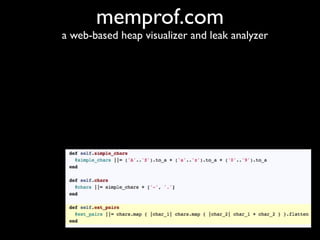
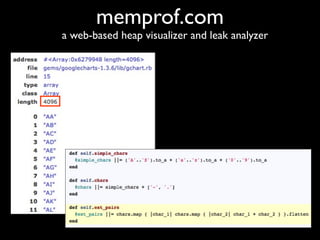
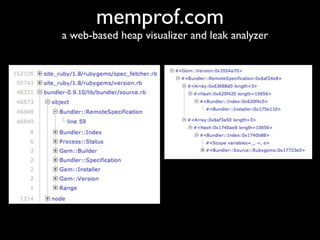
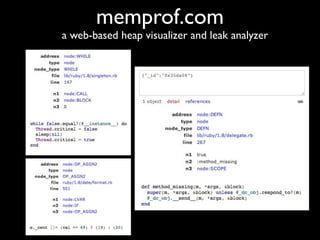
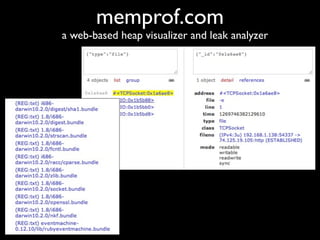
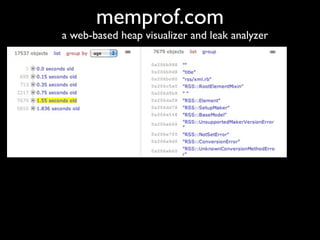
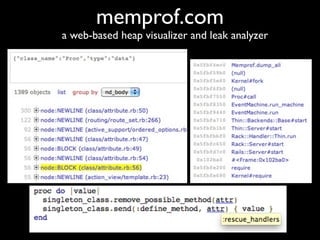
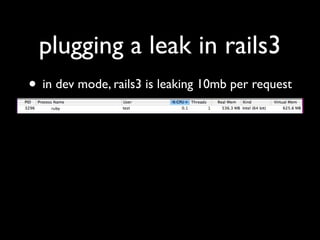
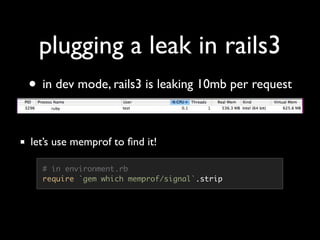
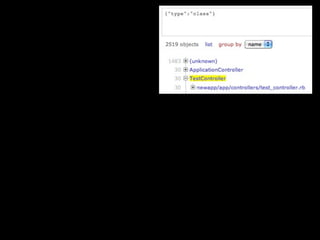
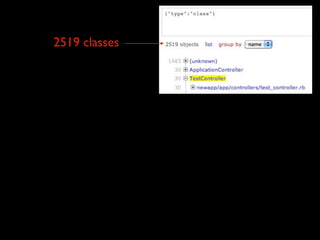
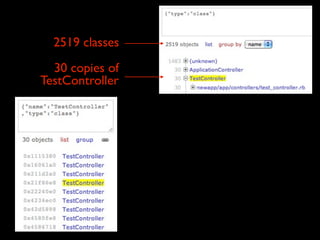
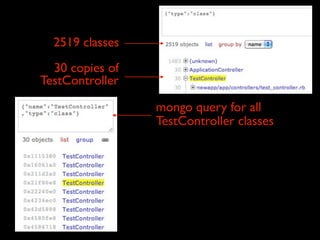
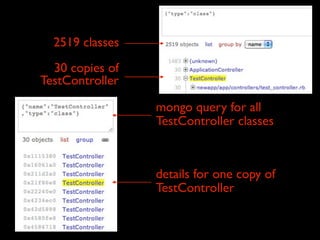
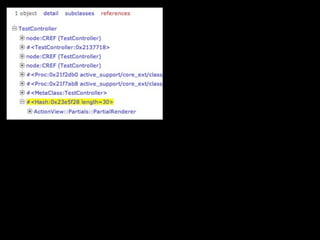
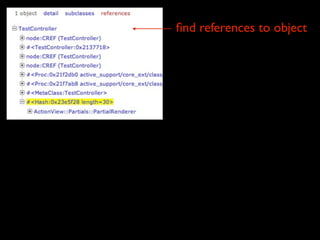
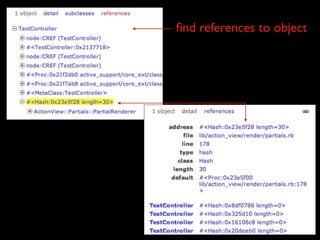
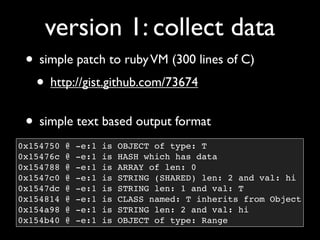
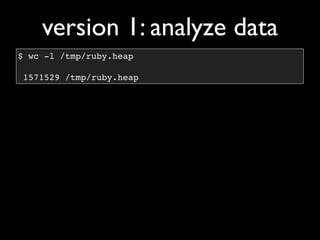
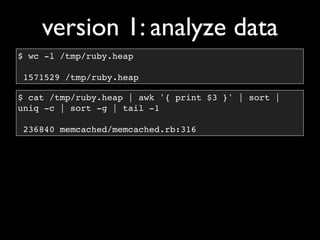
The document discusses building a Ruby debugger by collecting data on Ruby objects in memory and analyzing that data. It describes two versions of the debugger: Version 1 collects basic data but requires patching Ruby and has limited analysis, while Version 2 called Memprof collects more detailed data in JSON format without patching Ruby and allows deeper analysis using MongoDB. The second version provides a way to visualize and analyze Ruby memory usage and detect potential memory leaks.
























