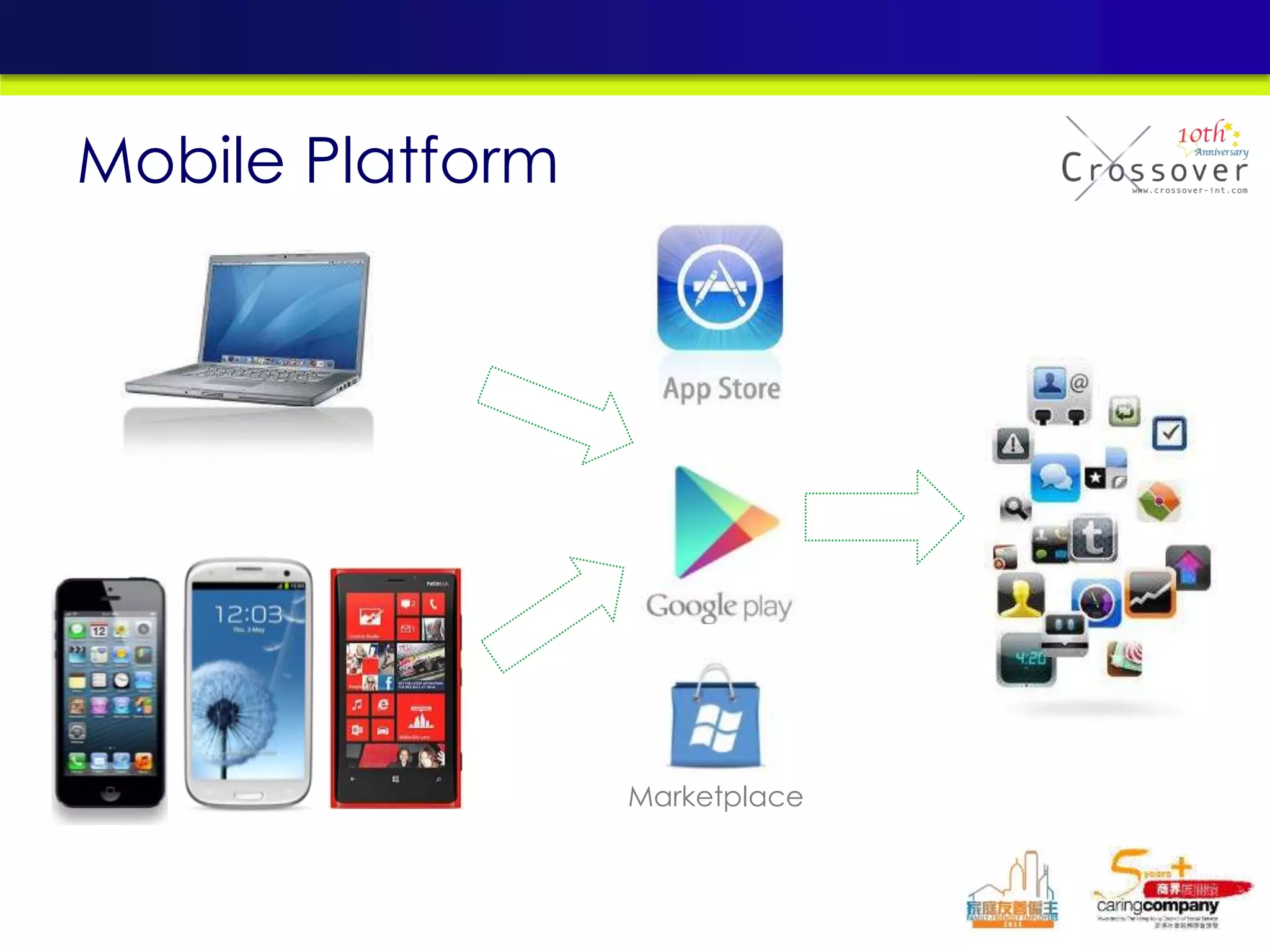
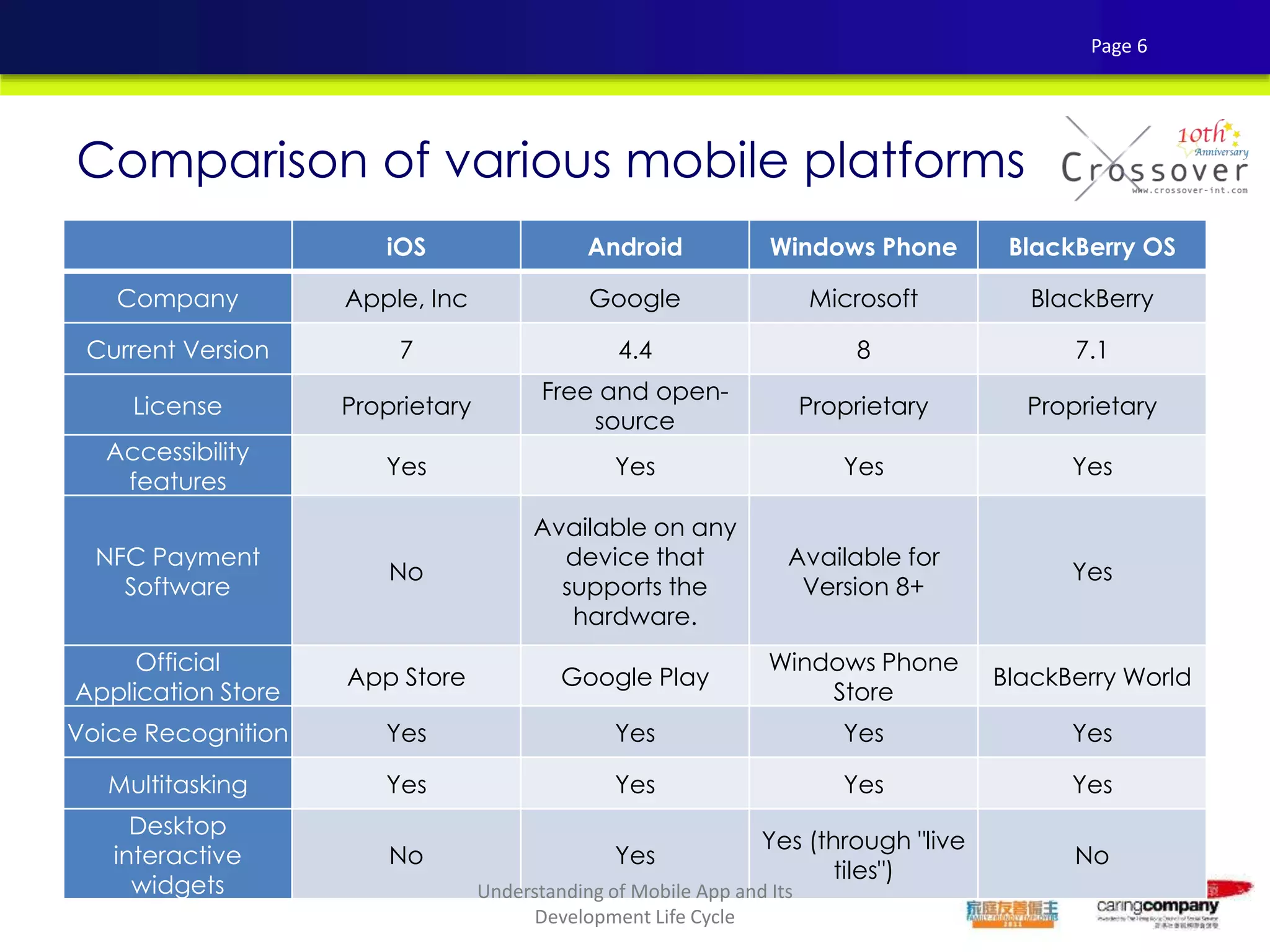
