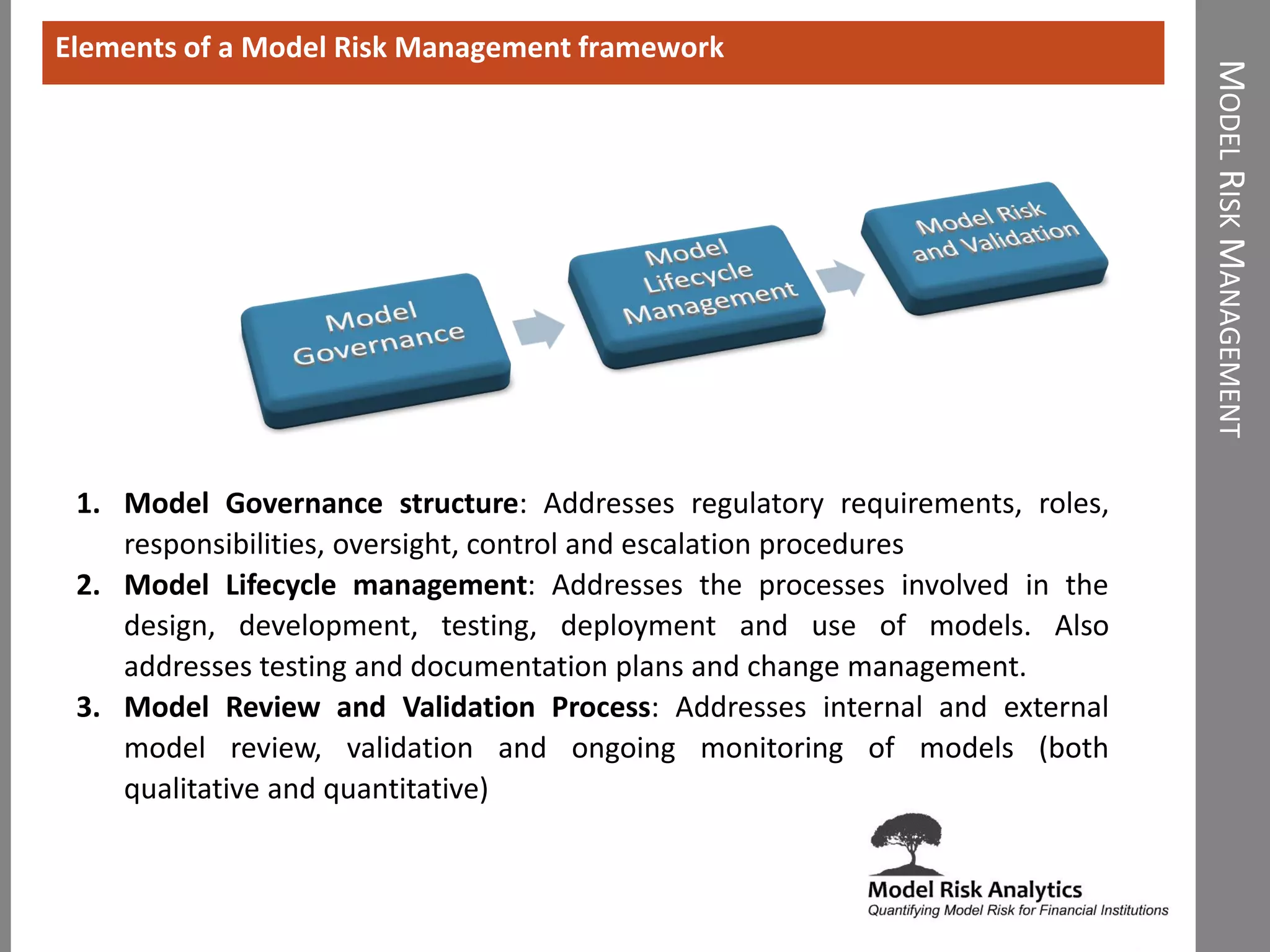
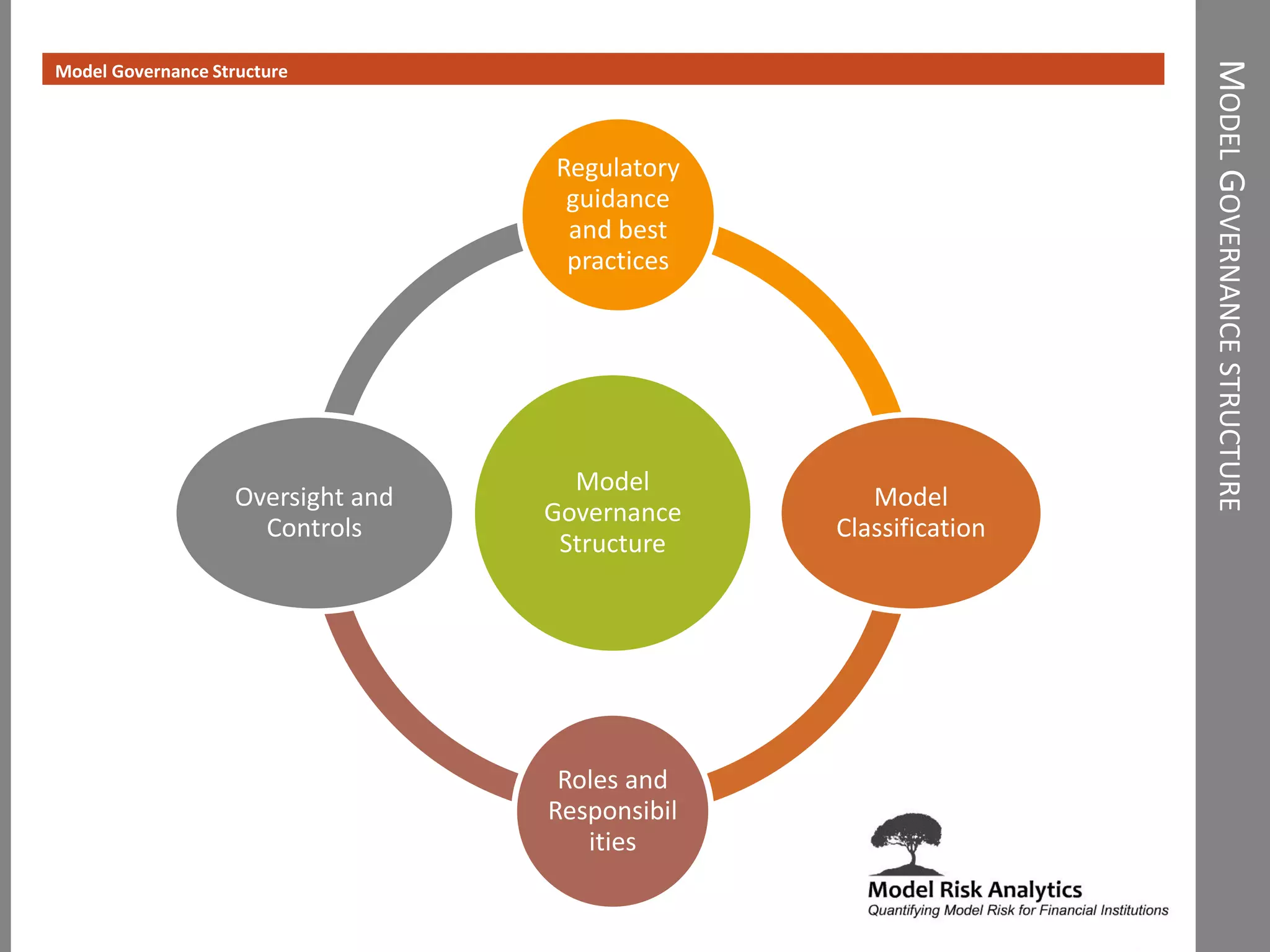
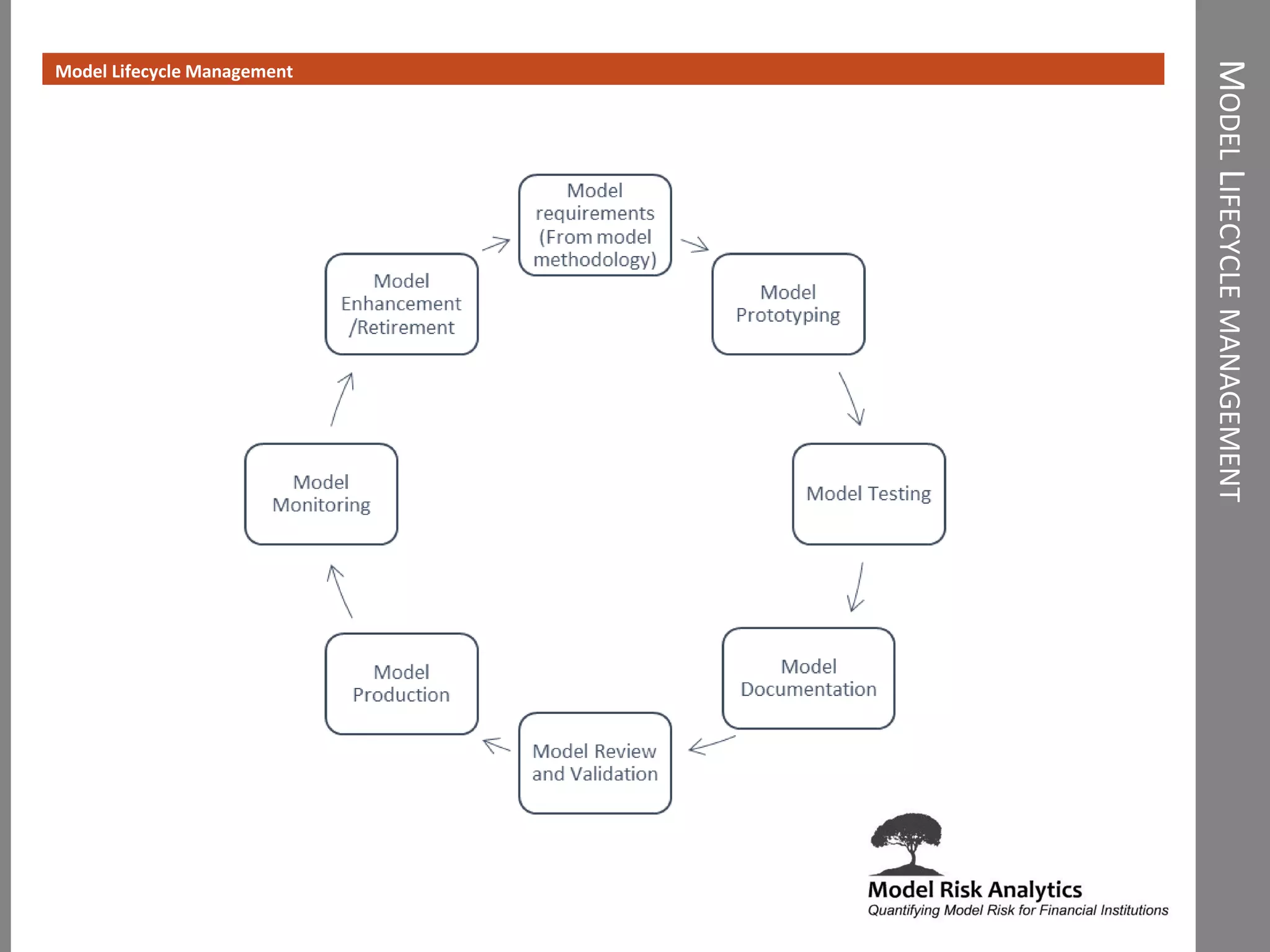
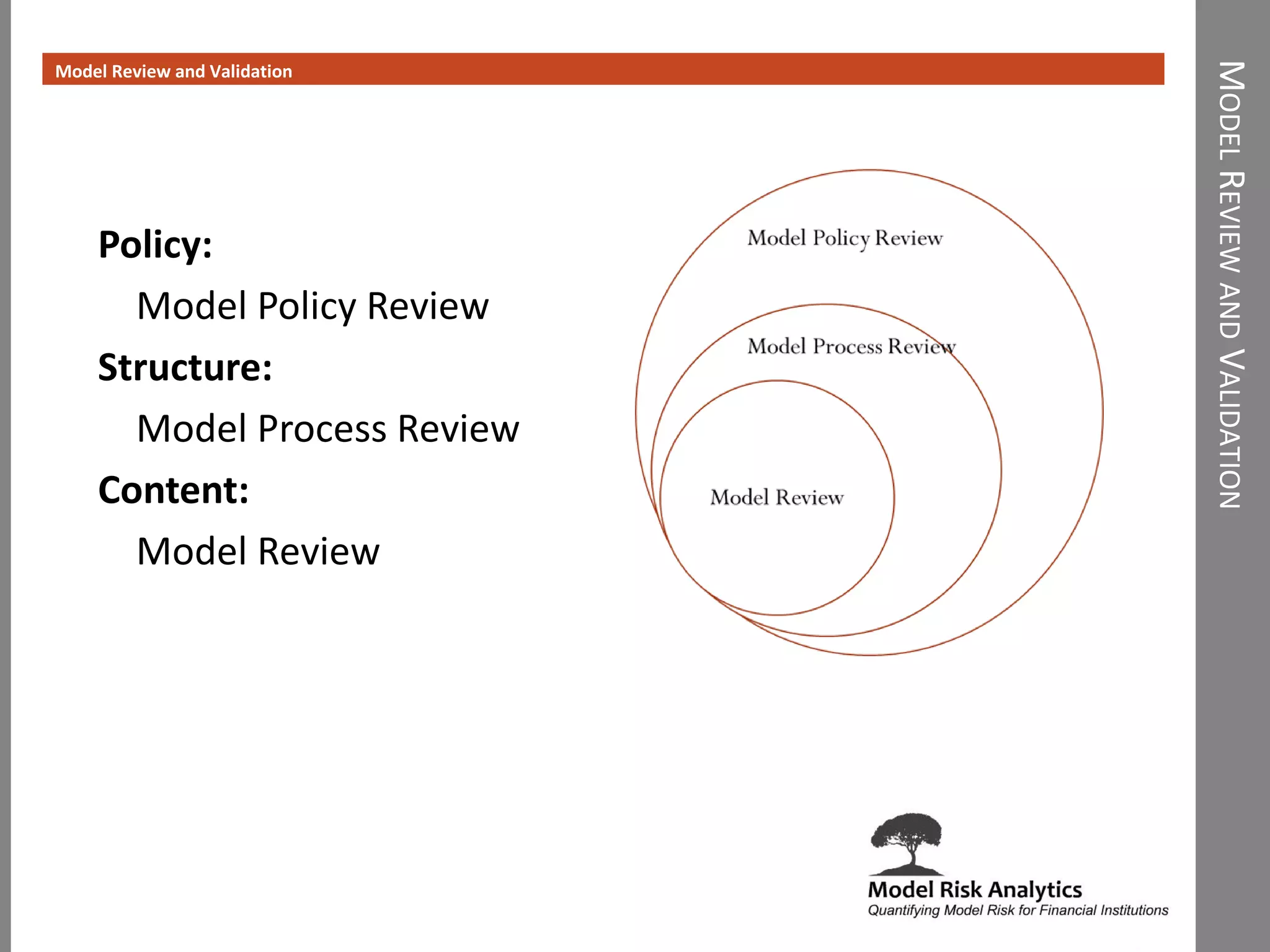
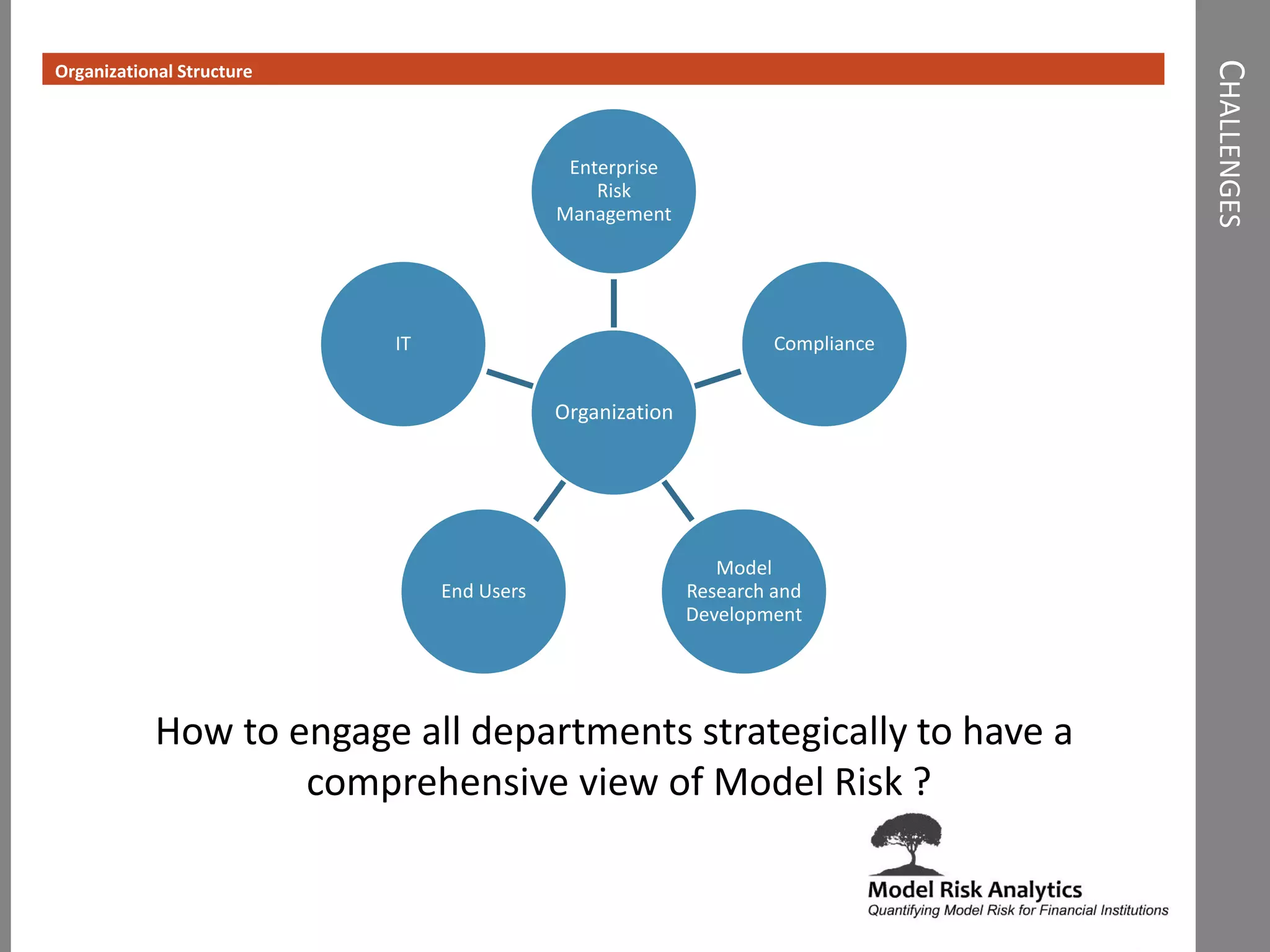
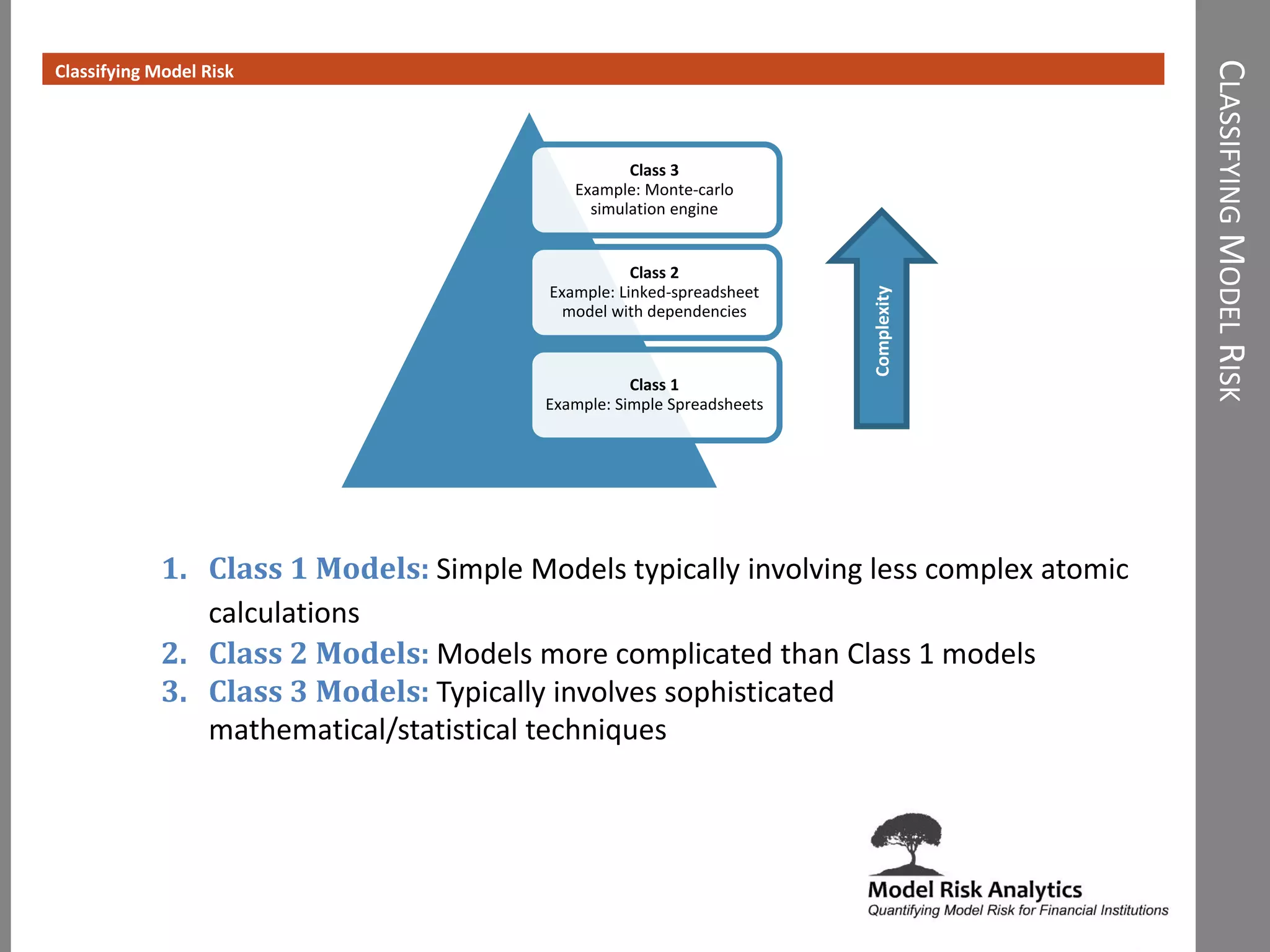
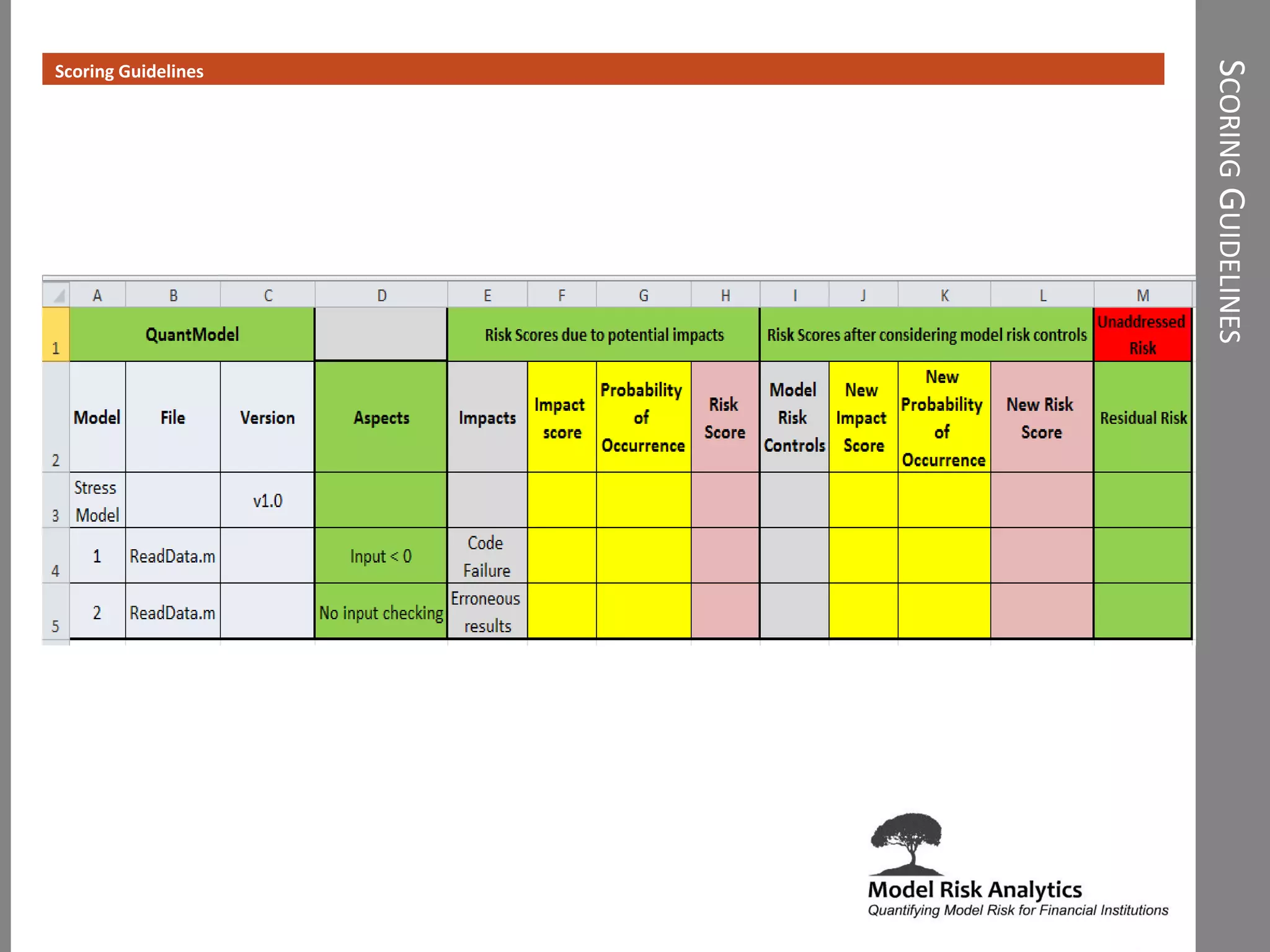
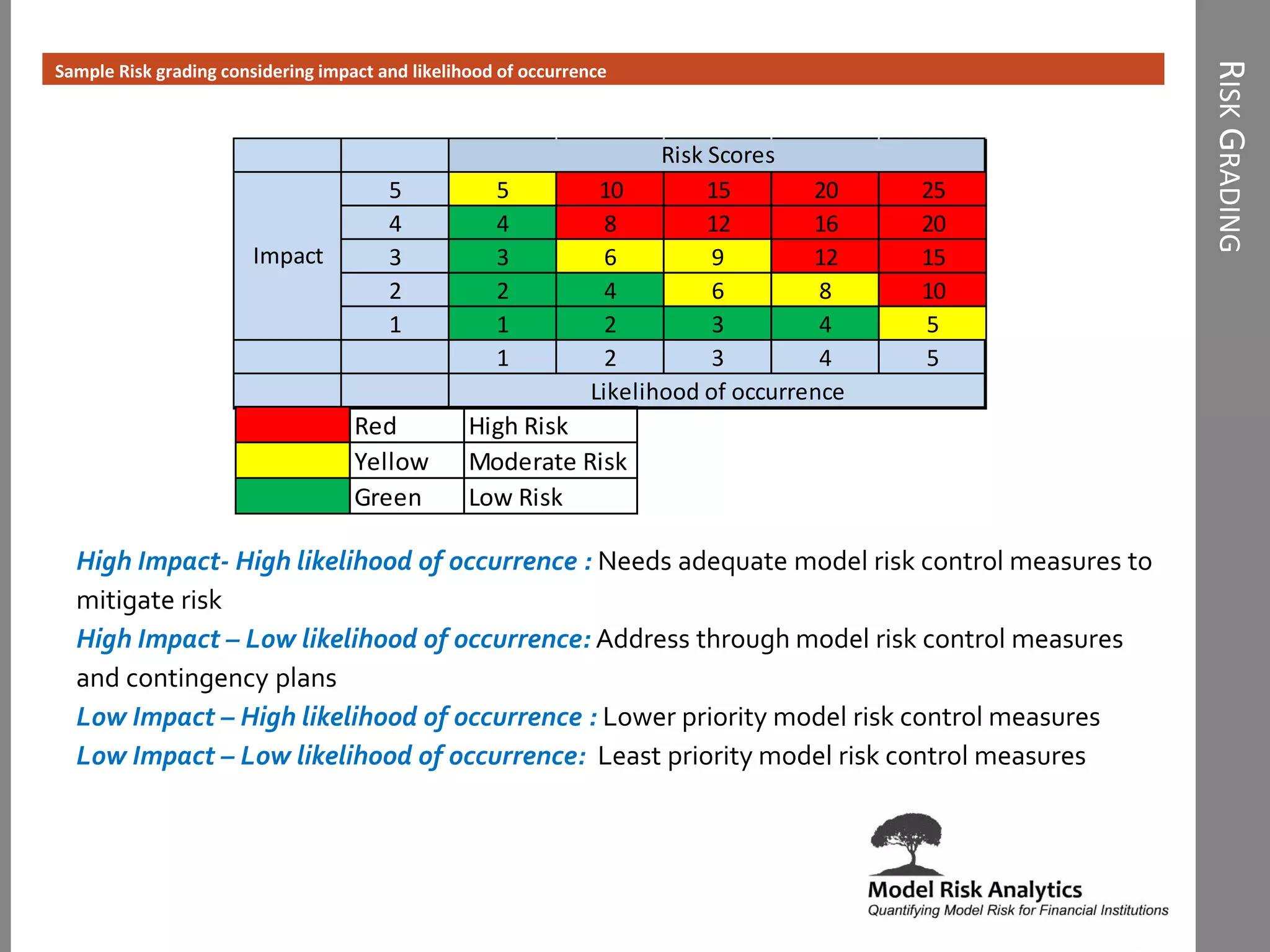
