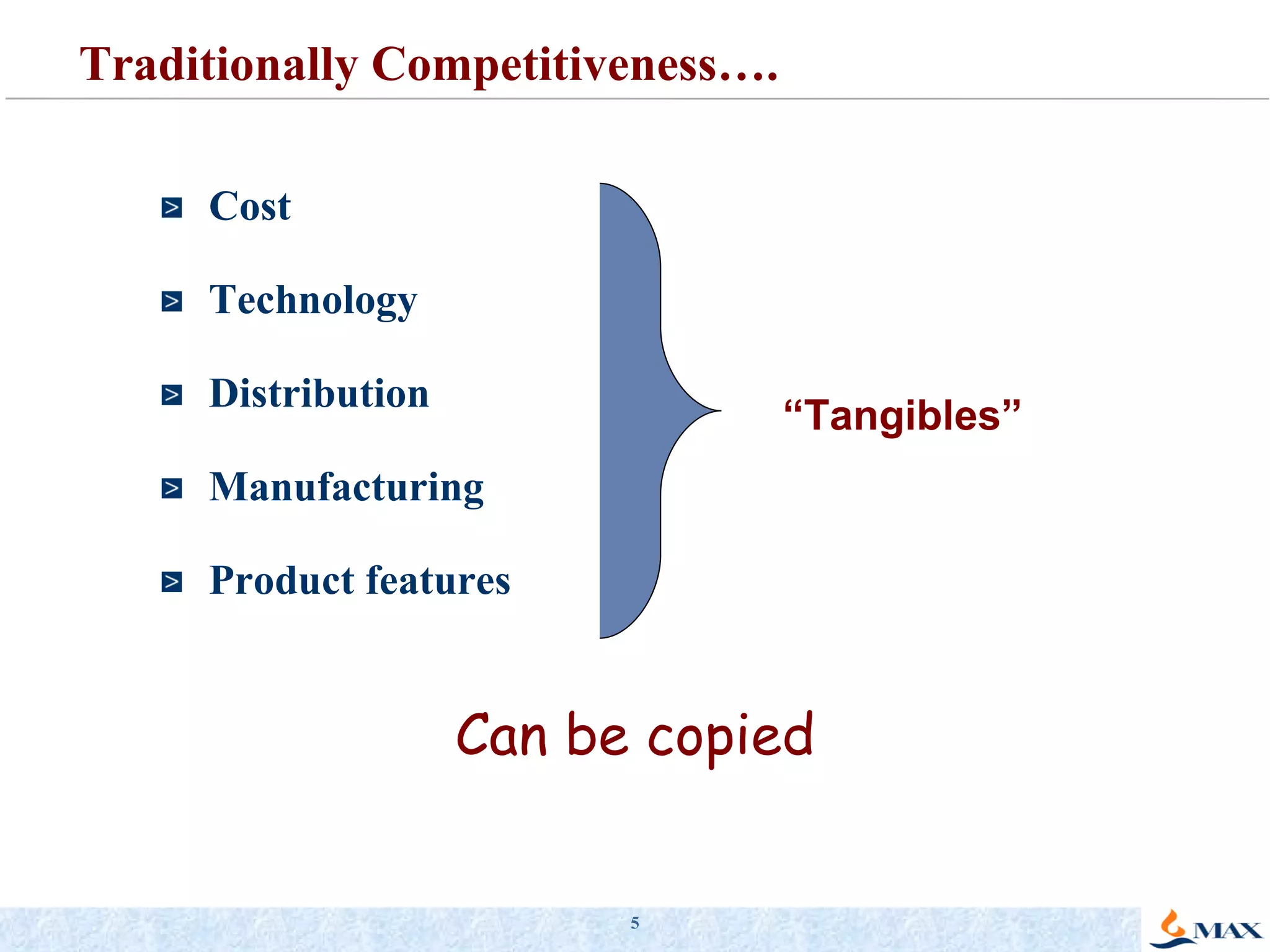
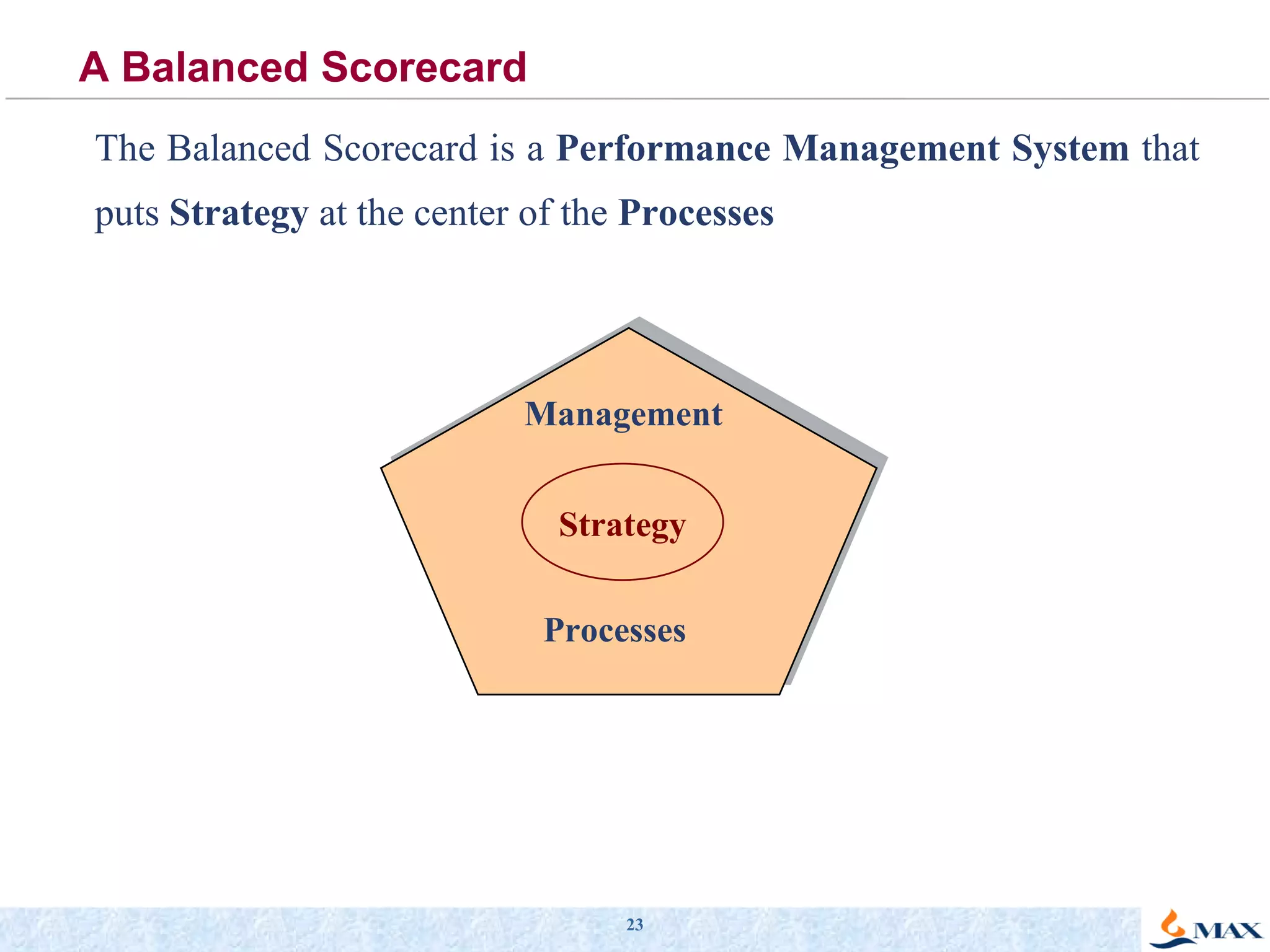
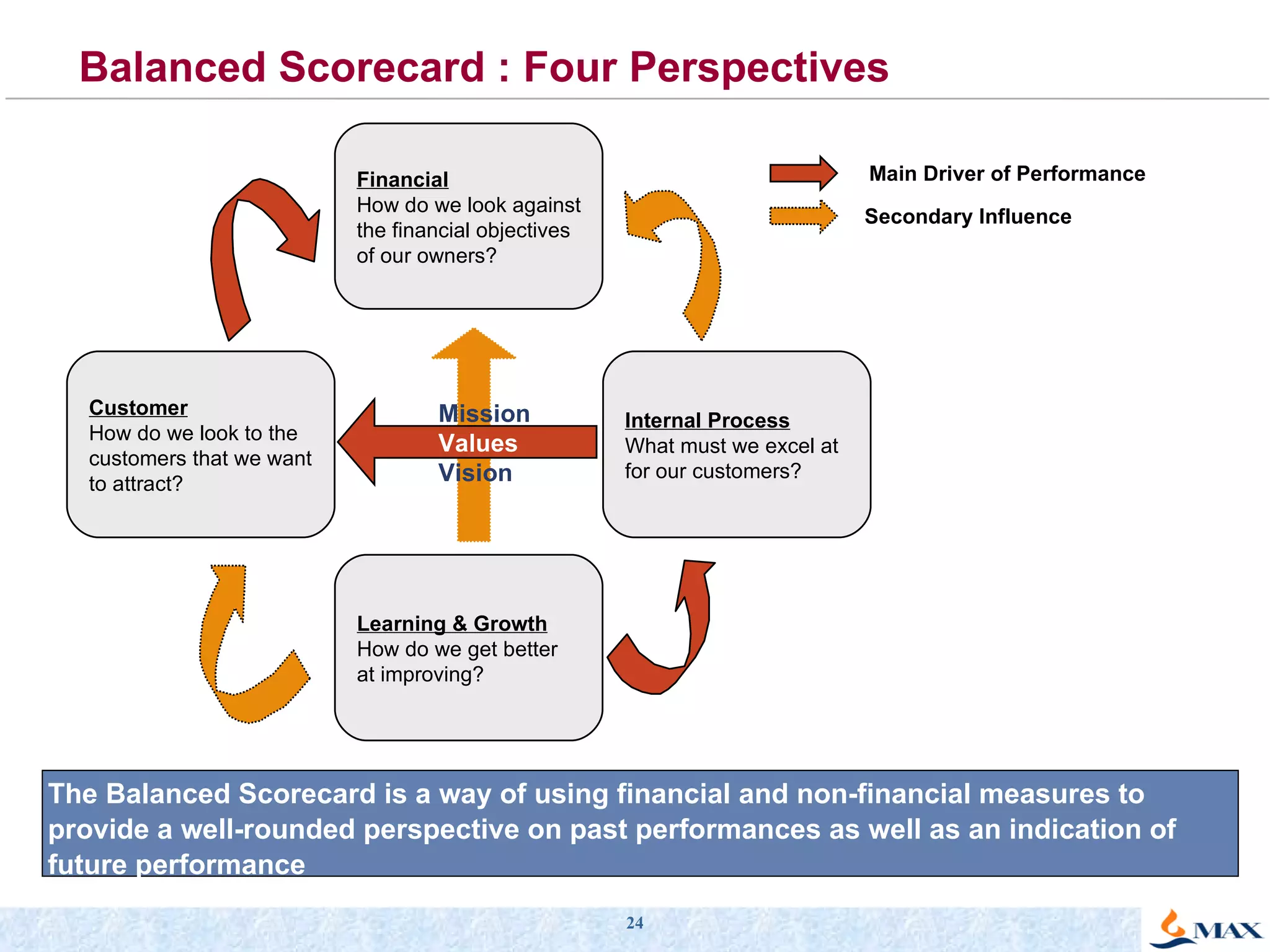
