Embed presentation
Downloaded 188 times


![Command Line--master [--oplogSize <MB>]--slave –source <host> [--only <db>]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbreplicationmongosfapr20101-100430191028-phpapp02/85/MongoDB-Replication-Dwight-Merriman-3-320.jpg)






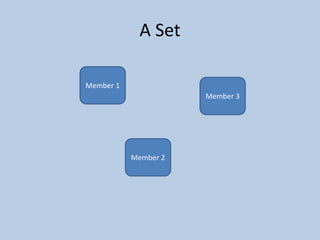
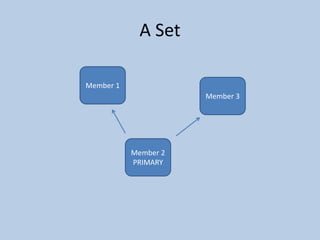
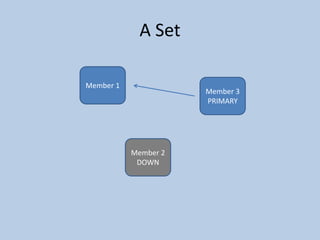
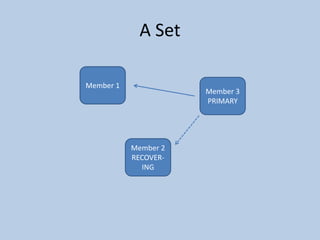
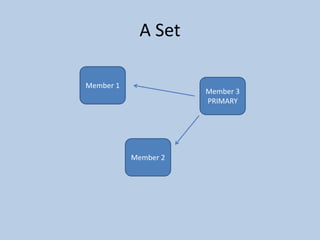




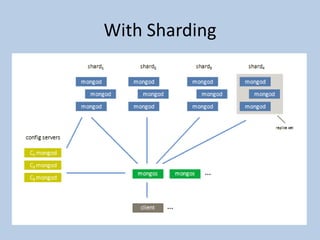
This document discusses MongoDB replication using replica sets. It describes how to configure and administer replica sets, which allow for asynchronous master-slave replication and automatic failover between members. Replica sets maintain multiple copies of data across multiple servers, provide redundancy and high availability, and can elect a new primary if one fails. The document outlines different replication topologies and member types in a replica set, and how replica sets integrate with sharded clusters in MongoDB.


![Command Line--master [--oplogSize <MB>]--slave –source <host> [--only <db>]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbreplicationmongosfapr20101-100430191028-phpapp02/85/MongoDB-Replication-Dwight-Merriman-3-320.jpg)
