![arrays
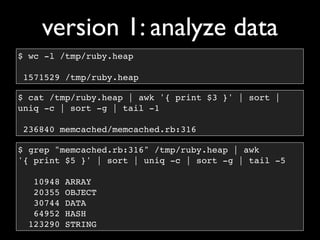
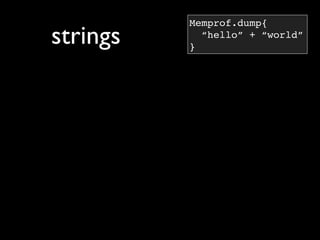
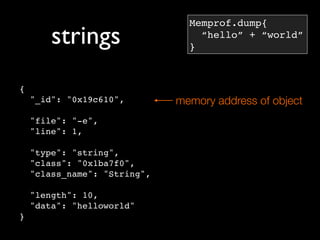
Memprof.dump{
[
1,
:b,
2.2,
“d”
]
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/debuggingruby-100430191200-phpapp01/85/Debugging-Ruby-Aman-Gupta-31-320.jpg)
![arrays
Memprof.dump{
[
1,
:b,
{
"_id": "0x19c5c0",
2.2,
“d”
"class": "0x1b0d18", ]
"class_name": "Array", }
"length": 4,
"data": [
1,
":b",
"0x19c750",
"0x19c598"
]
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/debuggingruby-100430191200-phpapp01/85/Debugging-Ruby-Aman-Gupta-32-320.jpg)
![arrays
Memprof.dump{
[
1,
:b,
{
"_id": "0x19c5c0",
2.2,
“d”
"class": "0x1b0d18", ]
"class_name": "Array", }
"length": 4,
"data": [
1, integers and symbols are
":b", stored in the array itself
"0x19c750",
"0x19c598"
]
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/debuggingruby-100430191200-phpapp01/85/Debugging-Ruby-Aman-Gupta-33-320.jpg)
![arrays
Memprof.dump{
[
1,
:b,
{
"_id": "0x19c5c0",
2.2,
“d”
"class": "0x1b0d18", ]
"class_name": "Array", }
"length": 4,
"data": [
1, integers and symbols are
":b", stored in the array itself
"0x19c750", floats and strings are
"0x19c598" separate ruby objects
]
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/debuggingruby-100430191200-phpapp01/85/Debugging-Ruby-Aman-Gupta-34-320.jpg)

