Let's be honest. AWS DMS looks simple on the surface, but the real challenges often show up mid-migration, leaving you scrambling. The official documentation can only take you so far. What you really need is advice from someone who's been in the trenches.
That's exactly why we're hosting this webinar. Join our Mydbops expert, Arun, for a practical, no-fluff session on AWS Database Migration Service. He's spent countless hours using DMS for complex client migrations and has learned firsthand what works, what breaks, and what the manuals don't tell you.
In this webinar, our speaker will break down:
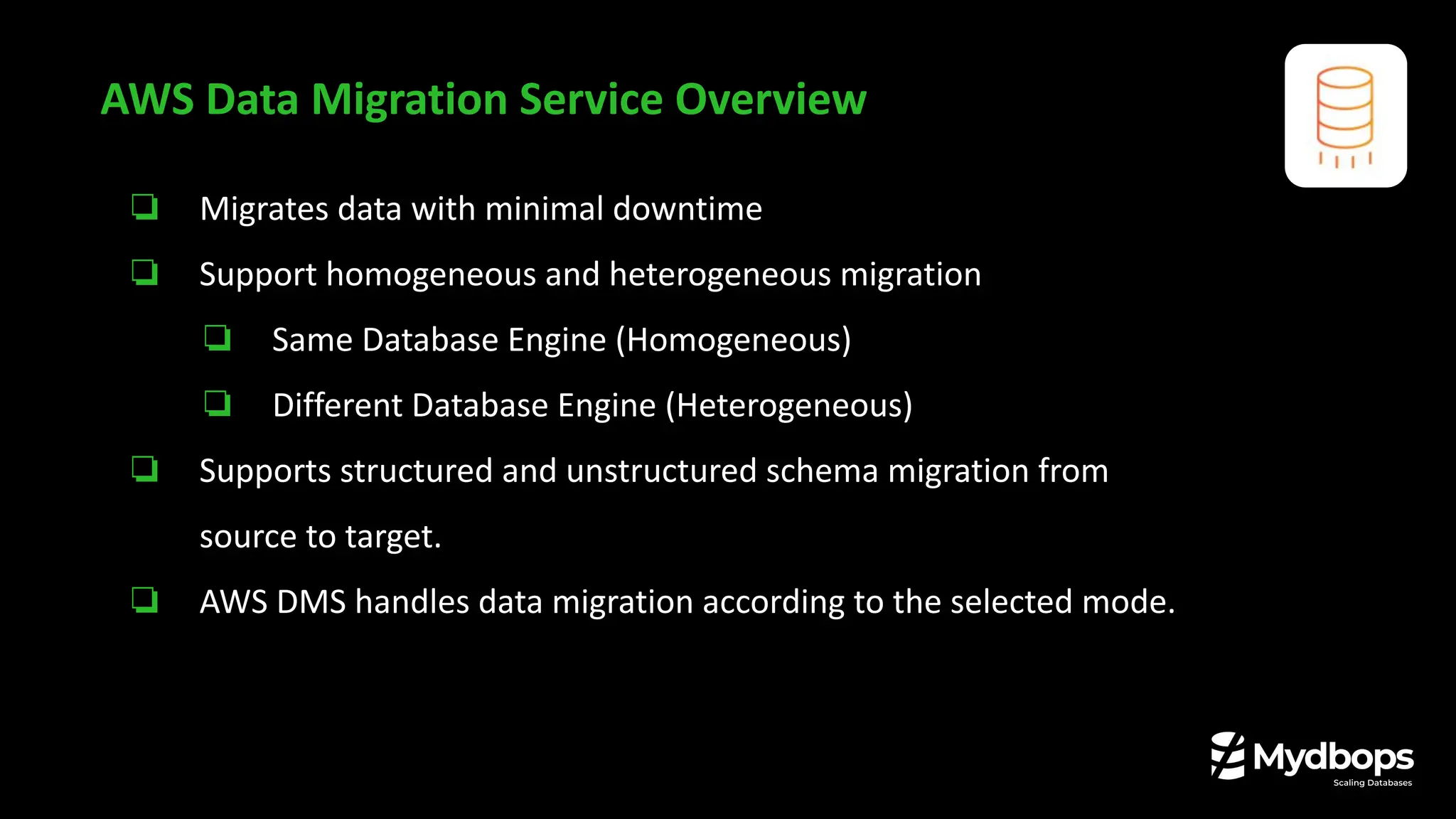
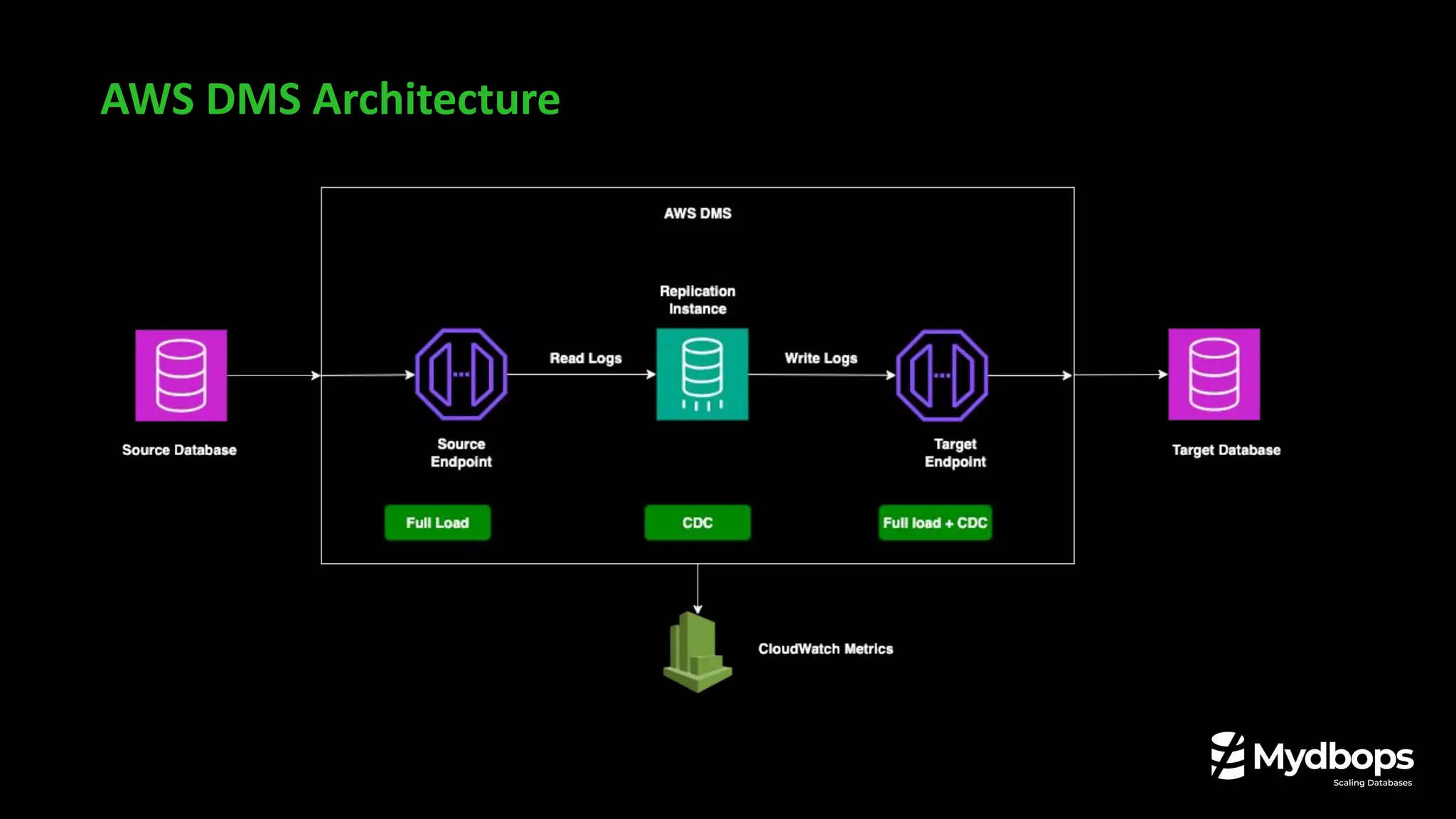
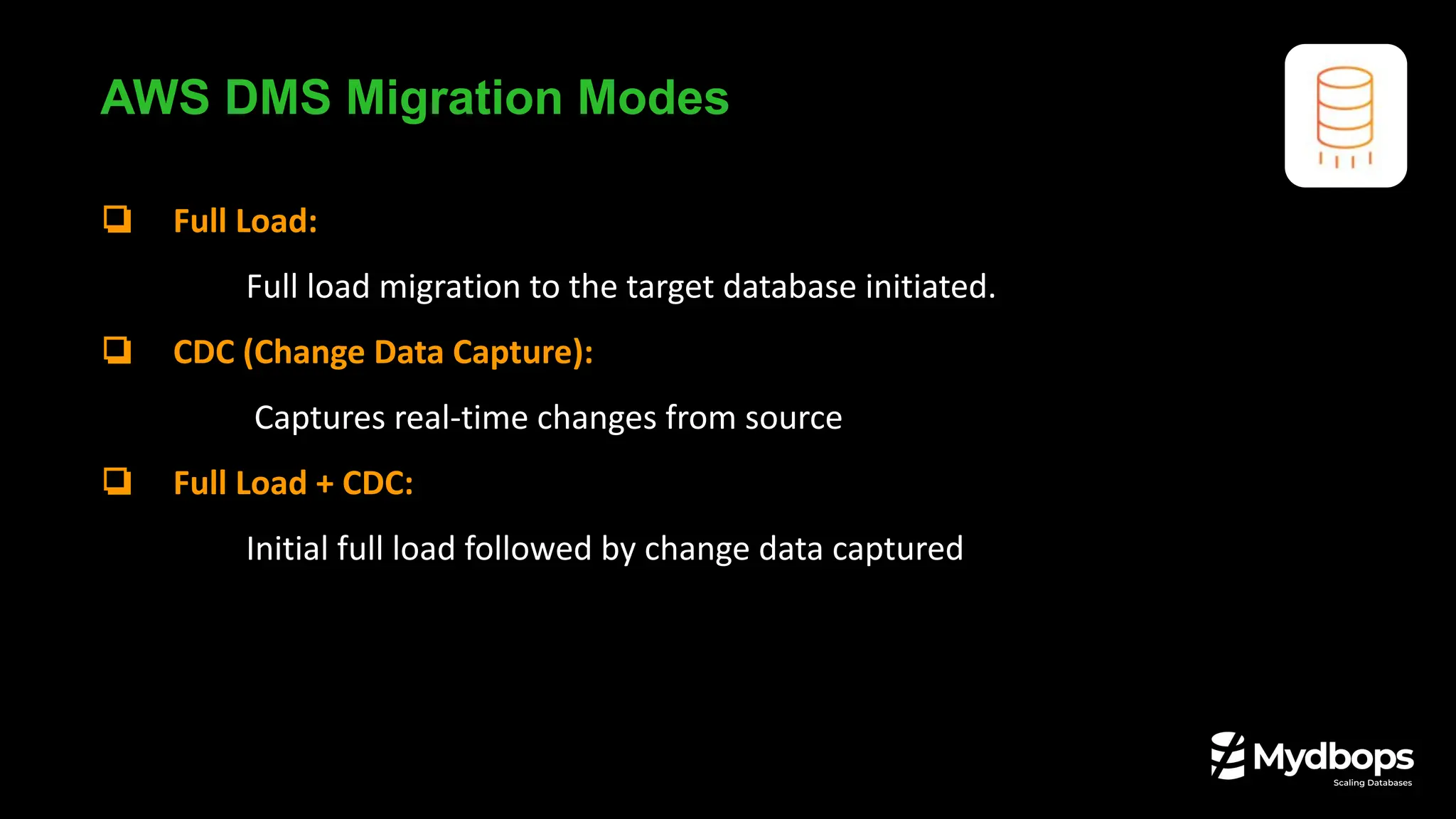
How DMS Actually Works
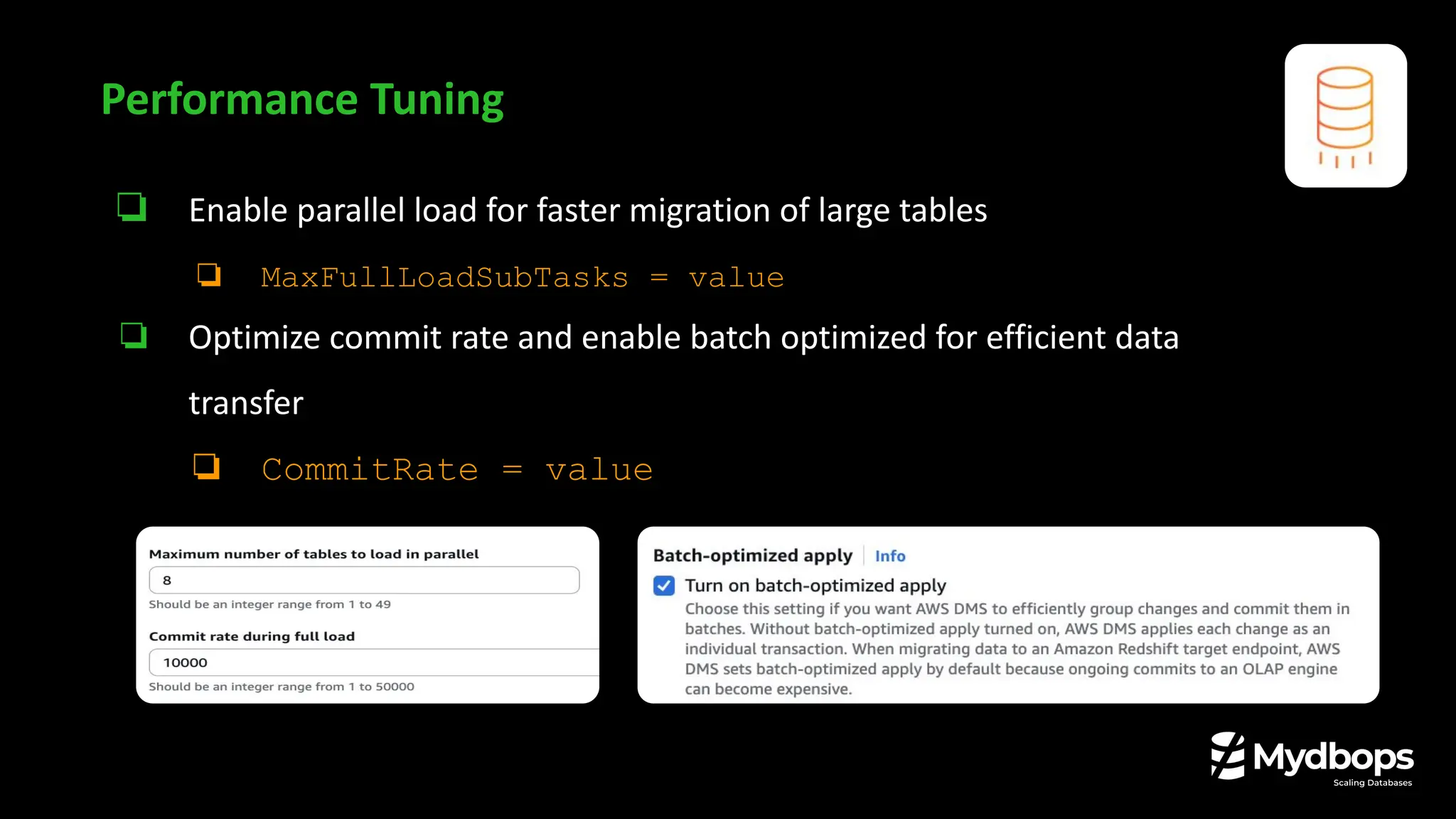
Performance Tuning That Makes a Difference
Real-World Migration Strategies That Work
The Honest Truth: When Not to Use DMS
Essential Security & Validation Tips
Mydbops Managed Services specializes in taking the pain out of database management while optimizing performance. Since 2015, we have been providing top-notch support and assistance for the top three open-source databases: MySQL, MongoDB, and PostgreSQL.
Our team offers a wide range of services, including assistance, support, consulting, 24/7 operations, and expertise in all relevant technologies. We help organizations improve their database's performance, scalability, efficiency, and availability.
Contact us: info@mydbops.com
Visit: https://www.mydbops.com/
#mydbops #database #webinar #dba #opensource #techtalk #live #devops #cloud #AWSDMS #DatabaseMigration #AWS #CloudComputing #DevOps #DMS