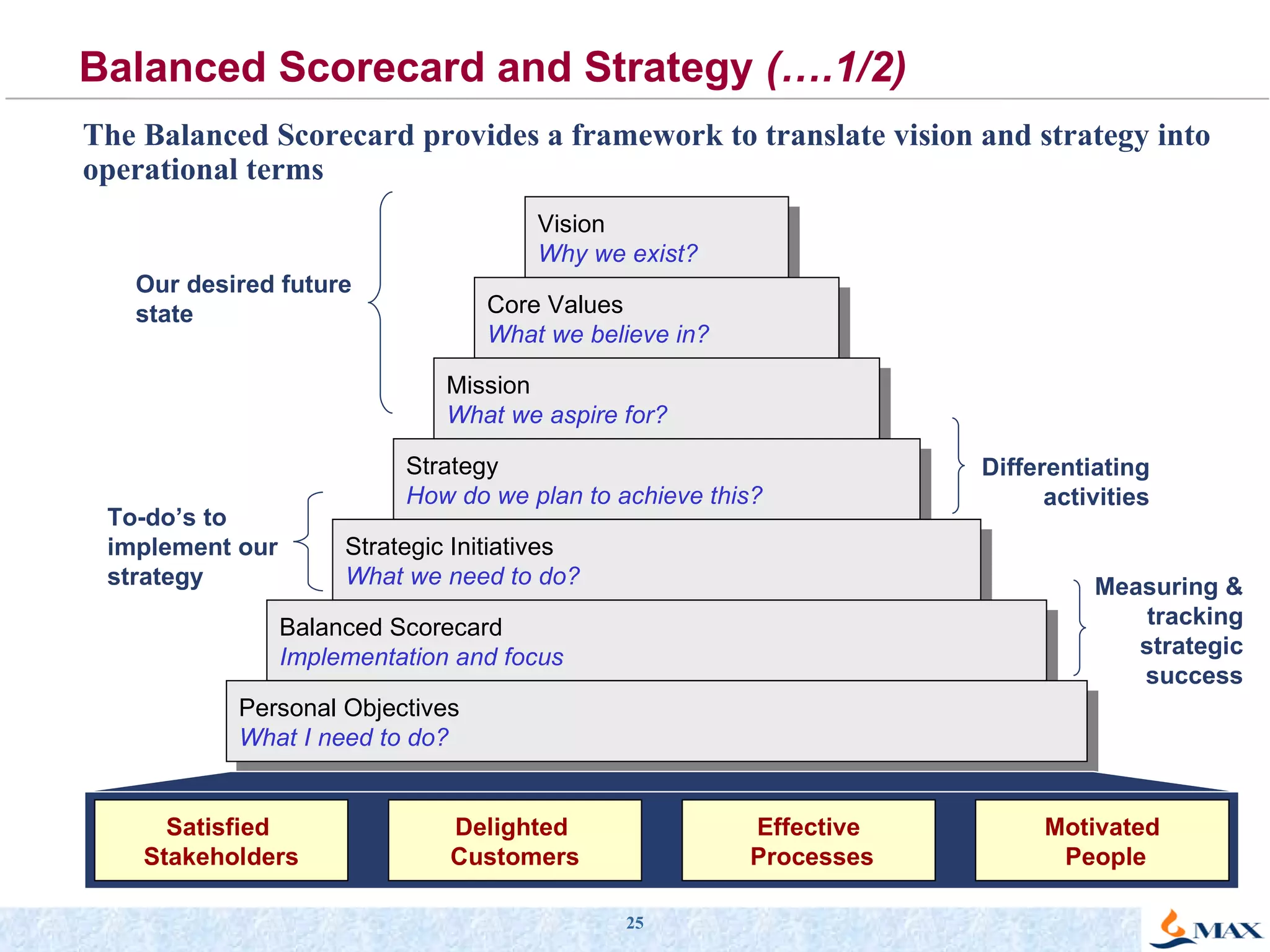
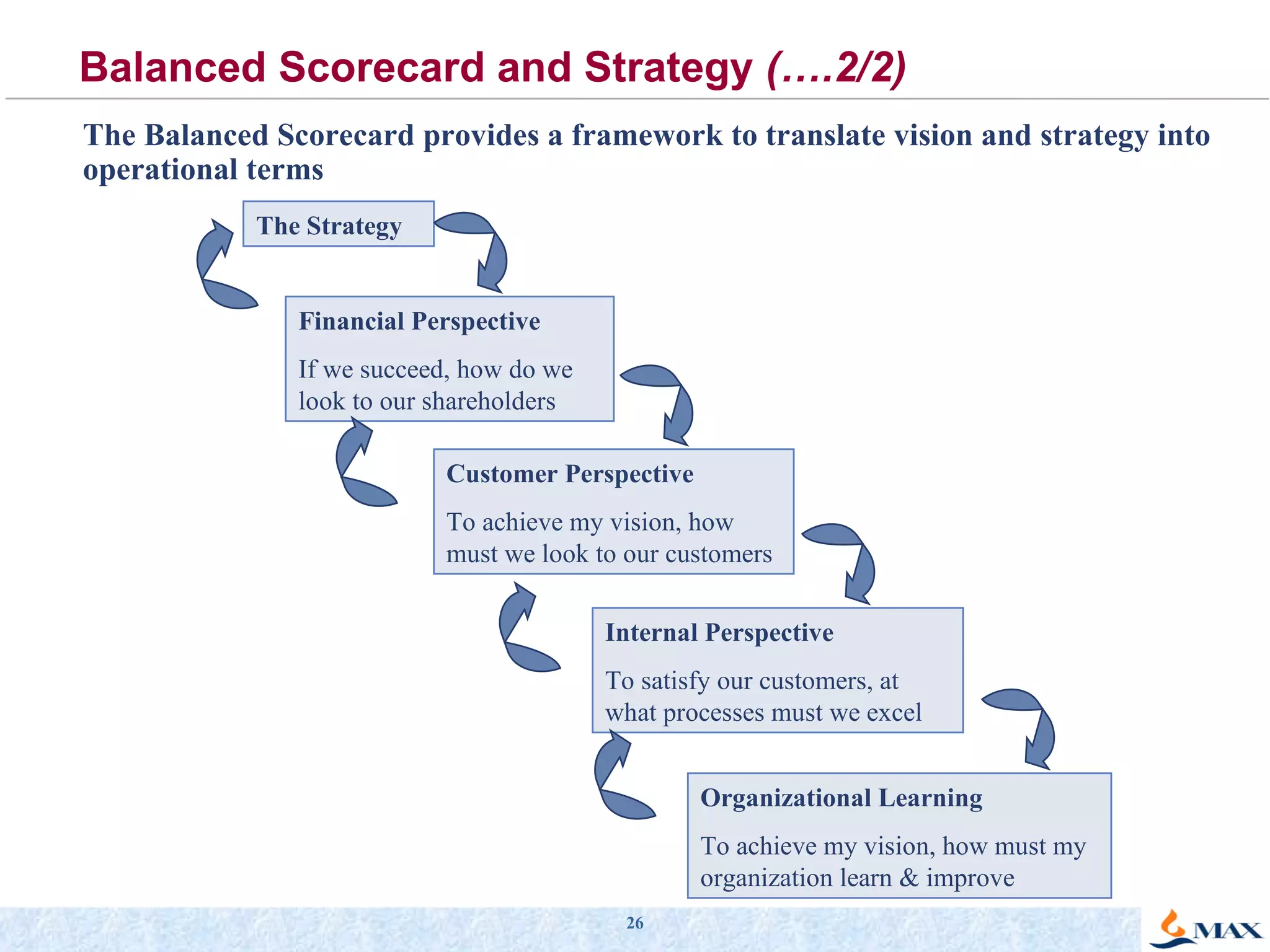