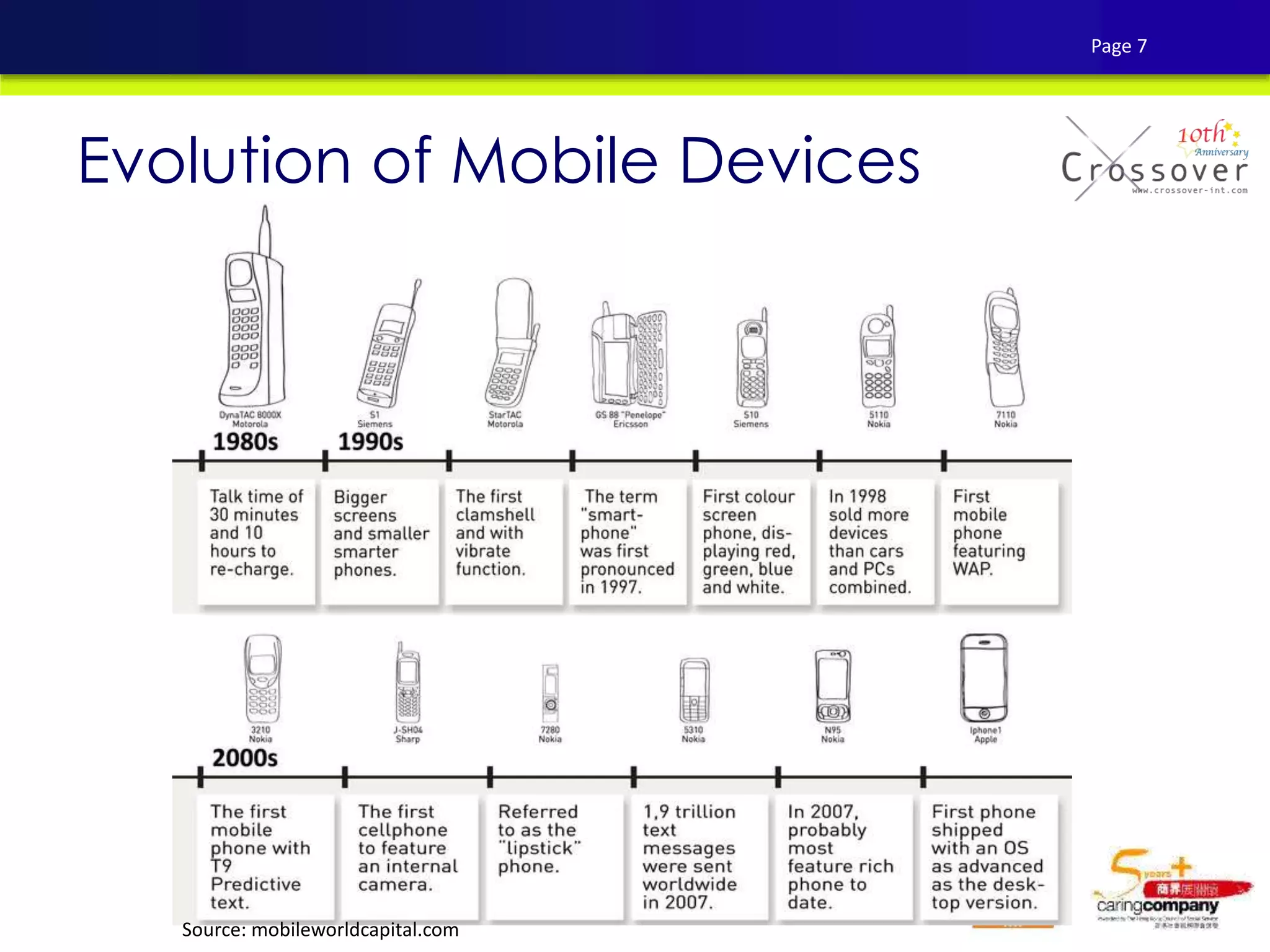
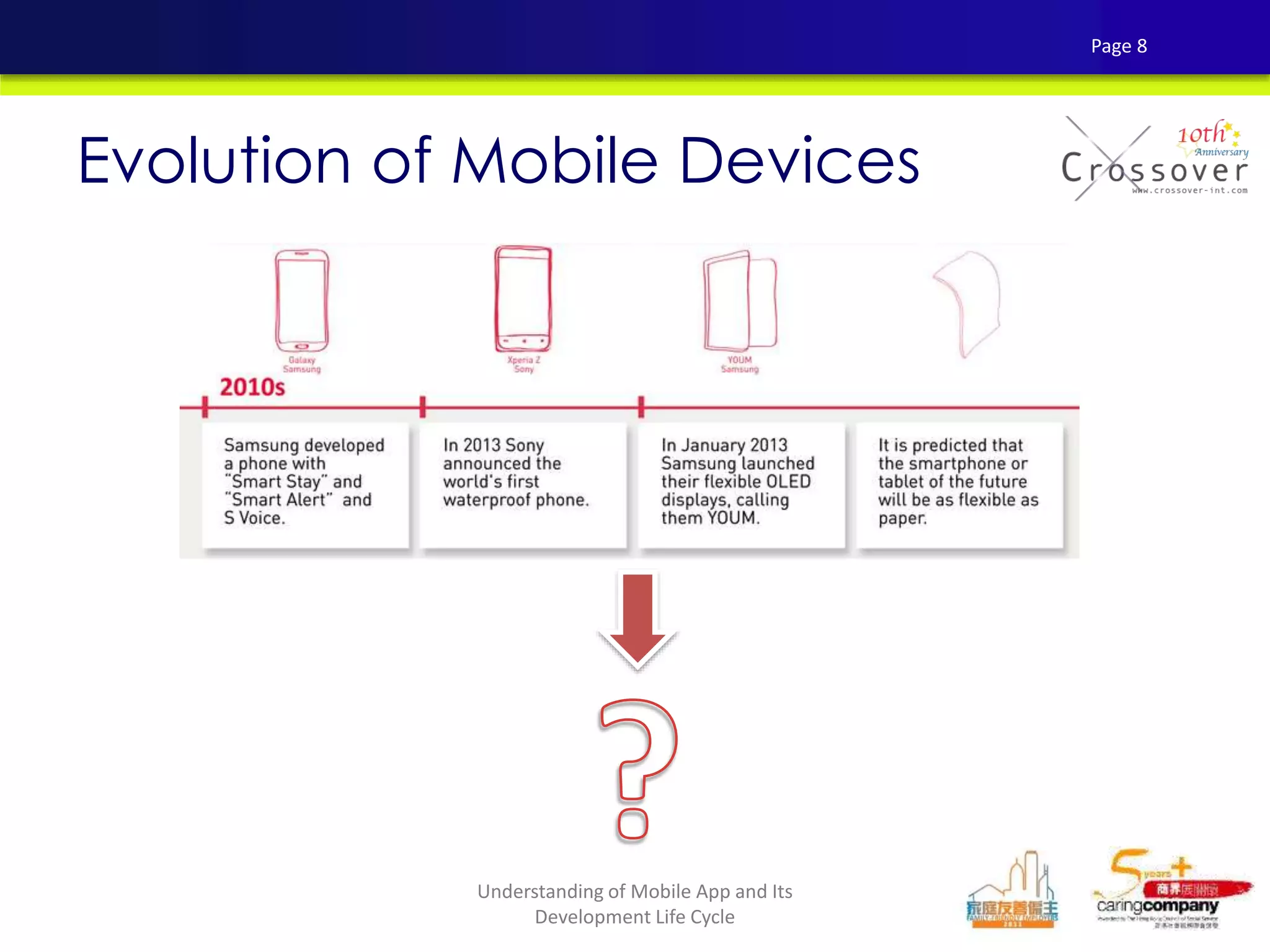
