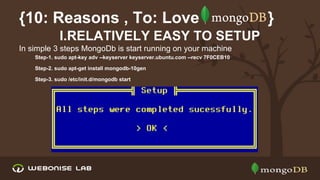
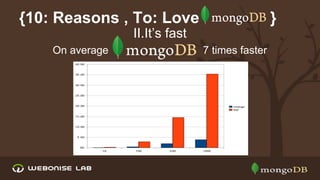
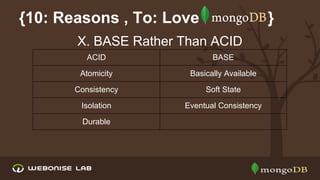
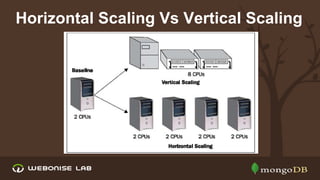
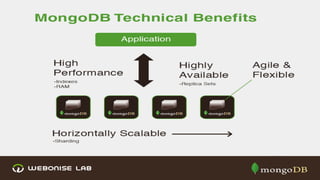
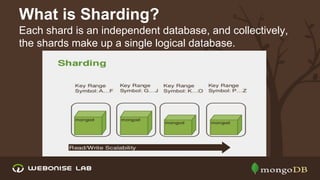
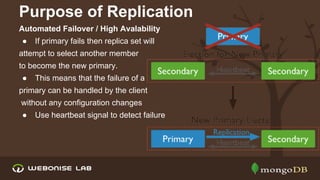
The document discusses scalability and high availability in MongoDB through the use of replica sets and sharding. It outlines the advantages of using replica sets including automated failover, data redundancy, and read scaling, while also explaining sharding as a method of horizontal scaling by distributing data across multiple nodes. A demo for setting up a replica set in production is provided, emphasizing the ease of setup and performance benefits.