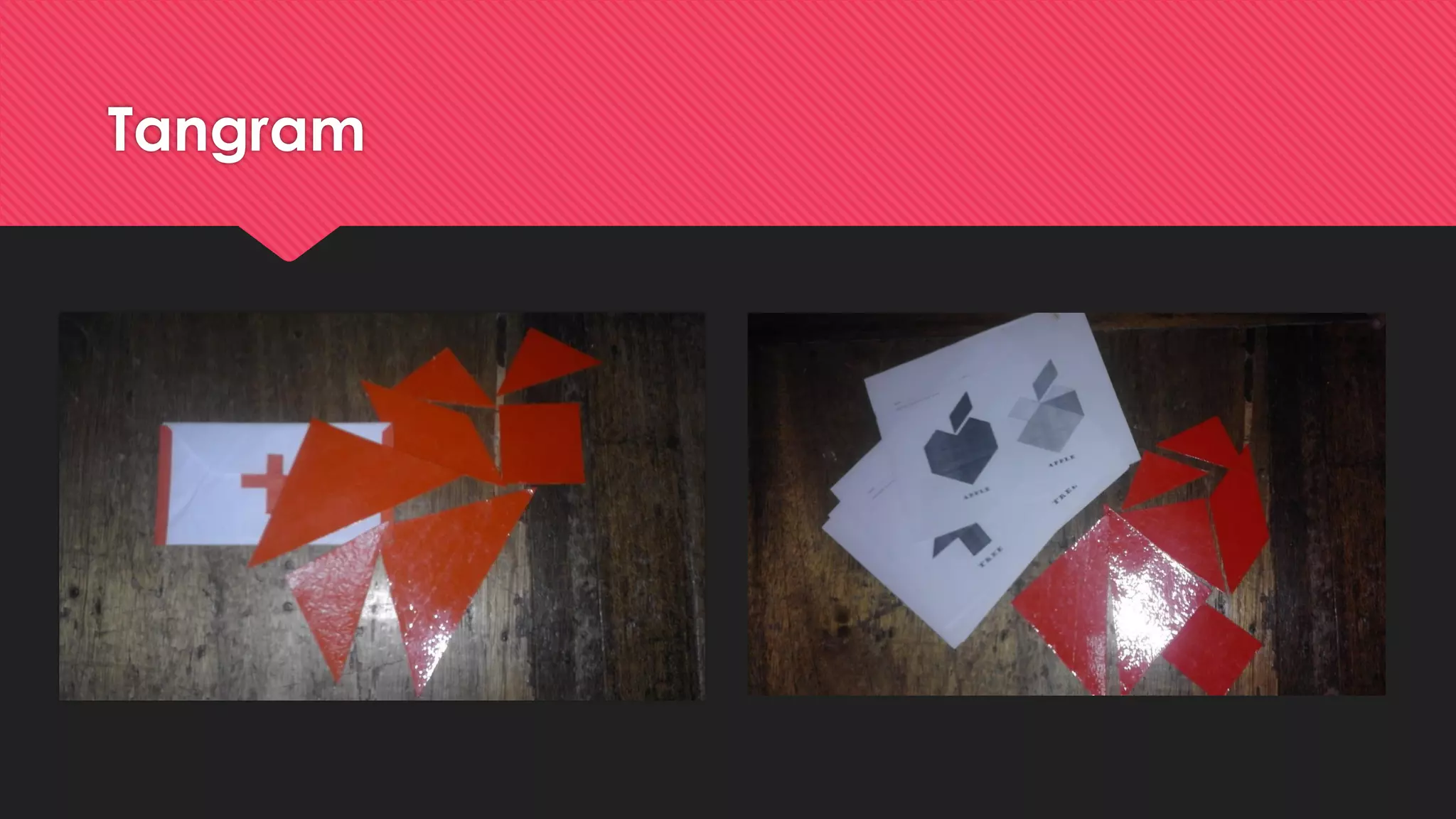
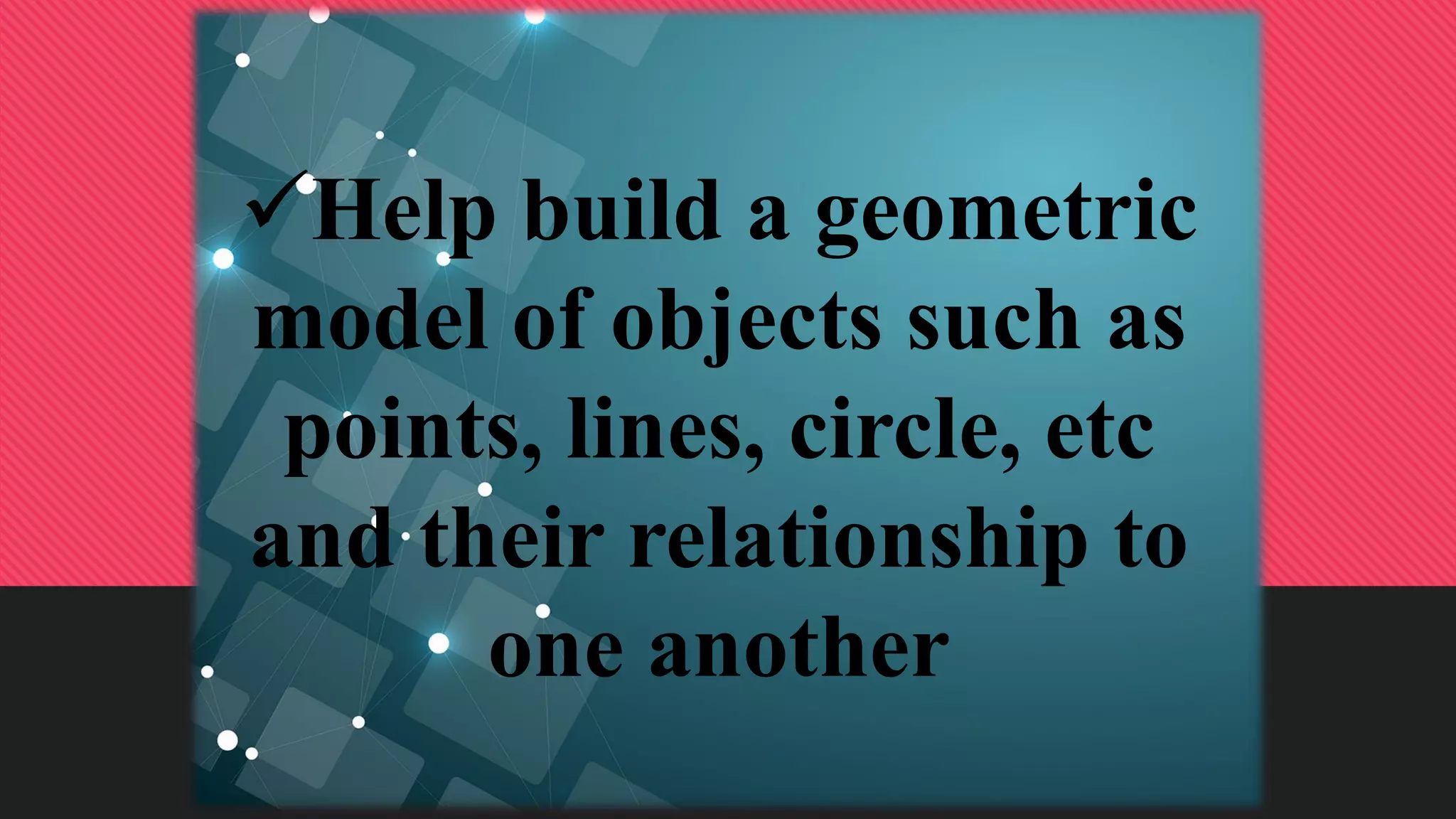
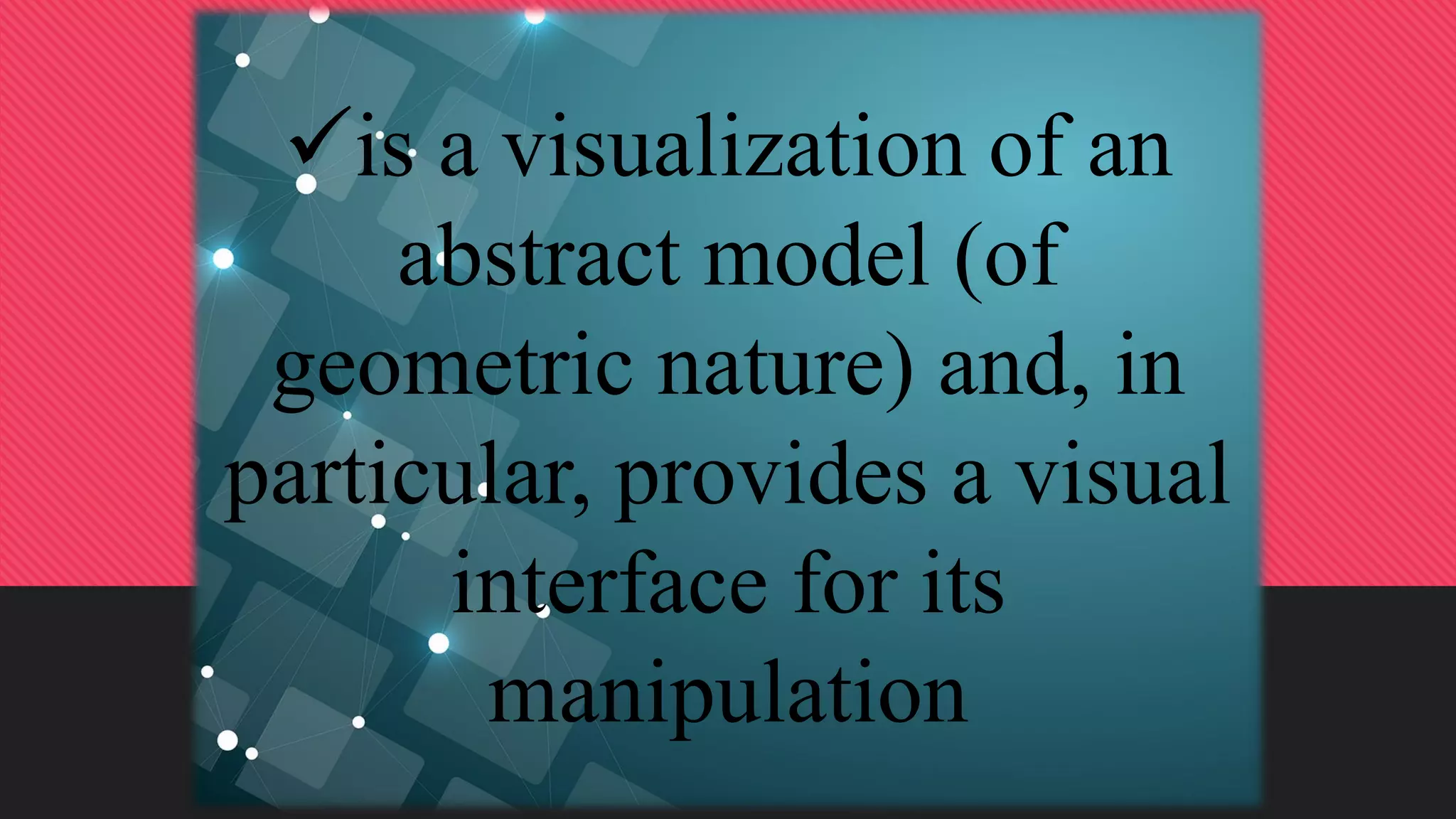
