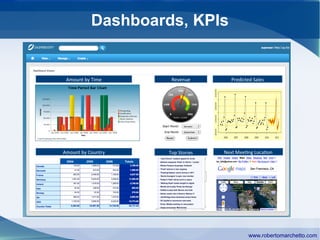
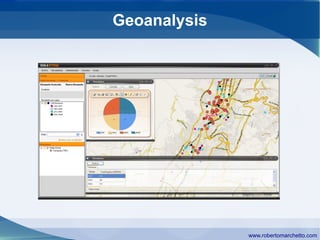
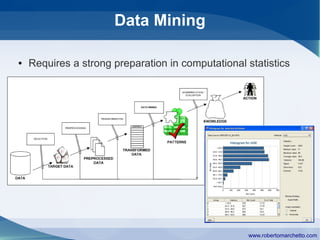
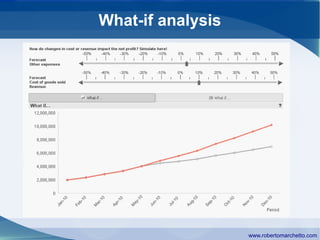
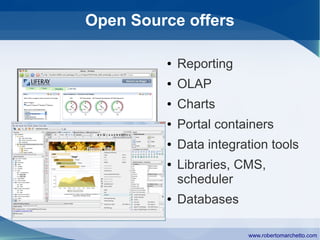
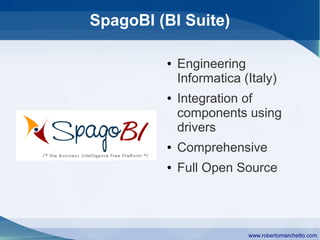
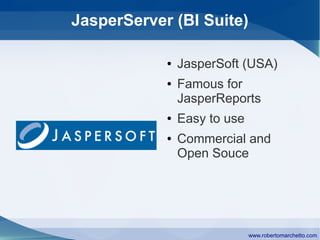
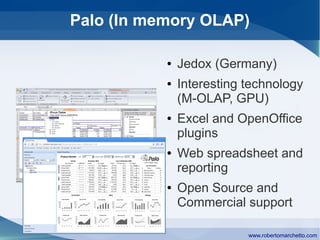
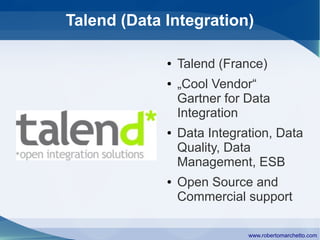
The document discusses the history and concepts of business intelligence (BI). It was first introduced in 1958 as a way to provide current information to engineers and scientists. BI is now defined as processes and technologies to gather, store, analyze and provide access to data to help users make informed decisions. The main concepts are collecting data from different sources, integrating and cleaning the data, and providing business analysis for managers. Key aspects of BI include data warehousing, online transaction processing, online analytical processing, relational and multidimensional databases, metrics/KPIs, dashboards, and data mining.







![MDX
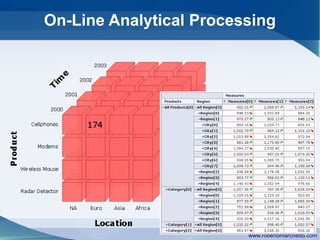
● Multidimensional Expressions (MDX) is a query
language for OLAP databases
● MDX is to OLAP as SQL queries are to OLTP
databases
● Powerfull on computing indexes and navigating
through OLAP dimensions
● SELECT
{[Measures].[Store Sales]} ON COLUMNS
{[Date].[2002], [Date].[2003]} ON ROWS
FROM Sales
WHERE ([Store].[USA].[CA])
www.robertomarchetto.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/businessintelligenceeng-110625154637-phpapp01/85/Business-Intelligence-Open-Source-12-320.jpg)