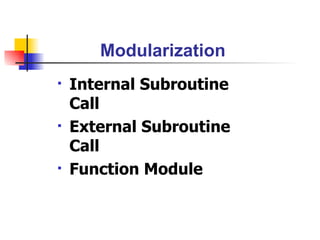
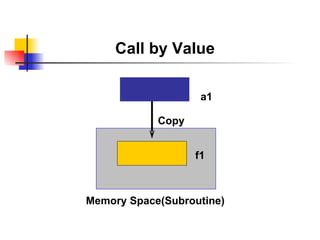
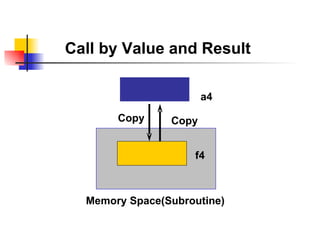
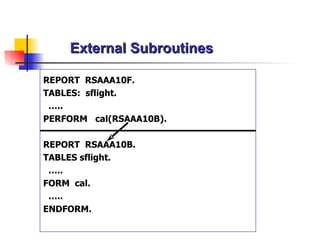
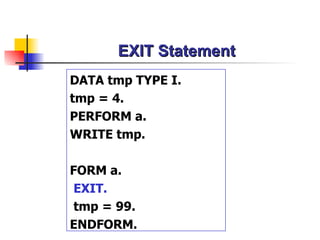
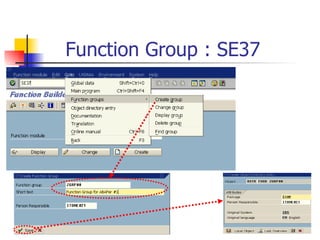
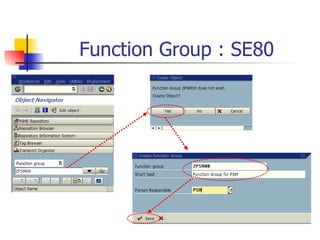
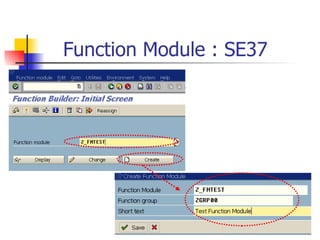
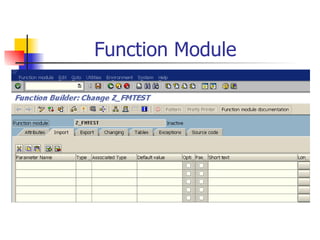
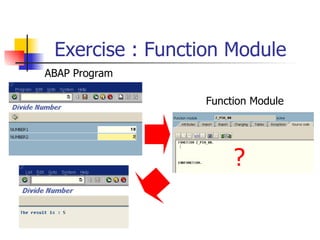
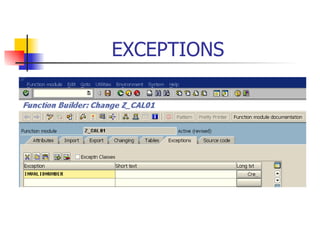
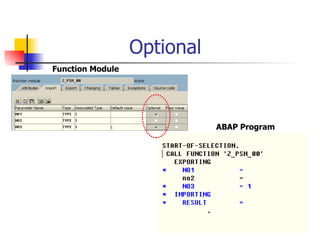
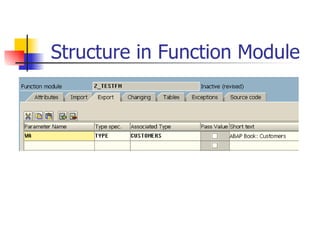
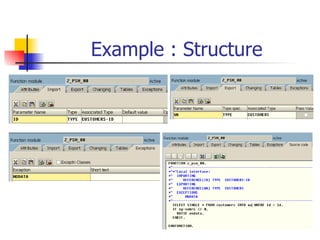
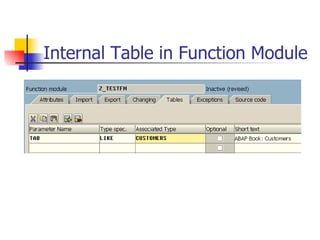
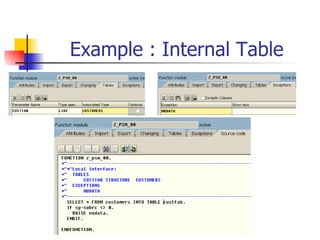
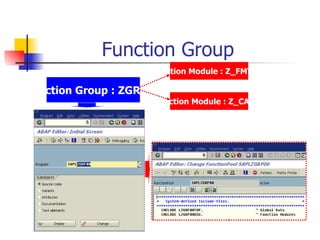
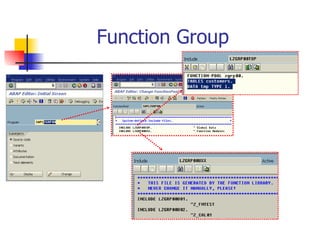
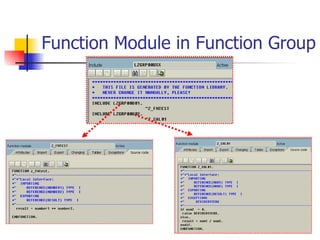
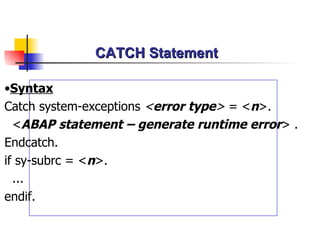
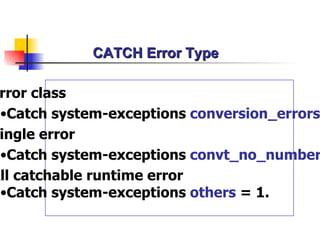
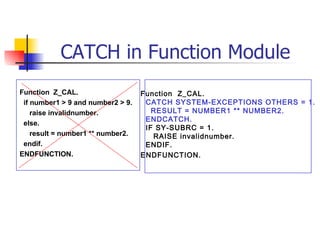
The document discusses modularization in ABAP including subroutine calls, passing parameters, function modules, function groups, and the CATCH statement. It provides examples of calling subroutines, passing different types of parameters, defining and calling function modules and groups, and using the CATCH statement to handle exceptions.