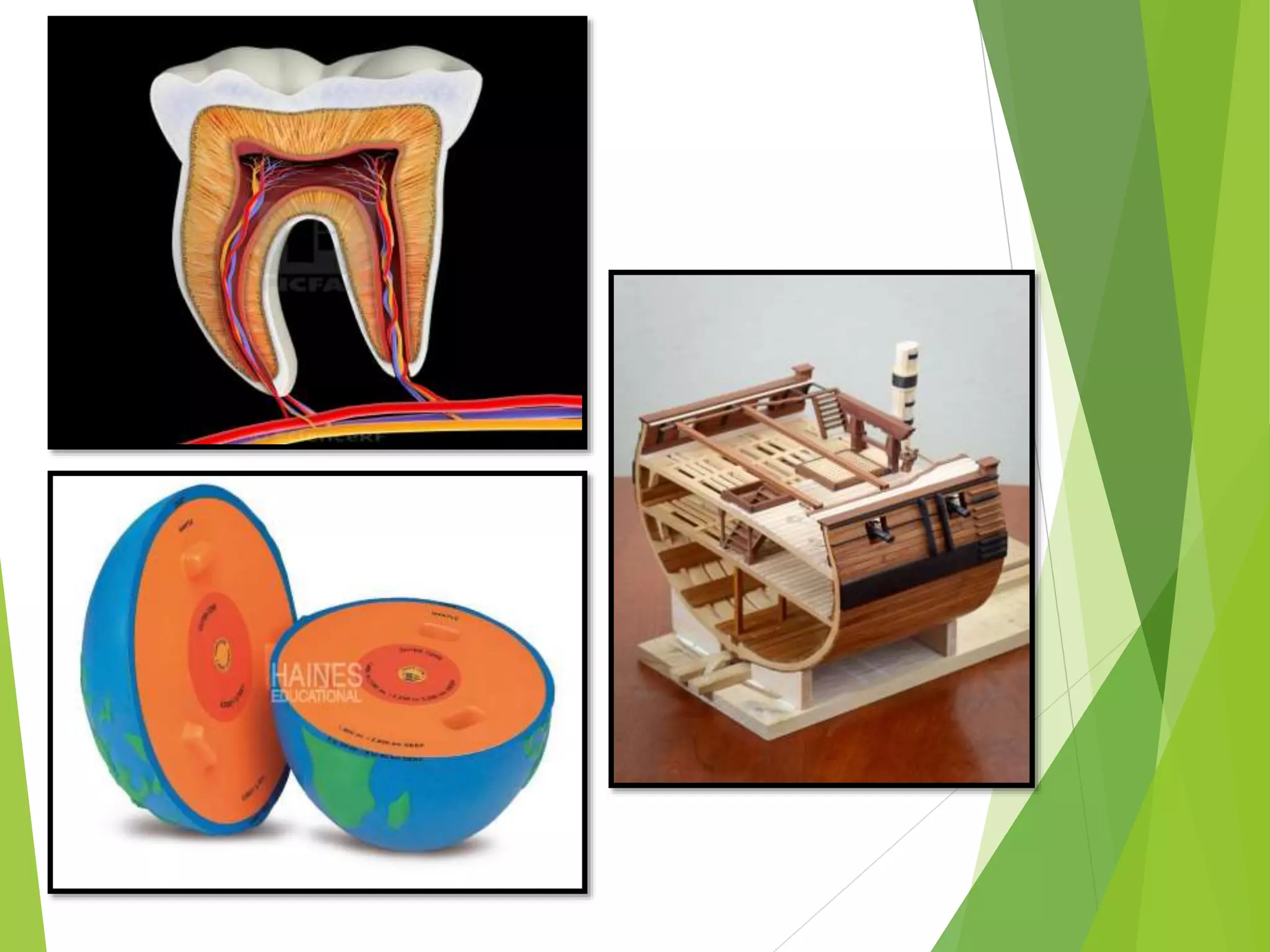
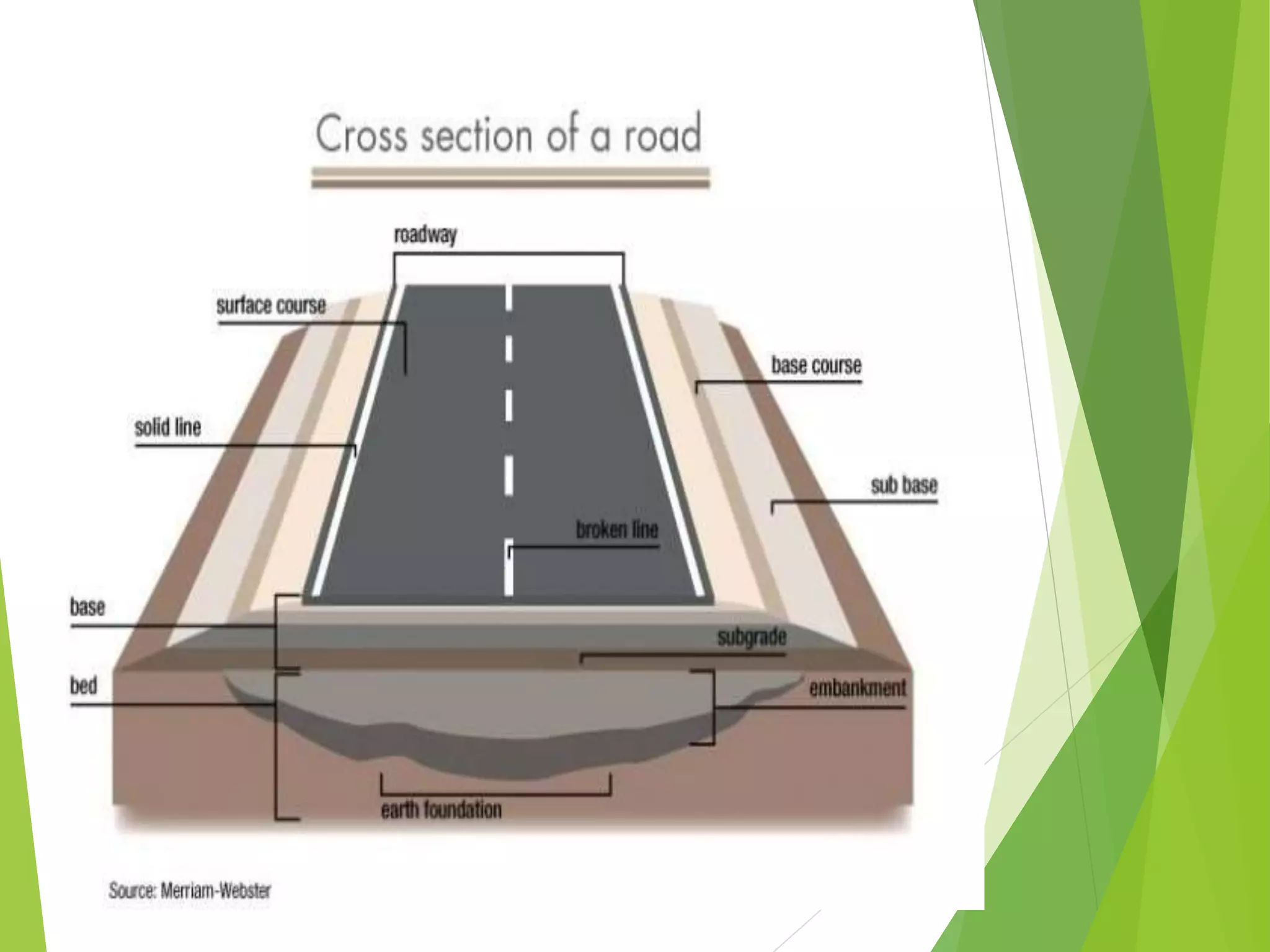
The document defines models as recognizable 3D representations of real or abstract things or systems. Models can be used to enlarge small objects or reduce large objects so they can be observed. They can also demonstrate interior structures or movements clearly. There are several types of models: solid models replicate externals; cross-sectional models show internals; working models demonstrate functioning; and constructional models show how parts assemble. Models enhance learning by engaging multiple senses, saving time and effort, and helping recall. They make complex ideas simpler and applications clearer.