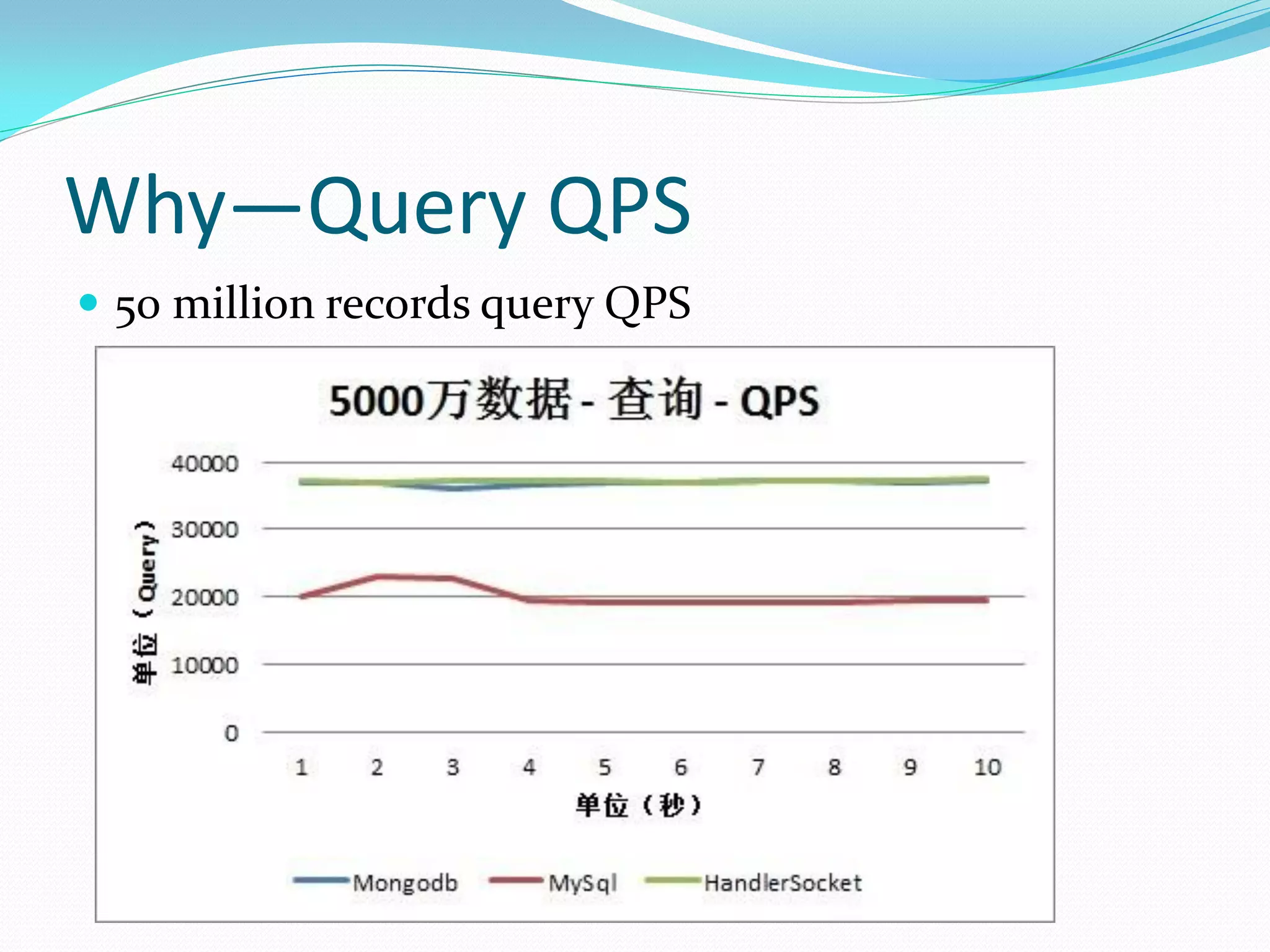
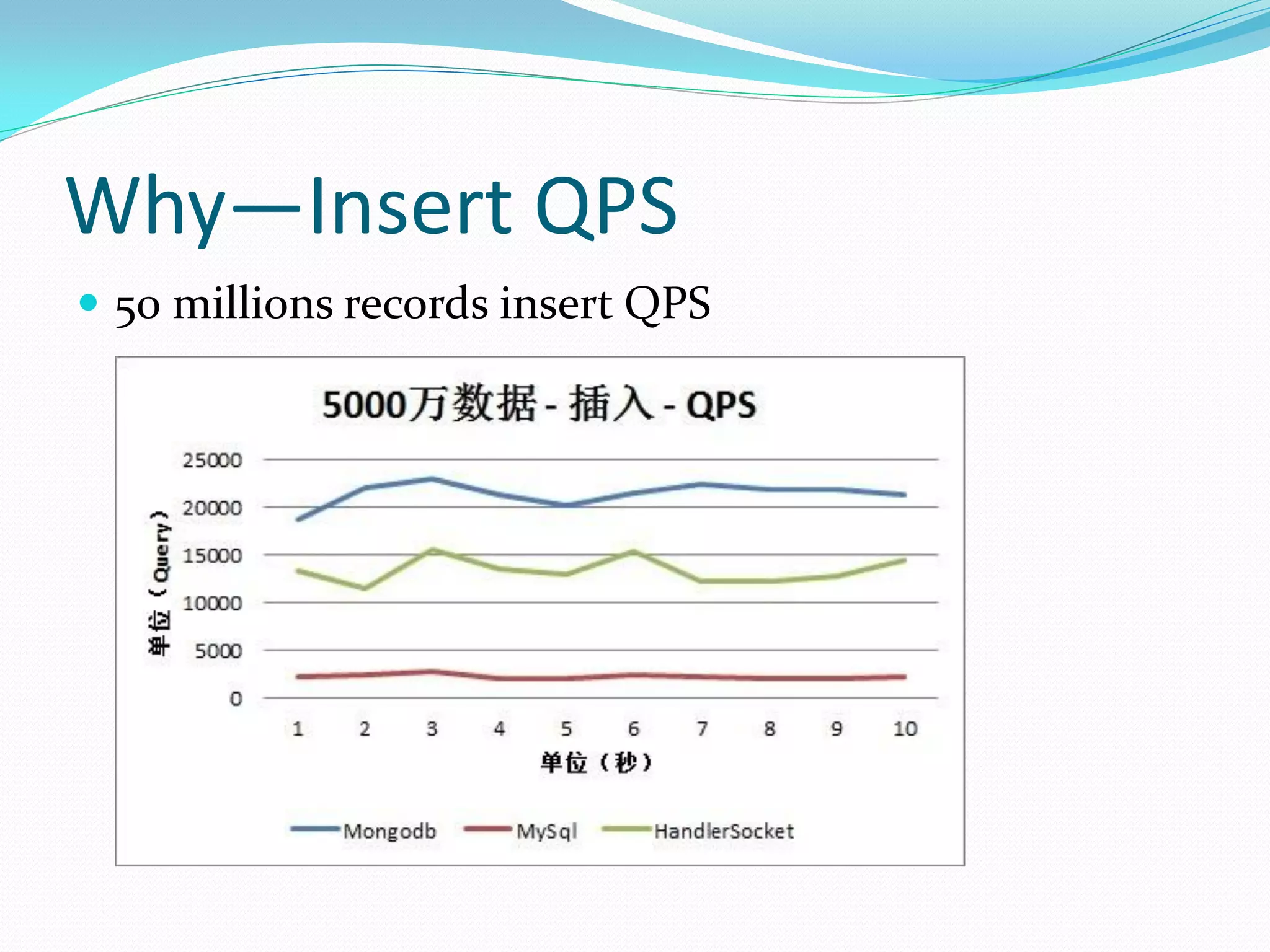
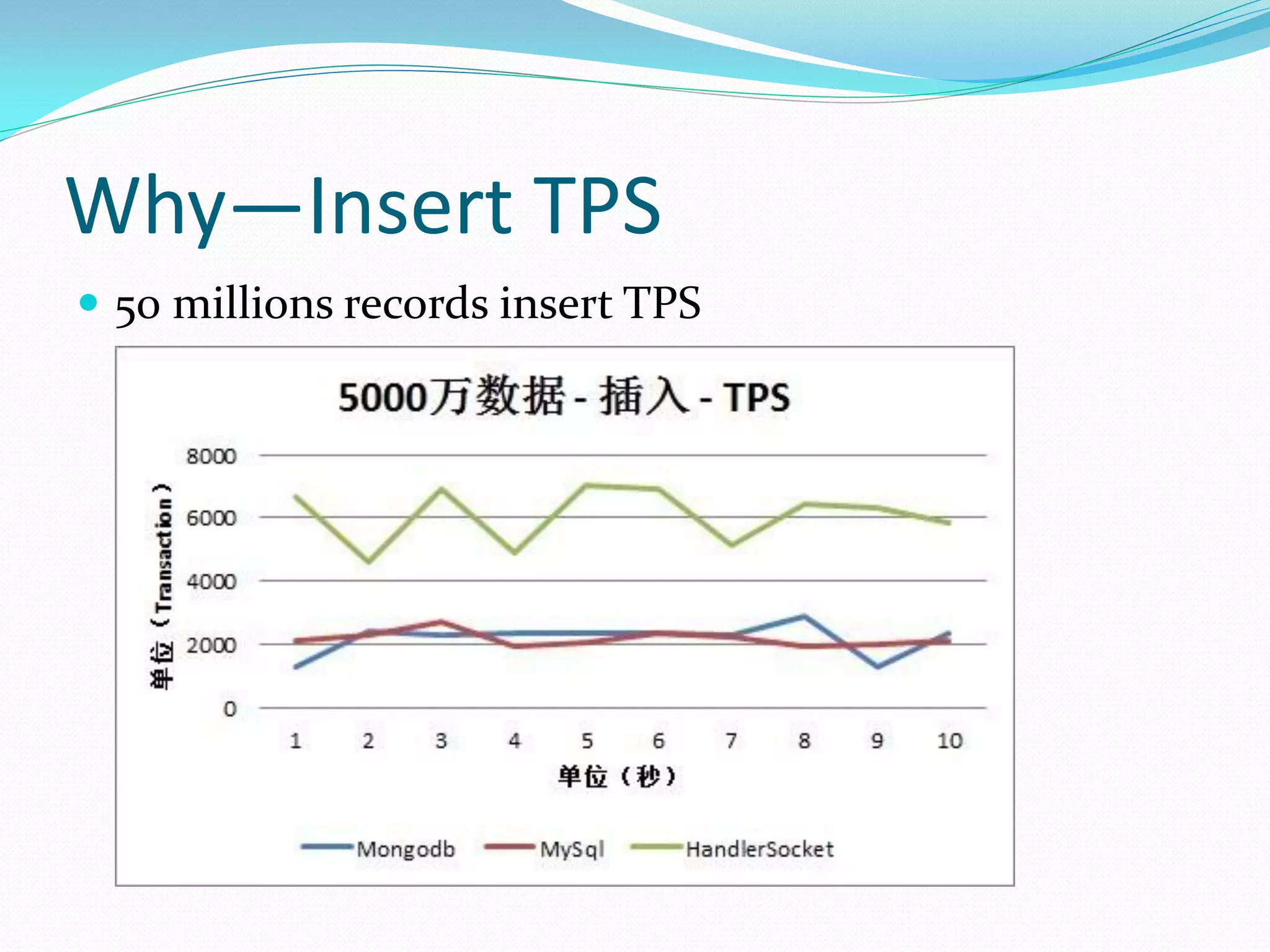