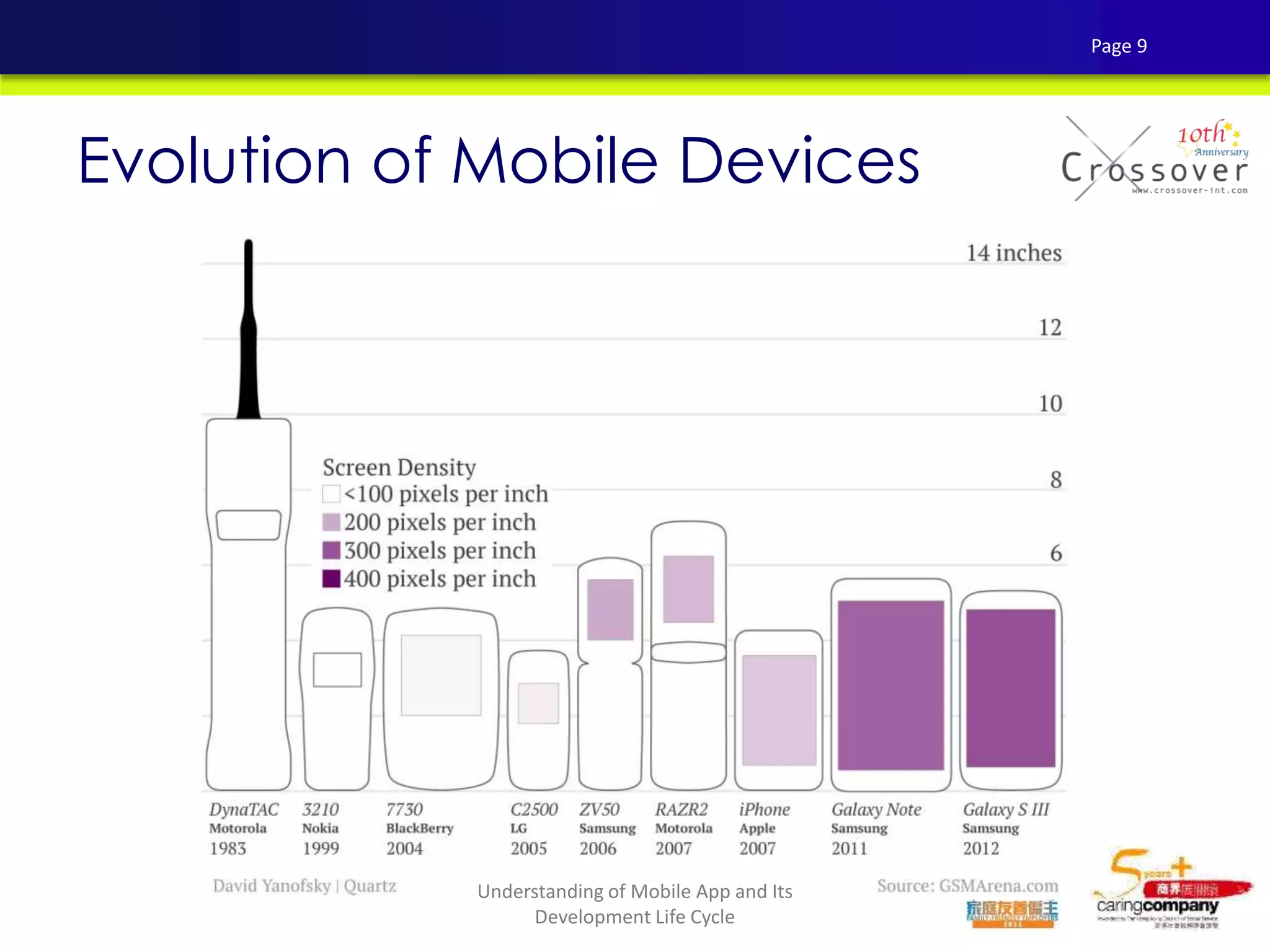
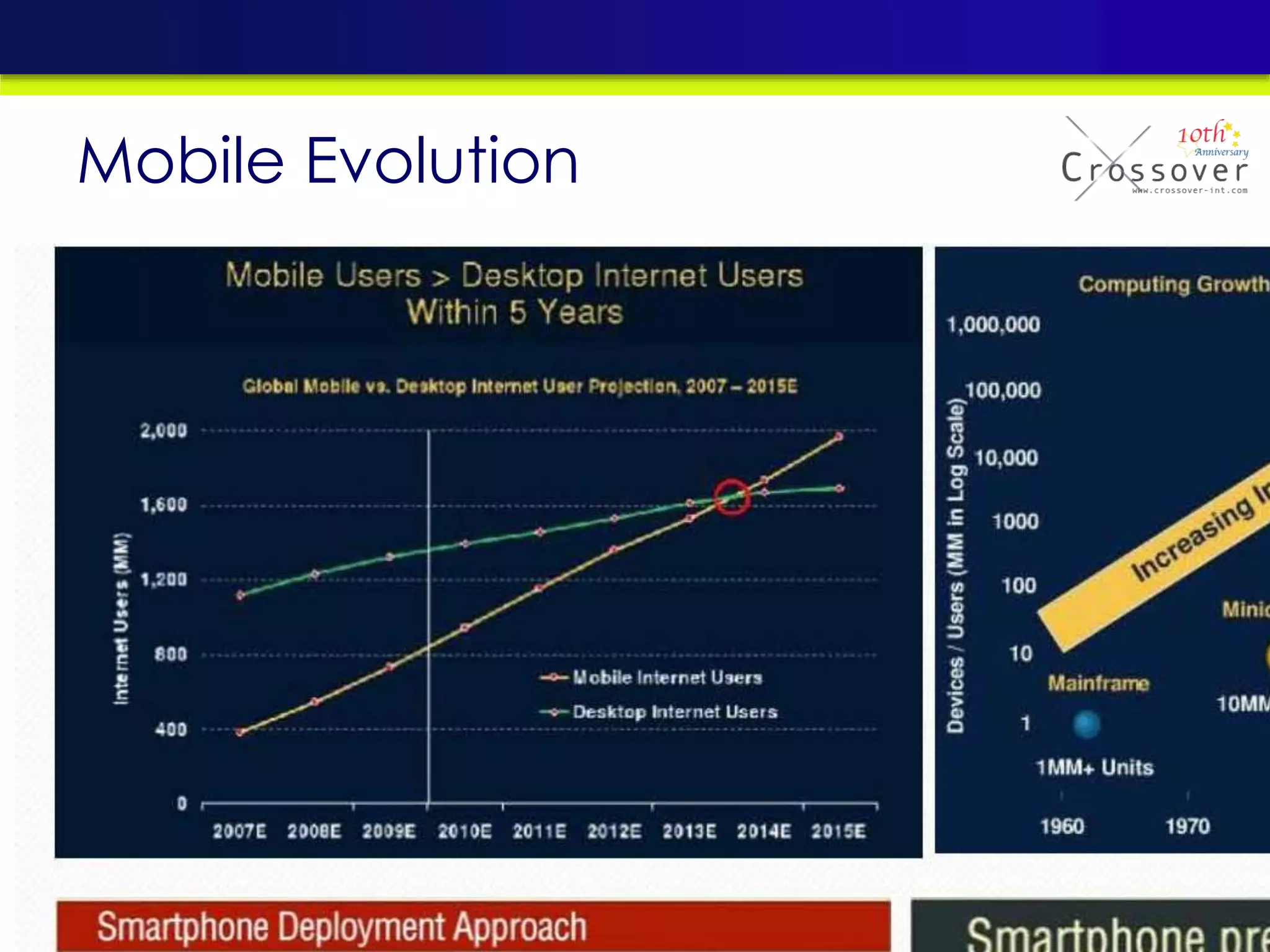
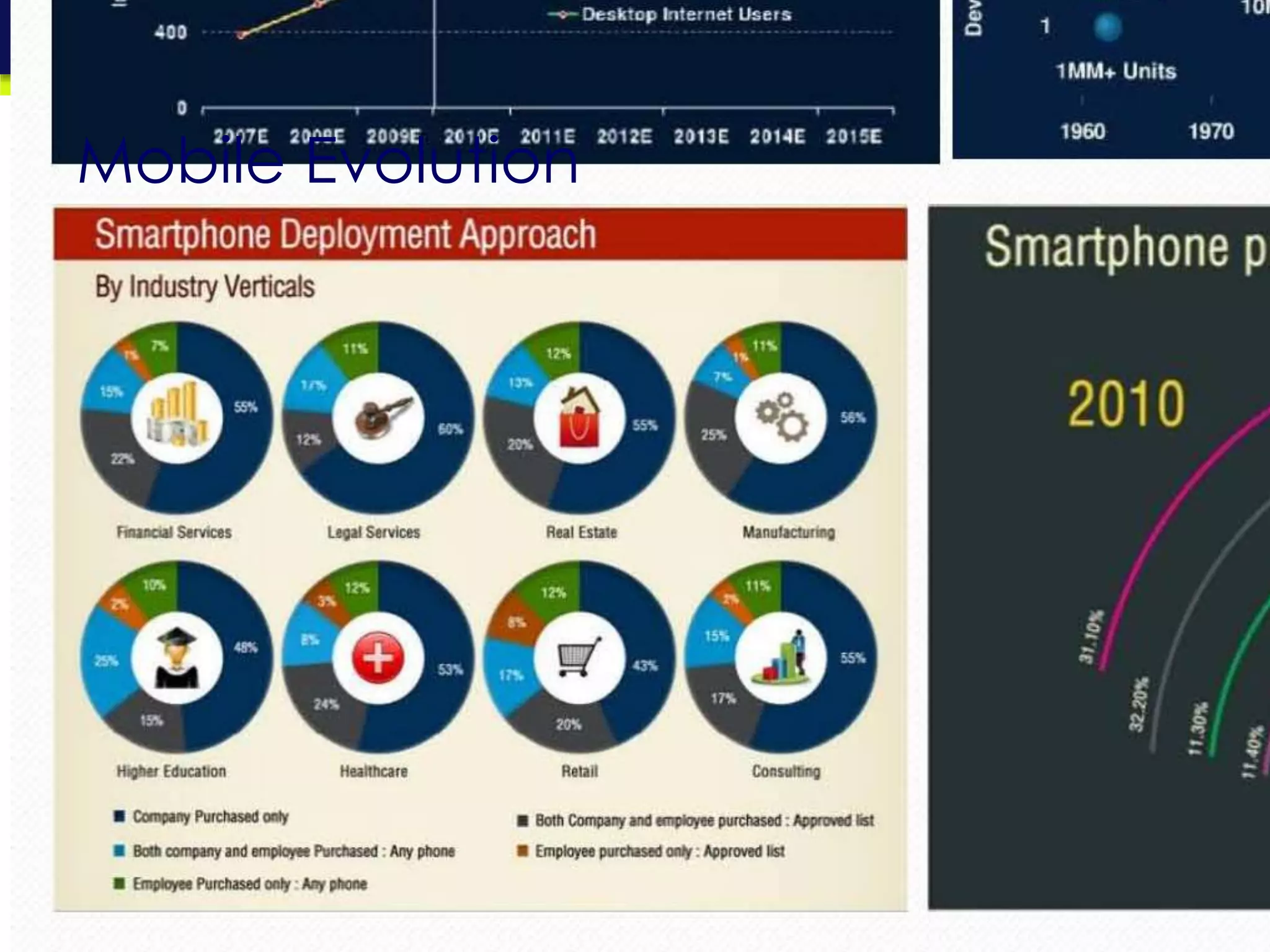
