Join Monu Mahto, Mydbops expert, as he takes us through the latest enhancements in MariaDB focusing on performance improvements, robust security features, and scalability updates. Whether you're a DBA, developer, or architect, this session equips you with insights to make the most of MariaDB in your production environments.
What You’ll Learn:
• Key performance improvements in recent MariaDB versions
• Security enhancements to protect your workloads
• Tips to scale MariaDB effectively
• Real-world use cases and practical recommendations
Explore more webinars, blogs, and services:
https://www.mydbops.com
Mydbops Managed Services specializes in taking the pain out of database management while optimizing performance. Since 2015, we have been providing top-notch support and assistance for the top three open-source databases: MySQL, MongoDB, and PostgreSQL.
Our team offers a wide range of services, including assistance, support, consulting, 24/7 operations, and expertise in all relevant technologies. We help organizations improve their database's performance, scalability, efficiency, and availability.
Contact us: info@mydbops.com
Visit: https://www.mydbops.com/
#MariaDB #Webinar #Mydbops #OpenSourceDatabase #PerformanceTuning #DatabaseSecurity #Scalability #DBA







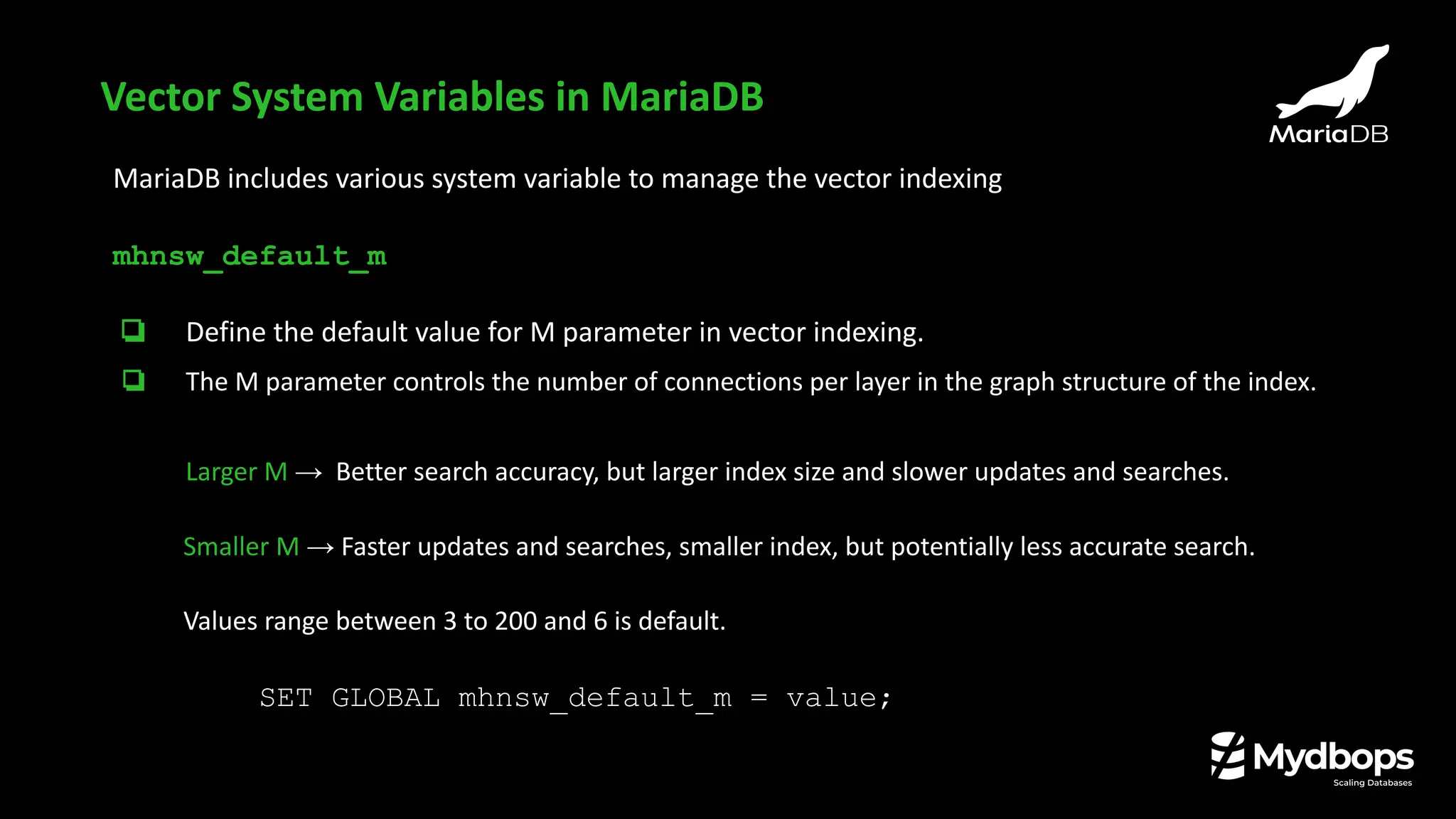
![❏ Available from MariaDB 11.6
❏ Helps in replica creation (without source)
❏ Useful for
❏ cloning a new Replica
❏ doing PITR ,
❏ ensuring backups are replication-consistent
❏ Works similar like --slave-infooption of mariabackup
❏ --dump-slave=[value]
❏ Default value is 1 which print change-master command in dump file
❏ Value 2 the adds only change-master (not active)
dump-slave flag in mariadb-dump](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mydbopsmariadbnewfeaturesslides-250926092020-05c4d3d5/75/What-s-New-in-MariaDB-Performance-Security-and-Beyond-Mydbops-Webinar-Edition-43-9-2048.jpg)















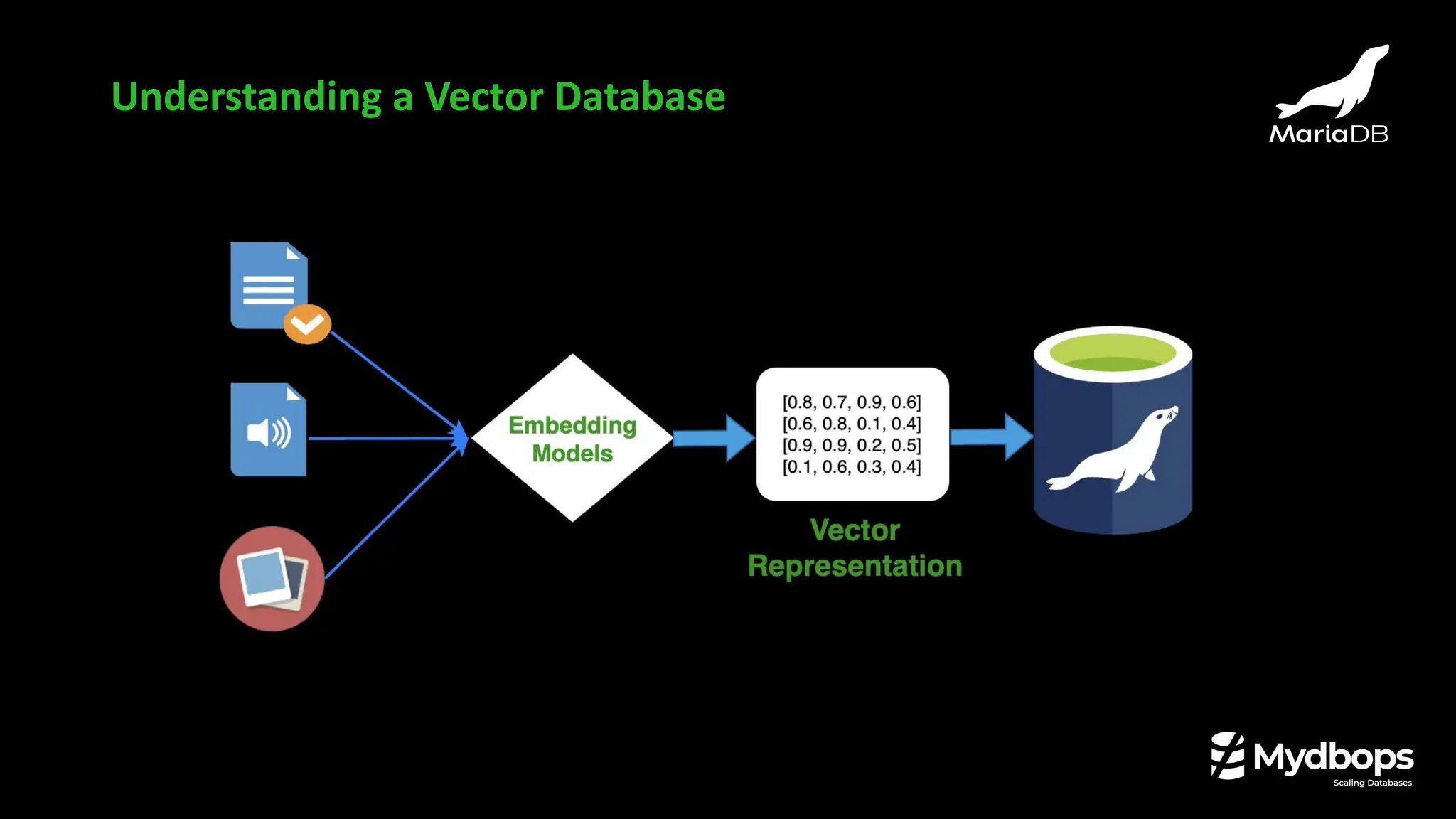
![❏ Vector is a numerical representation of data.
