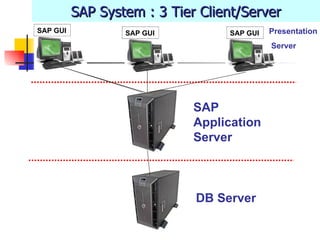
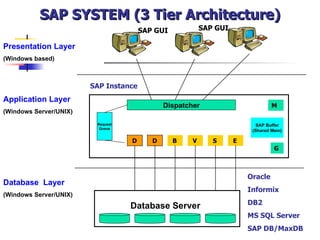
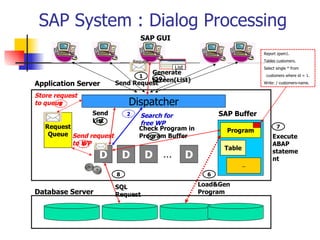
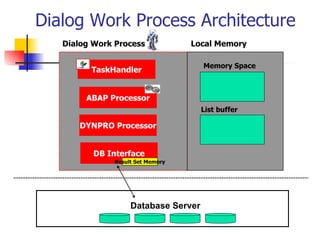
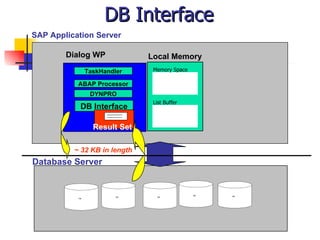
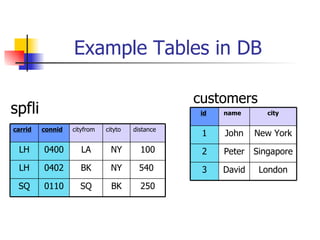
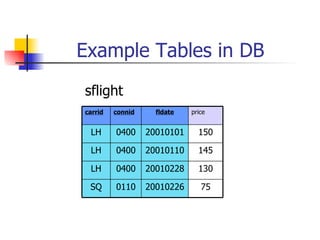
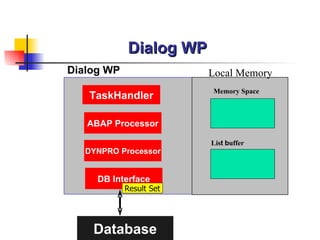
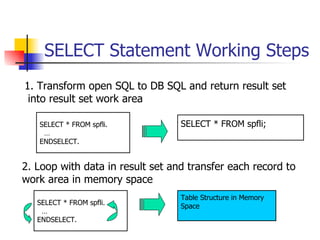
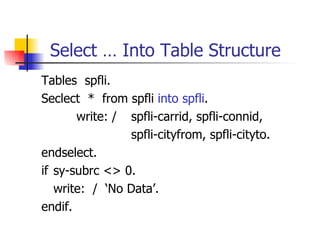
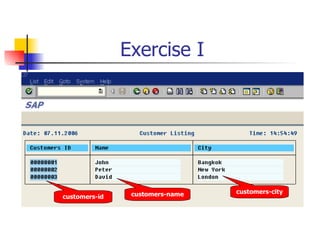
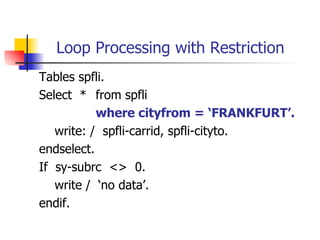
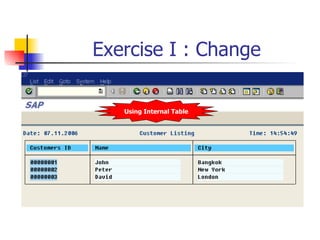
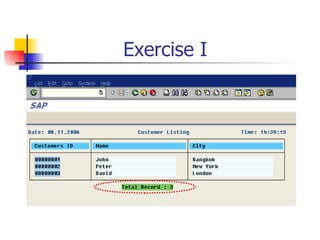
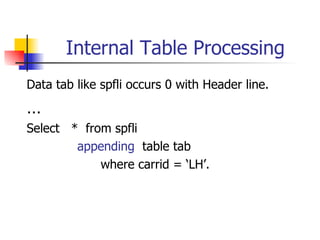
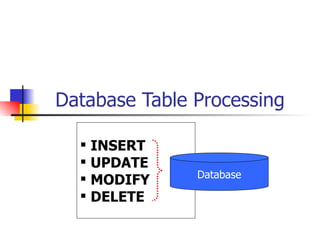
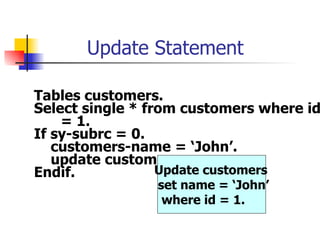
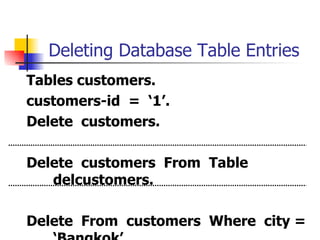
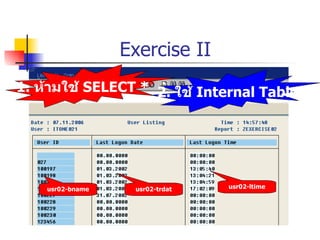
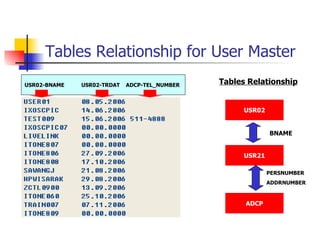
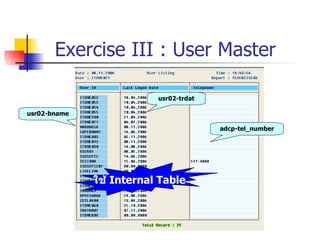
This document discusses Open SQL internal table concepts in ABAP including:
