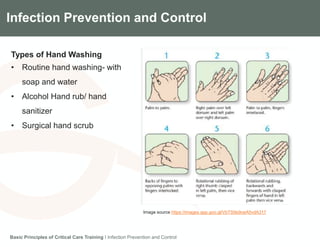
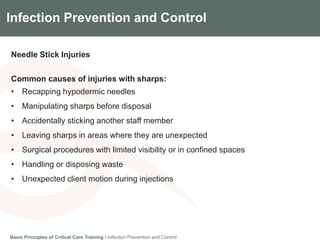
The document discusses infection prevention and control in intensive care units. It outlines the importance of infection control, the pillars of infection control including isolation, decontamination, prudent antibiotic use and hand hygiene. It describes the hospital infection control program and roles. Key infection control principles are universal practices, methods like hand hygiene, personal protective equipment, decontamination and cleaning. Needlestick injury prevention and the importance of proper sharps disposal are also covered.