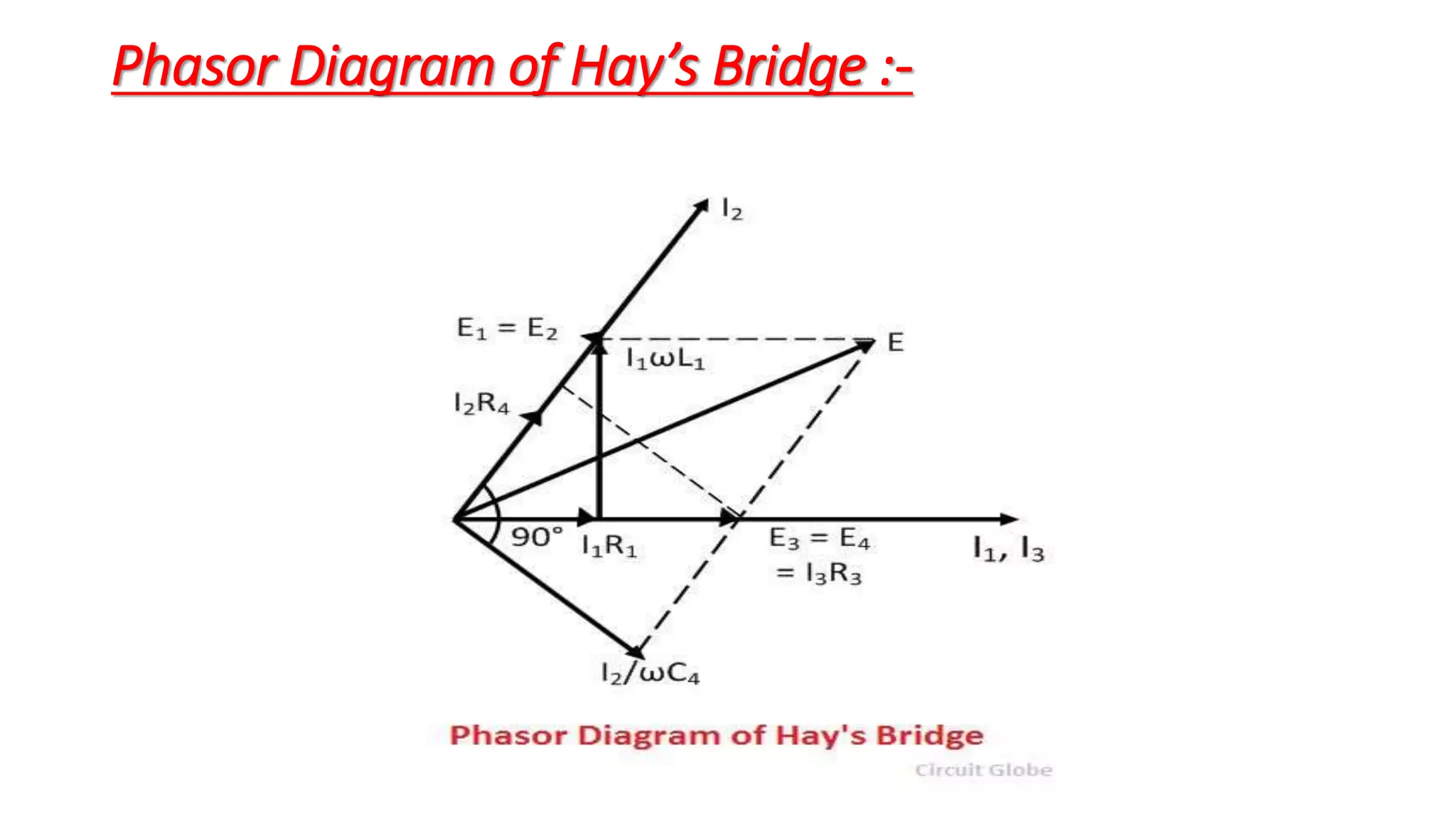
The document discusses Hay's Bridge, which is used to determine the self-inductance of a circuit and is an advanced form of Maxwell's Bridge suitable for high-quality factor measurements. It details the construction and functioning of the bridge, where an unknown inductor is compared with a standard capacitor, and adjustments are made for achieving a balanced condition. The summary also hints at theoretical aspects and equations relevant to the balance condition in Hay's Bridge.