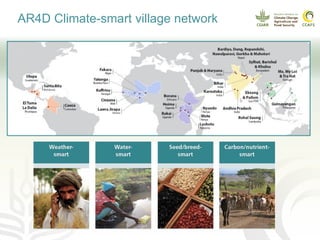
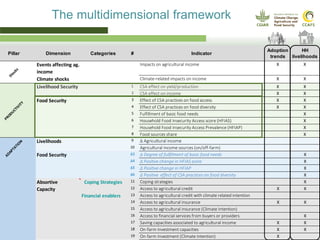
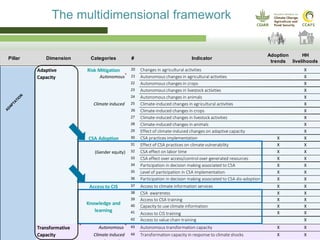
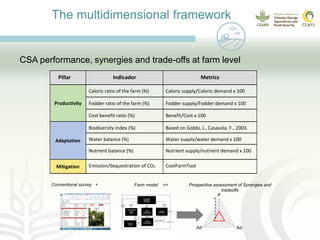
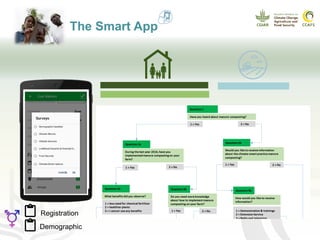
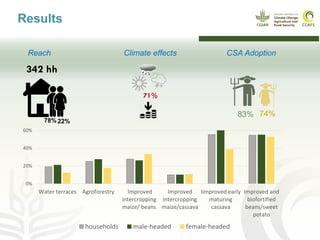
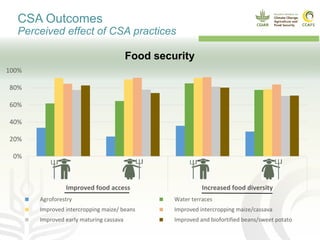
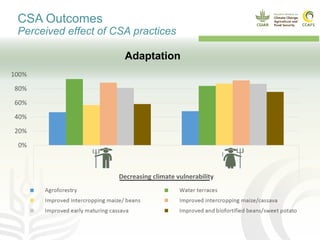
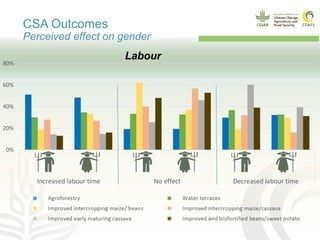
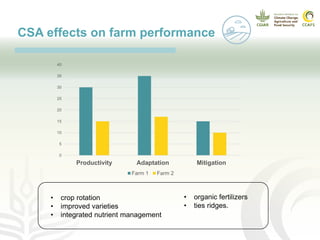
This document presents a multidimensional framework for monitoring climate-smart agriculture (CSA) outcomes at farm and household levels. The framework includes standard indicators to assess CSA adoption, effects on food security and livelihoods, and farm performance. Data will be collected using an integrated ICT-based tool to allow for systematic, rapid and reliable monitoring. The framework and tool aim to provide a cost-effective way to understand CSA adoption trends and synergies or trade-offs across productivity, adaptation, mitigation and other dimensions at multiple levels.