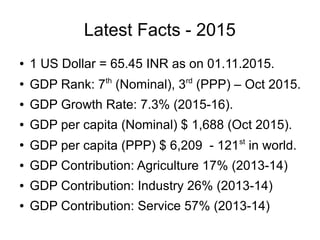
1. The document provides an overview of the Indian economy, including key economic indicators and statistics from 2015.
2. It outlines the structure and characteristics of the Indian economy, such as its developing status, agricultural base, and economic reforms since the 1990s that have liberalized the economy.
3. The economic reforms have transformed India into one of the fastest growing economies in the world with an average growth rate of 7% over the past two decades.