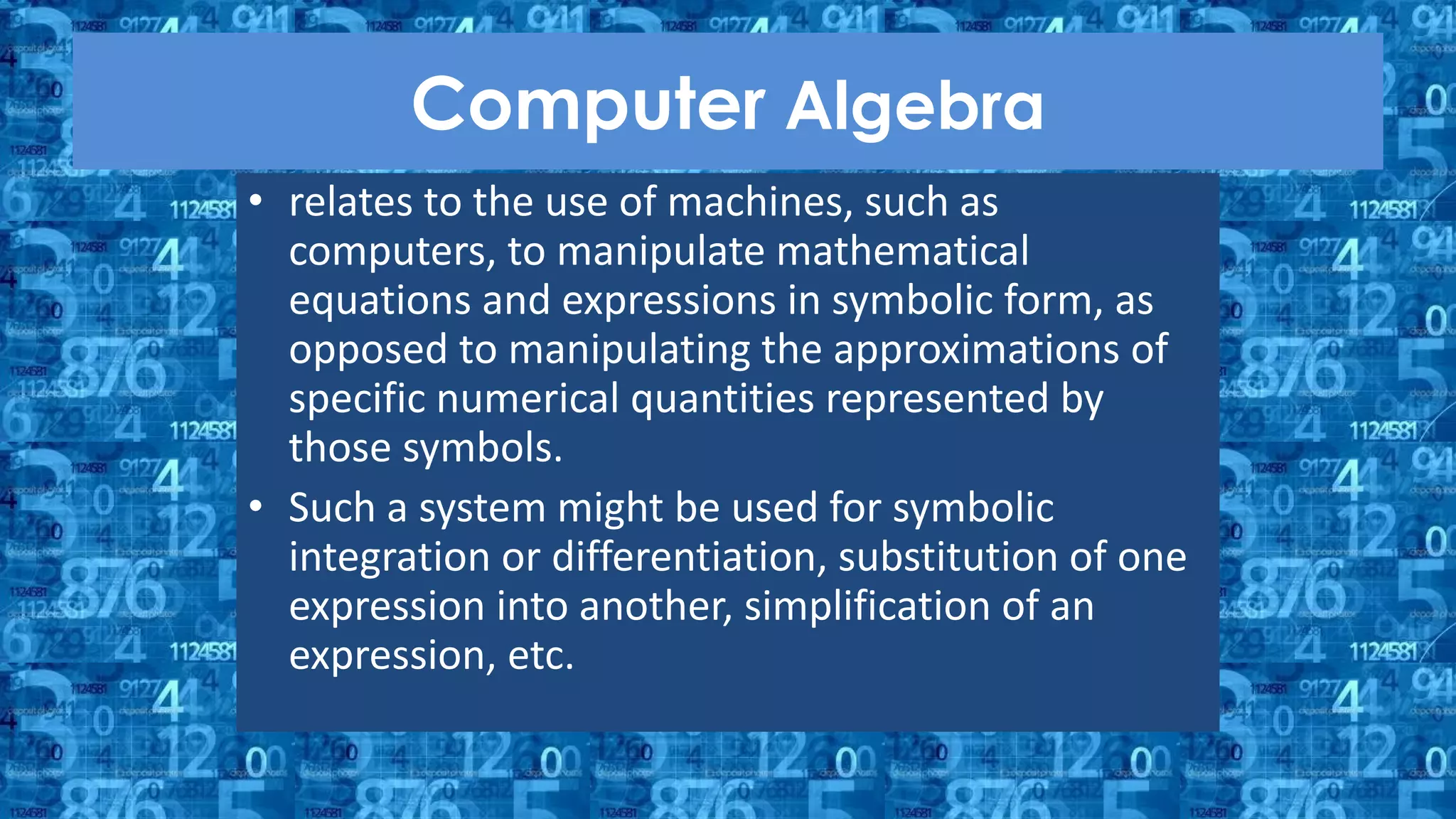
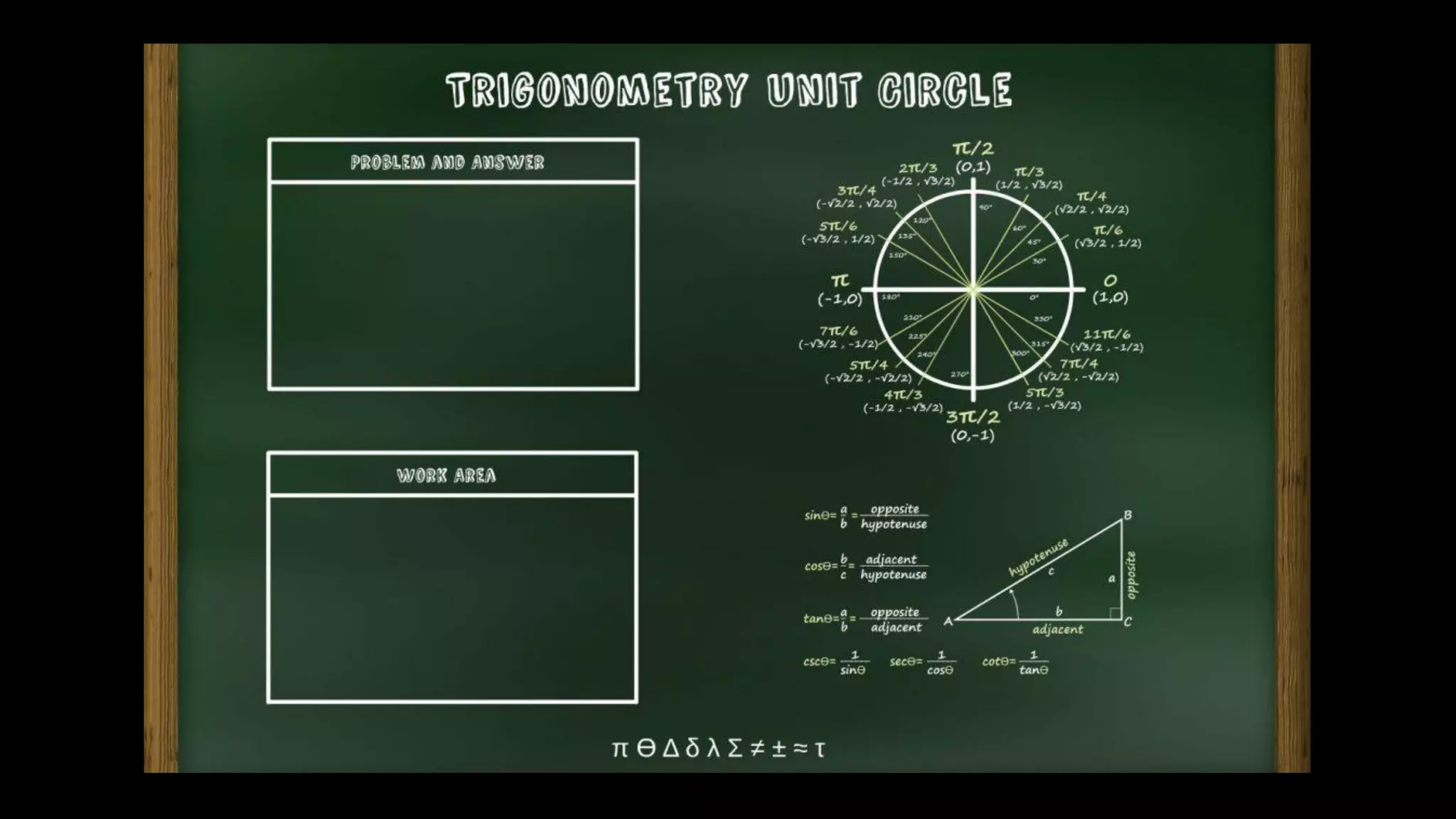
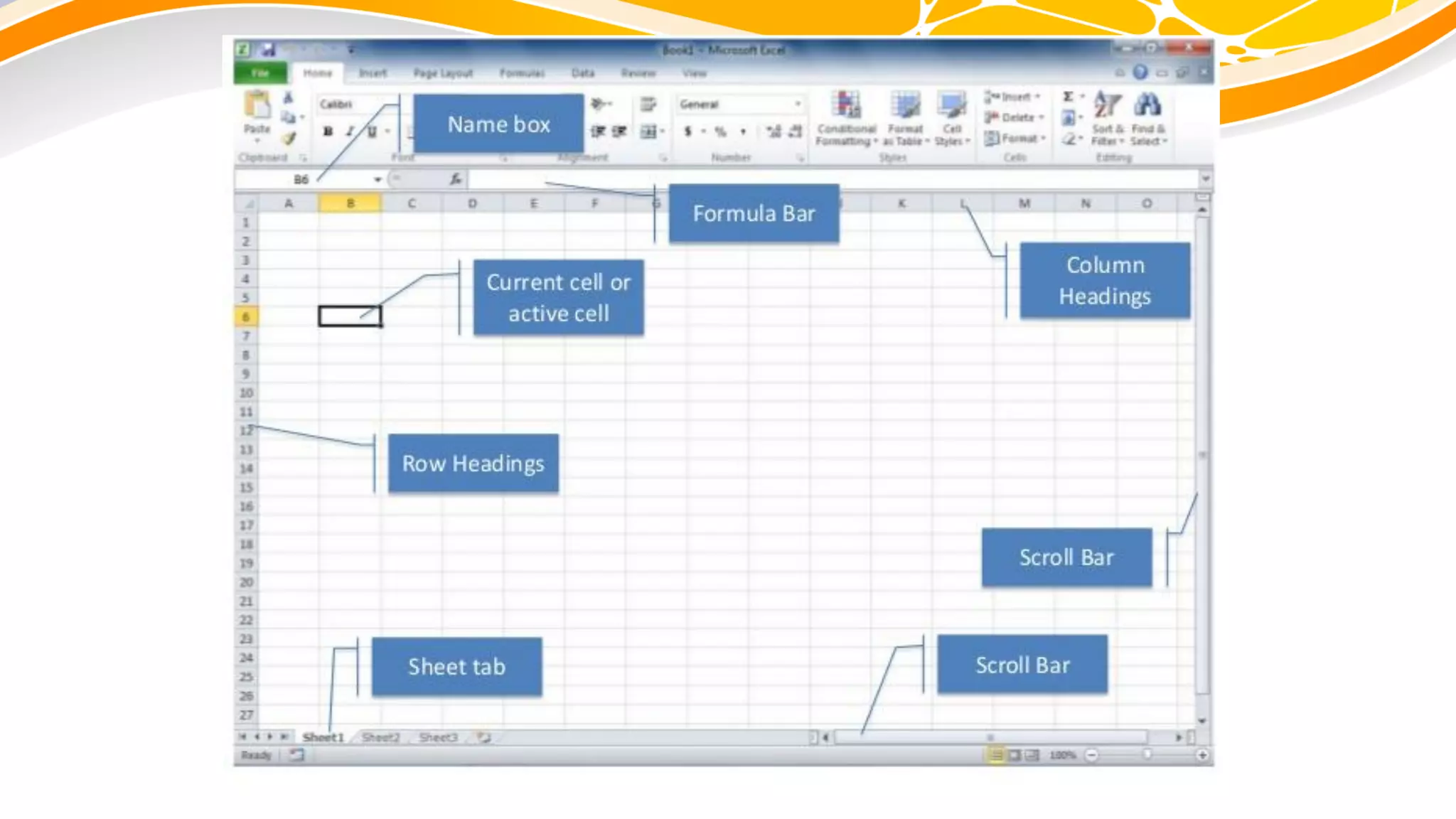