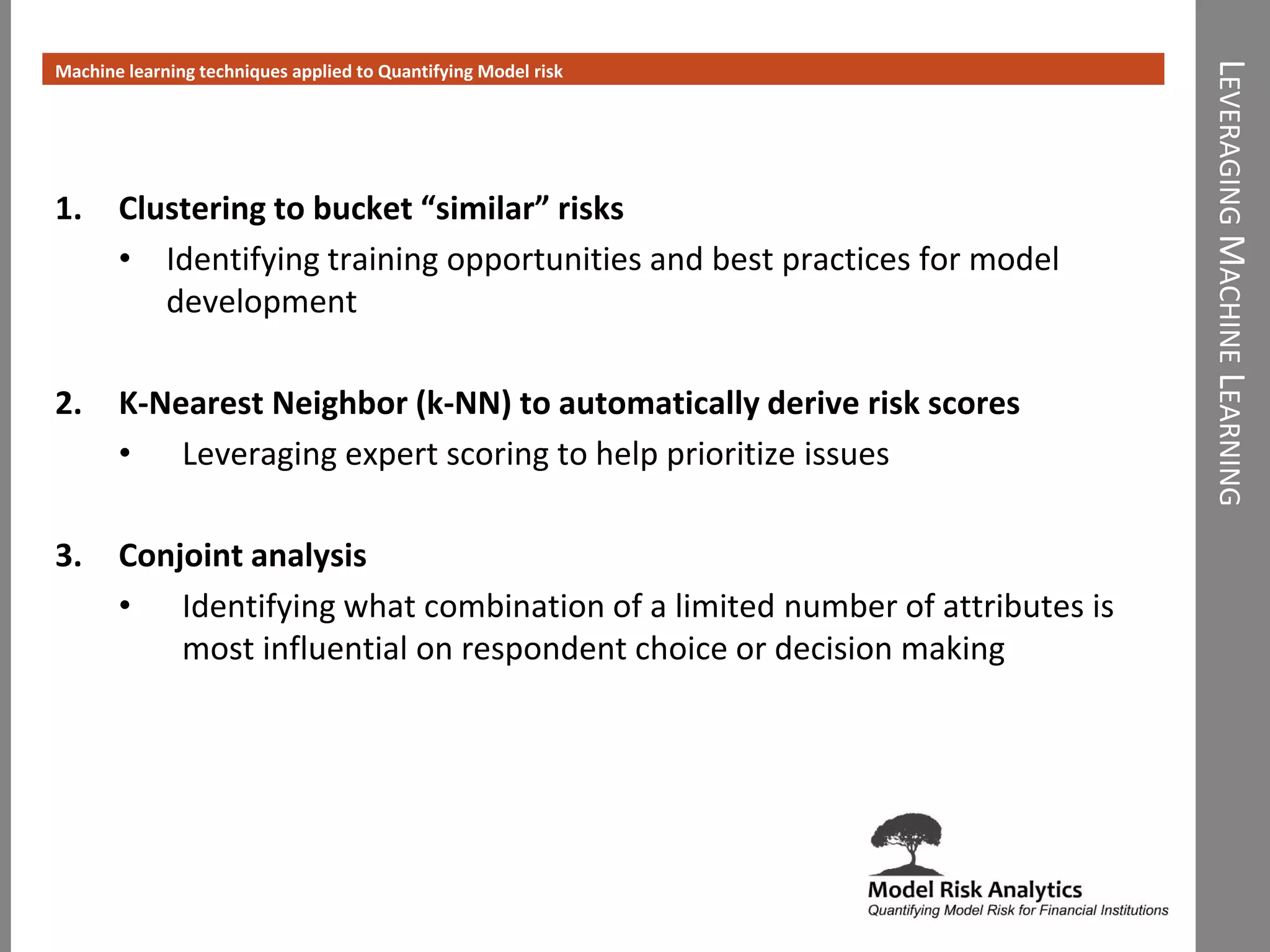
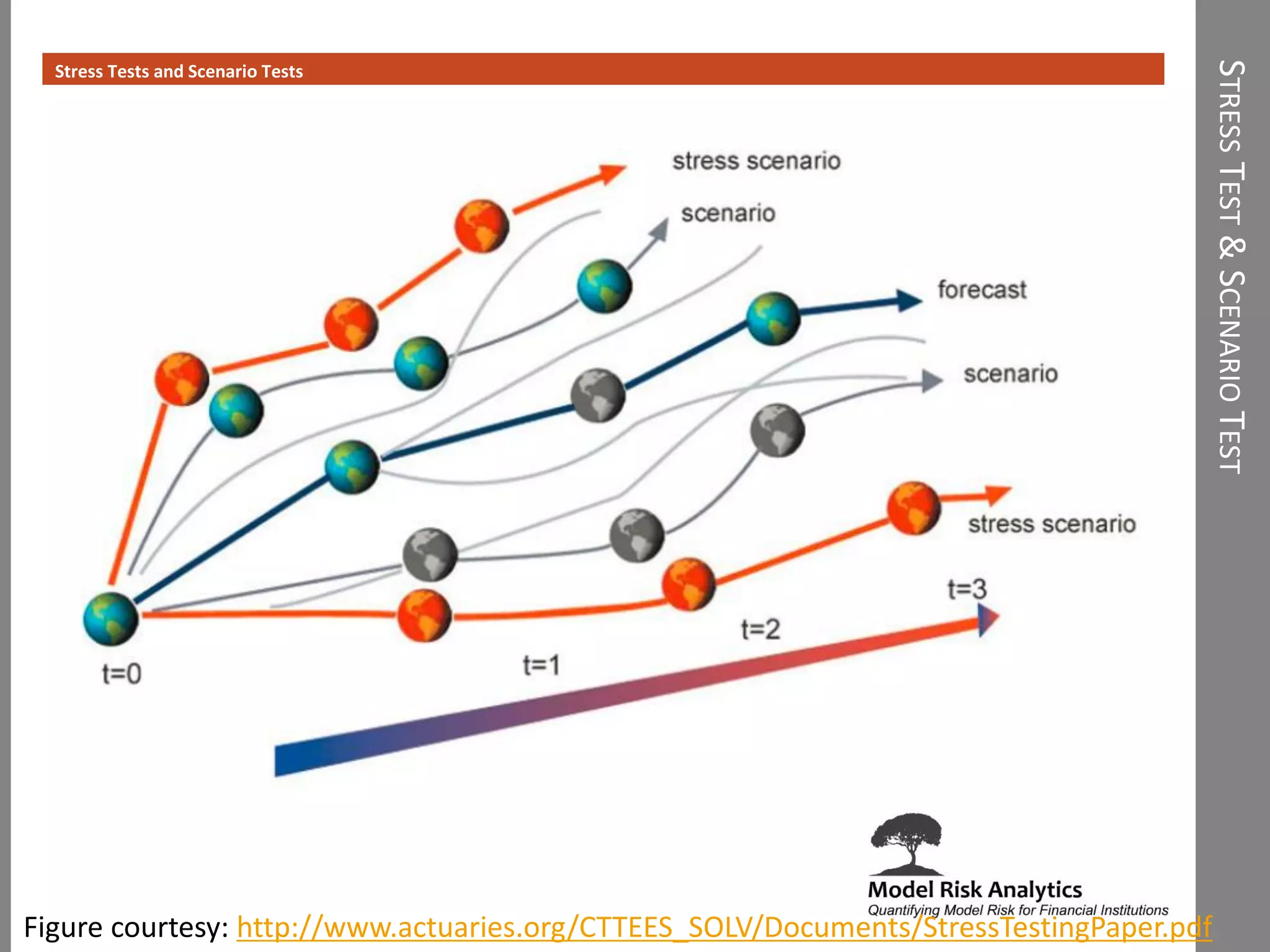
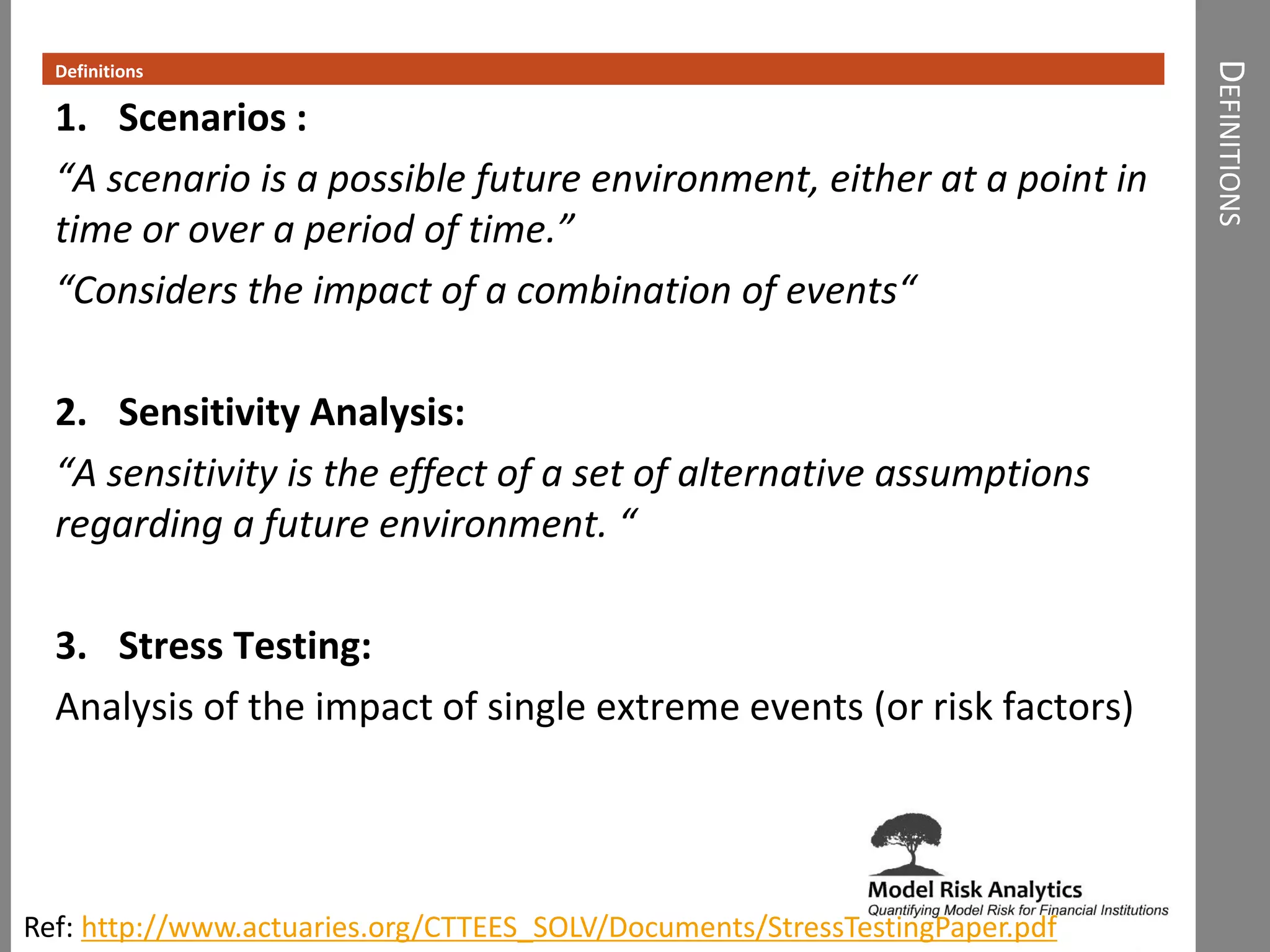
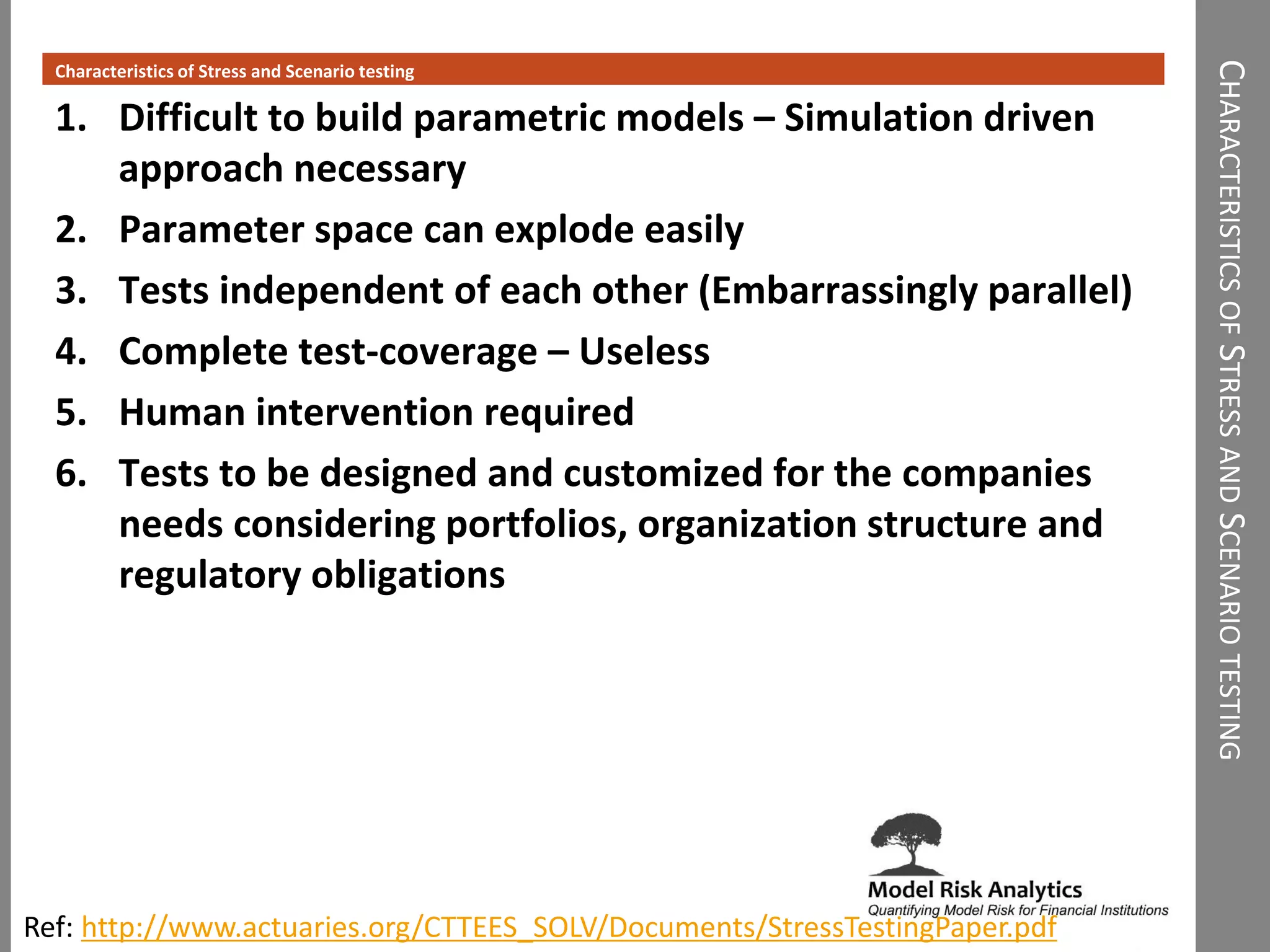
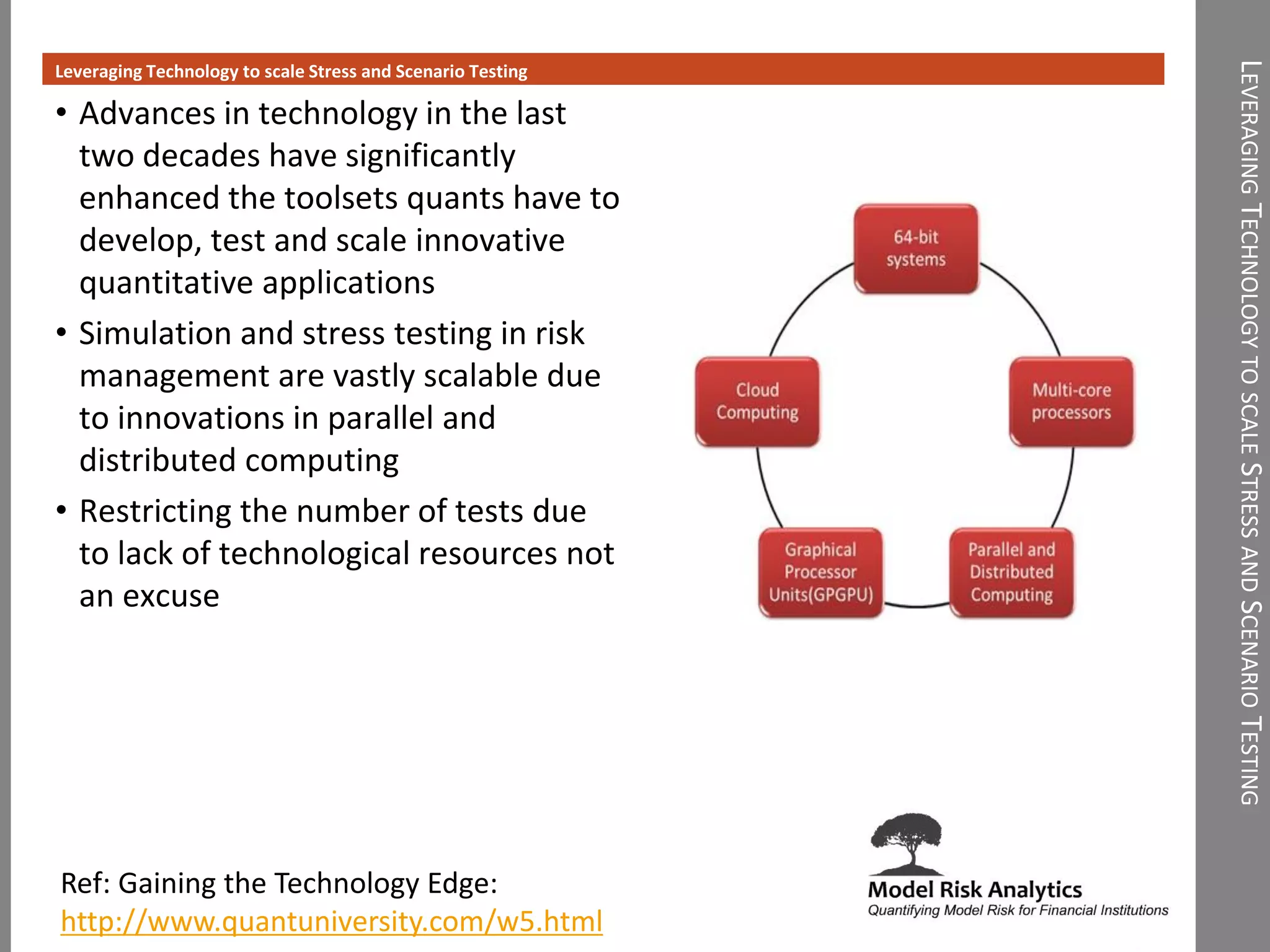
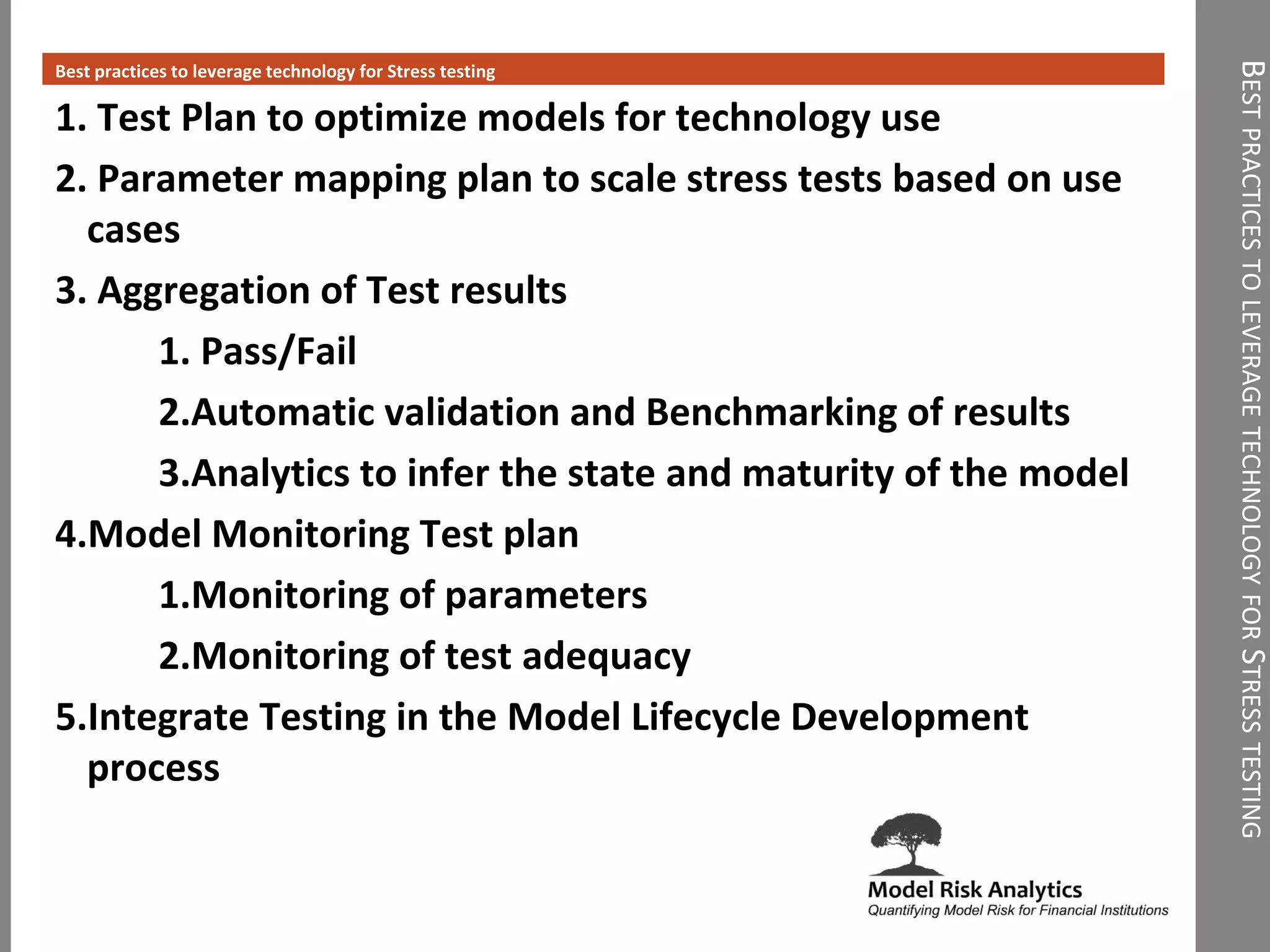
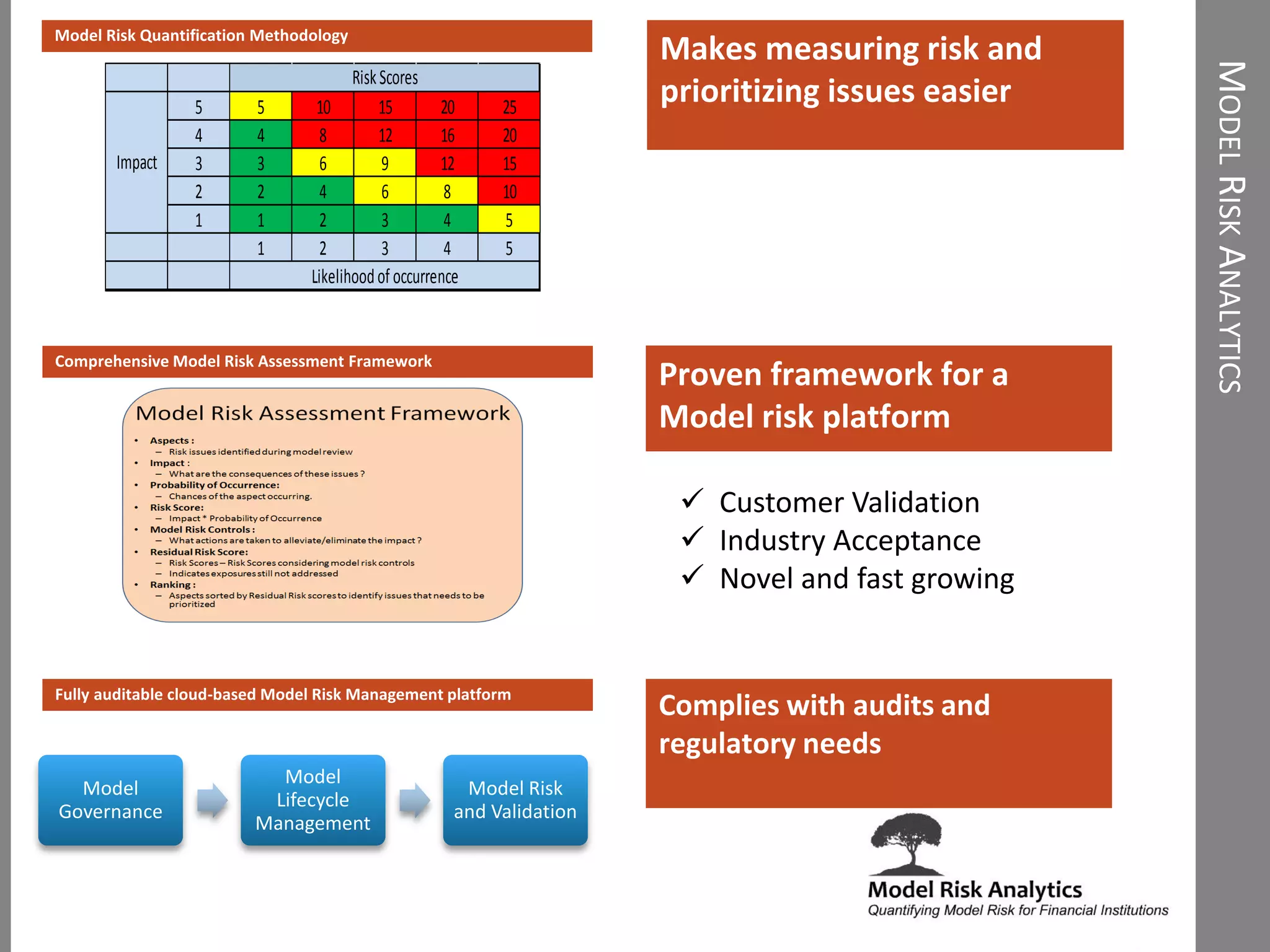