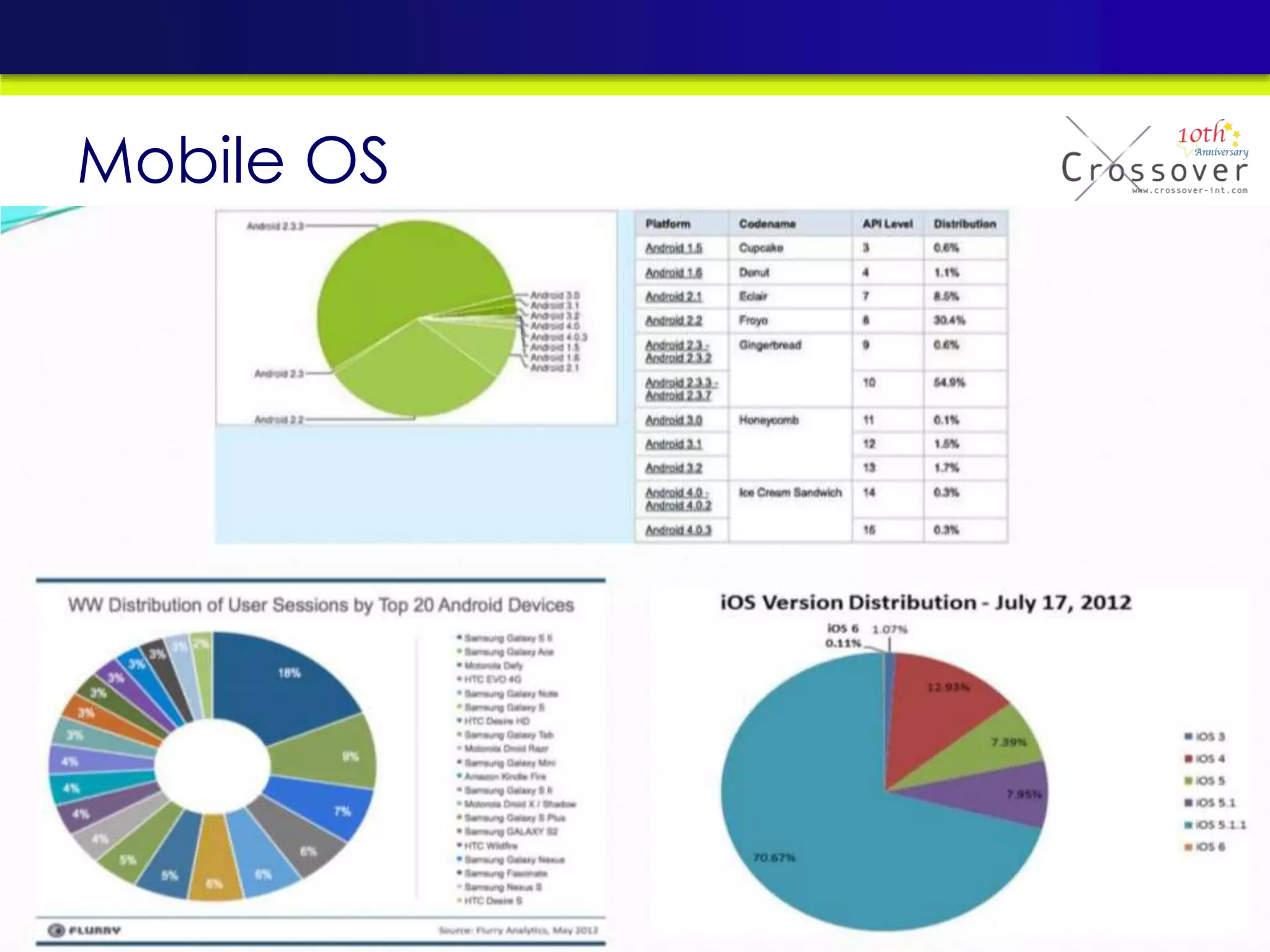
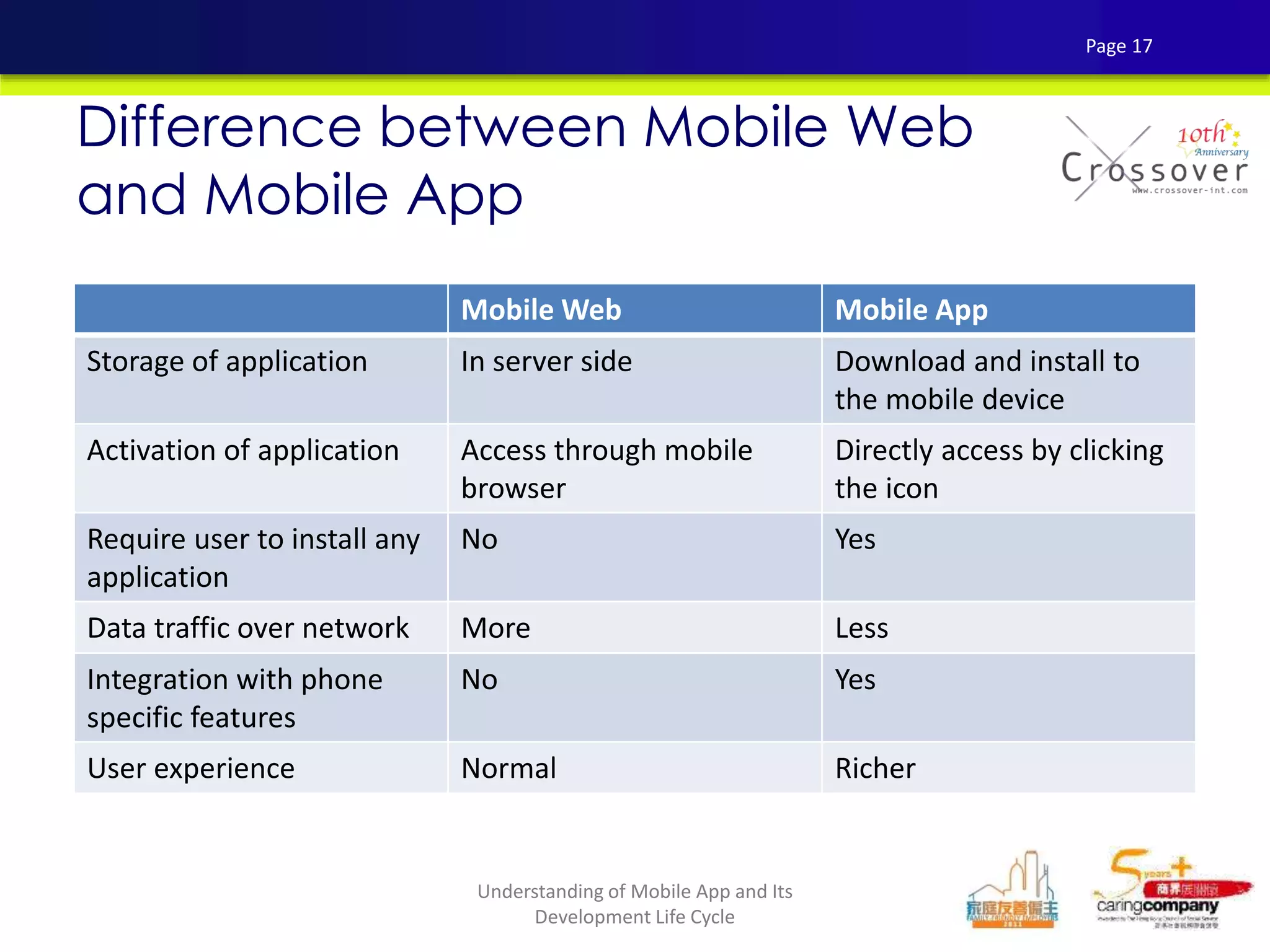
