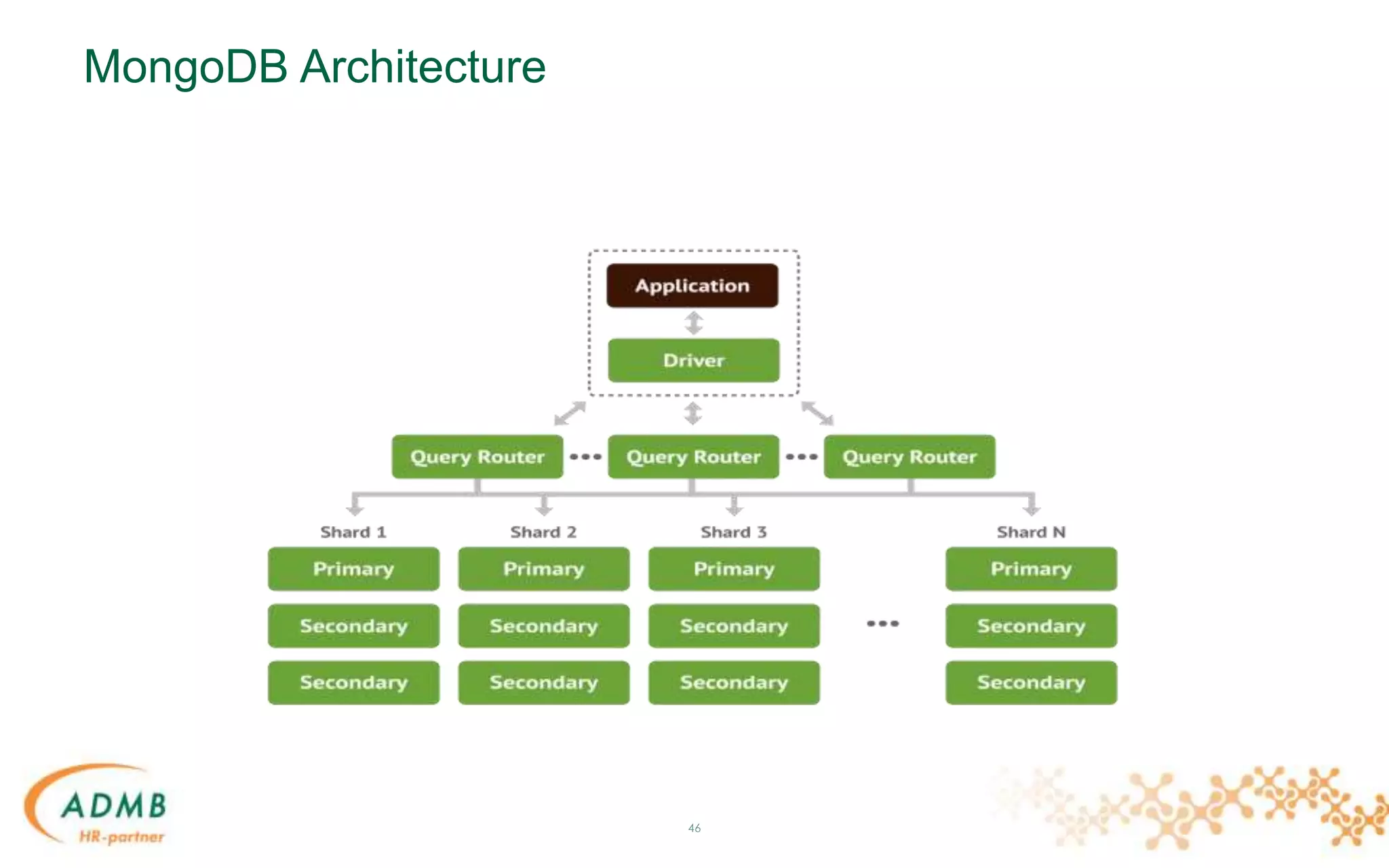
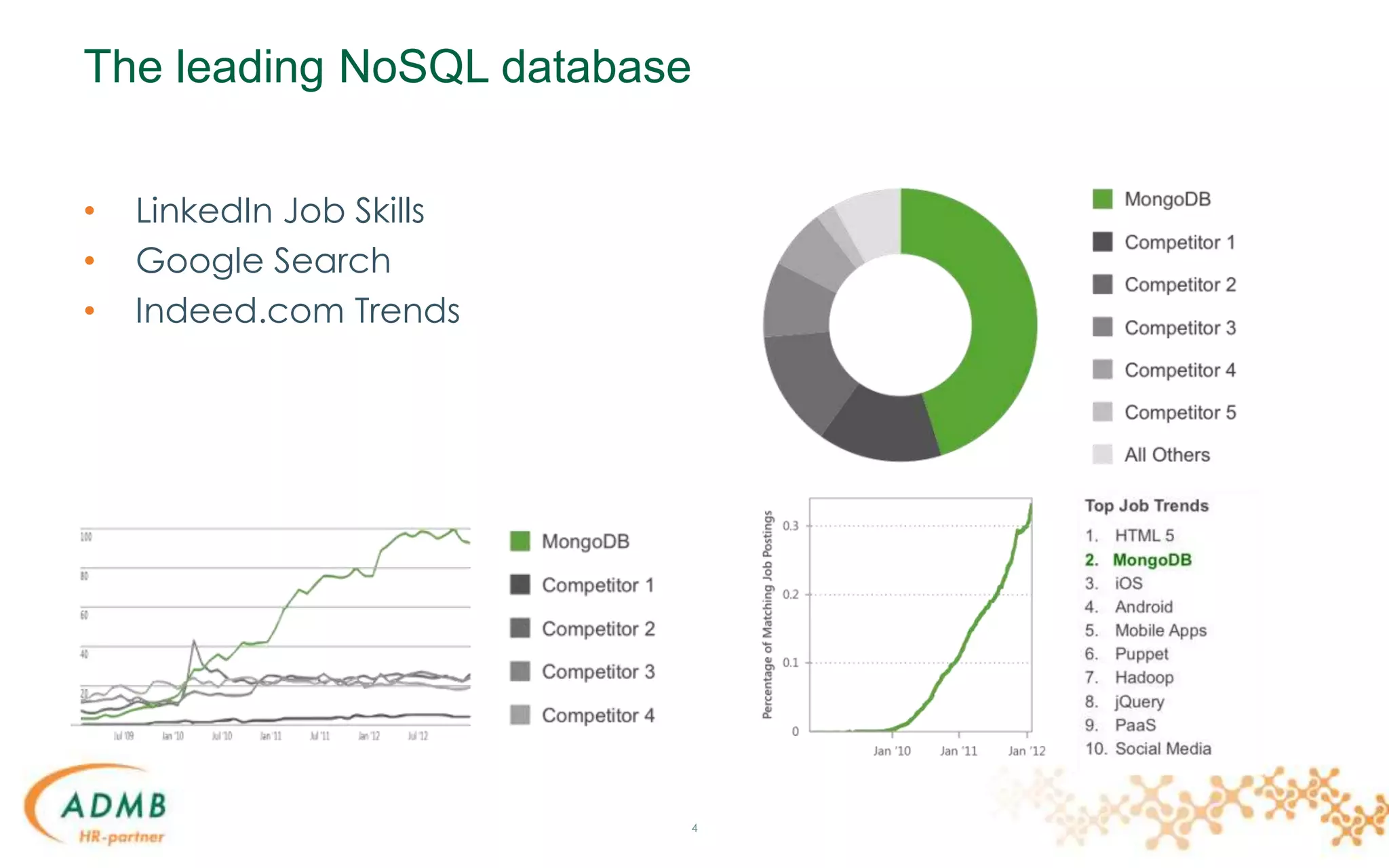
This document provides an overview of MongoDB for Java developers. It discusses what MongoDB is, how it compares to relational databases, common use cases, data modeling approaches, CRUD