❏ An array of numbers.
❏ Lists of numbers that represent things like text, images, or audio.
❏ Numerical vectors are typically generated using embedding models.
❏ Example
“I like MariaDB”
An embedding model can turn that into a list of numbers.
[0.8, 0.1, 0.9, 0.3, 0.7]
What is Vector ?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mydbopsmariadbnewfeaturesslides-250926092020-05c4d3d5/75/What-s-New-in-MariaDB-Performance-Security-and-Beyond-Mydbops-Webinar-Edition-43-34-2048.jpg)







![❏ MariaDB offers a VECTOR INDEX for fast vector searches.
❏ Distance function options: Euclidean (default) or Cosine.
❏ Only one vector index per table.
MariaDB [vectordb]> Alter table embeddings ADD VECTOR INDEX
embedding_vec_idx_1 (embedding) DISTANCE=cosine;
ERROR 1235 (42000): This version of MariaDB doesn't yet support 'multiple
VECTOR indexes'
Vector index](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mydbopsmariadbnewfeaturesslides-250926092020-05c4d3d5/75/What-s-New-in-MariaDB-Performance-Security-and-Beyond-Mydbops-Webinar-Edition-43-44-2048.jpg)
![Using default distance function (EUCLIDEAN)
Alter table embeddings ADD VECTOR INDEX embedding_vec_idx (embedding);
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.035 sec)
Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
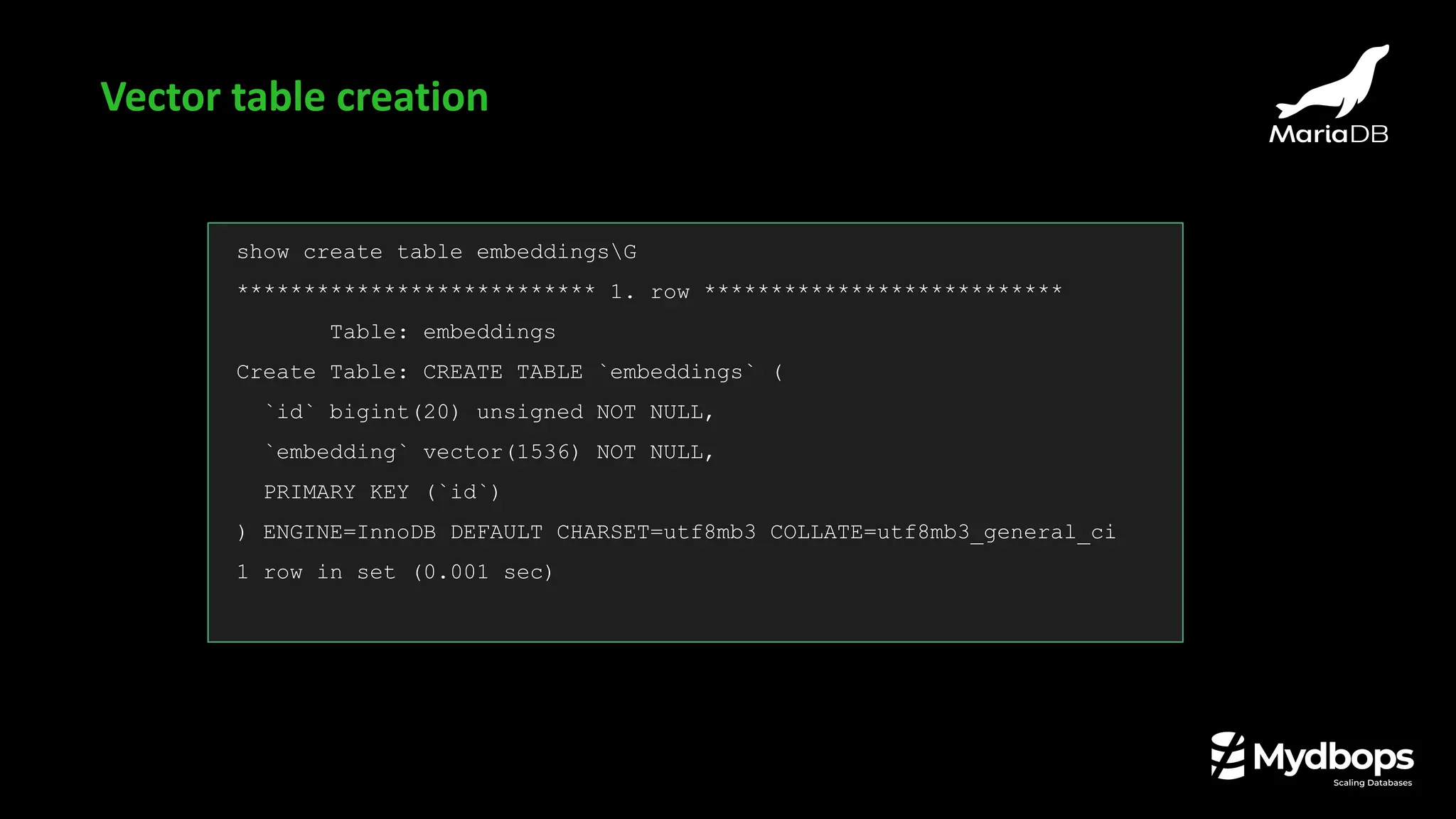
MariaDB [vectordb]> show create table embeddingsG
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Table: embeddings
Create Table: CREATE TABLE `embeddings` (
`id` bigint(20) unsigned NOT NULL,
`embedding` vector(1536) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
VECTOR KEY `embedding_vec_idx` (`embedding`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb3 COLLATE=utf8mb3_general_ci
1 row in set (0.002 sec)