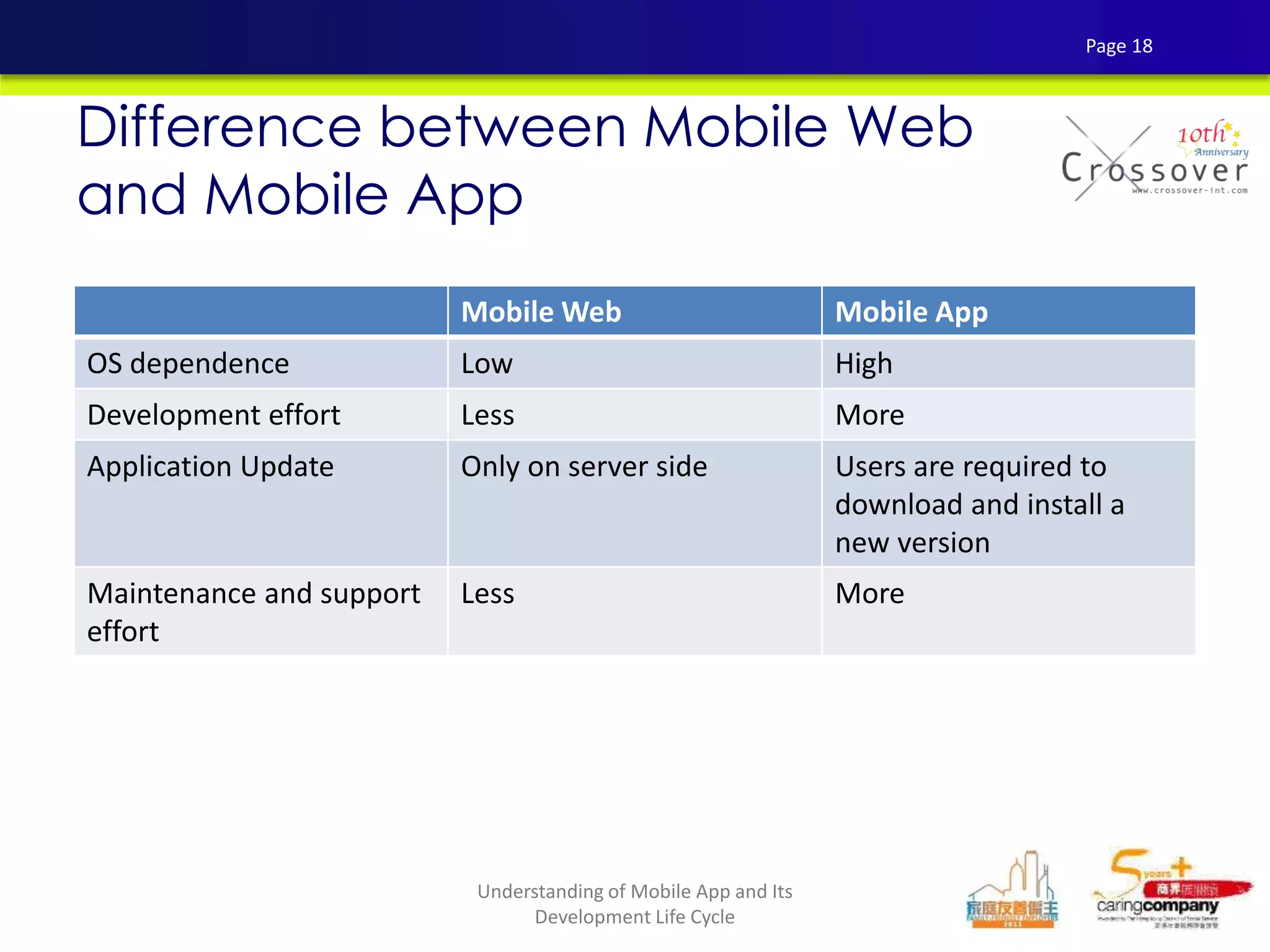
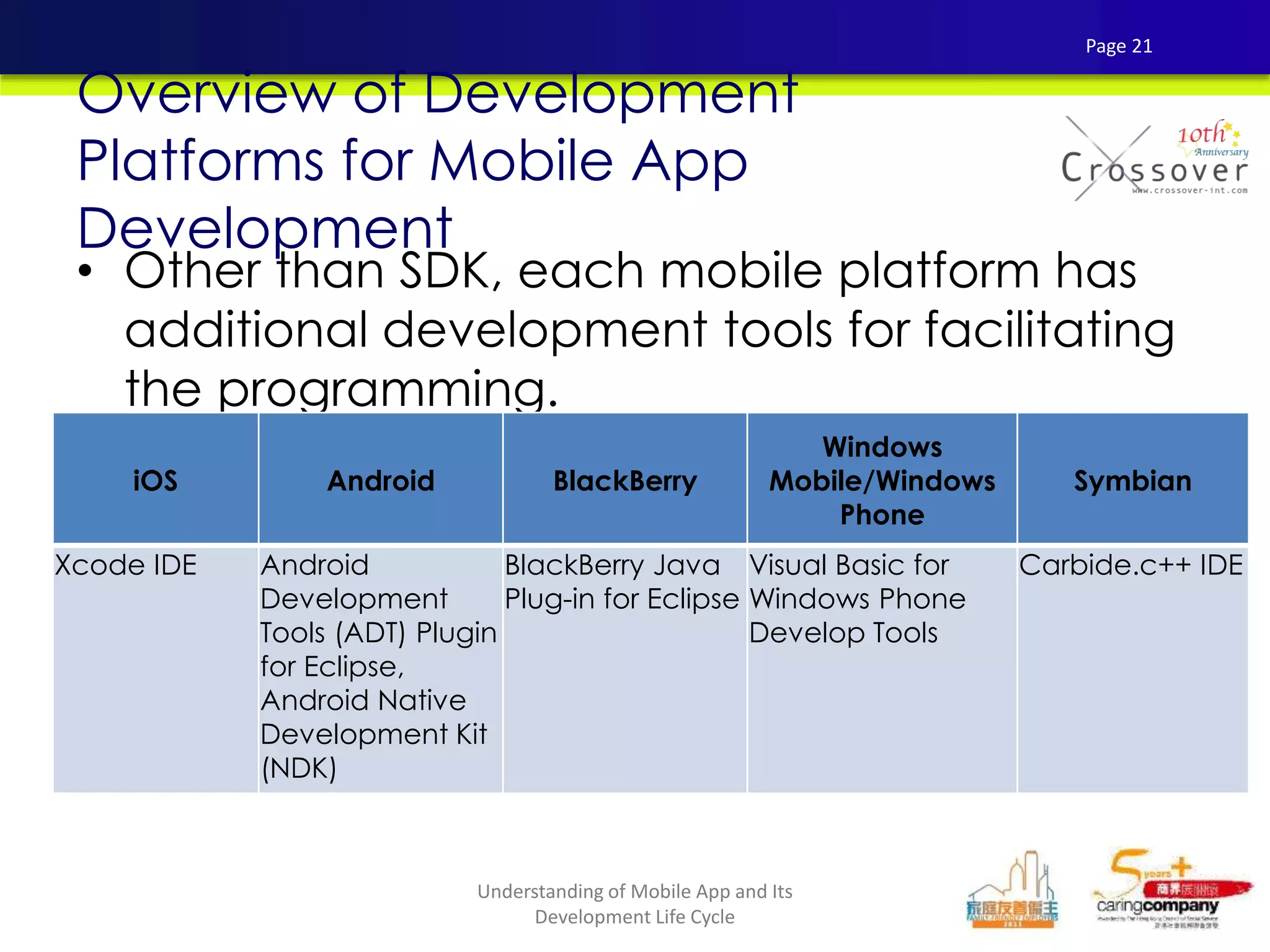
