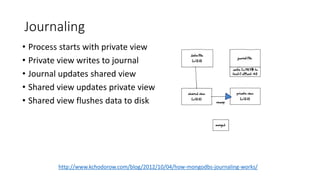
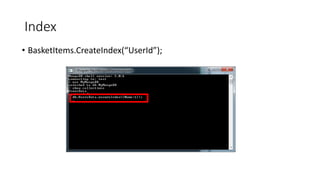
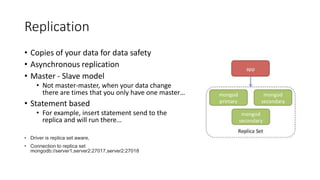
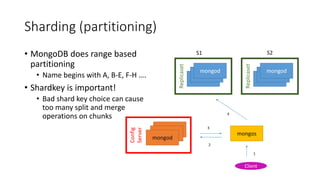
This document discusses MongoDB and provides information on why it is useful, how it works, and best practices. Specifically, it notes that MongoDB is a noSQL database that is easy to use, scalable, and supports high performance and availability. It is well-suited for flexible schemas, embedded documents, and complex relationships. The document also covers topics like BSON, CRUD operations, indexing, map reduce, transactions, replication, and sharding in MongoDB.