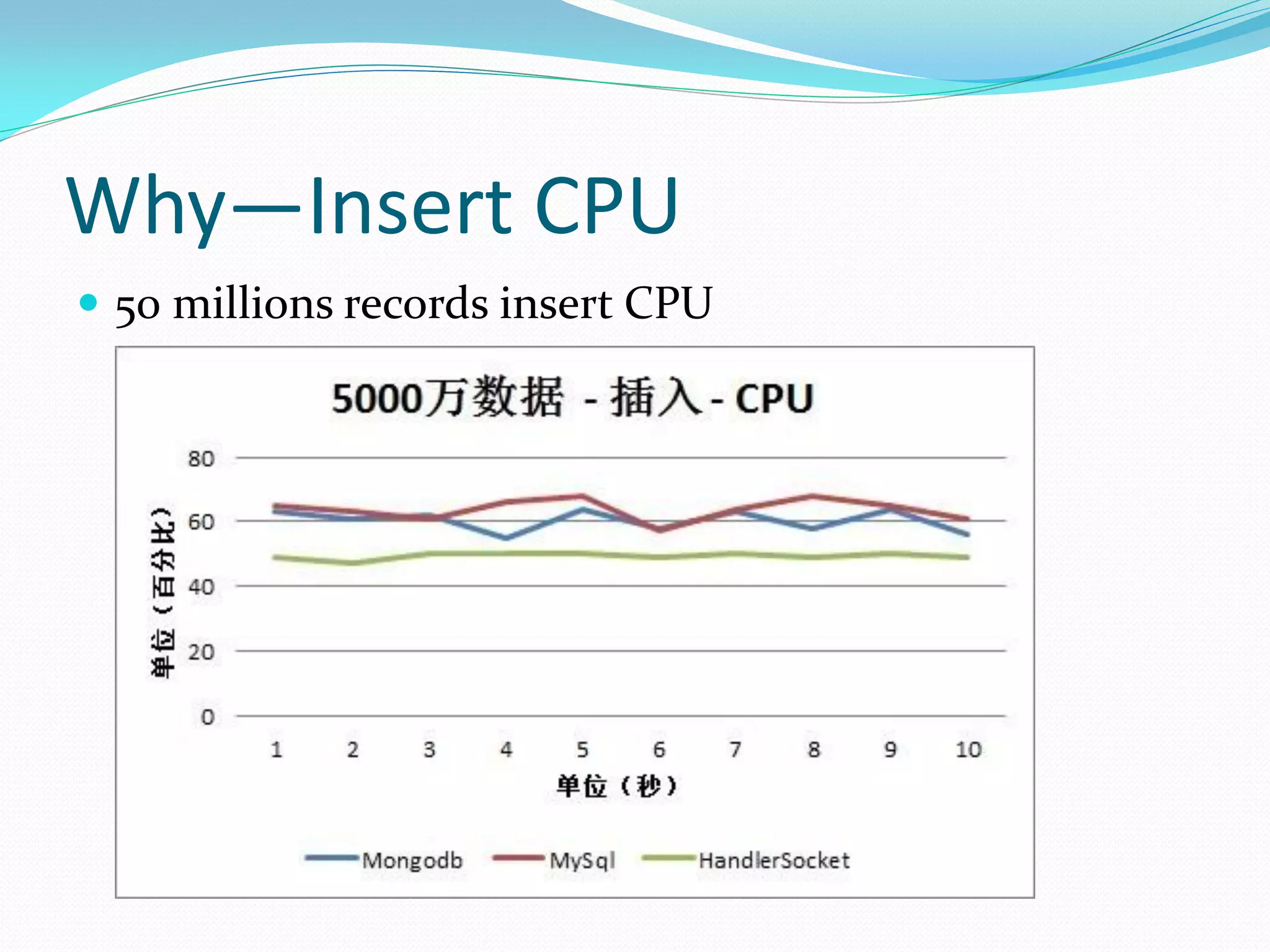
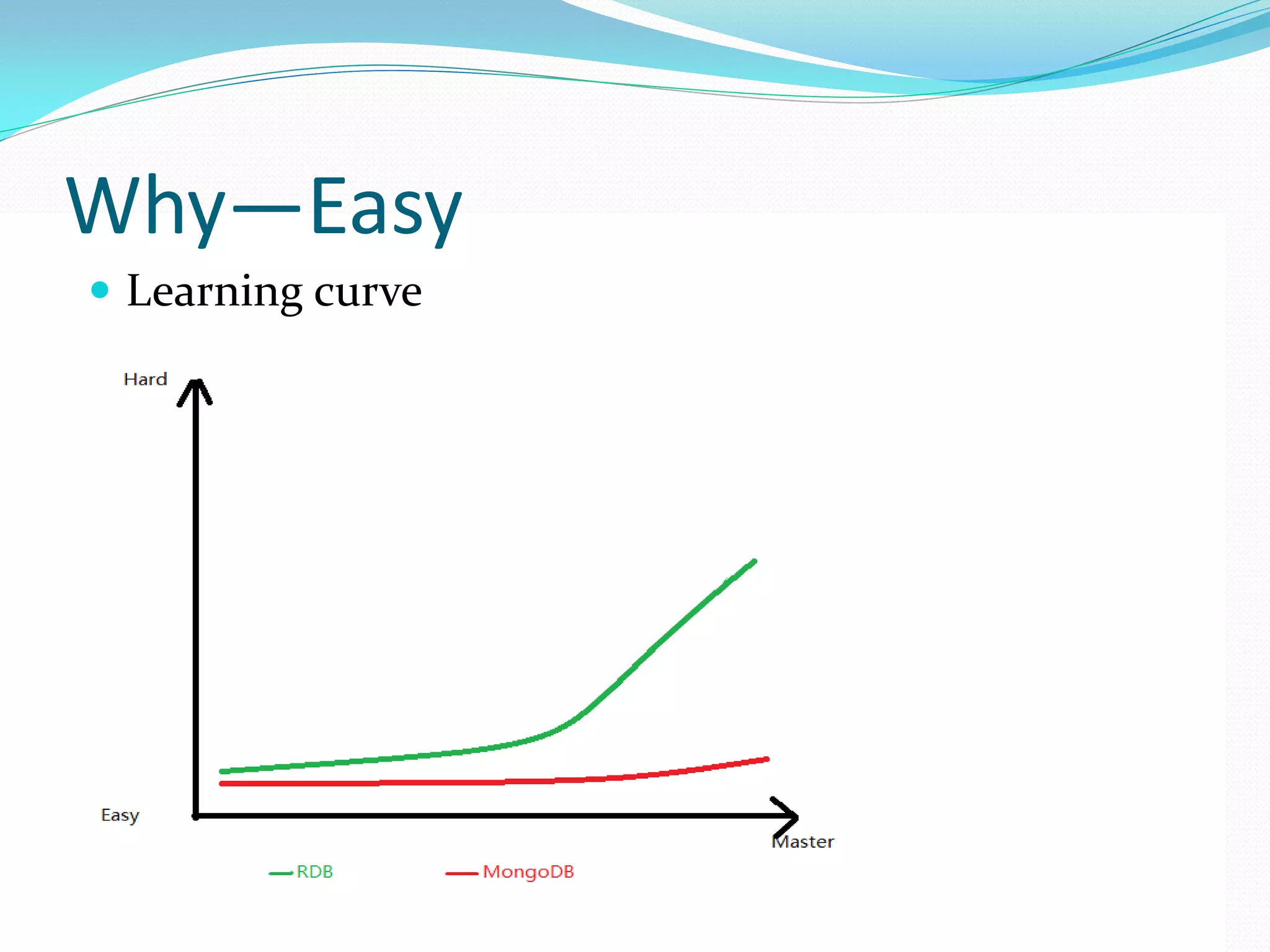
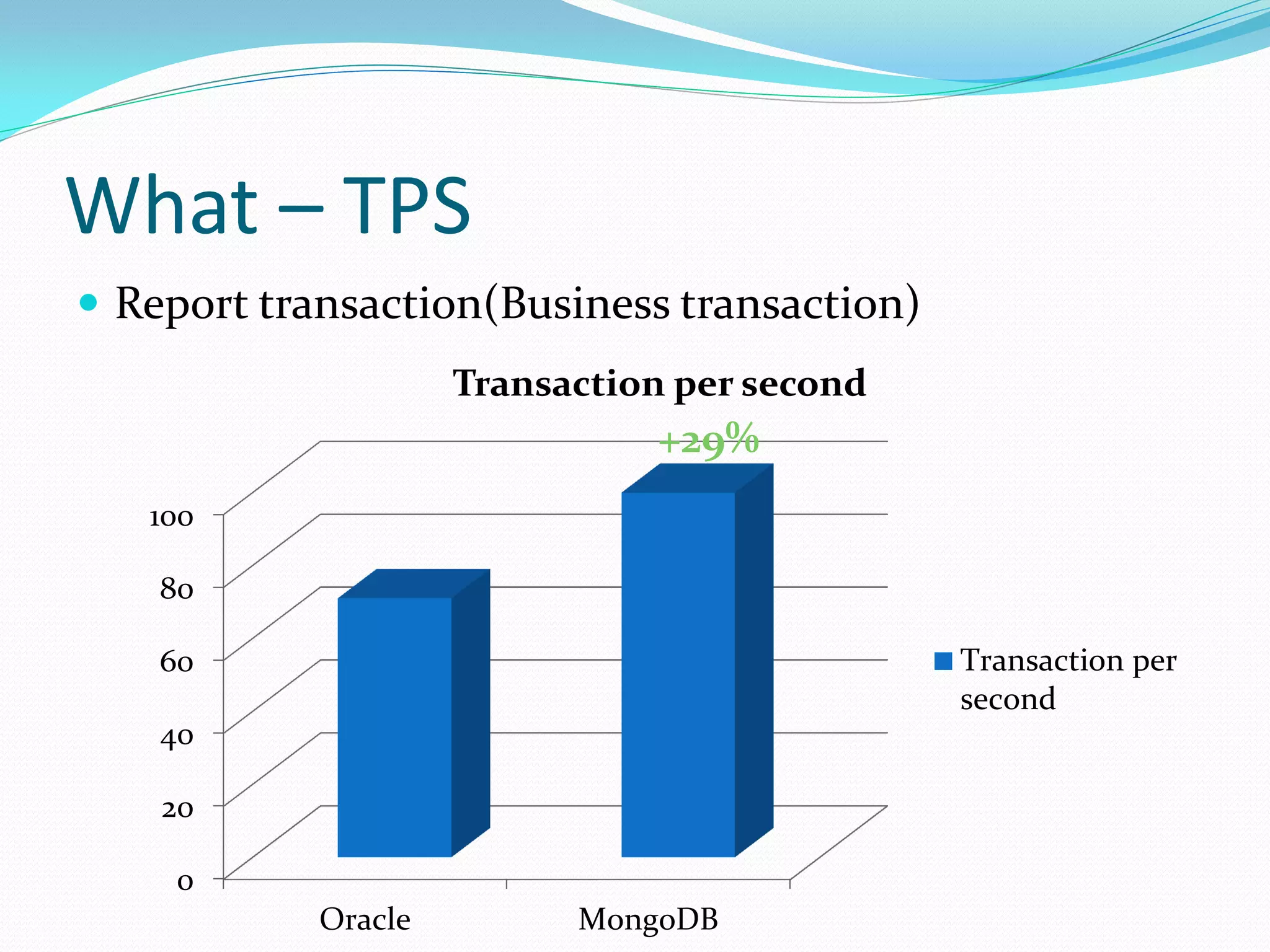
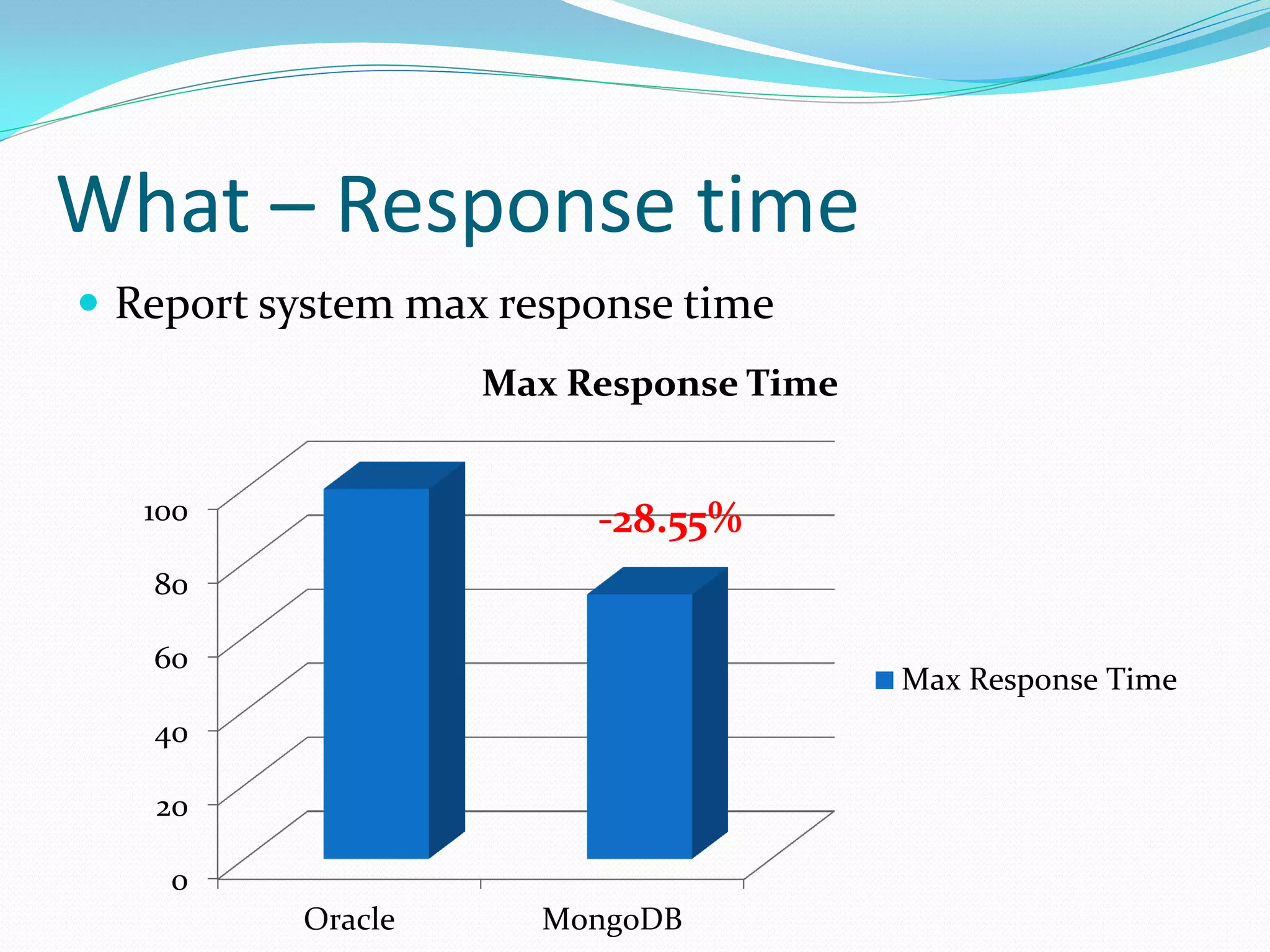