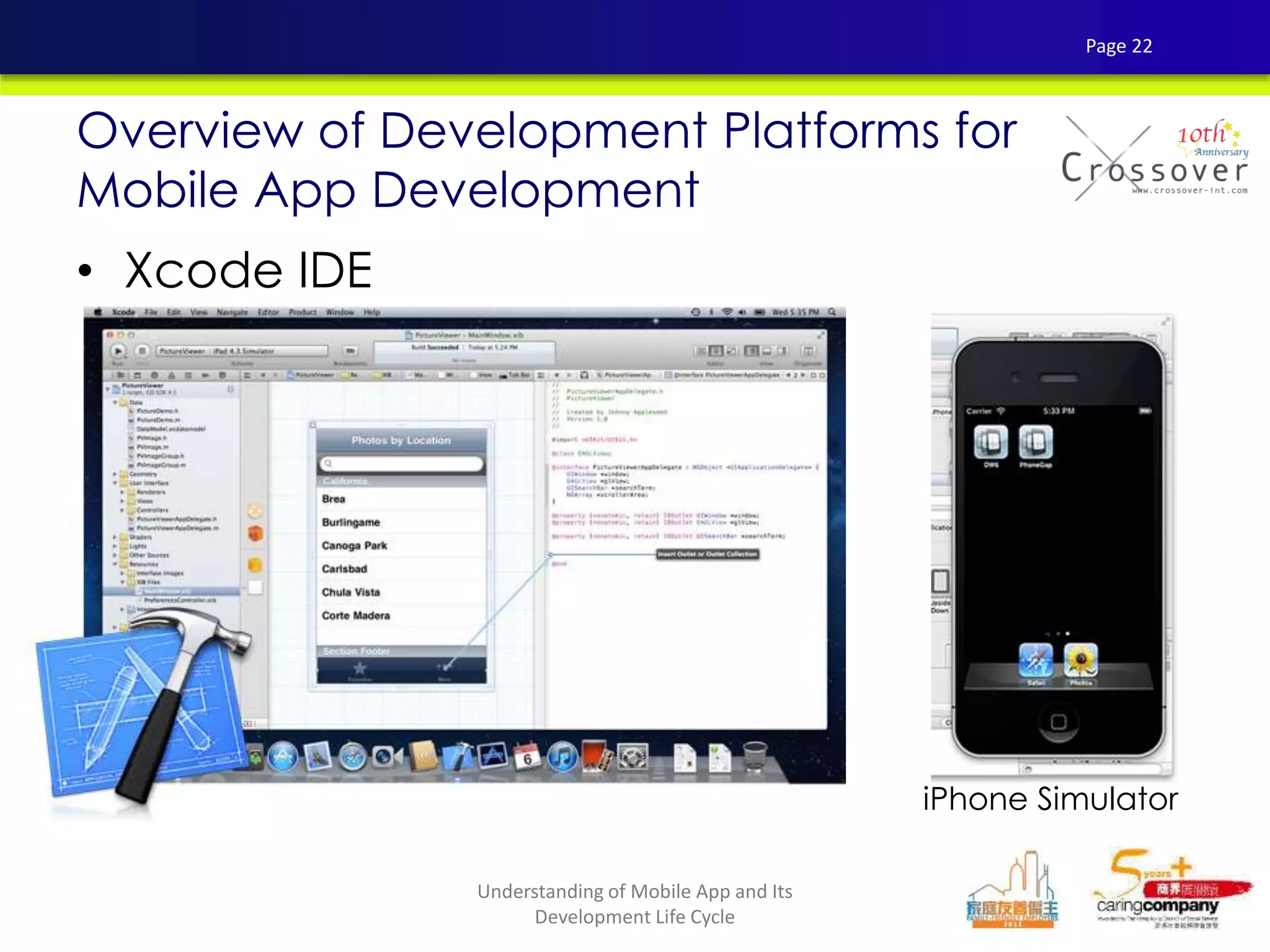
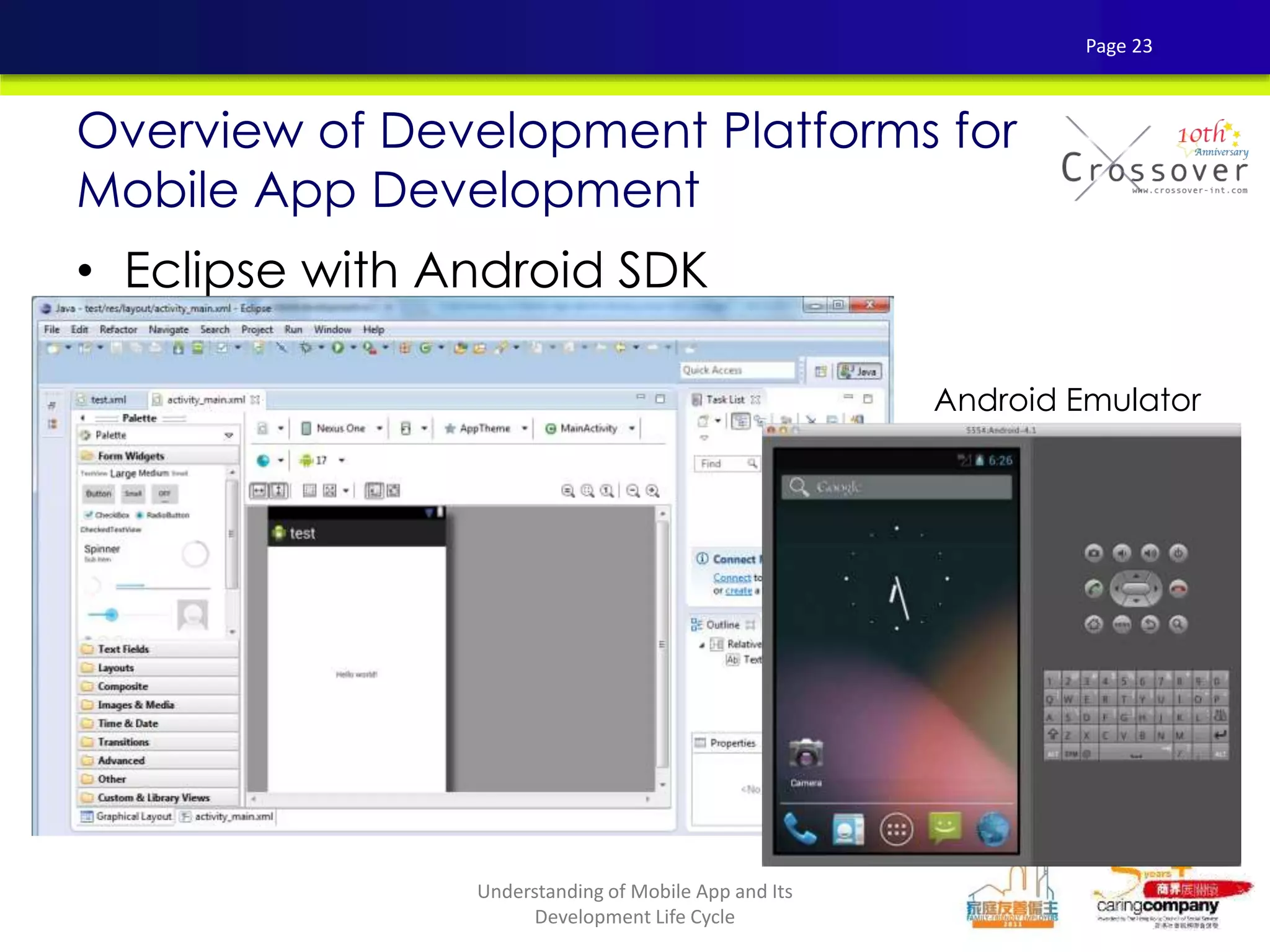
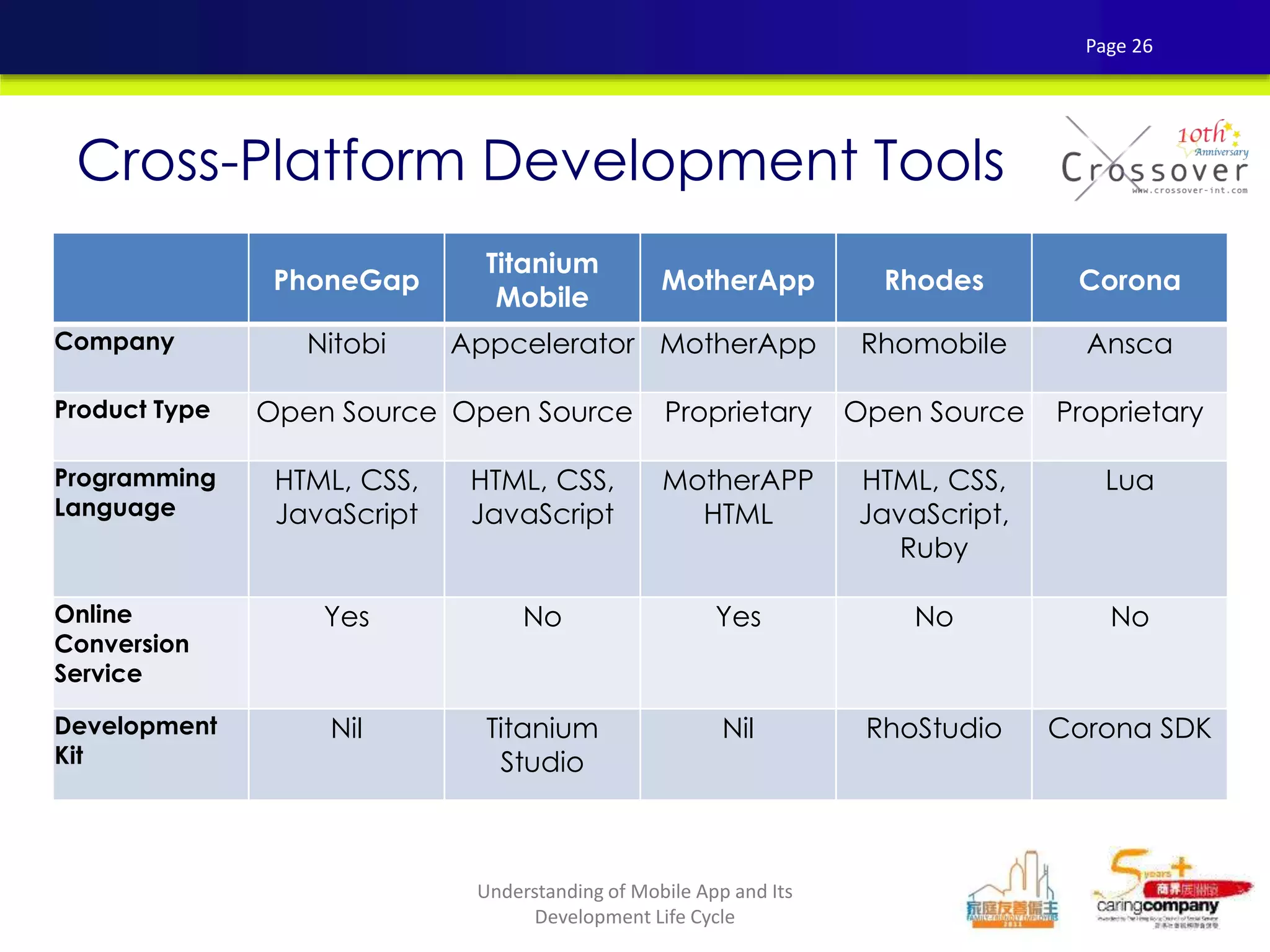
