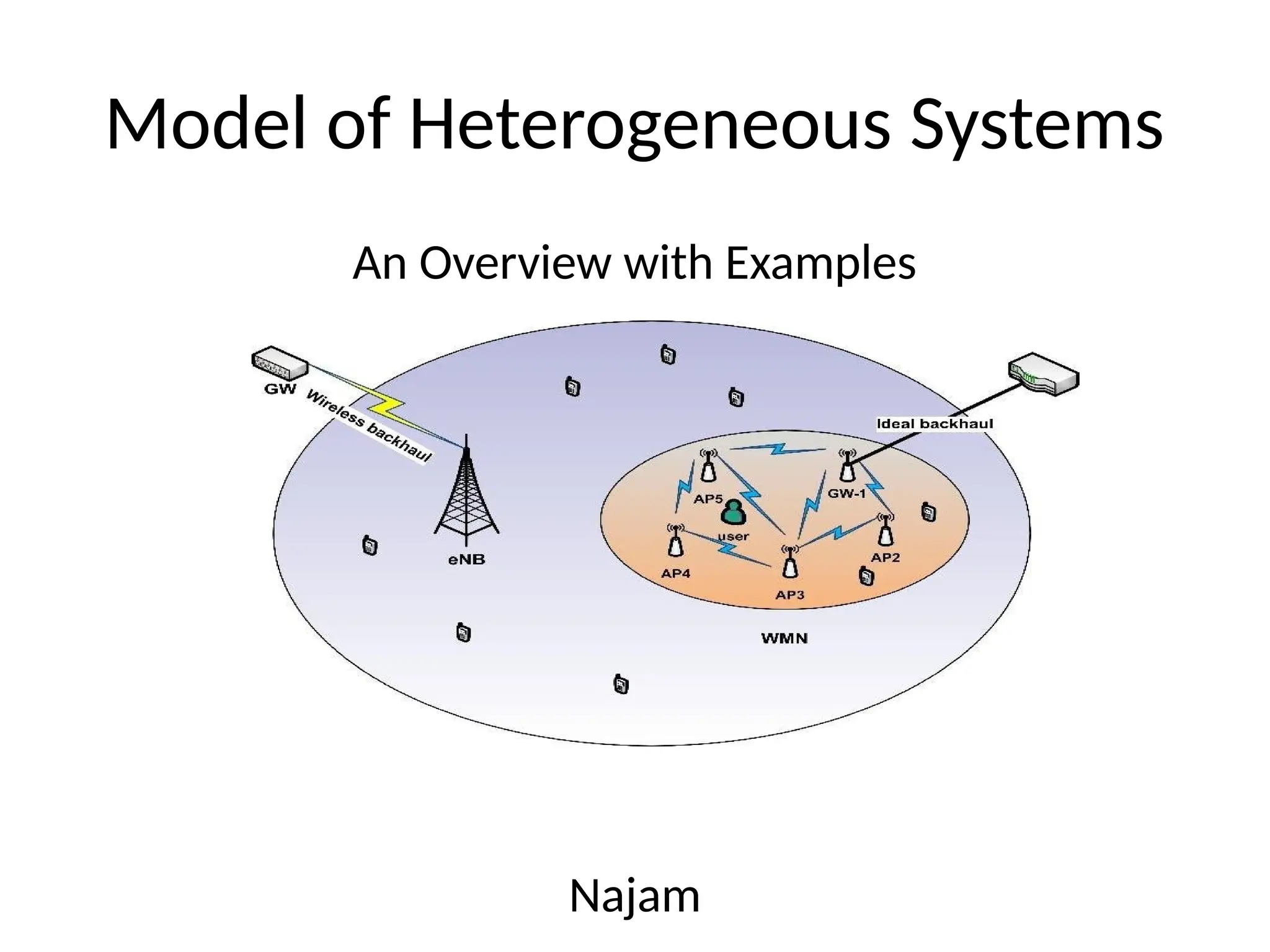
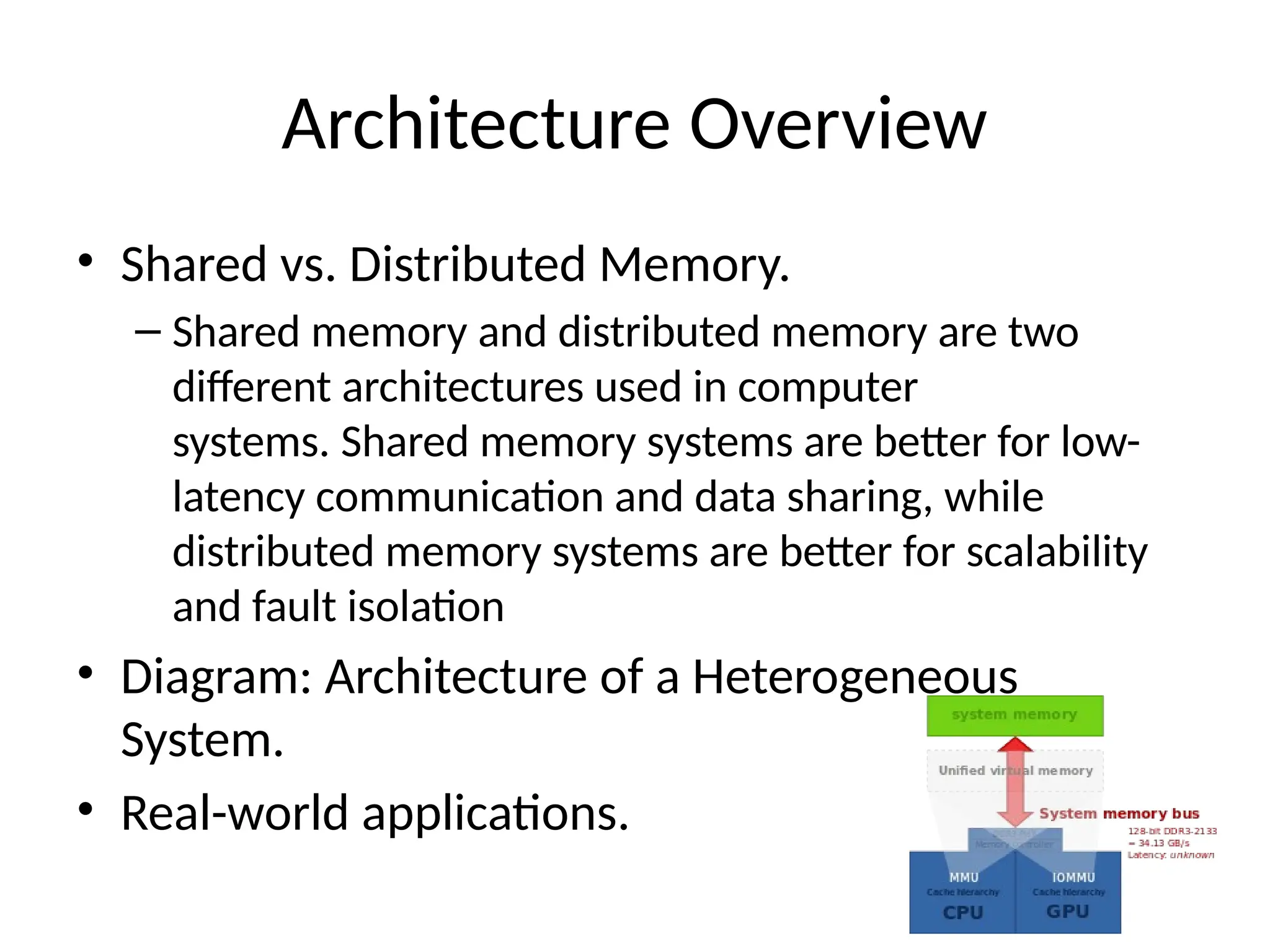
Heterogeneous systems consist of diverse components like CPUs, GPUs, and FPGAs, which enhance performance and energy efficiency in modern computing. They play a crucial role in sectors such as AI, IoT, and big data, leveraging advantages from different architectures for efficient data processing. Challenges include compatibility issues and programming complexity, but solutions exist to optimize performance across these varied systems.