Vector index creation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mydbopsmariadbnewfeaturesslides-250926092020-05c4d3d5/75/What-s-New-in-MariaDB-Performance-Security-and-Beyond-Mydbops-Webinar-Edition-43-45-2048.jpg)
![Using cosine distance function
Alter table embeddings ADD VECTOR INDEX embedding_vec_idx_cosine (embedding) DISTANCE=cosine;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.026 sec)
Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
MariaDB [vectordb]> show create table embeddingsG
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Table: embeddings
Create Table: CREATE TABLE `embeddings` (
`id` bigint(20) unsigned NOT NULL,
`embedding` vector(1536) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
VECTOR KEY `embedding_vec_idx_cosine` (`embedding`) `DISTANCE`=cosine
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb3 COLLATE=utf8mb3_general_ci
1 row in set (0.003 sec)
Vector index creation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mydbopsmariadbnewfeaturesslides-250926092020-05c4d3d5/75/What-s-New-in-MariaDB-Performance-Security-and-Beyond-Mydbops-Webinar-Edition-43-46-2048.jpg)

![❏ VEC_FromText(text)
Converts a text representation of a vector (e.g., '[1.0, 2.5, 3.0]') into the VECTOR data type.
Vector distance functions in MariaDB
select hex(vec_fromtext('[4,5,6]'));
+------------------------------+
| hex(vec_fromtext('[4,5,6]')) |
+------------------------------+
| 000080400000A0400000C040 |
+------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.001 sec)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mydbopsmariadbnewfeaturesslides-250926092020-05c4d3d5/75/What-s-New-in-MariaDB-Performance-Security-and-Beyond-Mydbops-Webinar-Edition-43-48-2048.jpg)
![❏ VEC_ToText(vector)
Converts a binary vector into a json array of numbers (floats).