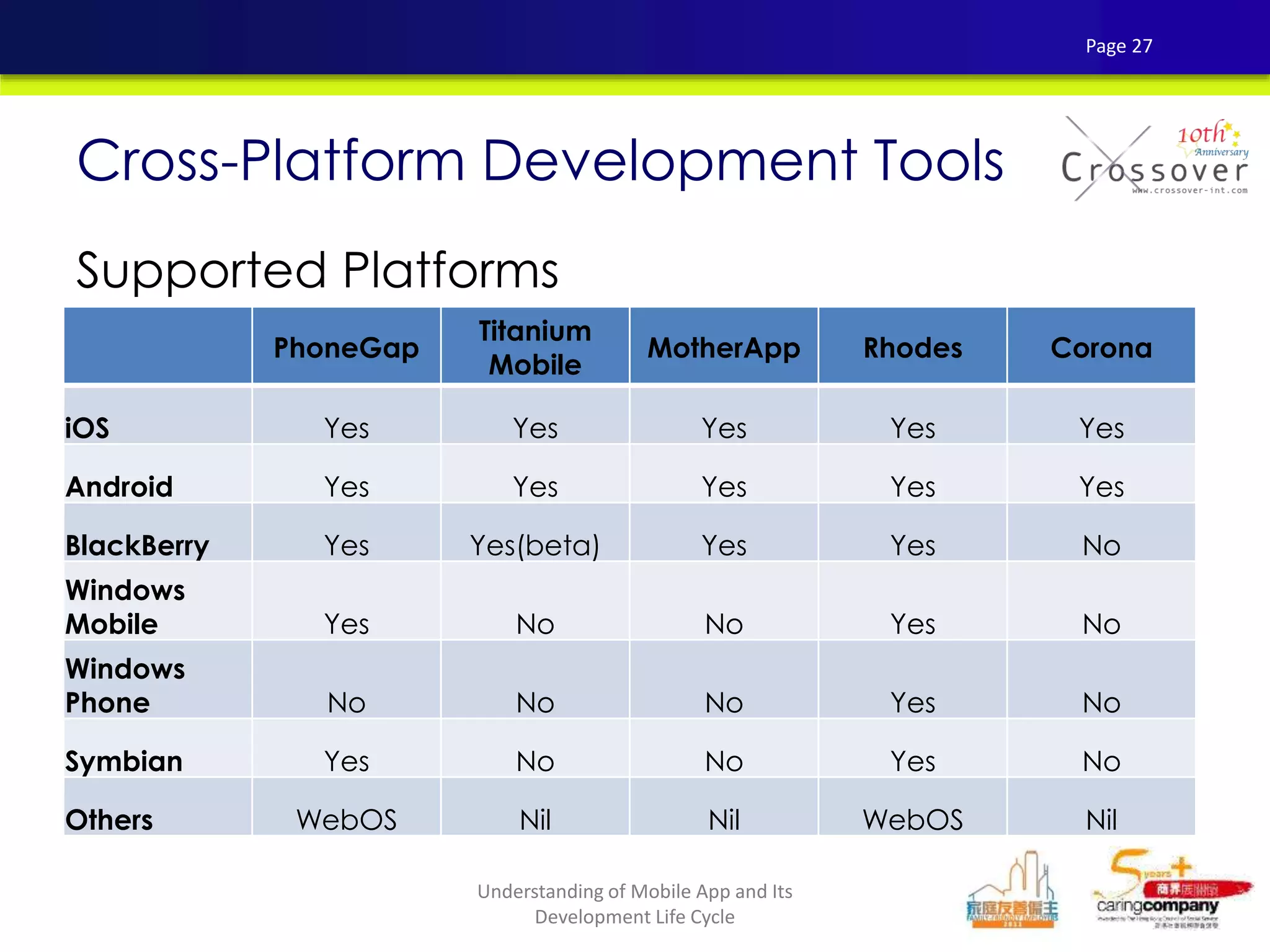
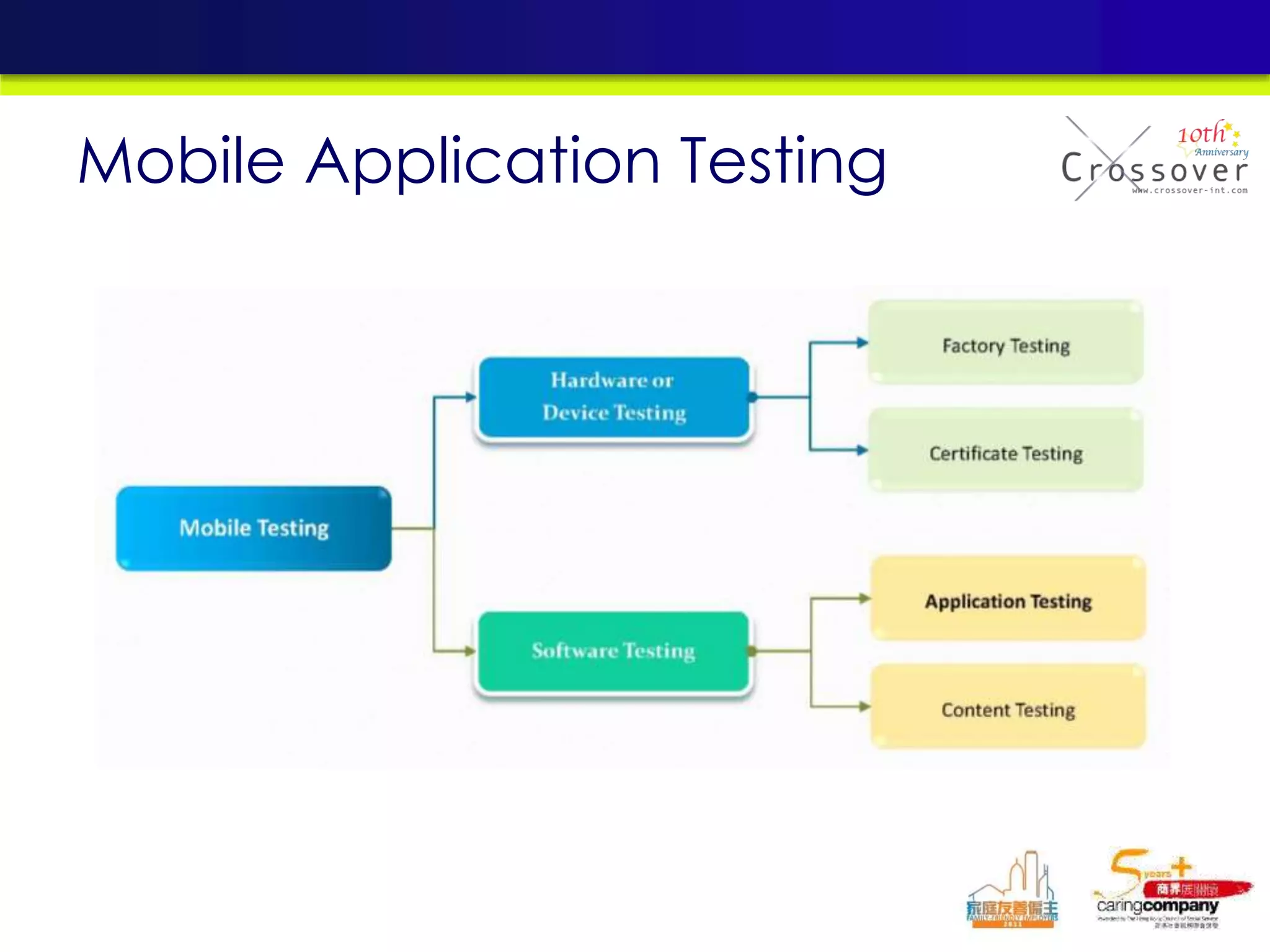
