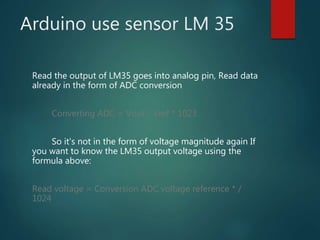
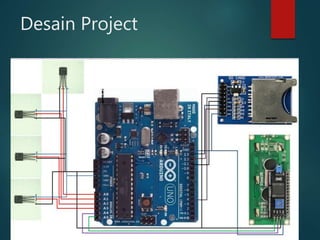
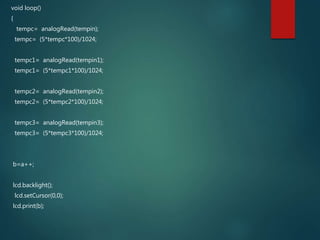
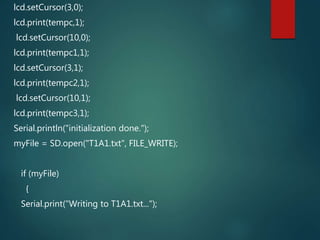
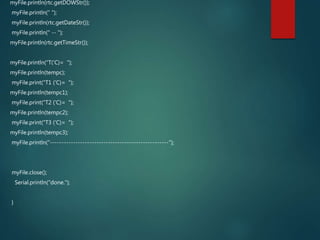
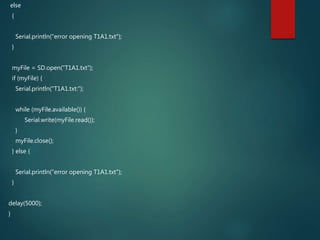
This document describes a temperature monitoring device that uses 4 LM35 temperature sensors to measure temperature in each corner of a room. The temperatures are displayed on an LCD screen and recorded by an Arduino Uno onto a micro SD card stored in .txt files. The summaries are stored minute-by-minute for long term monitoring and analysis of temperature changes in the room.