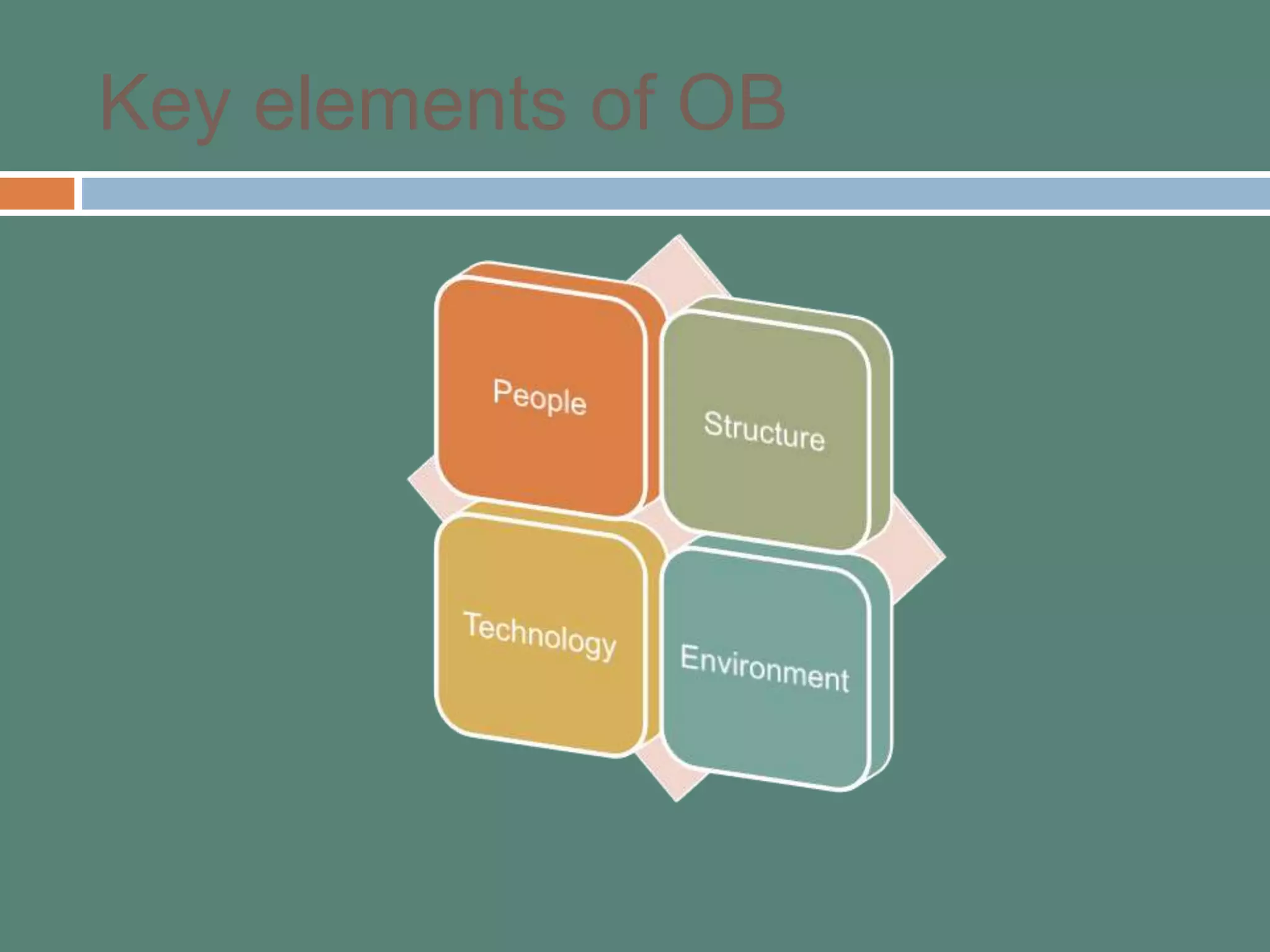
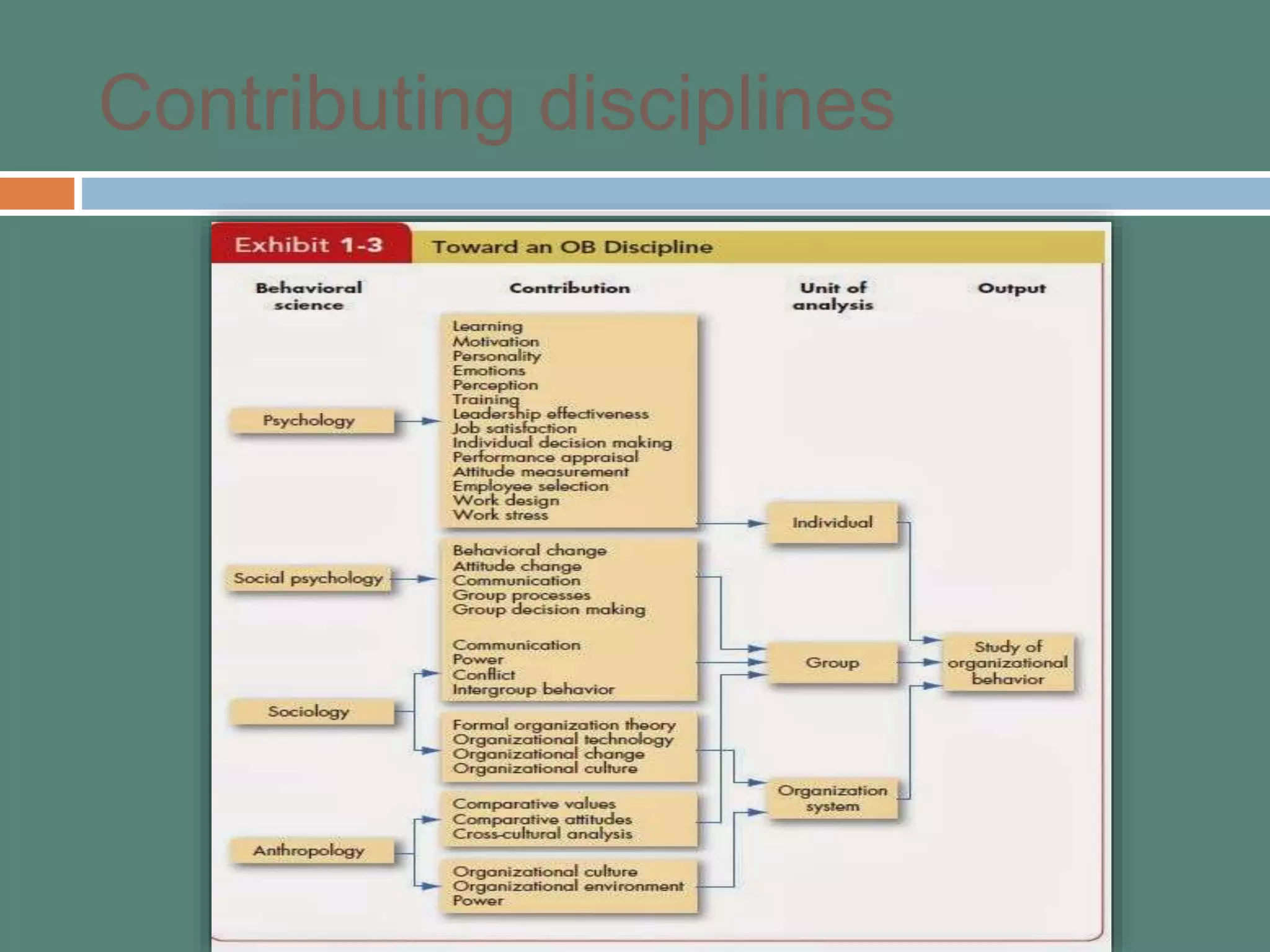
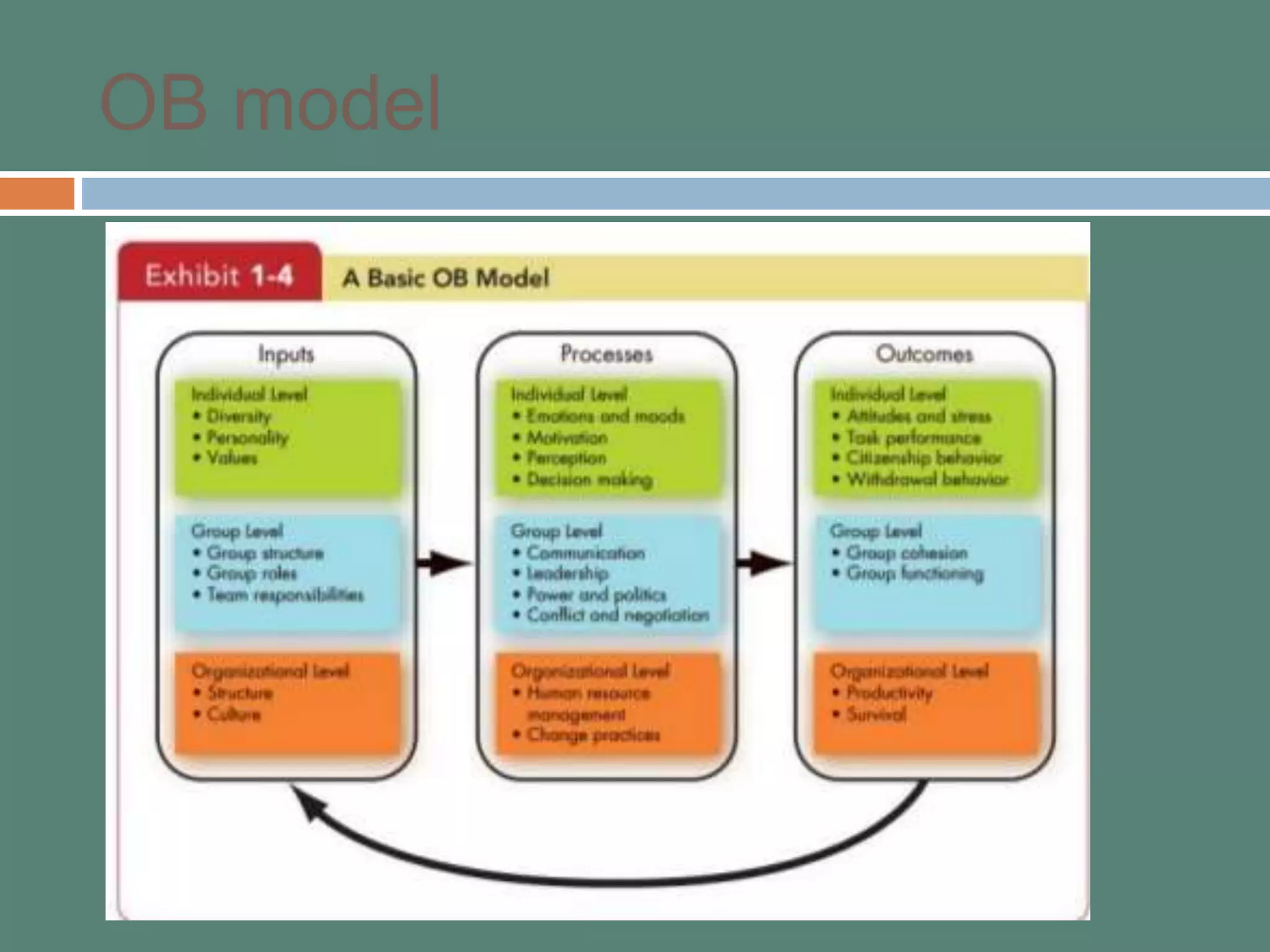
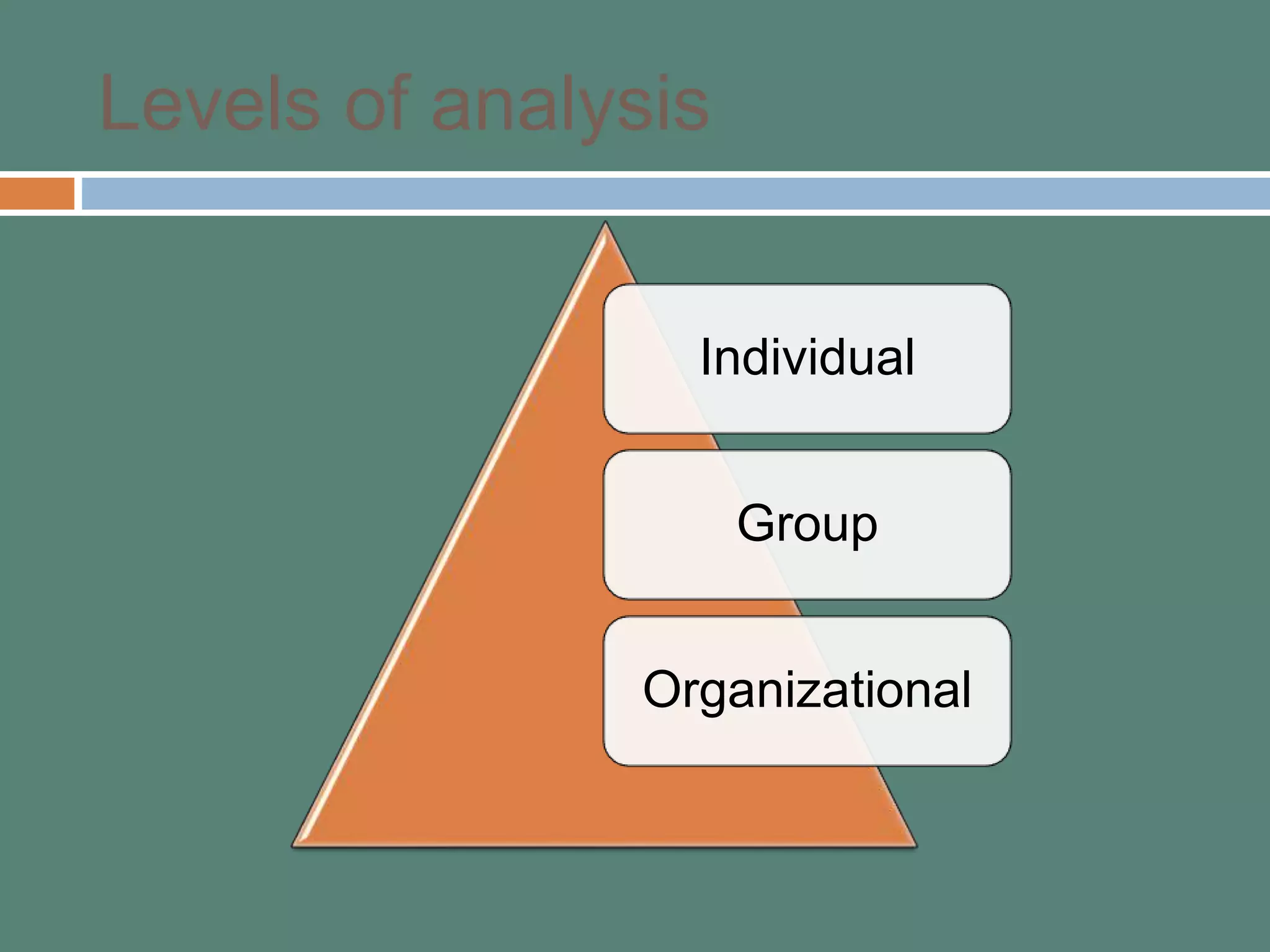