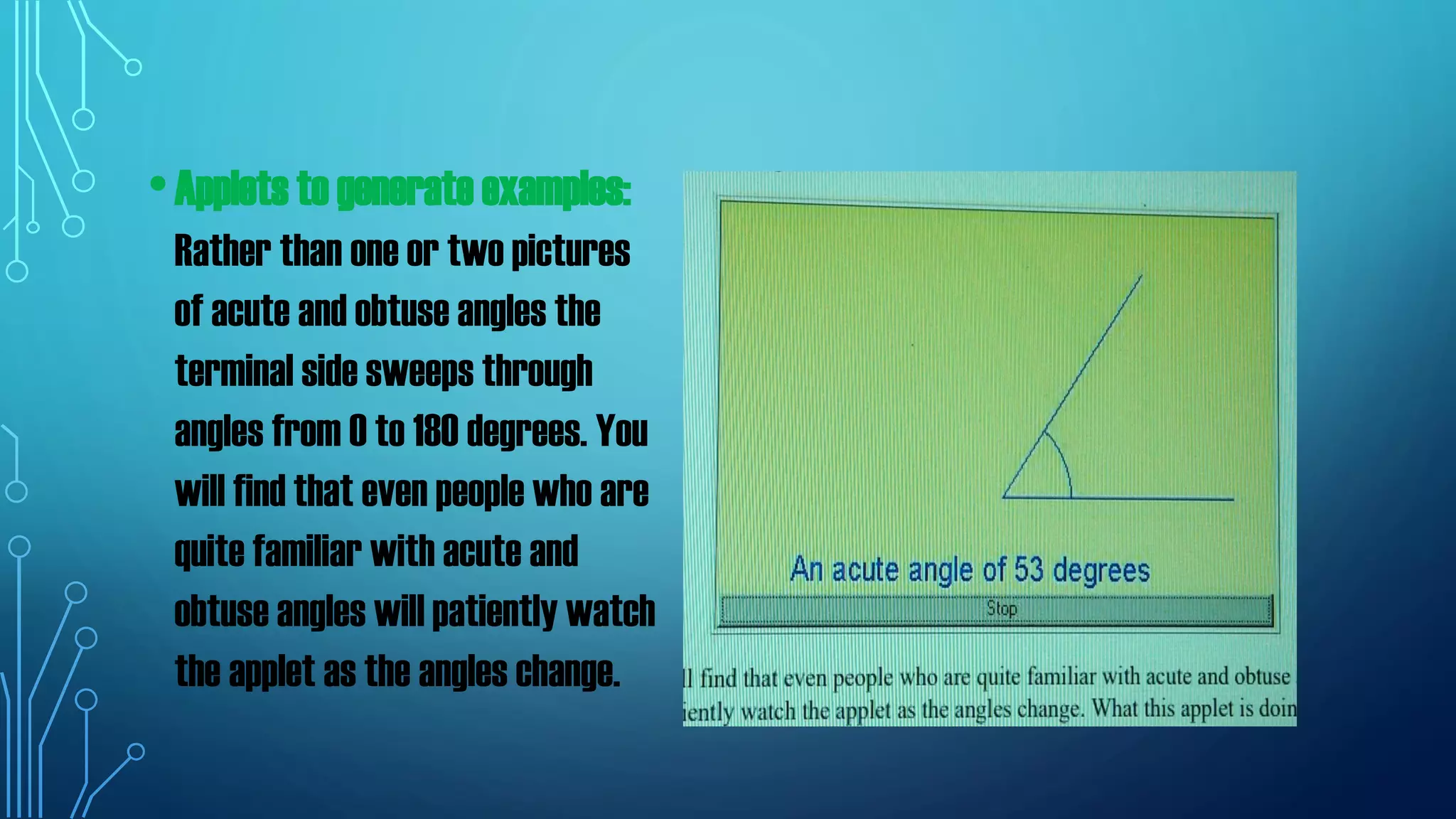
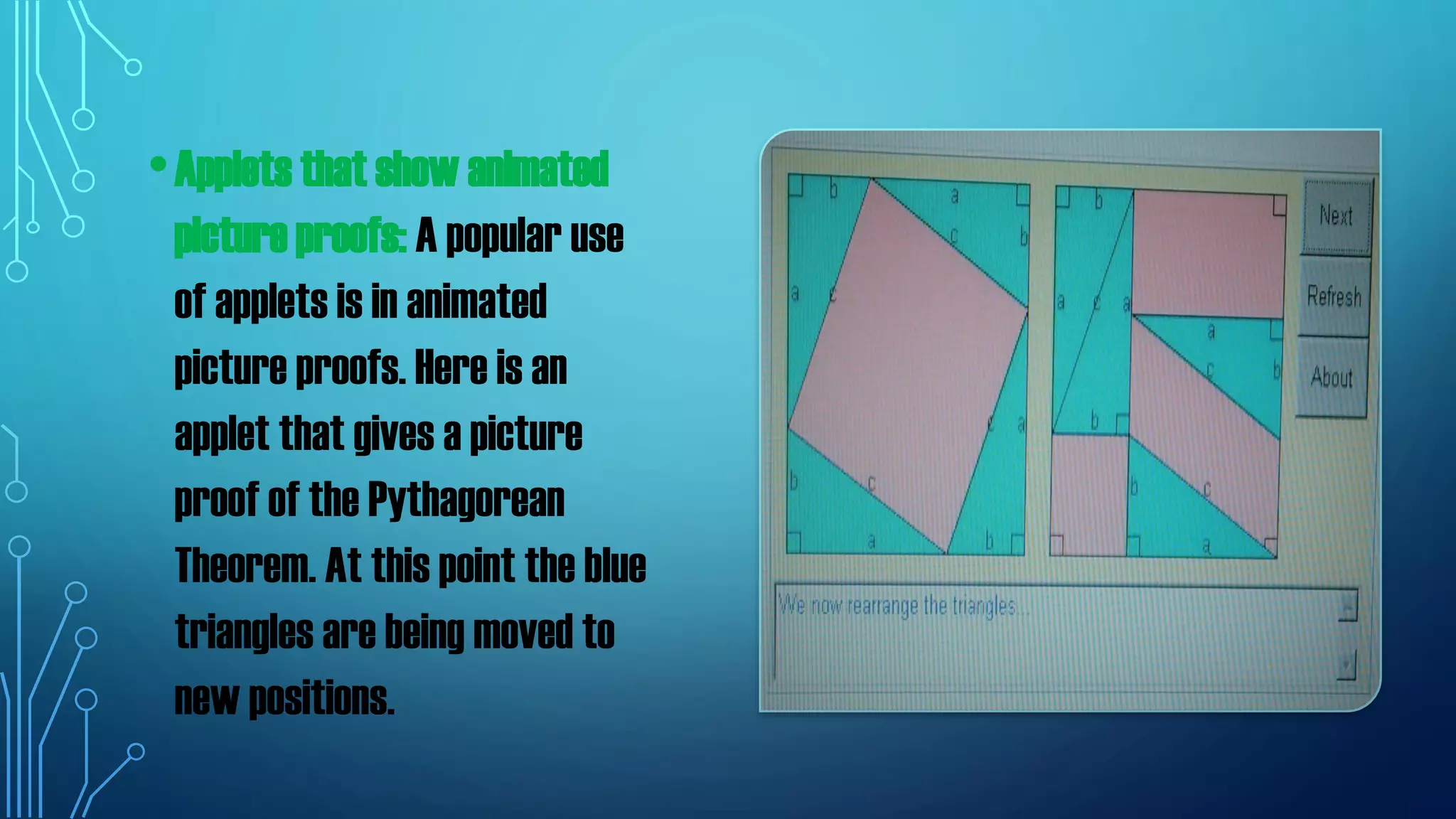
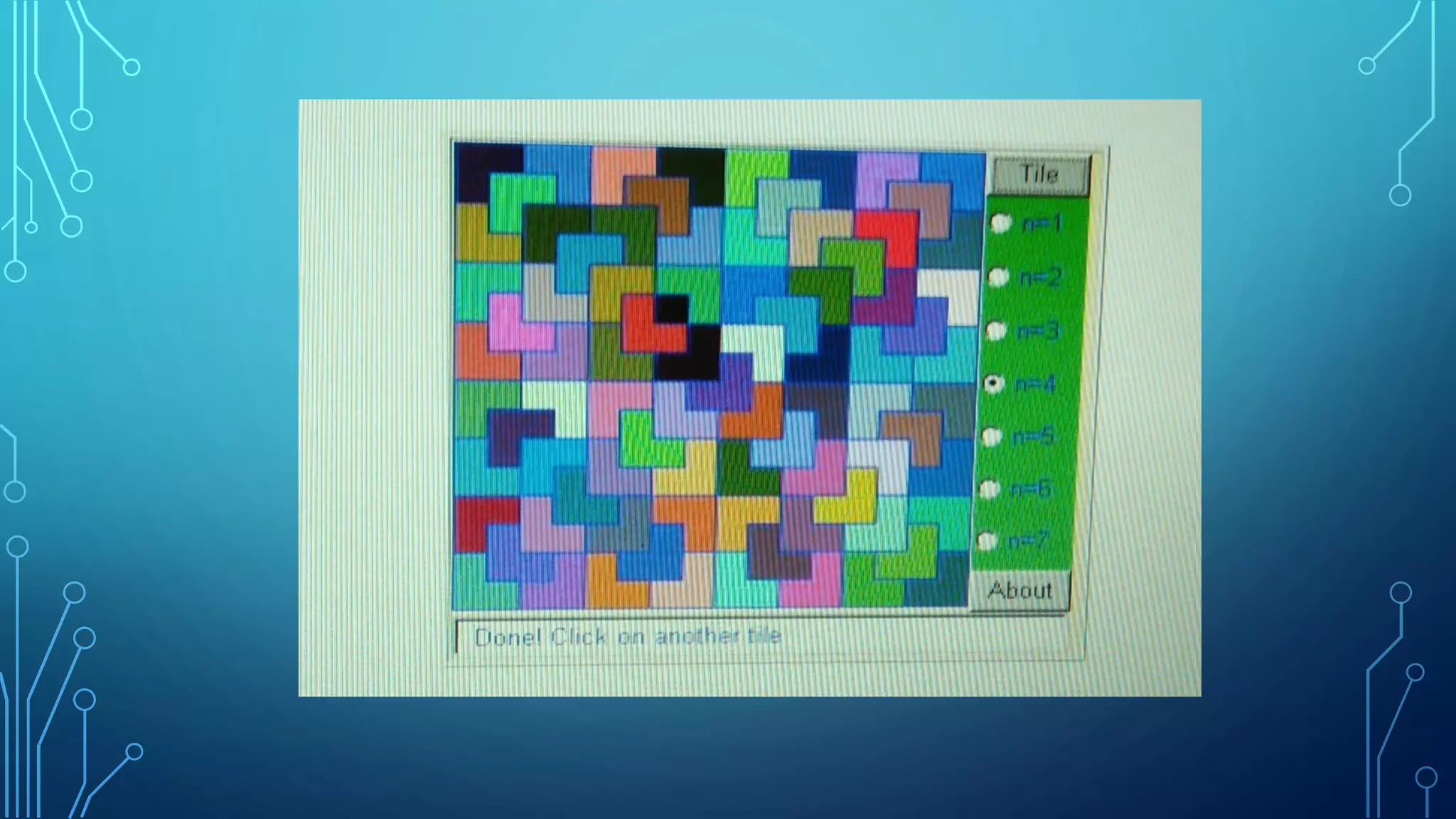
