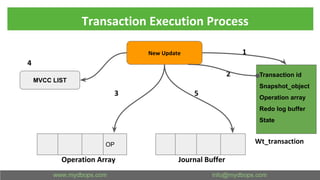
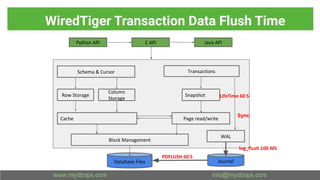
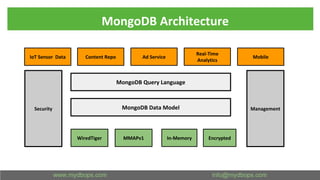
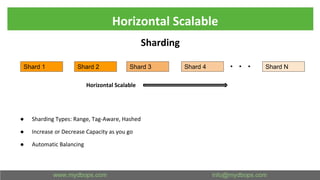
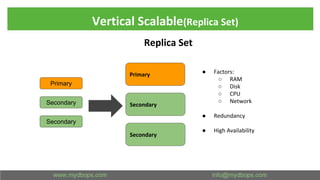
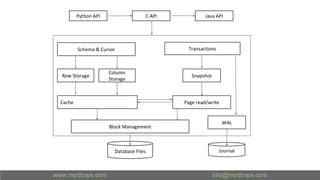
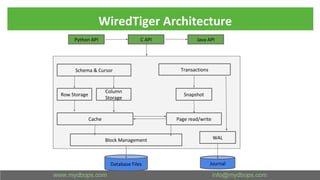
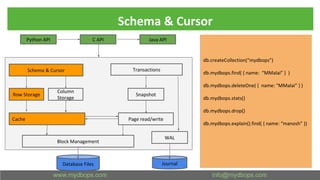
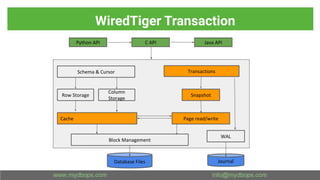
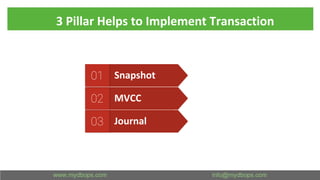
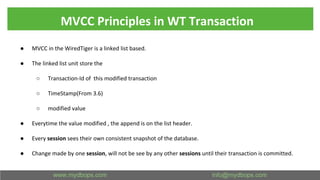
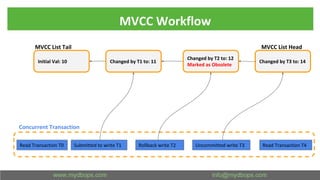
This document presents an in-depth overview of MongoDB's WiredTiger storage engine, focusing on its architecture, transaction management, and internal workings. It discusses MongoDB's evolution with WiredTiger, including transaction features introduced in various versions, as well as features like MVCC and journaling for data integrity. The presentation outlines practical implications for developers and DBA practitioners, emphasizing best practices for managing transactions and performance optimization.














![Thread Safe
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
WT_CONNECTION *conn;
WT_SESSION *session;
WT_CURSOR *cursor;
wt_thread_t threads[NUM_THREADS];
int i;
home = example_setup(argc, argv);
error_check(wiredtiger_open(home, NULL, "create", &conn));
error_check(conn->open_session(conn, NULL, NULL, &session));
error_check(session->create(session, "table:access",
"key_format=S,value_format=S"));
error_check(session->open_cursor(
session, "table:access", NULL, "overwrite", &cursor));
cursor->set_key(cursor, "key1");
cursor->set_value(cursor, "value1");
error_check(cursor->insert(cursor));
error_check(session->close(session, NULL));
for (i = 0; i < NUM_THREADS; i++)
error_check(
__wt_thread_create(NULL, &threads[i], scan_thread,
conn));
for (i = 0; i < NUM_THREADS; i++)
error_check(__wt_thread_join(NULL, threads[i]));
error_check(conn->close(conn, NULL));
return (EXIT_SUCCESS);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbwiredtigerinternals-190427132130/85/MongoDB-WiredTiger-Internals-Journey-To-Transactions-23-320.jpg)




![WiredTiger Transaction Snapshot
snap_min-T1 snap_max-T4
Submit Transaction Interval(0, T1) TRANSACTION INTERVAL BEING EXECUTED [ T1 , T4] Transaction interval to be executed
T5
. . . Commit T1 Rollback T2 Uncommit T3
T4 Moment](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbwiredtigerinternals-190427132130/85/MongoDB-WiredTiger-Internals-Journey-To-Transactions-32-320.jpg)