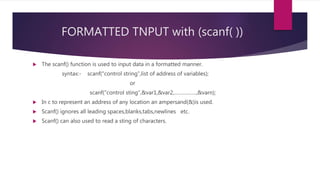
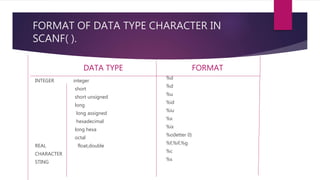
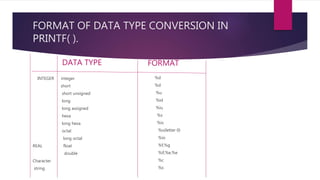
The document explains input and output operations in the C programming language, highlighting functions such as printf() and scanf() which are part of the stdio.h library. It details unformatted and formatted I/O functions, including their syntax and usage for handling data input from keyboards and output to monitors. Additionally, it discusses software engineering principles related to program documentation and data naming conventions.