operations, indexing, aggregation, replication, sharding, and tools for integrating MongoDB with Java applications. The document contains multiple code examples and concludes with a demonstration of building a sample app with MongoDB.





![From relational databases to MongoDB
8
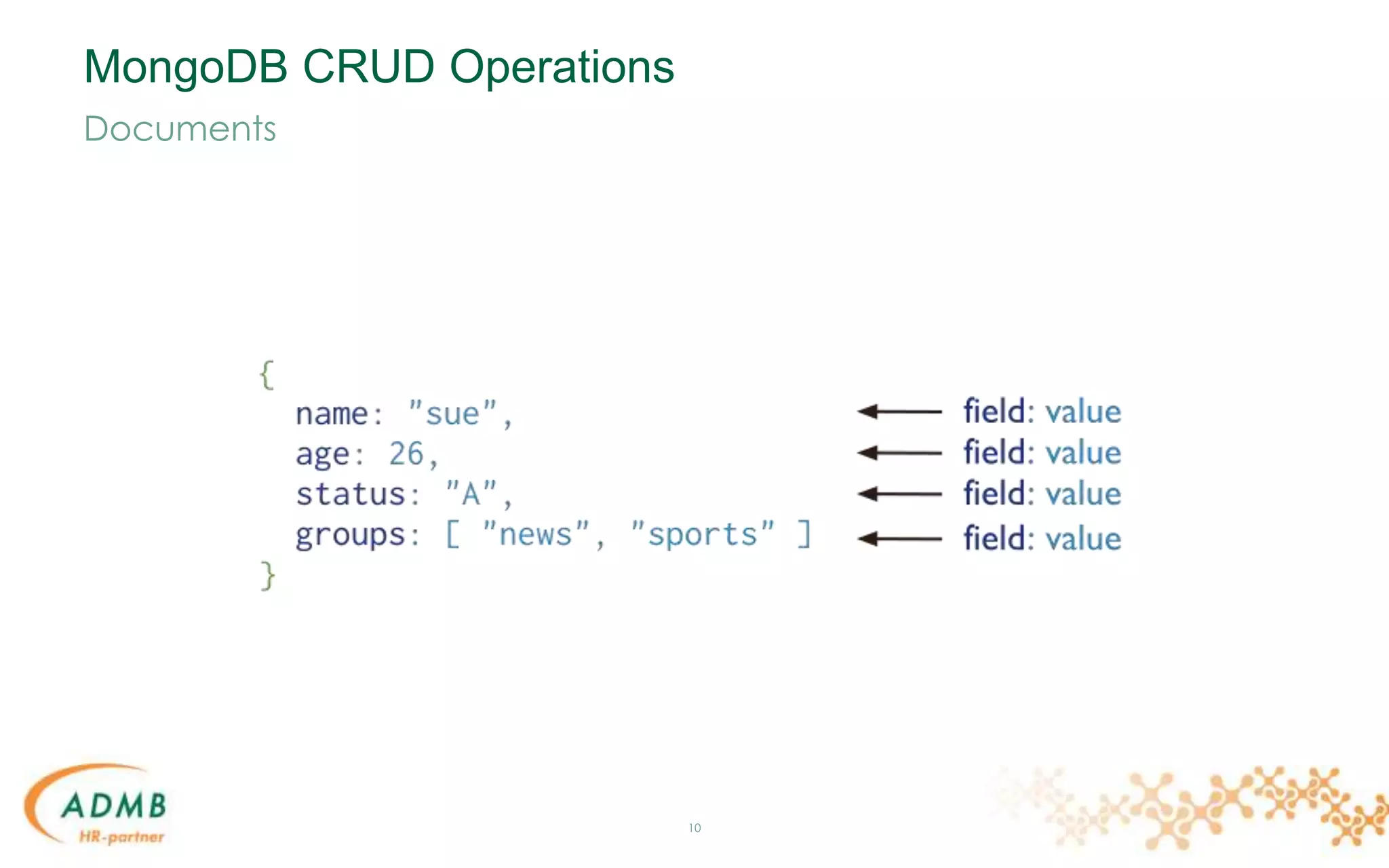
{
first_name: "Anthony",
surname: "Slabinck",
city: "Bruges",
location: [45.123,47.232],
cars: [
{ model: "Bentley",
year: 1973,
value: 100000 },
{ mode: "Rolls Royce",
year: 1965,
value: 330000 } ]
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodb-150306034646-conversion-gate01/75/MongoDB-8-2048.jpg)
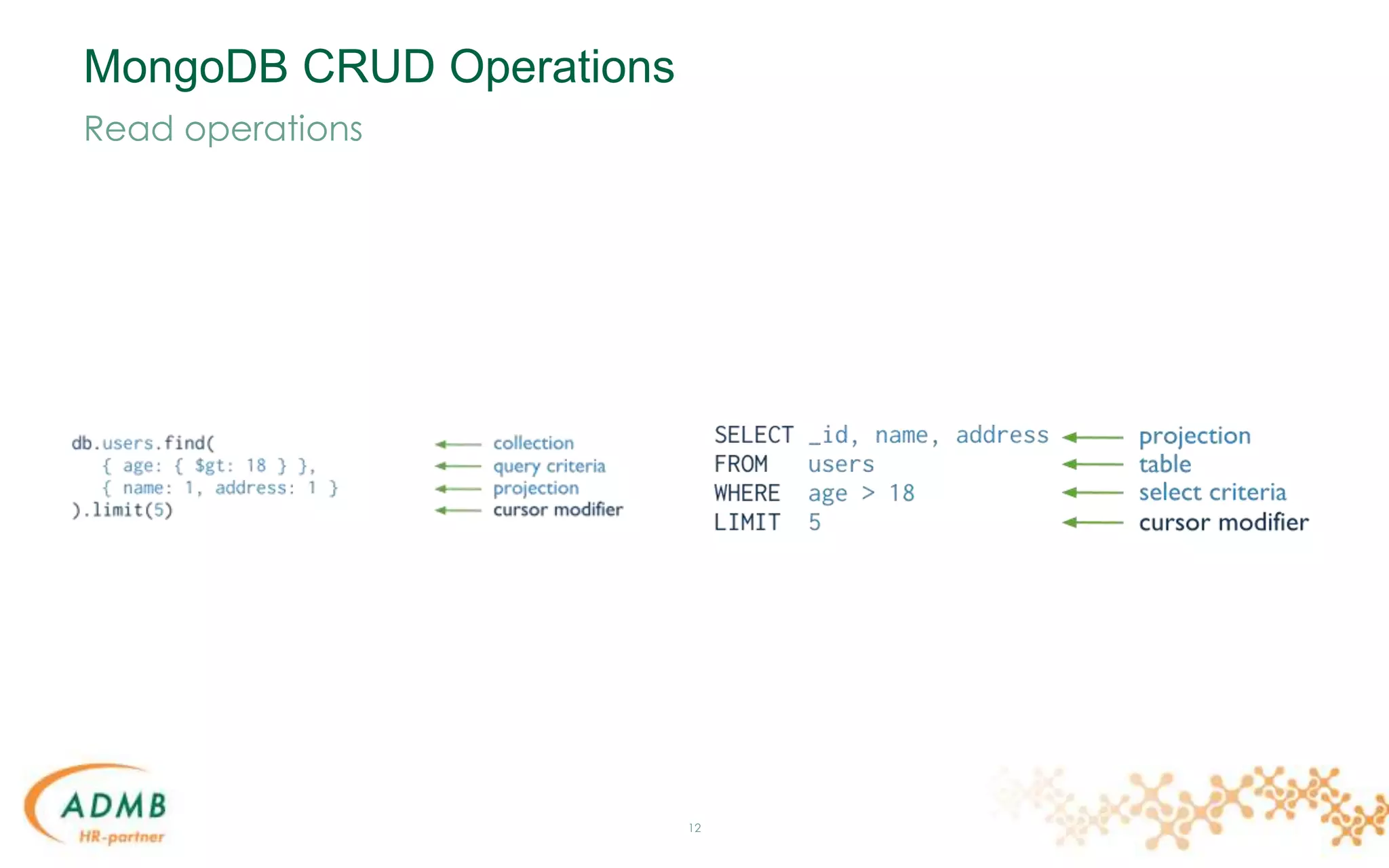
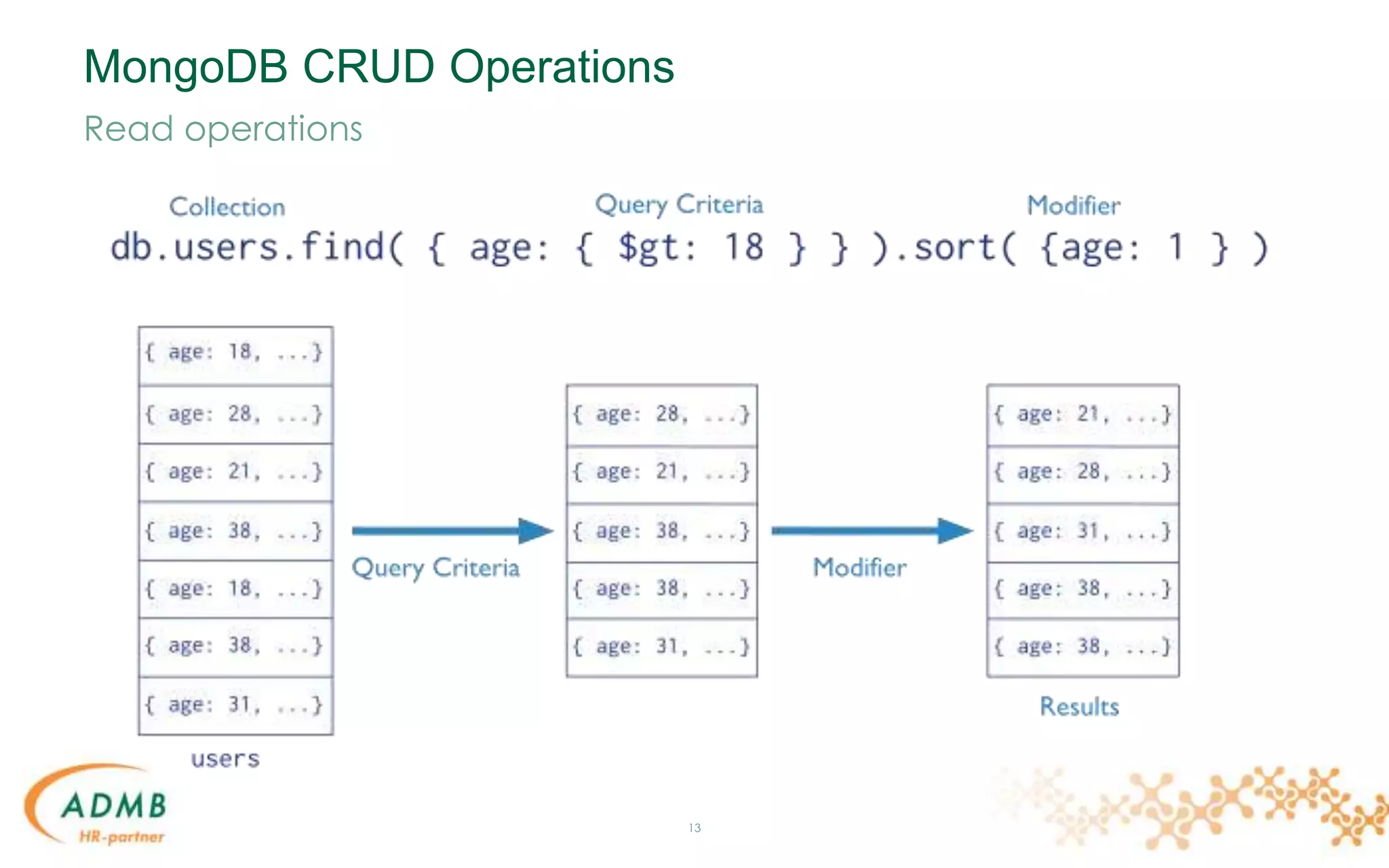
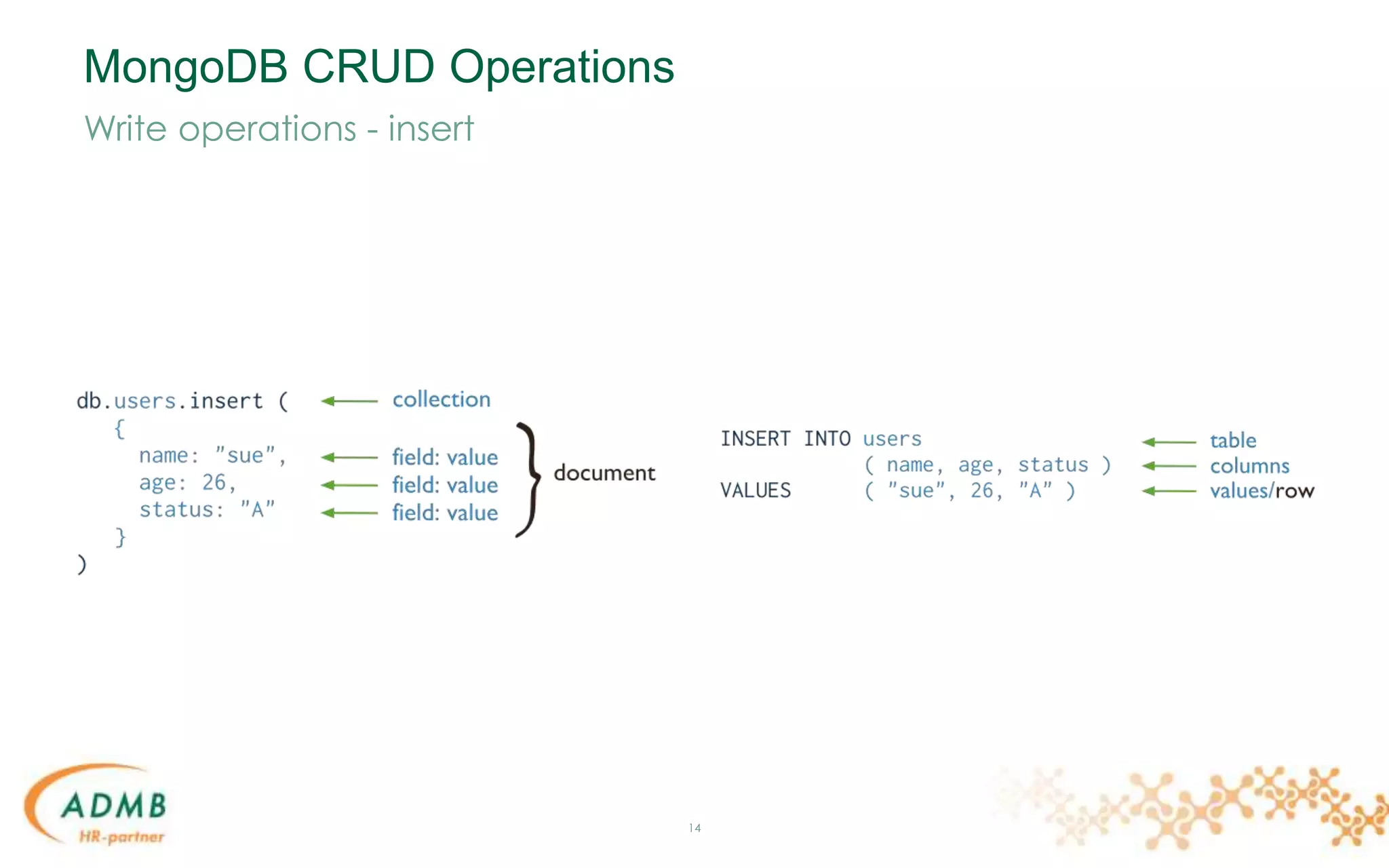
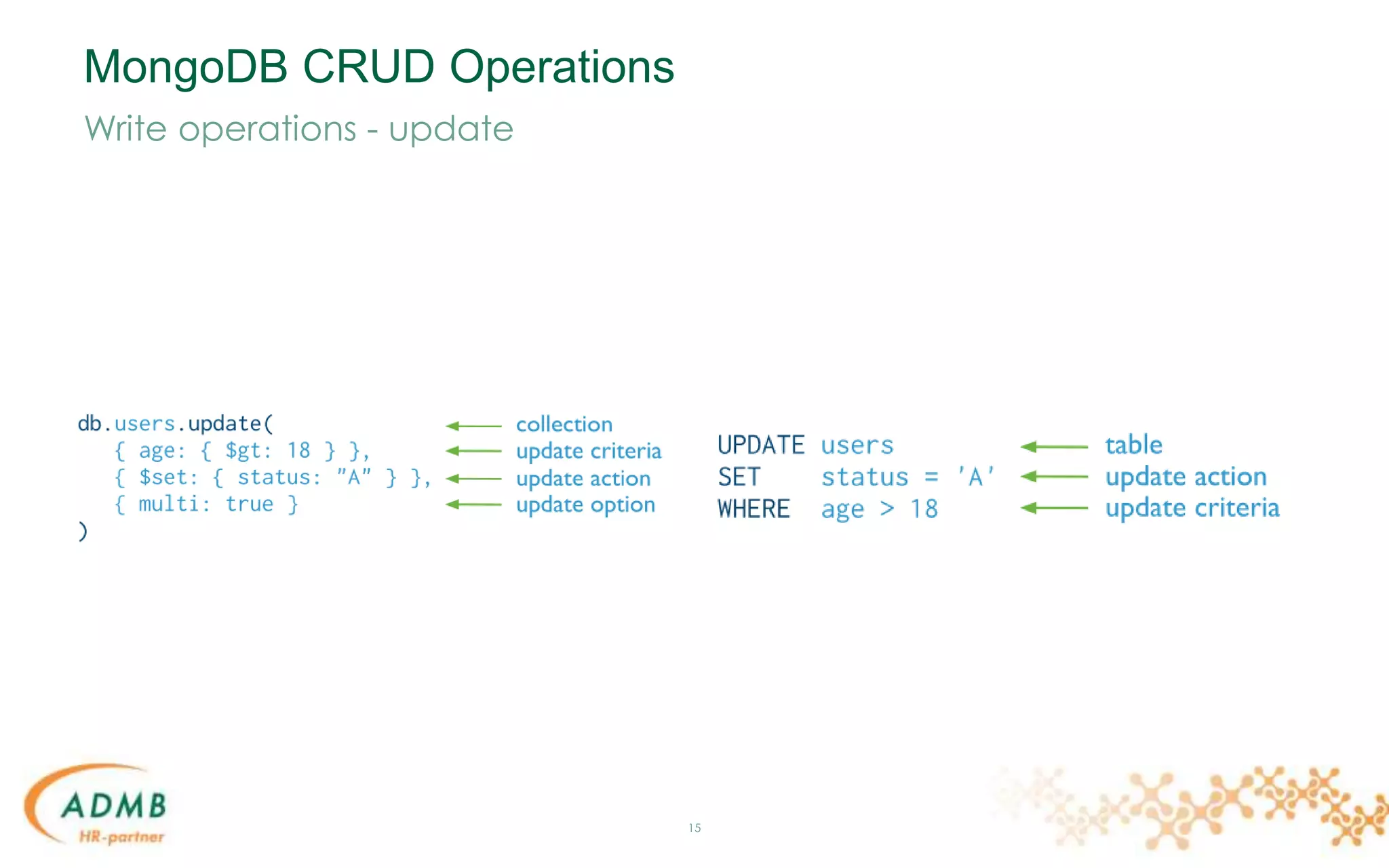
![Data Model
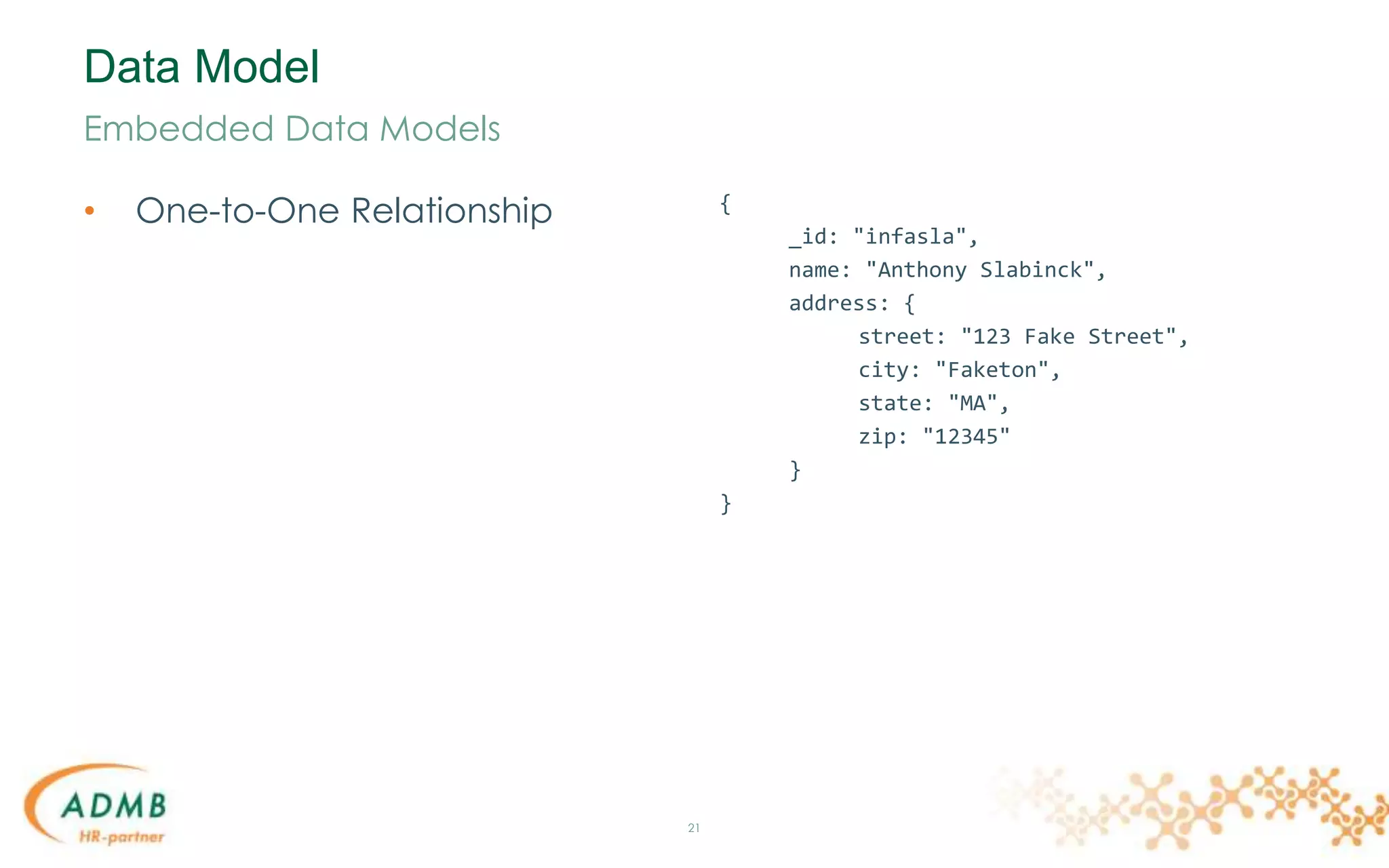
