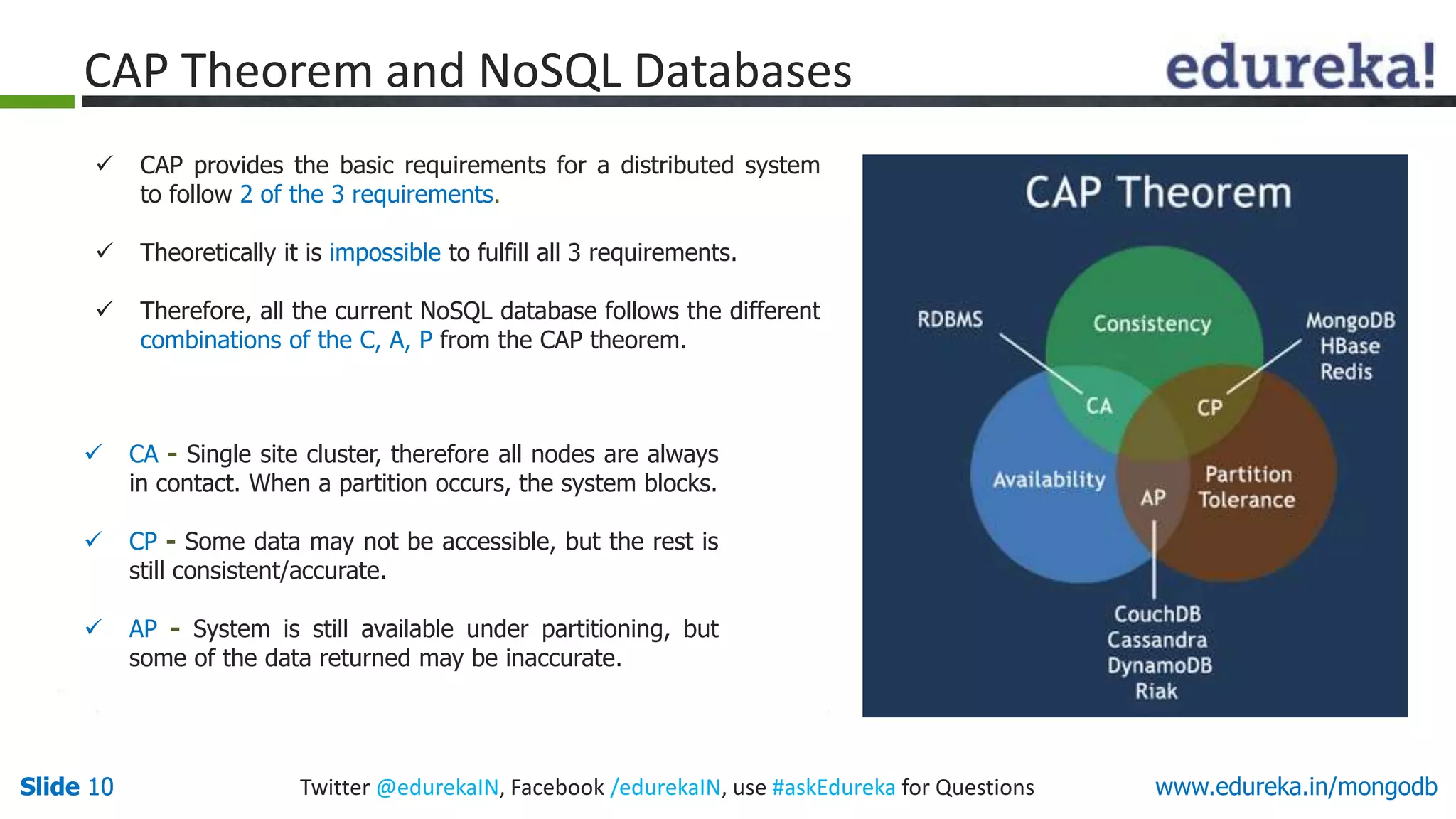
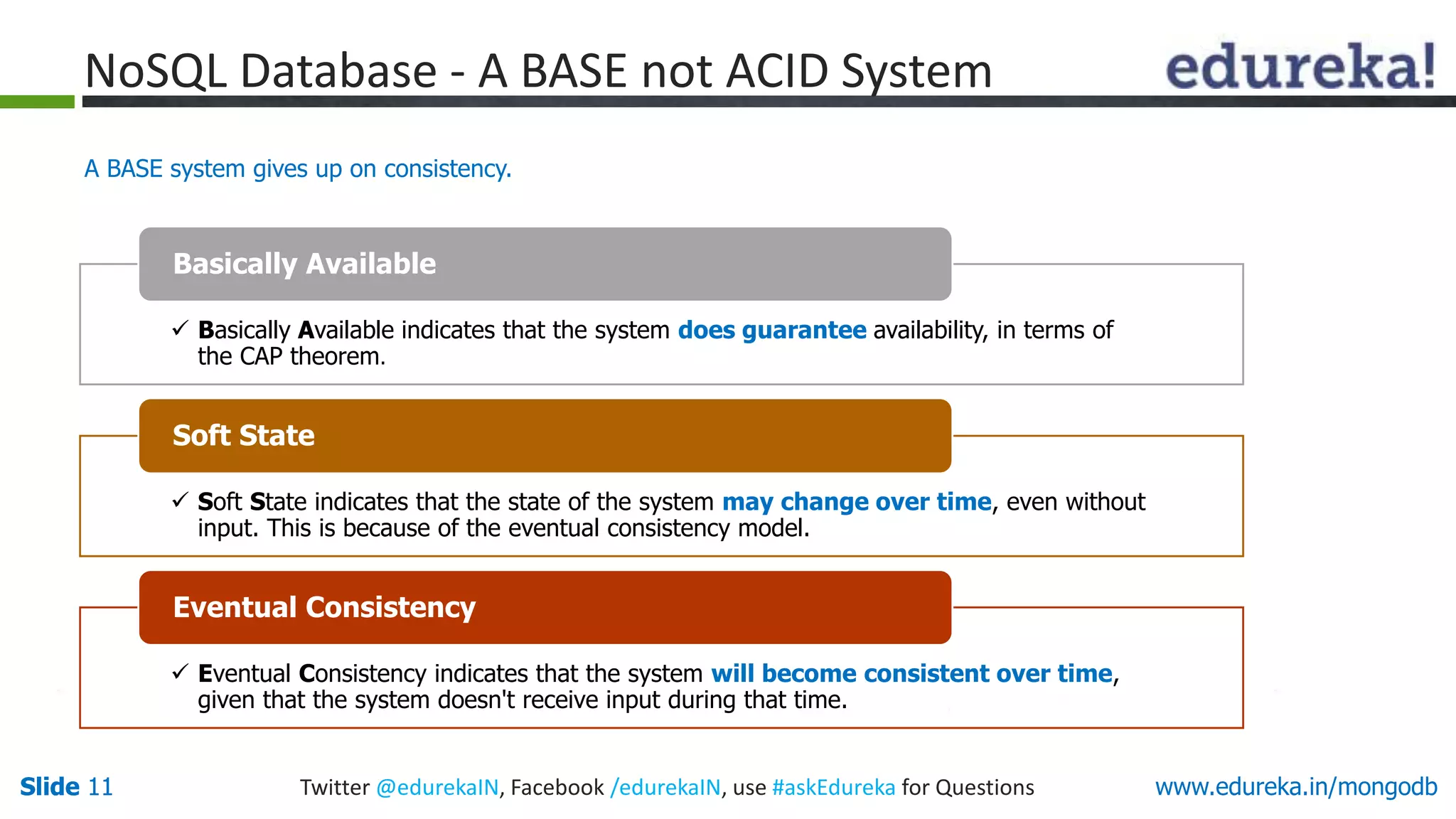
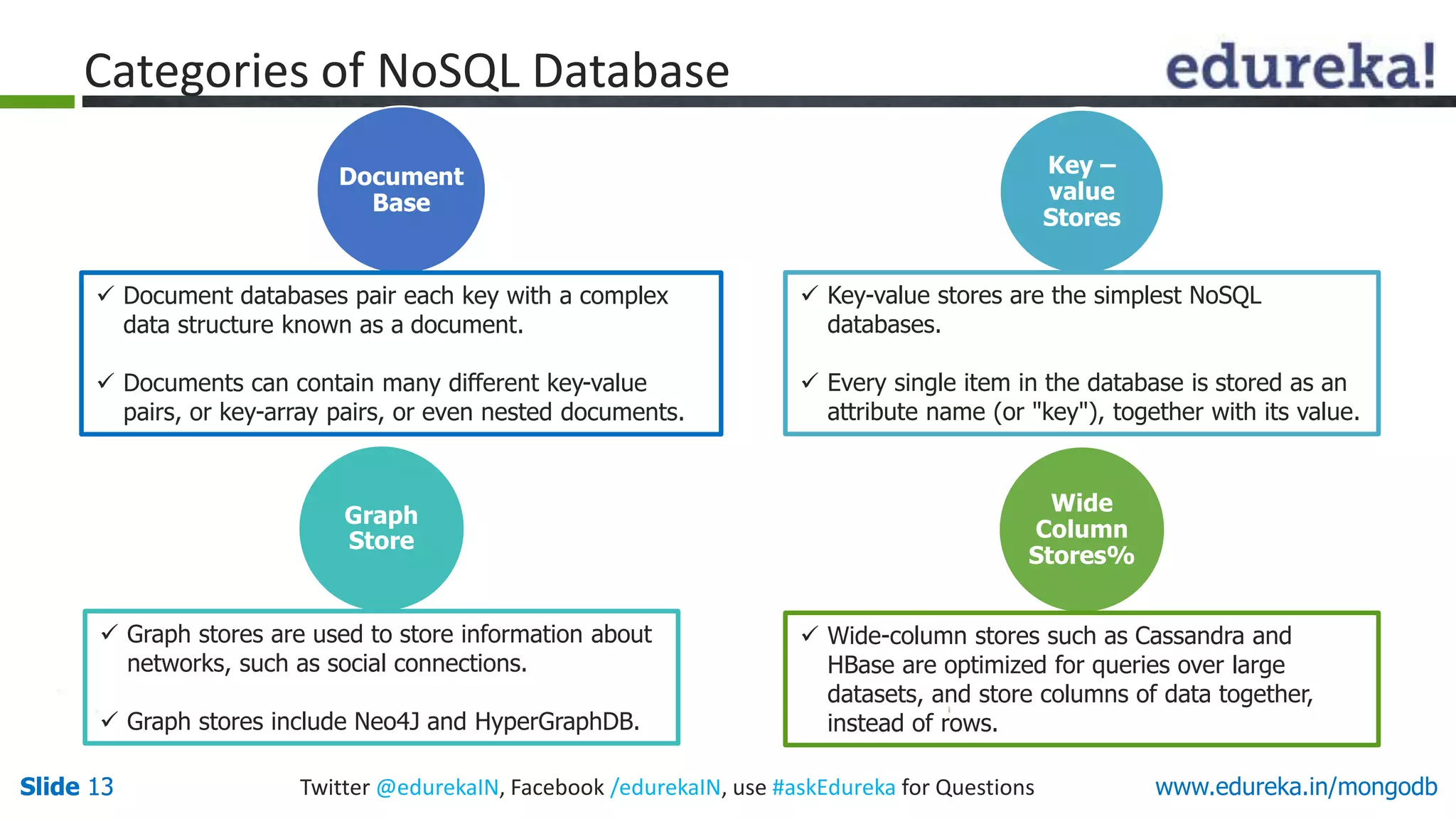
The document is a presentation on MongoDB that covers:
1) Why NoSQL databases are needed and the benefits of MongoDB over SQL databases.
2) How MongoDB solves problems related to big data by allowing horizontal scaling and high performance.
3) Examples of how MongoDB is used by companies for applications like content management, analytics, and caching.


![Slide 20 Twitter @edurekaIN, Facebook /edurekaIN, use #askEdureka for QuestionsSlide 20 www.edureka.in/mongodb
While in MongoDB® schema design will have one
collection post and has the following structure.