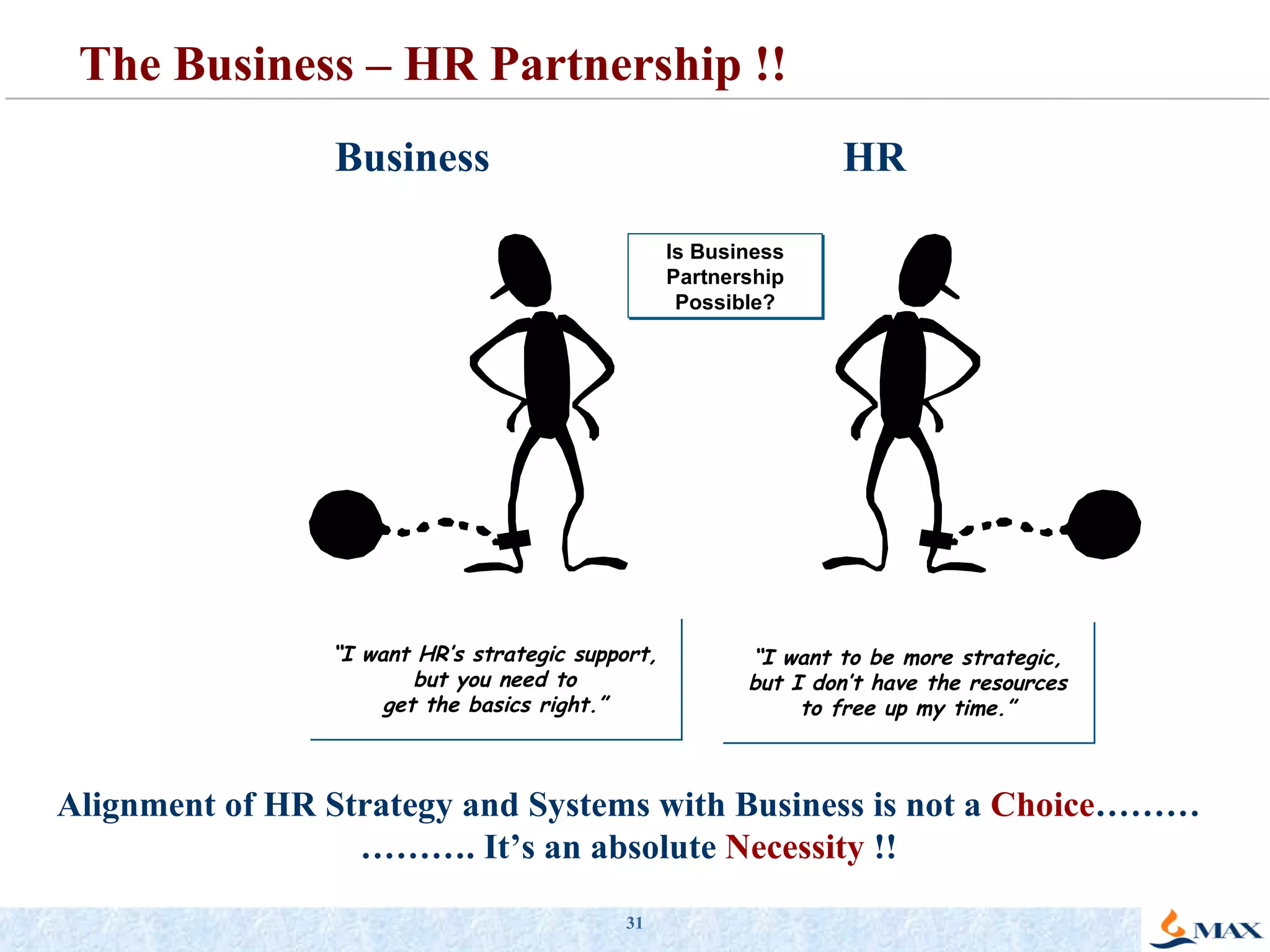
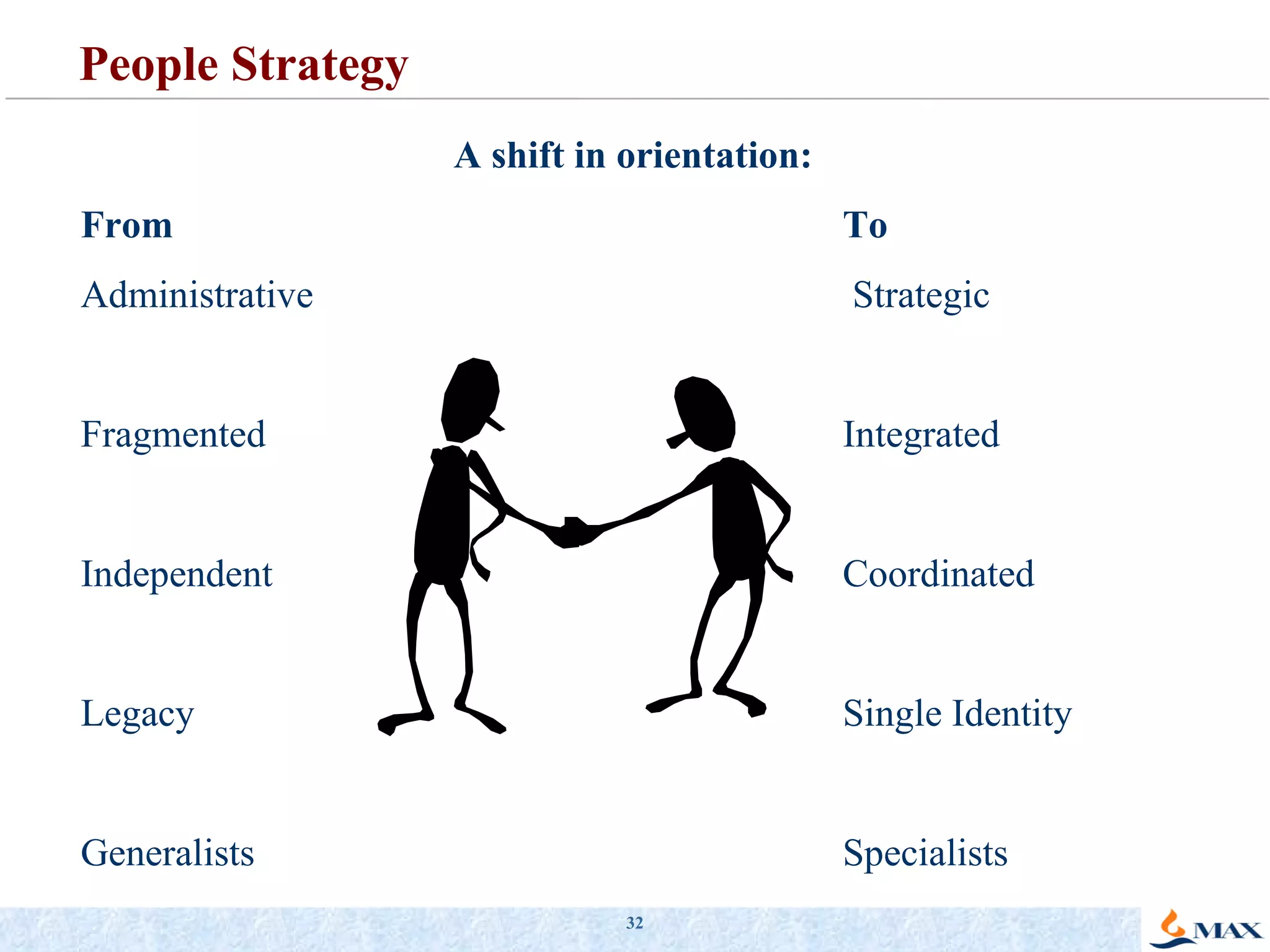
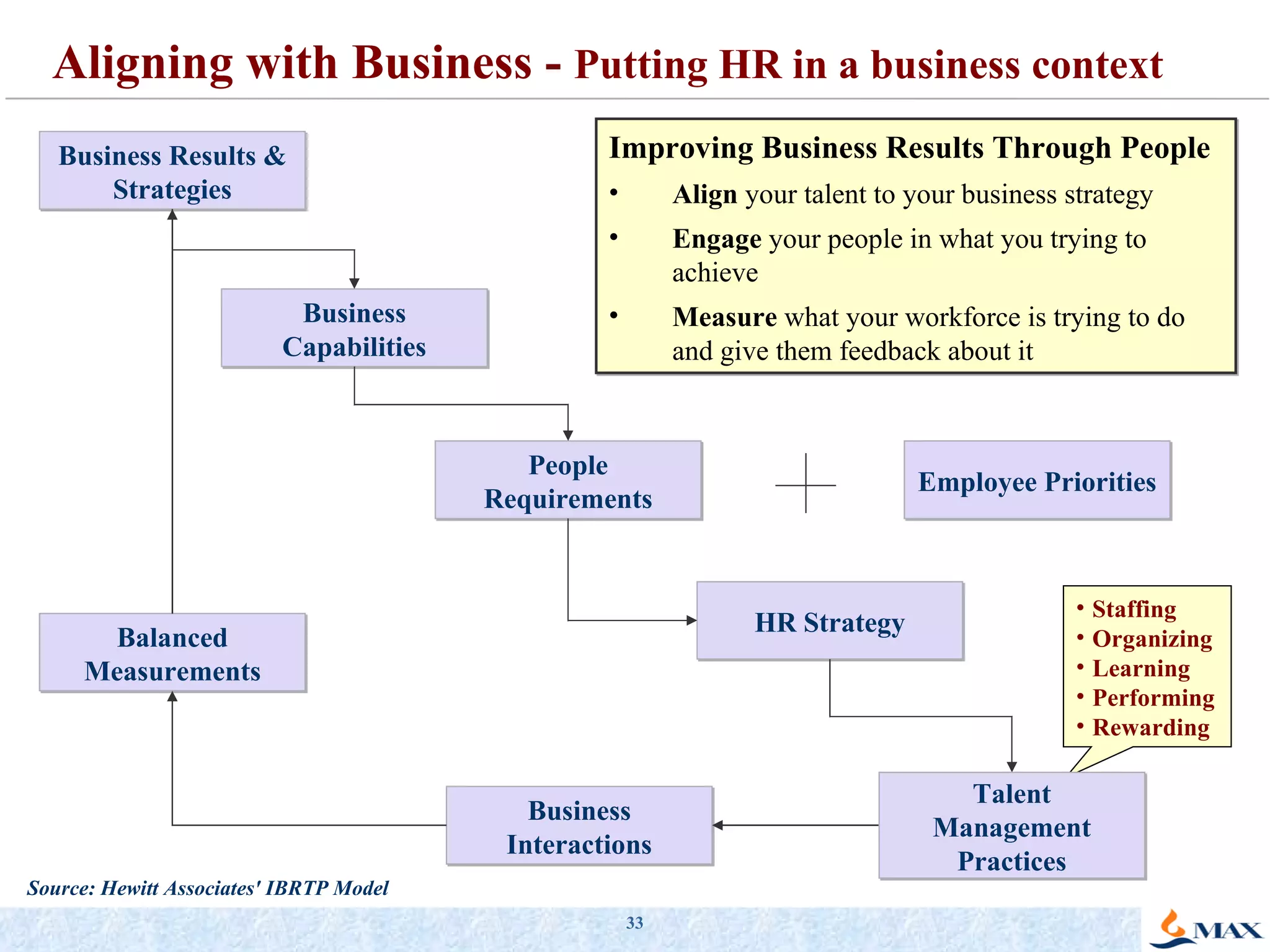