• One-to-Many Relationship
22
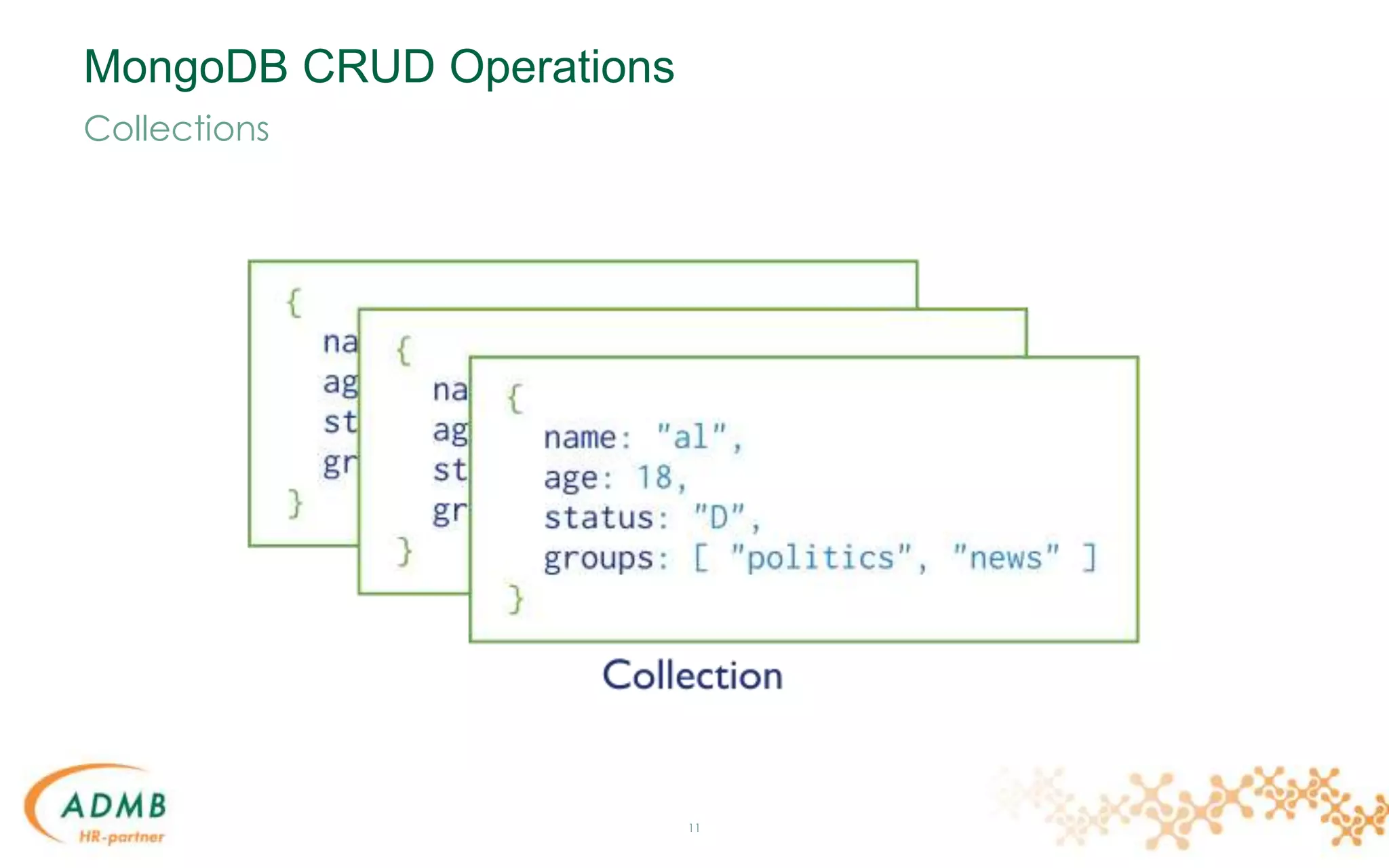
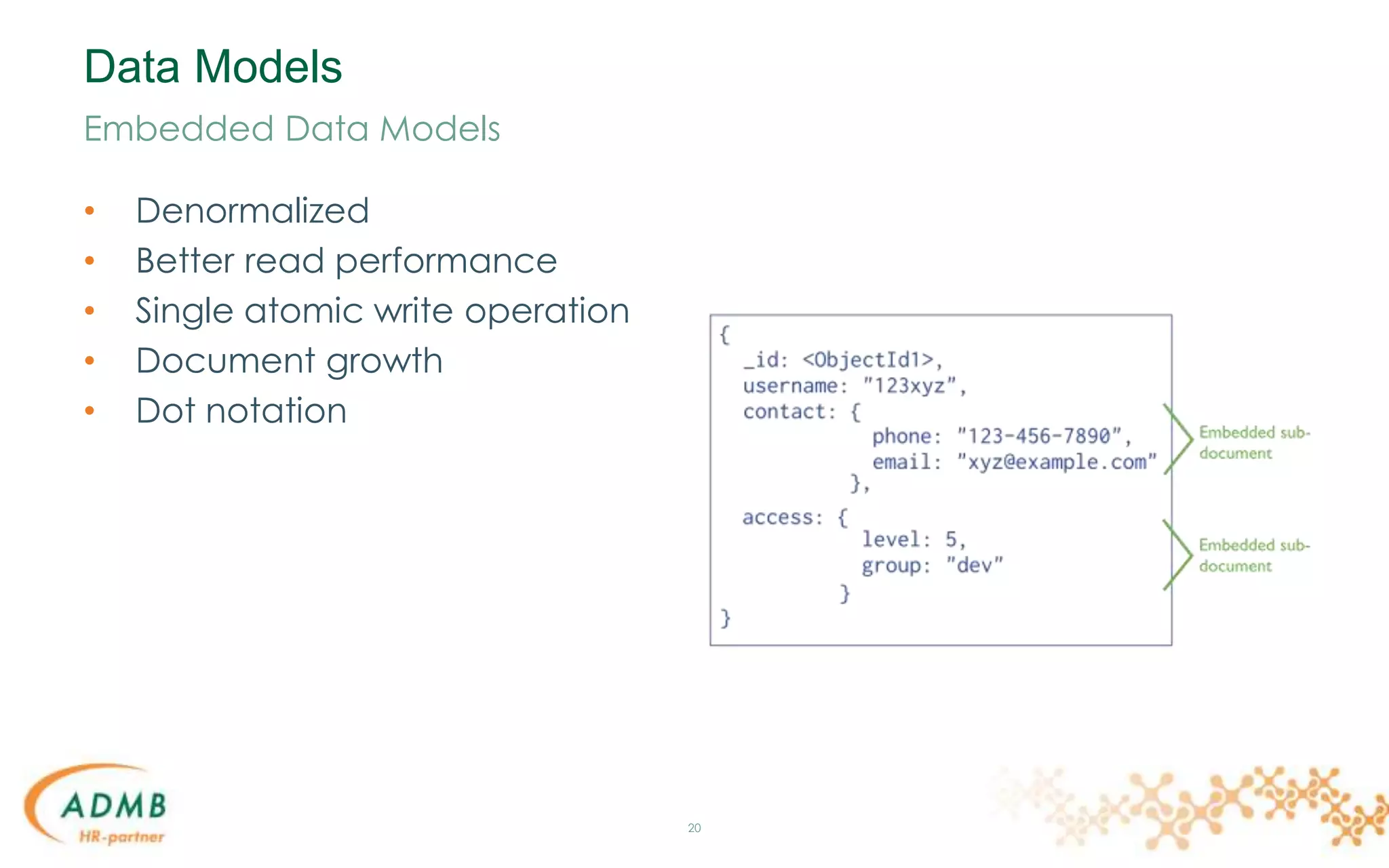
Embedded Data Models
{
_id: "infasla",
name: "Anthony Slabinck",
addresses: [
{ street: "123 Fake Street",
city: "Faketon",
state: "MA",
zip: "12345" },
{ street: "1 Other Street",
