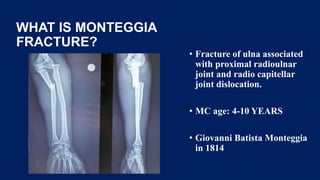
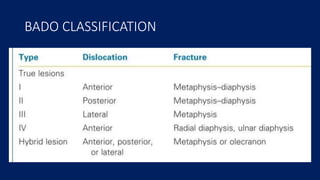
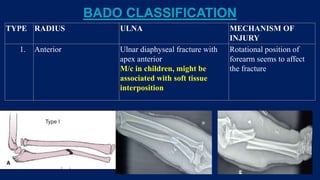
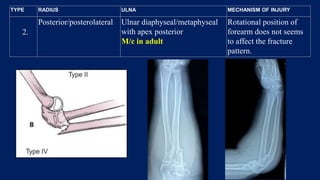
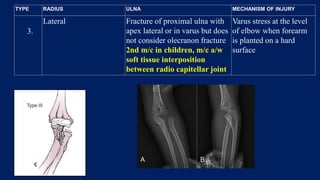
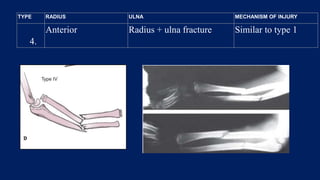
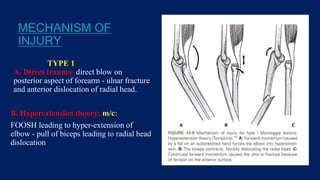
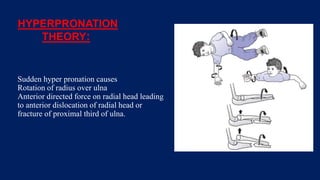
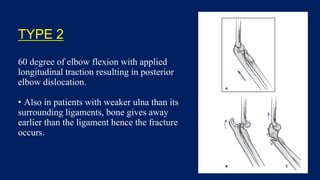
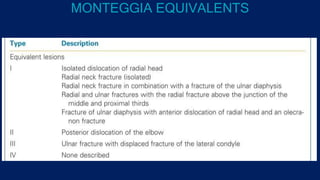
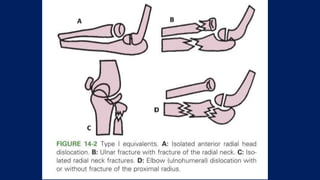
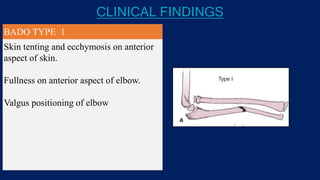
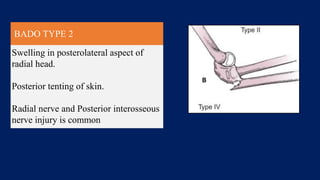
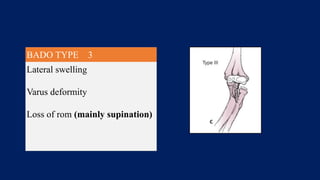
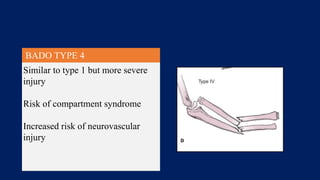
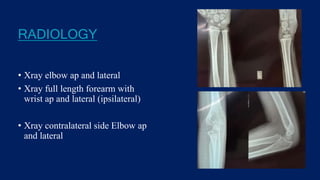
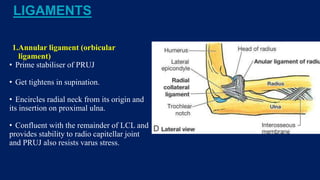
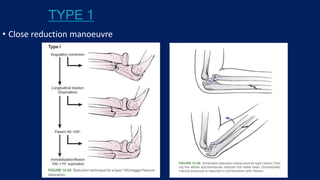
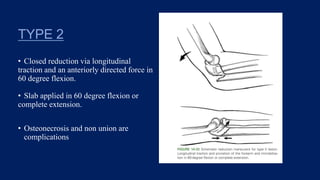
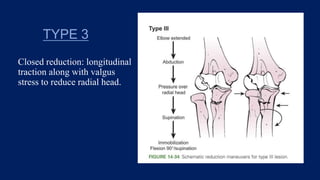
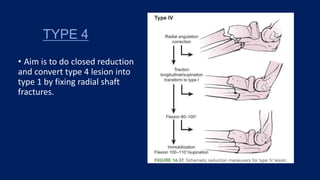
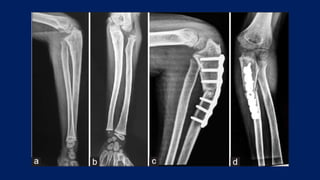
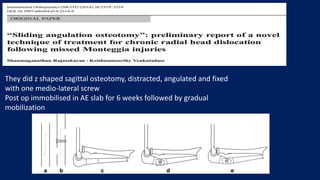
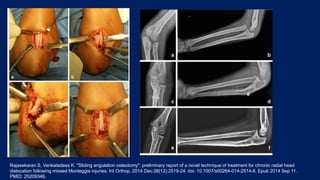
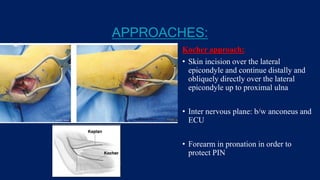
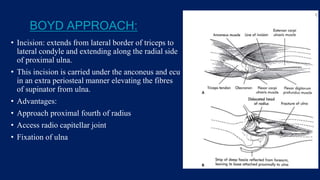
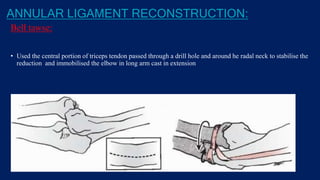
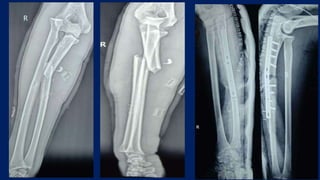
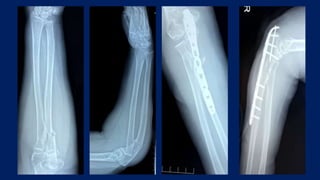
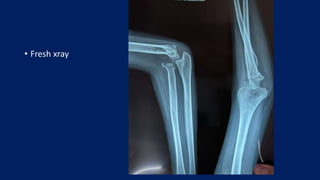
Monteggia fractures involve an ulna fracture associated with dislocation of the proximal radioulnar joint and are most common in children aged 4-10. The Bado and Letts classifications detail various types based on fracture characteristics and mechanisms of injury, guiding treatment options that range from non-operative reduction to surgical interventions. Complications such as nerve injuries and chronic deformities can arise if fractures are not properly diagnosed and treated.