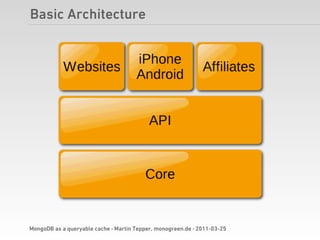
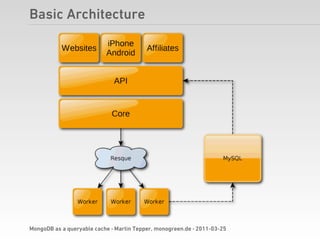
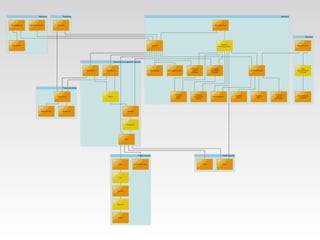
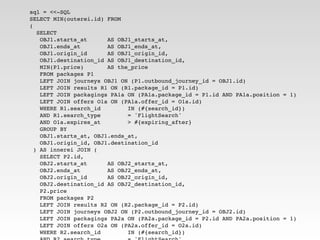
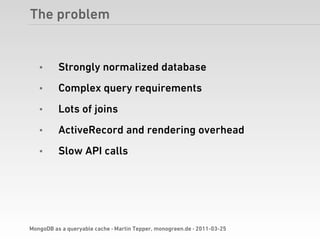
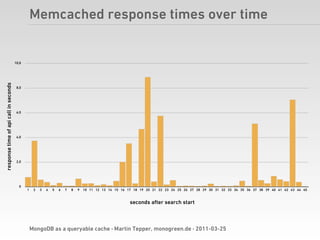
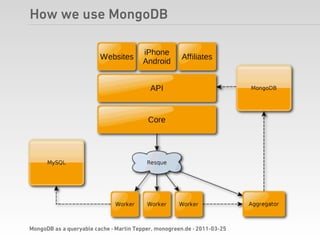
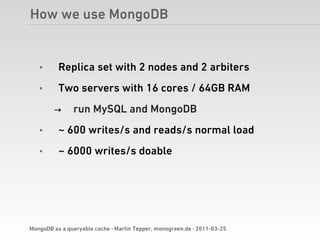
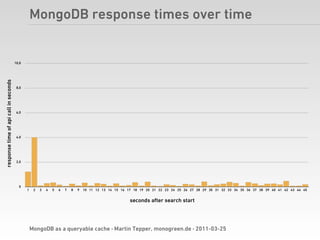
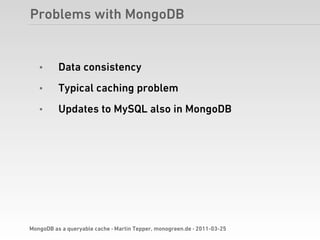
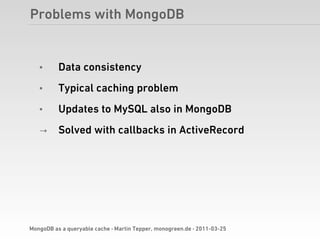
Martin Tepper presented on using MongoDB as a queryable cache for Travel IQ, a meta search engine for flights and hotels. Travel IQ was experiencing slow API response times due to complex queries on its normalized SQL database. MongoDB was implemented as a caching layer to store denormalized offer data to allow for faster querying. This improved response times but also led to some headaches around data consistency and segmentation faults that were later addressed.