![hashes
Memprof.dump{
{
:a => 1,
“b” => 2.2
{ }
"_id": "0x19c598", }
"type": "hash",
"class": "0x1af170",
"class_name": "Hash",
"default": null,
"length": 2,
"data": [
[ ":a", 1 ],
[ "0xc728", "0xc750" ]
]
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/debuggingruby-100430191200-phpapp01/85/Debugging-Ruby-Aman-Gupta-36-320.jpg)
![hashes
Memprof.dump{
{
:a => 1,
“b” => 2.2
{ }
"_id": "0x19c598", }
"type": "hash",
"class": "0x1af170",
"class_name": "Hash",
"default": null,
"length": 2,
"data": [
[ ":a", 1 ],
hash entries as key/value
[ "0xc728", "0xc750" ] pairs
]
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/debuggingruby-100430191200-phpapp01/85/Debugging-Ruby-Aman-Gupta-37-320.jpg)
![hashes
Memprof.dump{
{
:a => 1,
“b” => 2.2
{ }
"_id": "0x19c598", }
"type": "hash",
"class": "0x1af170",
"class_name": "Hash",
"default": null, no default proc
"length": 2,
"data": [
[ ":a", 1 ],
hash entries as key/value
[ "0xc728", "0xc750" ] pairs
]
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/debuggingruby-100430191200-phpapp01/85/Debugging-Ruby-Aman-Gupta-38-320.jpg)








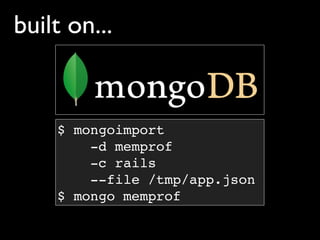
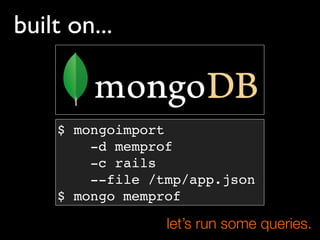

![what types of objects?
> db.rails.distinct(‘type’)
[‘array’,
‘bignum’,
‘class’,
‘float’,
‘hash’,
‘module’,
‘node’,
‘object’,
‘regexp’,
‘string’,
...]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/debuggingruby-100430191200-phpapp01/85/Debugging-Ruby-Aman-Gupta-50-320.jpg)












![how many objs per type?
[
...,
{type: ‘array’, count: 7621},
{type: ‘string’, count: 69139},
{type: ‘node’, count: 365285}
]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/debuggingruby-100430191200-phpapp01/85/Debugging-Ruby-Aman-Gupta-63-320.jpg)
![how many objs per type?
[
...,
{type: ‘array’, count: 7621},
{type: ‘string’, count: 69139},
{type: ‘node’, count: 365285}
]
lots of nodes](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/debuggingruby-100430191200-phpapp01/85/Debugging-Ruby-Aman-Gupta-64-320.jpg)
![how many objs per type?
[
...,
{type: ‘array’, count: 7621},
{type: ‘string’, count: 69139},
{type: ‘node’, count: 365285}
]
lots of nodes
• nodes represent ruby code
• stored like any other ruby object
• makes ruby completely dynamic](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/debuggingruby-100430191200-phpapp01/85/Debugging-Ruby-Aman-Gupta-65-320.jpg)










