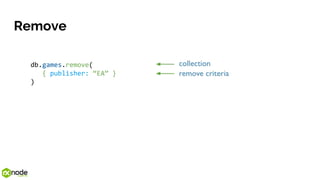
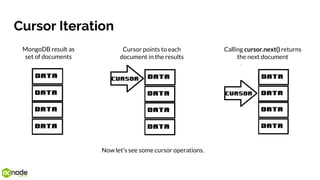
The document provides an introduction to MongoDB, explaining it as an open-source document-oriented NoSQL database that contrasts with traditional SQL databases. It covers concepts such as the document data model, CRUD operations, and the benefits and drawbacks of using MongoDB, including its schema-less design and fast scalability. Additionally, it outlines when to use or not use MongoDB based on application requirements.






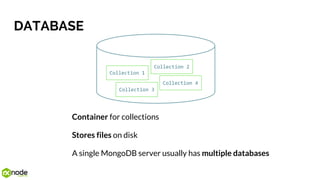


![Relational MongoDB
id hero game
0 Commander Shepard Mass Effect
1 Hawke Dragon Age
id name type hero_id
0 Sniper rifle Ranged combat 0
1 Daggers Melee combat 1
2 Stealth Class skill 1
3 Tactical cloak Class skill 0
HERO
SKILL
{
_id: <ObjectID>,
name: “Commander Shepard”,
game: “Mass Effect”,
skills: [{
name: “Sniper rifle”,
type: “Ranged combat”,
}, {
name: “Tactical cloak”,
type: “Class skill”,
}]
}
HERO](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontomongodb-170519140936/85/Introduction-to-MongoDB-17-320.jpg)
![MongoDB Documents are Typed
{
name : “J. Shepard”,
title : “Commander”,
Address : {
address1:
“Tiberius Tower”,
address2:
“Citadel”,
pincode : “11E
SR2”,
}
expertise: [ “Sniper”, “Combat”, “Tech”, “Reapers”],
employee_number : 320,
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontomongodb-170519140936/85/Introduction-to-MongoDB-18-320.jpg)

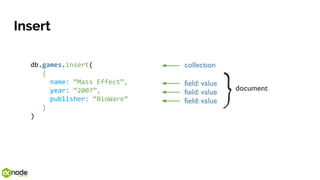
![Find
db.games.find(
{ year: “2007” },
{ name: 1, publisher: 1, _id: 0 }
)
Result:
[{
name: “Mass Effect”,
publisher: “BioWare”
}]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontomongodb-170519140936/85/Introduction-to-MongoDB-21-320.jpg)