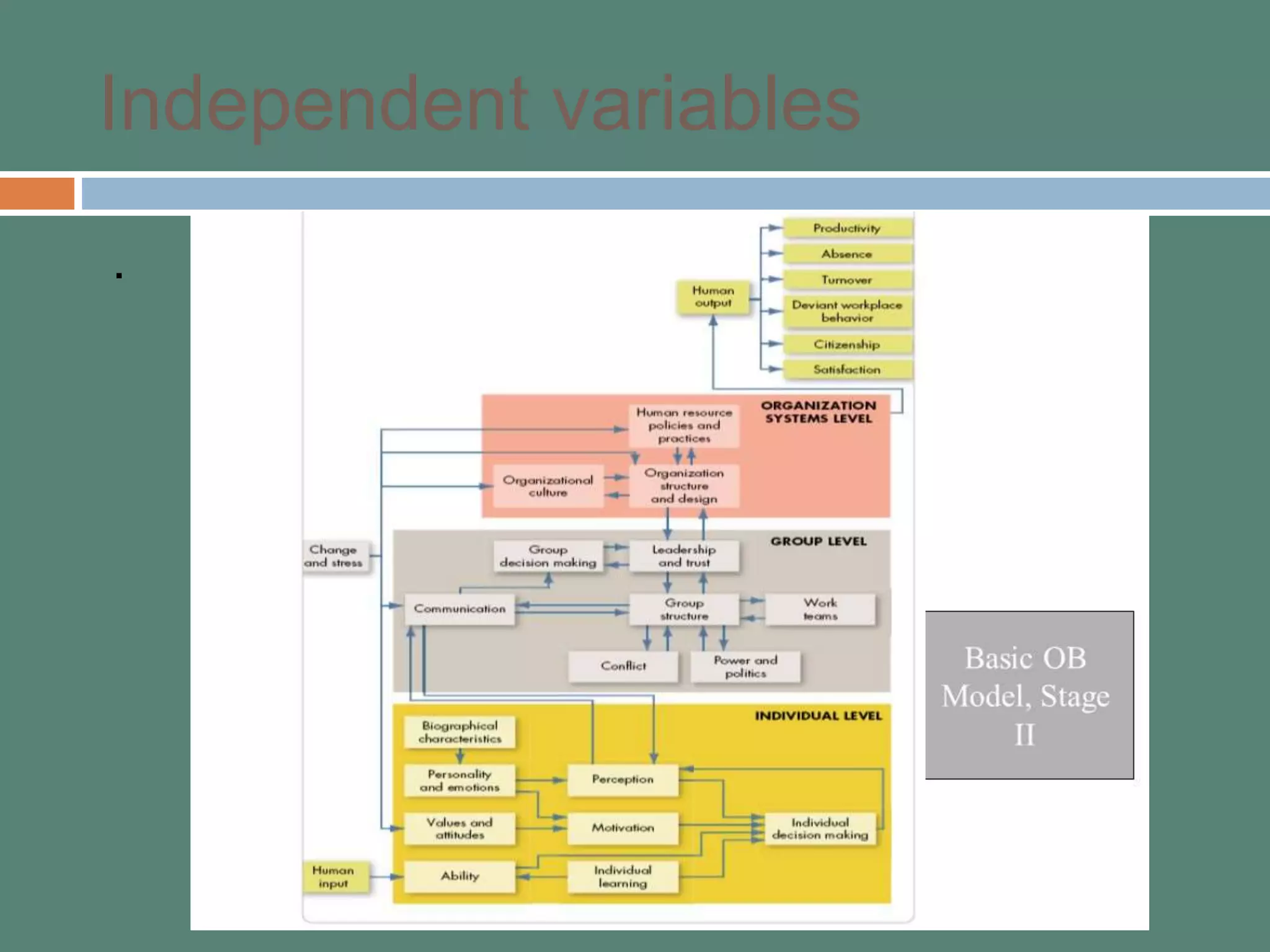
This document provides an introduction to organizational behavior (OB). It defines OB and outlines its key elements and scope. OB draws from contributing disciplines like psychology, sociology, social psychology, and anthropology. The document presents an OB model that identifies the primary independent variables (like personality, group structure, organizational culture) and dependent variables (like job satisfaction, productivity, turnover) in OB. It also discusses the three levels of analysis in OB: individual, group, and organizational.