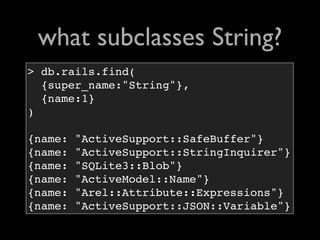
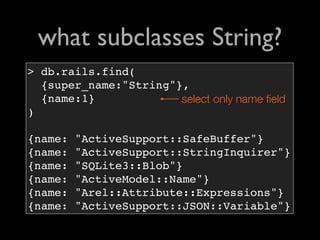




![the largest objects?
> db.rails.find(
{type:
{$in:['string','array','hash']}
},
{type:1,length:1}
).sort({length:-1}).limit(3)
{type: "string", length: 2308}
{type: "string", length: 1454}
{type: "string", length: 1238}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/debuggingruby-100430191200-phpapp01/85/Debugging-Ruby-Aman-Gupta-82-320.jpg)
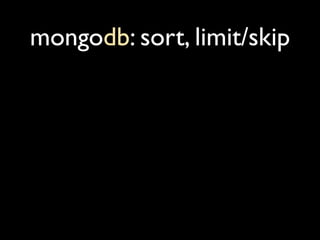







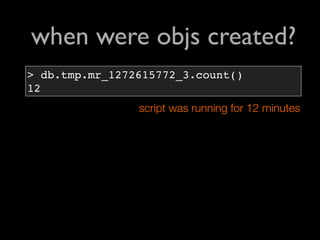
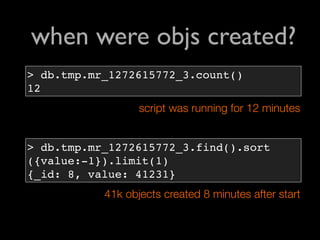
![when were objs created?
> db.rails.mapReduce(function(){
var secs = this.time - start_time;
var mins_since_start = secs % 60;
emit(mins_since_start, 1);
}, function(key, vals){
for(var i=0,sum=0; i<vals.length;
sum += vals[i++]);
return sum;
}, {
scope: { start_time: db.rails.find
().sort({time:1}).limit(1)[0].time }
} start_time = min(time)
)
{result:"tmp.mr_1272615772_3"}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/debuggingruby-100430191200-phpapp01/85/Debugging-Ruby-Aman-Gupta-91-320.jpg)


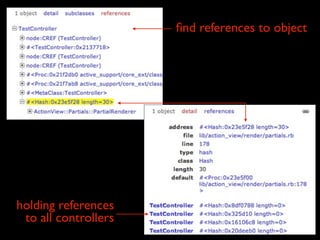
![references to this object?
ary = [“a”,”b”,”c”]
ary references “a”
“b” referenced by ary
• ruby makes it easy to “leak” references
• an object will stay around until all
references to it are gone
• more objects = longer GC = bad
performance
• must find references to fix leaks](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/debuggingruby-100430191200-phpapp01/85/Debugging-Ruby-Aman-Gupta-96-320.jpg)
![references to this object?
• db.rails_refs.insert({
_id:"0xary", refs:["0xa","0xb","0xc"]
})
create references lookup table](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/debuggingruby-100430191200-phpapp01/85/Debugging-Ruby-Aman-Gupta-97-320.jpg)
![references to this object?
• db.rails_refs.insert({
_id:"0xary", refs:["0xa","0xb","0xc"]
})
create references lookup table
• db.rails_refs.ensureIndex({refs:1})
add ‘multikey’ index to refs array](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/debuggingruby-100430191200-phpapp01/85/Debugging-Ruby-Aman-Gupta-98-320.jpg)
![references to this object?
• db.rails_refs.insert({
_id:"0xary", refs:["0xa","0xb","0xc"]
})
create references lookup table
• db.rails_refs.ensureIndex({refs:1})
add ‘multikey’ index to refs array
• db.rails_refs.find({refs:“0xa”})
efficiently lookup all objs holding a ref to 0xa](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/debuggingruby-100430191200-phpapp01/85/Debugging-Ruby-Aman-Gupta-99-320.jpg)