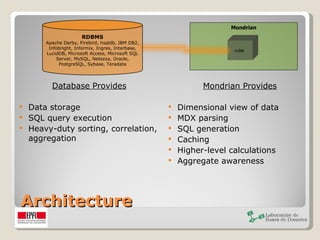
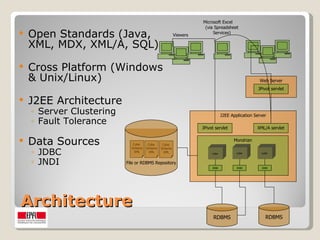
The document discusses Mondrian, an open source OLAP server written in Java. It can be used to develop a trajectory data warehouse and interactively analyze large datasets stored in SQL databases without writing SQL. Mondrian uses MDX and XML for querying and cube definition. It provides an OLAP view of relational data and enables fast, on-line analytical processing through aggregation and caching. GeoMondrian extends it with spatial/GIS data types and functions for geographical analysis.




![More on MDX MDX stands for MultiDimensional eXpressions query language De facto standard from Microsoft for SQL Server OLAP Services(now Analysis Services) MDX is for OLAP data cubes what SQL is for relational databases Looks like a SQL query but relies on a different model (close to the one used in spreadsheets) SELECT { [Measures].[Store Sales] } ON COLUMNS, { [Date].[2002], [Date].[2003] } ON ROWS FROM Sales WHERE ( [Store].[USA].[CA]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mondrian-geomondrianslides-091015060613-phpapp02/85/Mondrian-Geo-Mondrian-6-320.jpg)
![XML Cube Definition Mondrian uses XML “Schemas” to define the Cubes, like: < Cube name="Sales"> < Table name="sales"> < AggName name="agg_1"> < AggFactCount column="row count"/> < AggMeasure name="[Measures].[Unit Sales]" column="sum units"/> < AggMeasure name="[Measures].[Min Units]" column="min units"/> < AggMeasure name="[Measures].[Max Units]" column="max units"/> < AggMeasure name="[Measures].[Dollar Sales]" column="sum dollars"/> < AggLevel name="[Time].[Year]" column="year"/> < AggLevel name="[Time].[Quarter]" column="quarter"/> < AggLevel name="[Product].[Mfrid]" column="mfrid"/> < AggLevel name="[Product].[Brand]" column="brand"/> < AggLevel name="[Product].[Prodid]" column="prodid"/> </ AggName > </ Table > <!-- Rest of the cube definition --> </ Cube >](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mondrian-geomondrianslides-091015060613-phpapp02/85/Mondrian-Geo-Mondrian-7-320.jpg)
![It is the OLAP version of JDBC It is considered to be for OLAP, what JDBC API is for Relational Databases. Using a similar Java Syntax it is possible to query the OLAP Server from any Java Application import mondrian.olap.*; import java.io.PrintWriter; Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection( "Provider=mondrian;" + "Jdbc=jdbc:odbc:MondrianFoodMart;" + "Catalog=/WEB-INF/FoodMart.xml;", null, false); Query query = connection.parseQuery( "SELECT {[Measures].[Unit Sales], [Measures].[Store Sales]} on columns," + " {[Product].children} on rows " + "FROM [Sales] " + "WHERE ([Time].[1997].[Q1], [Store].[CA].[San Francisco])"); Result result = connection.execute(query); result.print(new PrintWriter(System.out));](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mondrian-geomondrianslides-091015060613-phpapp02/85/Mondrian-Geo-Mondrian-8-320.jpg)





![Example Query Example query: filter spatial dimension members based on distance from a feature SELECT { [Measures].[Population]} on columns, Filter( {[Unite geographique].[Region economique].members}, ST_Distance([Unitegeographique].CurrentMember.Properties("geom"),[Unite geographique].[Province].[Ontario].Properties("geom")) < 2.0 ) on rows FROM [Recensements] WHERE [Temps].[Rencensement 2001 (2001-2003)].[2001]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mondrian-geomondrianslides-091015060613-phpapp02/85/Mondrian-Geo-Mondrian-21-320.jpg)