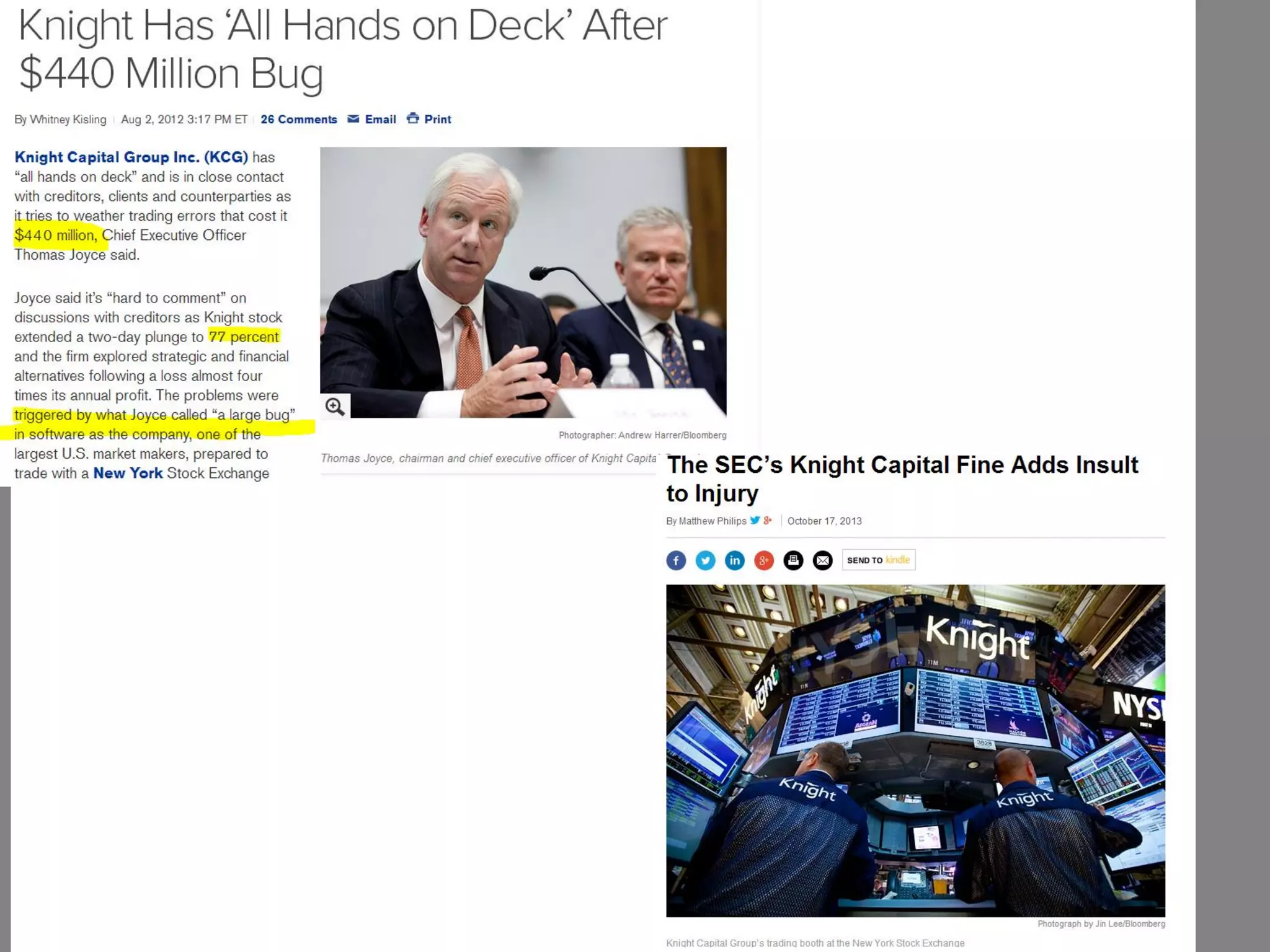
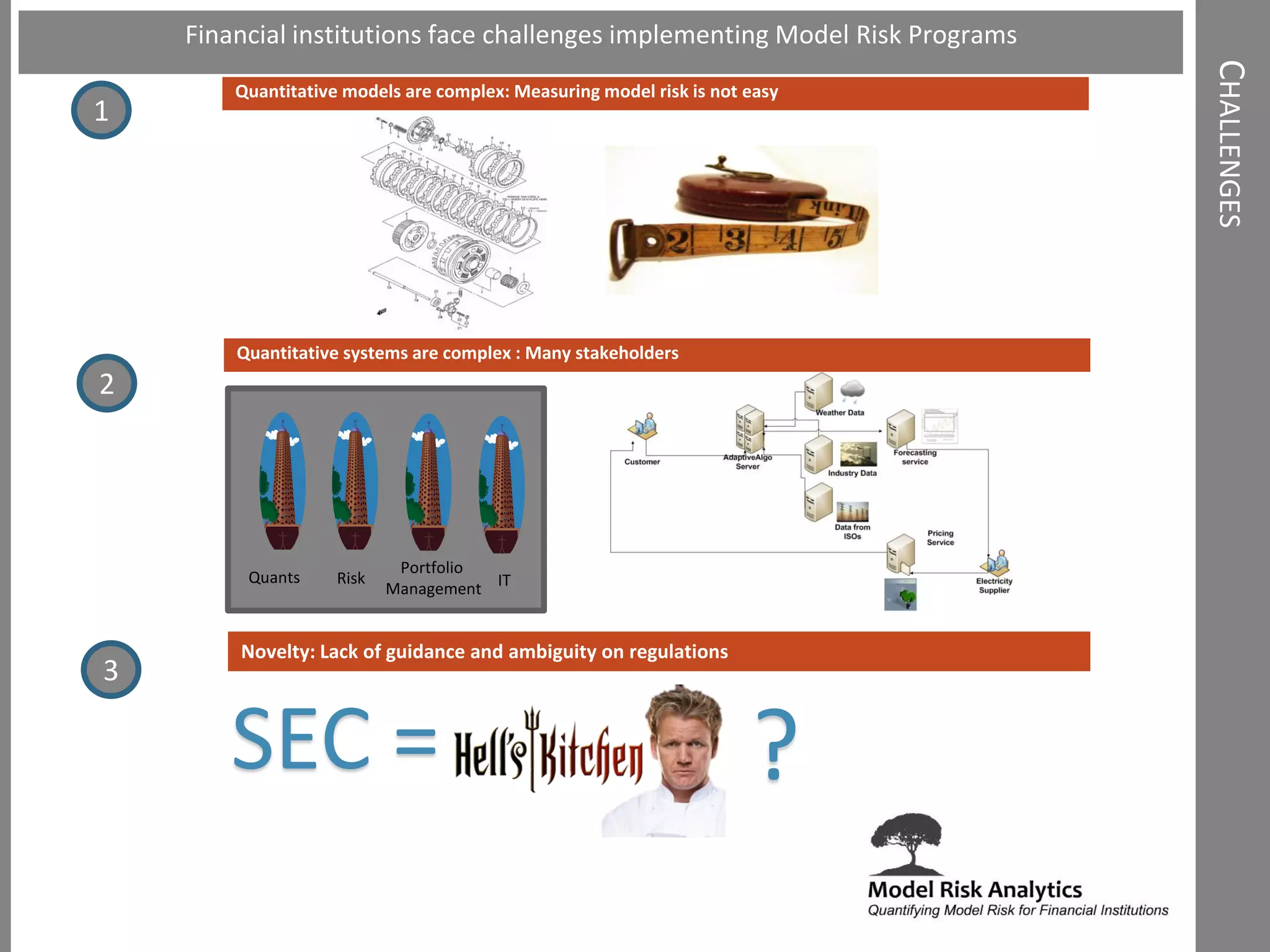
The document presents a framework-driven approach to model risk management in financial institutions, highlighting the importance of effective model governance, lifecycle management, and validation processes. It discusses the challenges