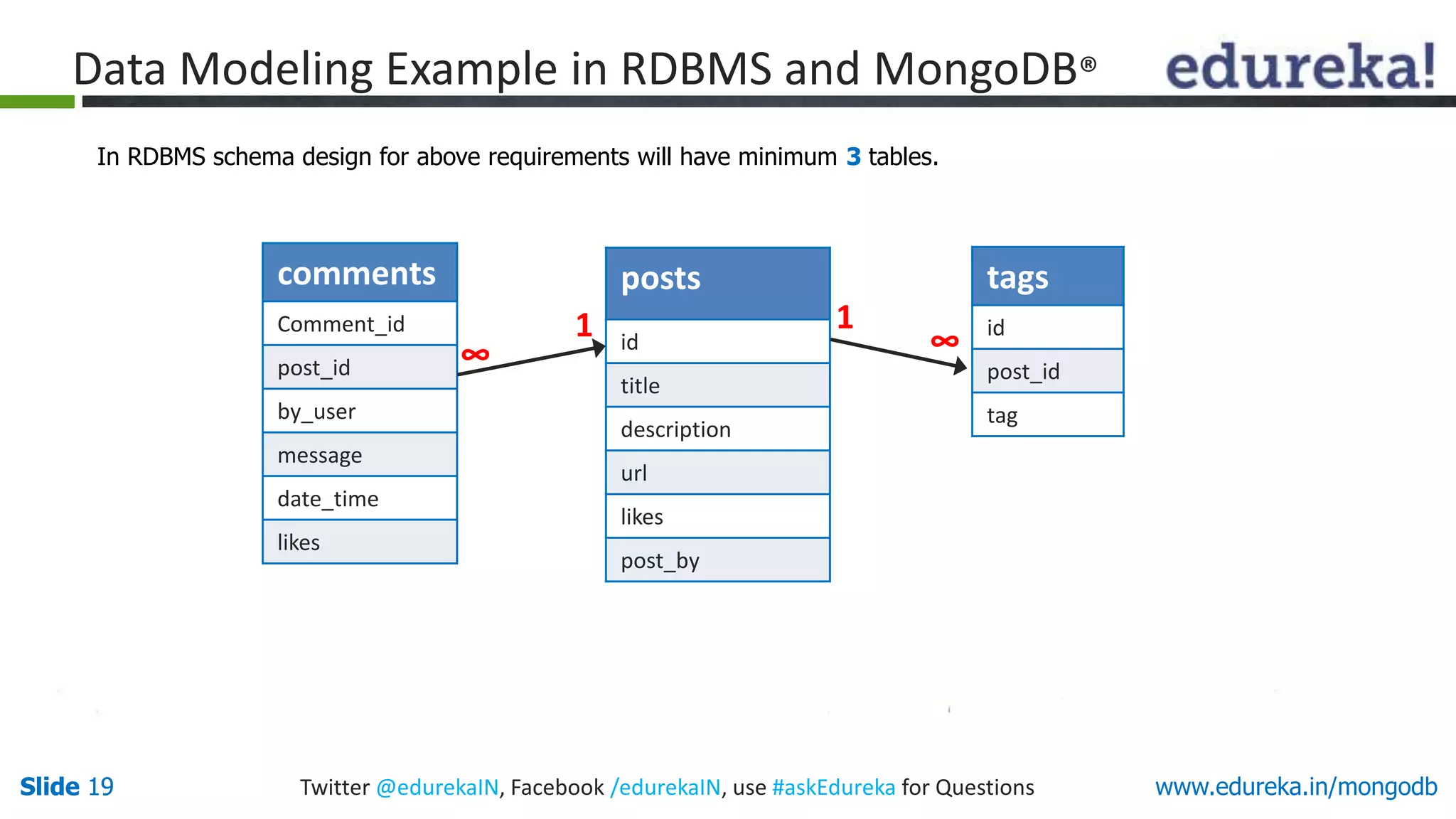
So while showing the data, in RDBMS we need to join
three tables and in Mongodb® data will be shown from
one collection only.
{
_id: POST_ID
title: TITLE_OF_POST,
description: POST_DESCRIPTION,
by: POST_BY,
url: URL_OF_POST,
tags: [ TAG1, TAG2, TAG3],
likes: TOTAL_LIKES,
comments: [
{
user:'COMMENT_BY',
message: TEXT,
dateCreated: DATE_TIME,
like: LIKES
},
{
user:'COMMENT_BY',
message: TEXT,
dateCreated: DATE_TIME,
like: LIKES
}
]
}
Data Modeling Example in RDBMS and MongoDB](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mdbwebinar-140716101909-phpapp02/75/Introduction-to-MongoDB-20-2048.jpg)