city: "Boston",
state: "MA",
zip: "12345"
}
]
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodb-150306034646-conversion-gate01/75/MongoDB-22-2048.jpg)
![Data Model
• One-to-Many Relationship
{ _id: "oreilly",
name: "O'Reilly Media",
founded: 1980,
location: "CA"
}
{ _id: 123456789,
title: "MongoDB: The Definitive Guide",
author: [ "Kristina Chodorow", "Mike Dirolf" ],
published_date: ISODate("2010-09-24"),
pages: 216,
language: "English",
publisher_id: "oreilly"
}
{ _id: 234567890,
title: "50 Tips and Tricks for MongoDB Developer",
author: "Kristina Chodorow",
published_date: ISODate("2011-05-06"),
pages: 68,
language: "English",
publisher_id: "oreilly"
}
24
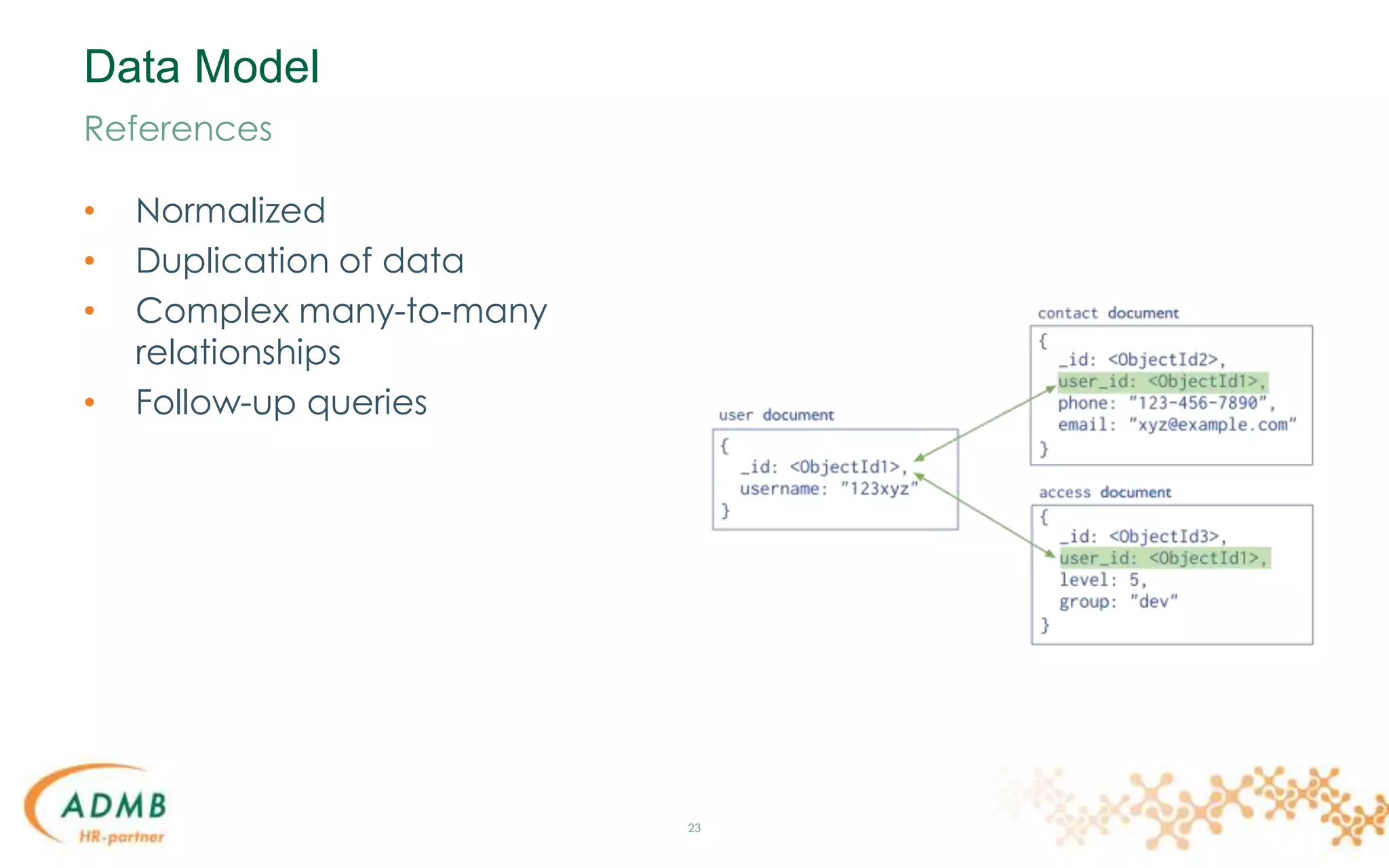
References](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodb-150306034646-conversion-gate01/75/MongoDB-24-2048.jpg)