faced in quantifying and managing model risk due to complex quantitative systems and regulatory requirements. Additionally, it emphasizes leveraging technology and analytics for stress testing and scenario analysis to enhance model risk management practices.





![MODELRISK
“Model refers to a quantitative method, system, or
approach that applies statistical, economic, financial,
or mathematical theories, techniques, and
assumptions to process input data into quantitative
estimates” [1]
Ref:
[1] . Supervisory Letter SR 11-7 on guidance on Model Risk
Model Risk Defined
Input
Assumptions/Data
Processing
component
Output/
Reporting
component](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modelriskanalyticsdataanalyticsfinancialpresentationjuly222014-share-140722181326-phpapp01/75/A-Framework-Driven-Approach-to-Model-Risk-Management-www-dataanalyticsfinancial-com-10-2048.jpg)
![MODELVALIDATION
“Model risk is the potential for adverse
consequences from decisions based on incorrect or
misused model outputs and reports. “ [1]
“Model validation is the set of processes and activities
intended to verify that models are performing as
expected, in line with their design objectives and
business uses. ” [1]
Ref:
[1] . Supervisory Letter SR 11-7 on guidance on Model Risk
Model Risk and Validation Defined](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modelriskanalyticsdataanalyticsfinancialpresentationjuly222014-share-140722181326-phpapp01/75/A-Framework-Driven-Approach-to-Model-Risk-Management-www-dataanalyticsfinancial-com-11-2048.jpg)