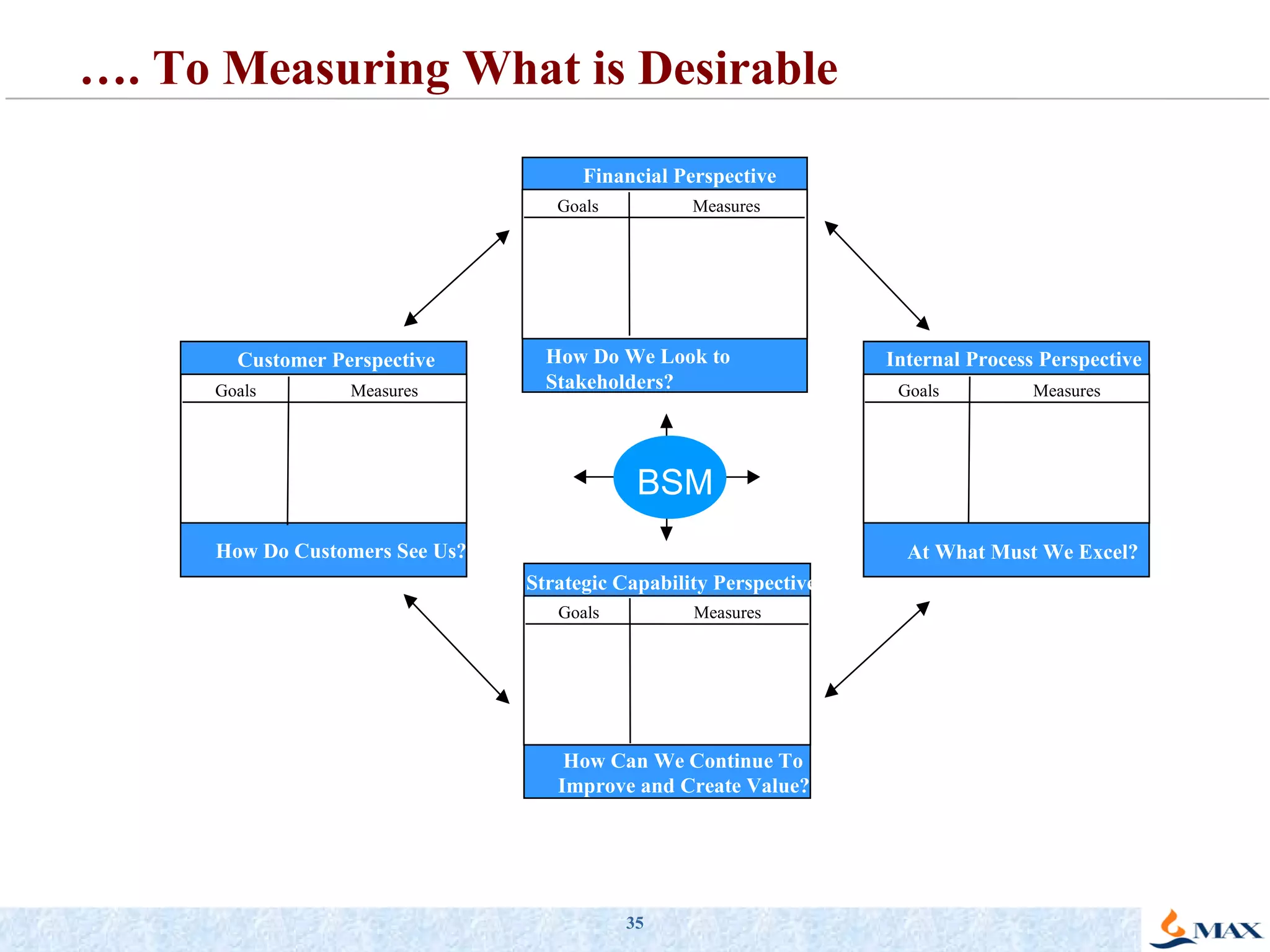
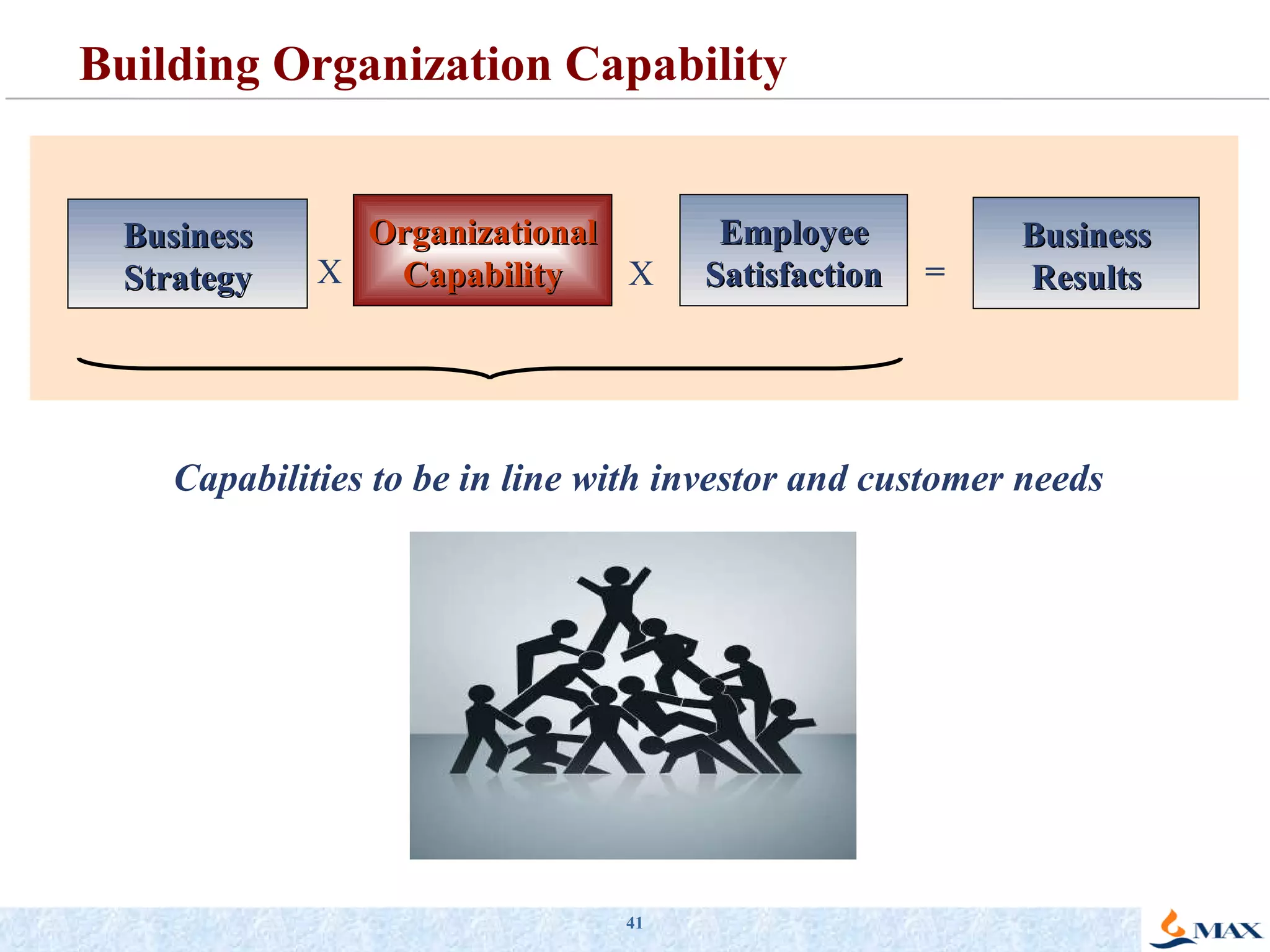
