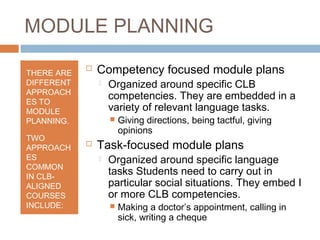
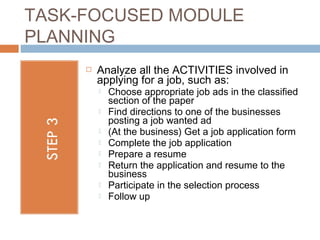
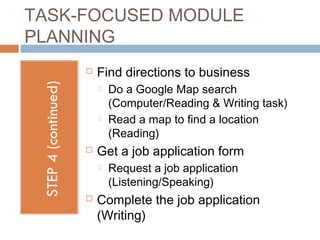
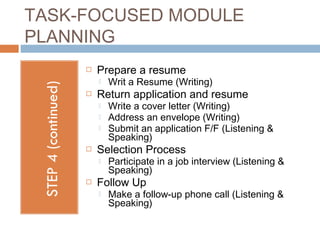
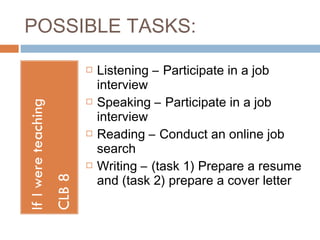
The document outlines the process of thematic, task-focused module planning aligned with Canadian Language Benchmarks (CLB). It emphasizes the importance of prior needs assessment, identification of relevant social situations, and the selection of appropriate tasks tailored to students' CLB levels. The benefits of module planning include easier lesson sequencing and the ability to reuse or adapt module plans for different classes.