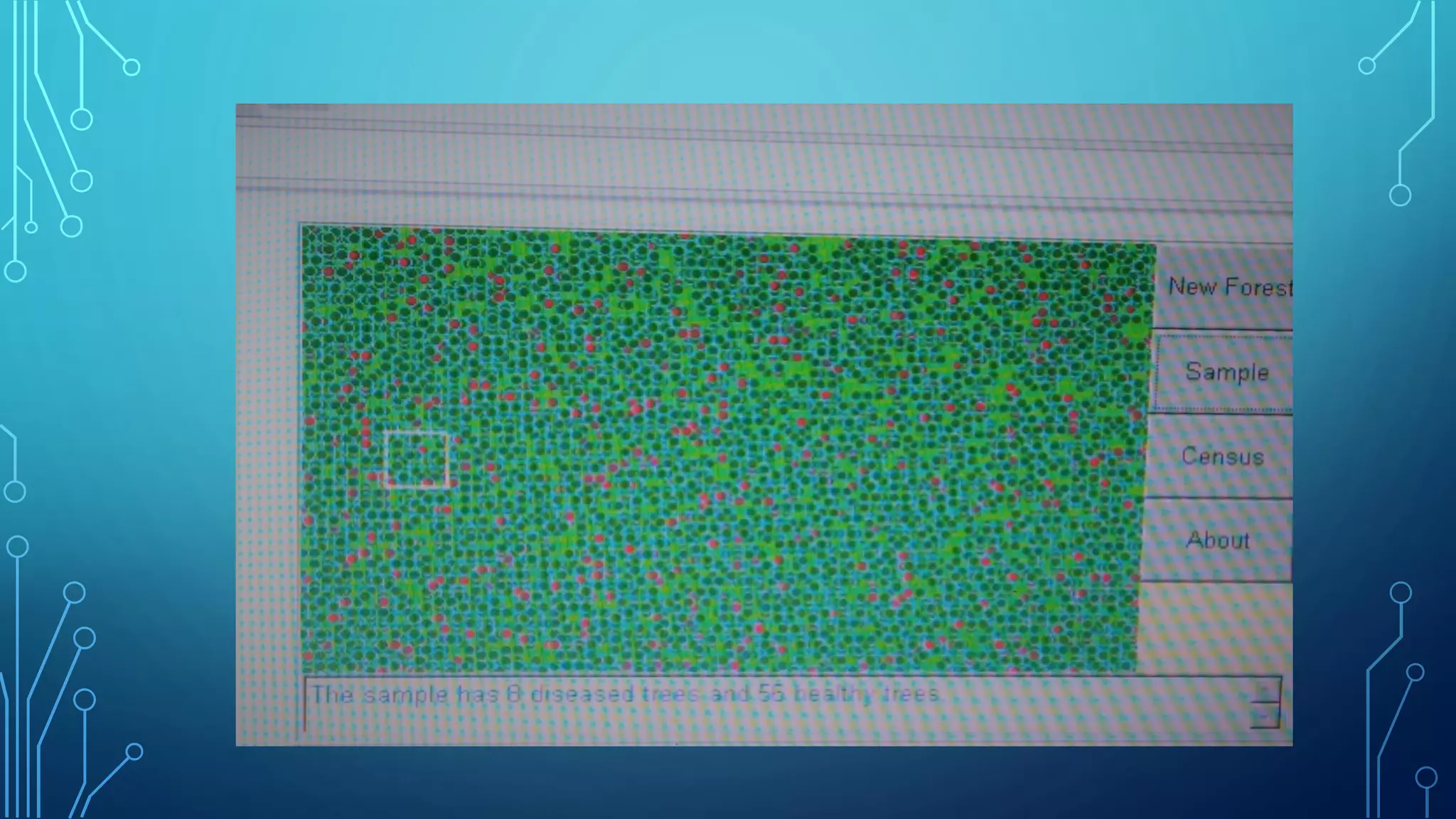
The document discusses the use of manipulatives and technology in teaching mathematics, emphasizing their role in enhancing students' understanding of mathematical concepts. It highlights various types of manipulatives, such as tangrams and graphing calculators, and outlines their pedagogical applications to promote hands-on learning and problem-solving skills. Additionally, the text addresses the integration of technology, including computer algebra systems and presentation software, to support instruction and engage learners in a more interactive and dynamic learning environment.