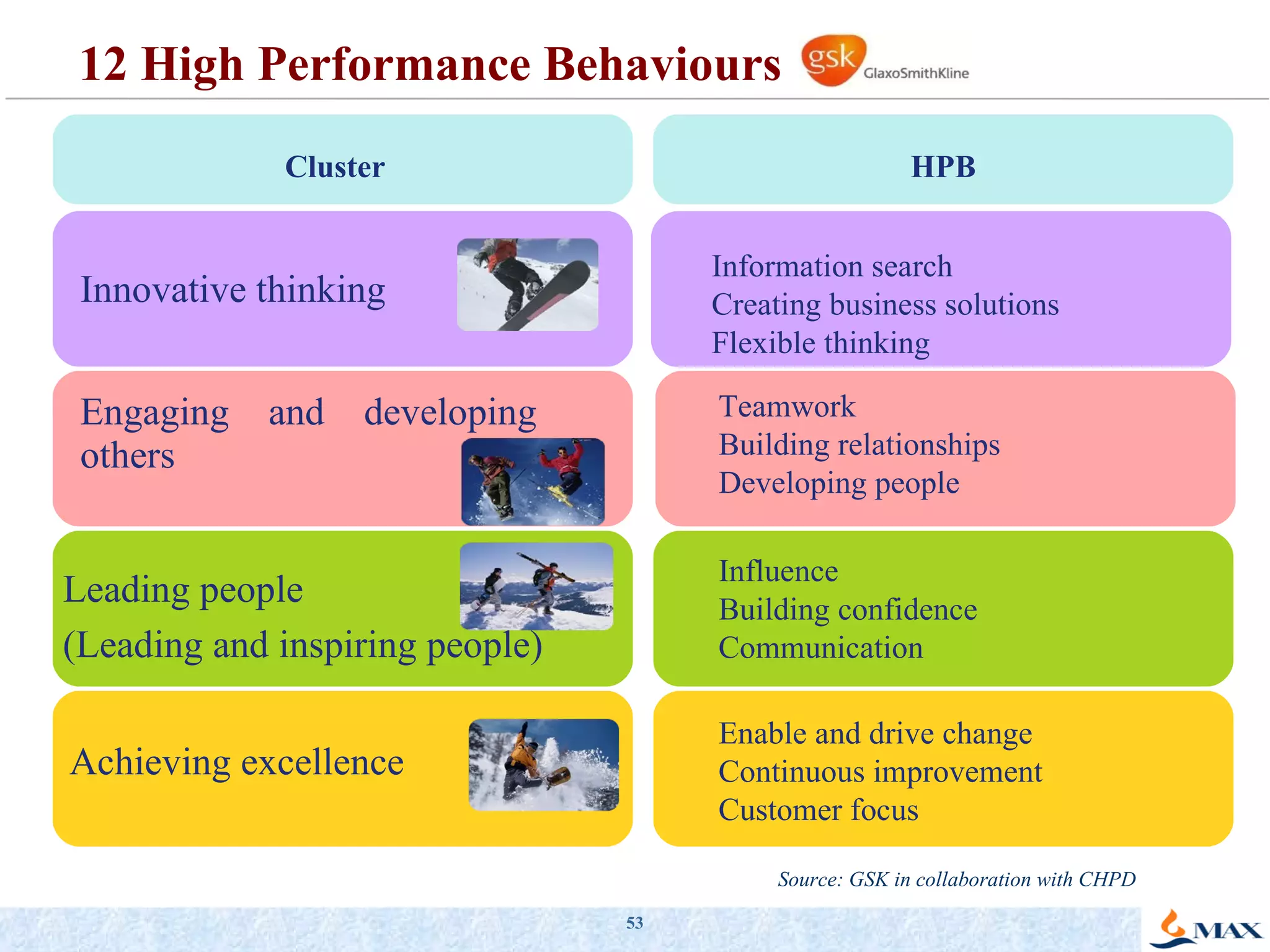
The document summarizes a presentation on strategic thinking and alignment. It discusses analyzing the current business landscape using SWOT analysis and translating strategy into operational terms using a balanced scorecard framework. It also provides examples of how two companies, Max India and GlaxoSmithKline, have aligned their human resources strategies to their business strategies.