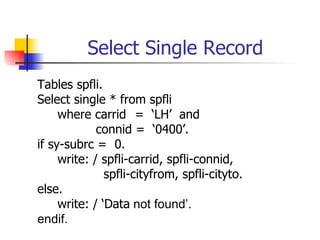
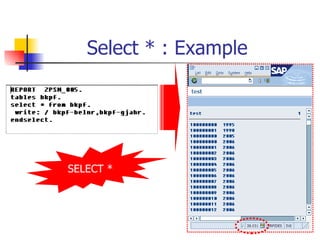
- Select statements to retrieve single or multiple records from database tables
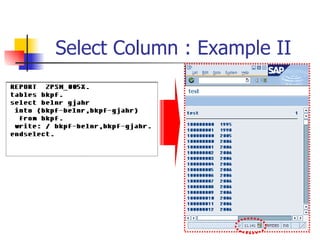
- Selecting specific columns instead of using SELECT *
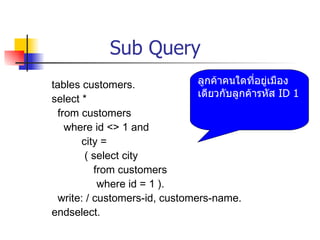
- Adding WHERE clauses to filter records by conditions
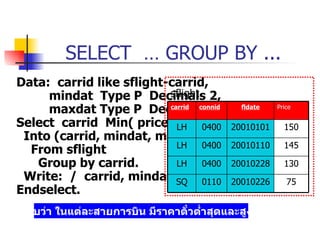
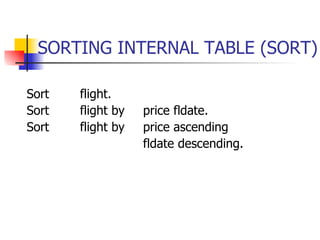
- Using ORDER BY to sort results
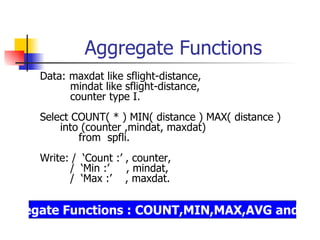
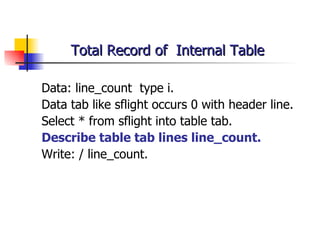
- Aggregate functions like COUNT, MIN, MAX to operate on groups
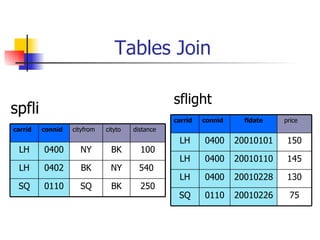
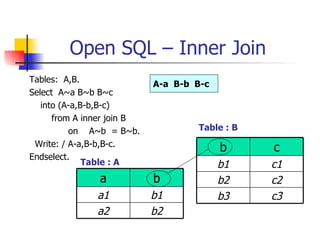
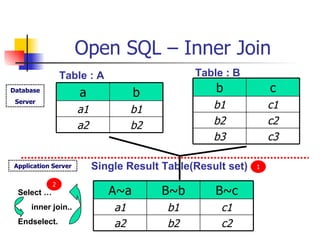
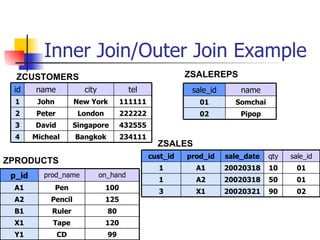
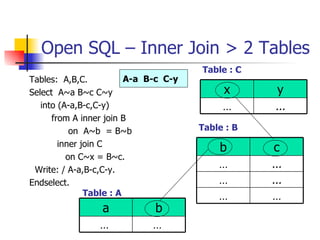
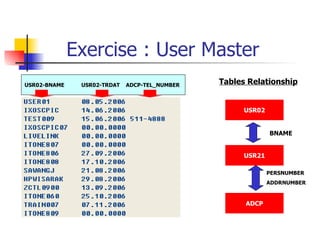
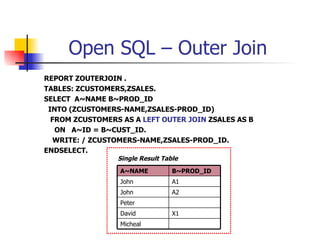
- Joining data from multiple tables using inner joins