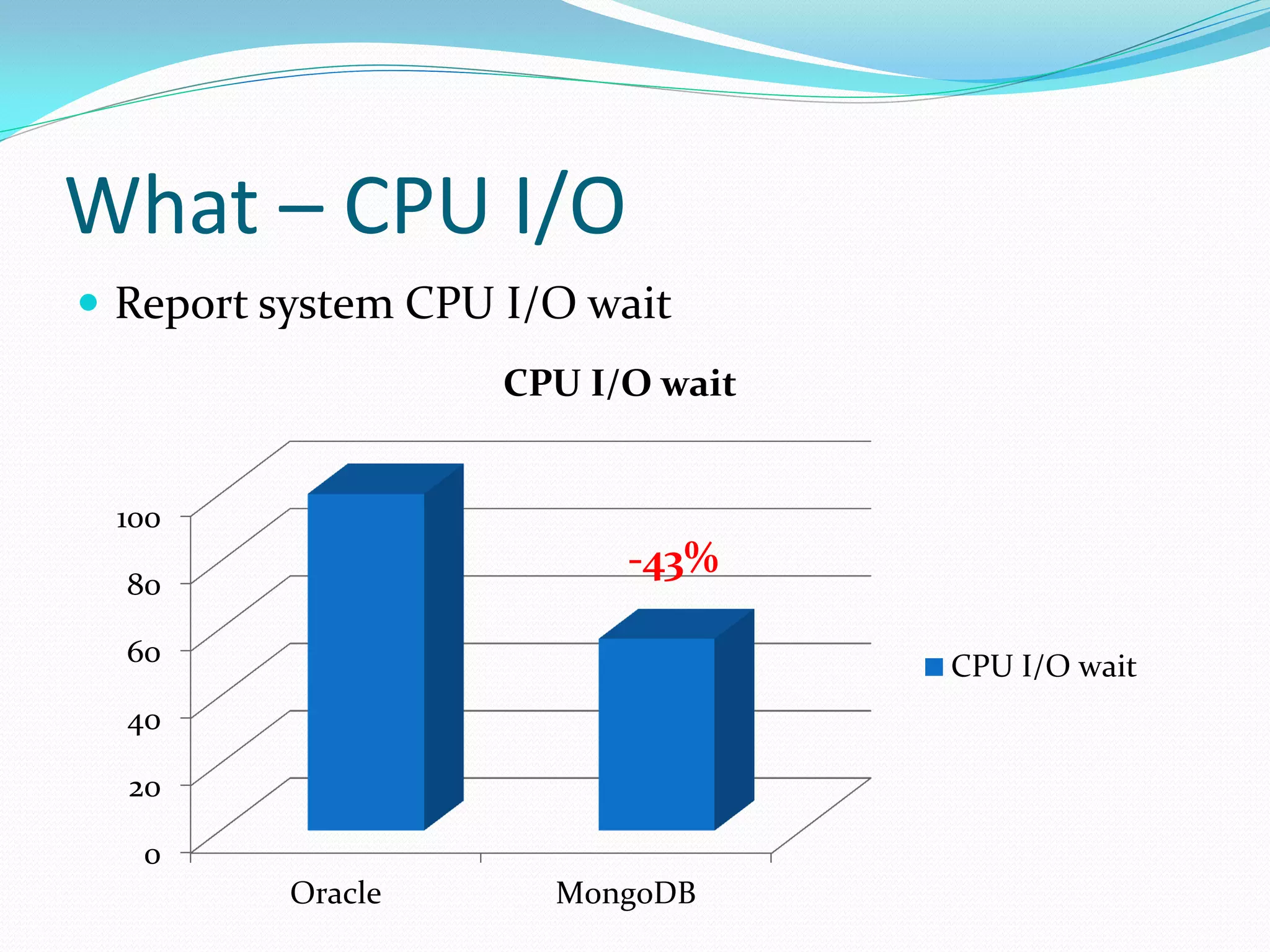
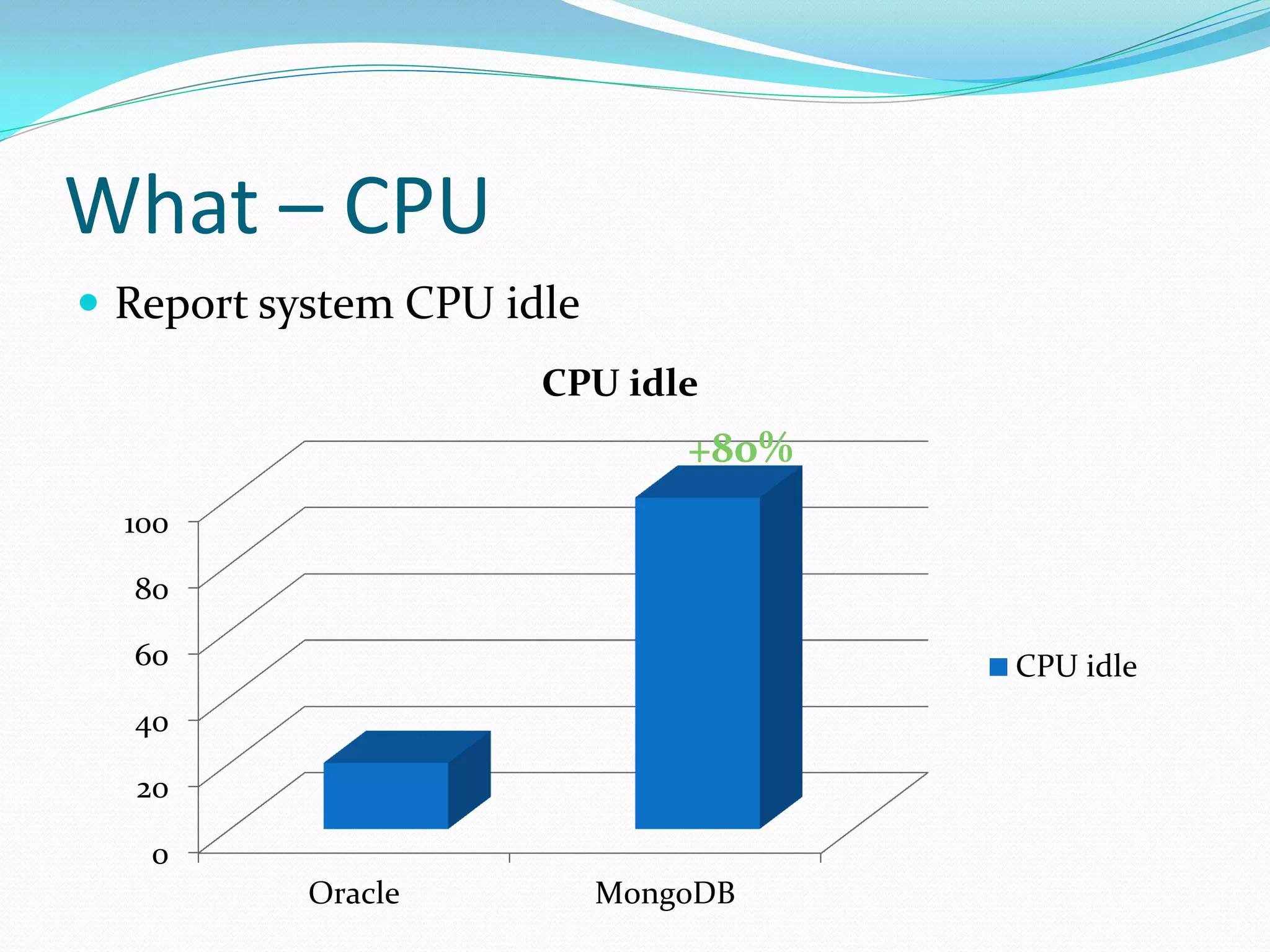
The document discusses the author's use of MongoDB, detailing its applications in report and log systems due to its performance with large datasets and ease of use compared to traditional relational databases. It highlights benefits such as high query and insert performance, scalability, and support for automatic sharding and indexing. The author also shares implementation strategies including the use of Object Document Mappers (ODM), replica sets, and customized document keys.
![Why and How I use MongoDB
{name:”Macro Huang”,
github:”macrohuang”,
location:”Beijing”,
email:[“macrohuang.whu@gamil.com”,”macroh
uang@126.com”]
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbbeijing-macro-130401140030-phpapp01/75/How-We-Use-MongoDB-in-Our-Advertising-System-1-2048.jpg)