Vector distance functions in MariaDB
SELECT VEC_ToText(x'e360d63ebe554f3fcdbc523f4522193f5236083d');
+---------------------------------------------------------+
| VEC_ToText(x'e360d63ebe554f3fcdbc523f4522193f5236083d') |
+---------------------------------------------------------+
| [0.418708,0.809902,0.823193,0.598179,0.0332549] |
+---------------------------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.001 sec)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mydbopsmariadbnewfeaturesslides-250926092020-05c4d3d5/75/What-s-New-in-MariaDB-Performance-Security-and-Beyond-Mydbops-Webinar-Edition-43-49-2048.jpg)



![Sample table
show create table vector_storeG
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Table: vector_store
Create Table: CREATE TABLE `vector_store` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL,
`embedding` vector(4) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb3 COLLATE=utf8mb3_general_ci
1 row in set (0.001 sec)
Inserting few records
INSERT INTO vector_store (name, embedding) VALUES ('cat',Vec_FromText('[0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4]'));
INSERT INTO vector_store (name, embedding) VALUES ('cat',Vec_FromText('[0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4]'));
INSERT INTO vector_store (name, embedding) VALUES ('dog', Vec_FromText('[0.11, 0.18, 0.29, 0.41]'));
INSERT INTO vector_store (name, embedding) VALUES ('apple', Vec_FromText('[0.7, 0.6, 0.8, 0.9]'));
INSERT INTO vector_store (name, embedding) VALUES ('banana', Vec_FromText('[0.71, 0.59, 0.81,
0.88]'));
Vector search example](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mydbopsmariadbnewfeaturesslides-250926092020-05c4d3d5/75/What-s-New-in-MariaDB-Performance-Security-and-Beyond-Mydbops-Webinar-Edition-43-54-2048.jpg)
![Selecting the records (vector data stored in binary format)
MariaDB [vectordb]> SELECT * FROM vector_store;
+----+--------+-------------------------------+
| id | name | embedding |
+----+--------+-------------------------------+
| 1 | cat | ���=��L>���>���> |
| 2 | cat | ���=��L>���>���> |
| 3 | dog | �G�=�Q8>�z�>���> |
| 4 | apple | 333?��?��L?fff? |
| 5 | banana | ��5?=?)O?�Ga? |
+----+--------+-------------------------------+
Vector search example](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mydbopsmariadbnewfeaturesslides-250926092020-05c4d3d5/75/What-s-New-in-MariaDB-Performance-Security-and-Beyond-Mydbops-Webinar-Edition-43-55-2048.jpg)
![Fetching in readable format using Vec_ToText function
SELECT name, Vec_ToText(embedding) AS embedding FROM vector_store;
+--------+---------------------------+
| name | embedding |
+--------+---------------------------+
| cat | [0.1,0.2,0.3,0.4] |
| cat | [0.1,0.2,0.3,0.4] |
| dog | [0.11,0.18,0.29,0.41] |
| apple | [0.7,0.6,0.8,0.9] |
| banana | [0.71,0.59,0.81,0.88] |
+--------+---------------------------+
5 rows in set (0.002 sec)
Vector search example](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mydbopsmariadbnewfeaturesslides-250926092020-05c4d3d5/75/What-s-New-in-MariaDB-Performance-Security-and-Beyond-Mydbops-Webinar-Edition-43-56-2048.jpg)
![Searching using VEC_DISTANCE_EUCLIDEAN
SELECT name, Vec_ToText(embedding) AS embedding FROM Vector_store ORDER BY
VEC_DISTANCE_EUCLIDEAN(embedding, Vec_FromText('[0.71,0.59,0.81,0.88]'));
+--------+------------------------+
| name | embedding |
+--------+------------------------+
| banana | [0.71,0.59,0.81,0.88] |
| apple | [0.7,0.6,0.8,0.9] |
| cat | [0.1,0.2,0.3,0.4] |
| cat | [0.1,0.2,0.3,0.4] |
| dog | [0.11,0.18,0.29,0.41] |
+--------+------------------------+
5 rows in set (0.005 sec)
Vector search example](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mydbopsmariadbnewfeaturesslides-250926092020-05c4d3d5/75/What-s-New-in-MariaDB-Performance-Security-and-Beyond-Mydbops-Webinar-Edition-43-57-2048.jpg)
![Searching using VEC_DISTANCE_COSINE
SELECT name, Vec_ToText(embedding) AS embedding FROM vector_store
ORDER BY VEC_DISTANCE_COSINE(embedding, Vec_FromText('[0.71,0.59,0.81,0.88]'));
+--------+------------------------+
| name | embedding |
+--------+------------------------+
| banana | [0.71,0.59,0.81,0.88] |
| apple | [0.7,0.6,0.8,0.9] |
| dog | [0.11,0.18,0.29,0.41] |
| cat | [0.1,0.2,0.3,0.4] |
| cat | [0.1,0.2,0.3,0.4] |
+--------+------------------------+
5 rows in set (0.002 sec)
Vector search example](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mydbopsmariadbnewfeaturesslides-250926092020-05c4d3d5/75/What-s-New-in-MariaDB-Performance-Security-and-Beyond-Mydbops-Webinar-Edition-43-58-2048.jpg)


