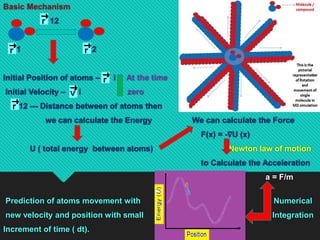
Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations calculate particle trajectories by integrating Newton's equations of motion. This document discusses the history and basic principles of MD, force fields, the NAMD simulation package, and applications. NAMD is a parallelized MD program for biomolecular simulations that uses spatial decomposition and multithreading. It supports features like CHARMM force fields, ensembles, and interactive modeling with VMD for structure visualization. MD simulations are useful for modeling protein structures, comparing protein templates, and predicting protein behavior through refinement of simulation approaches.