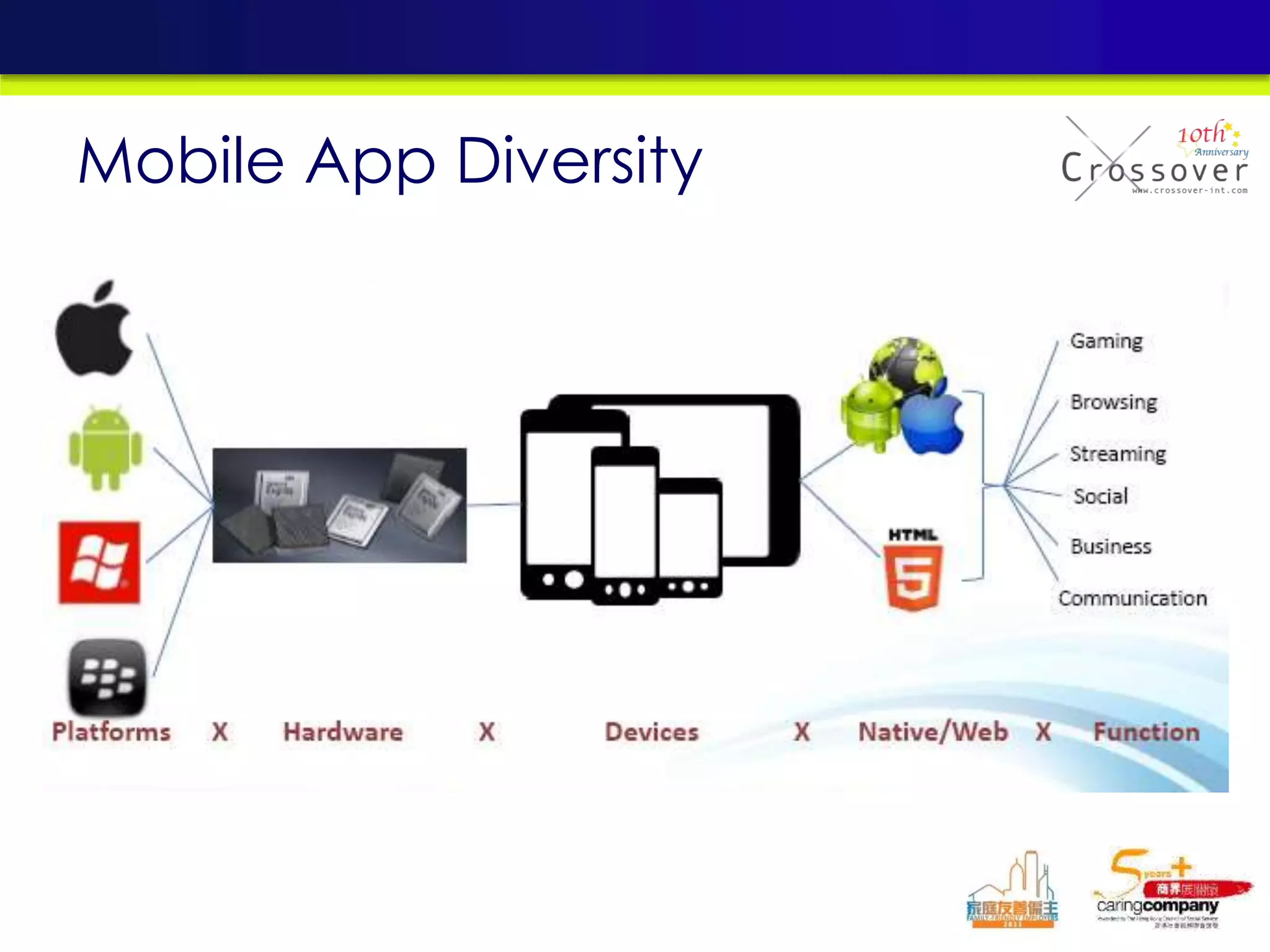
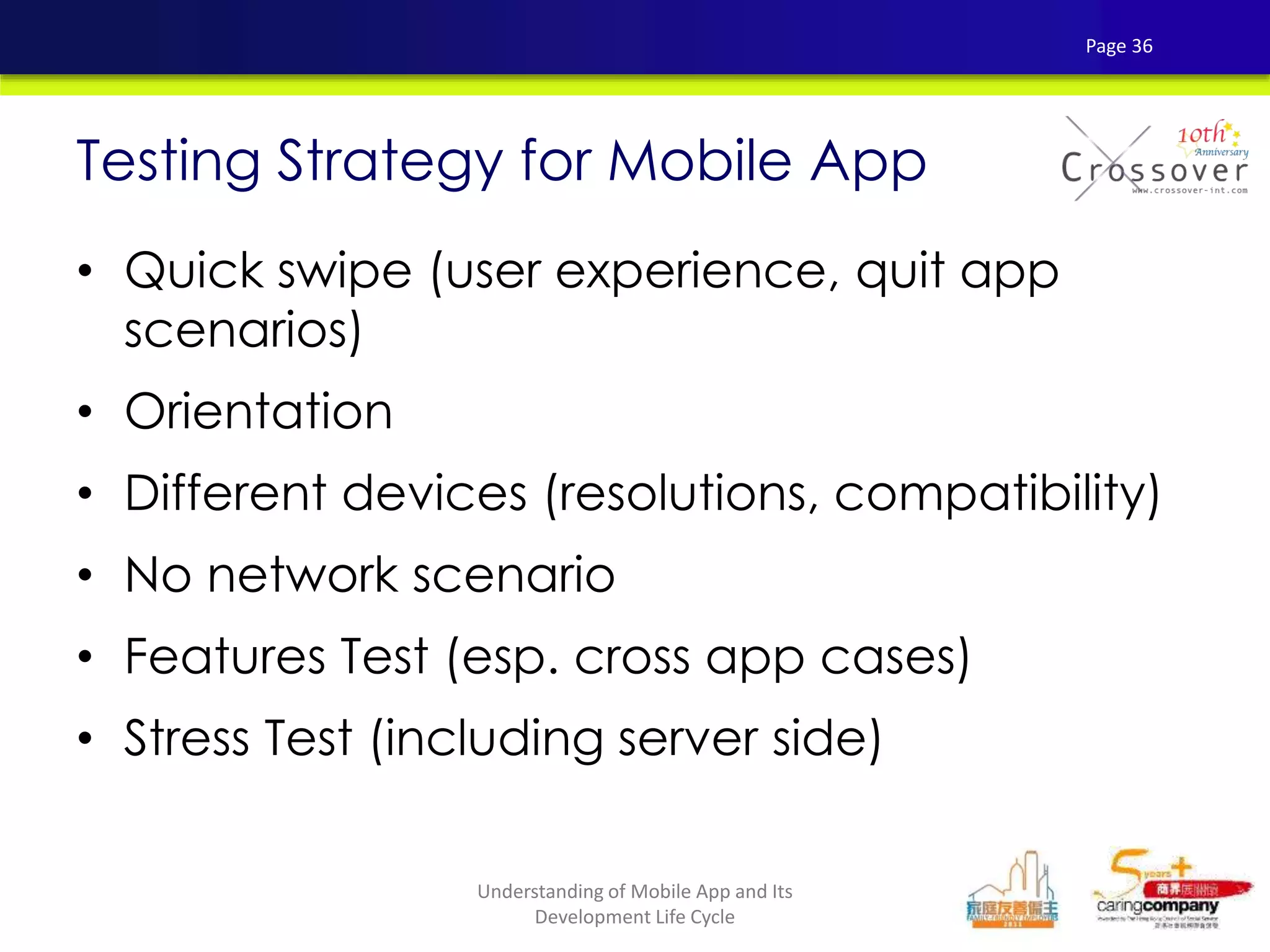
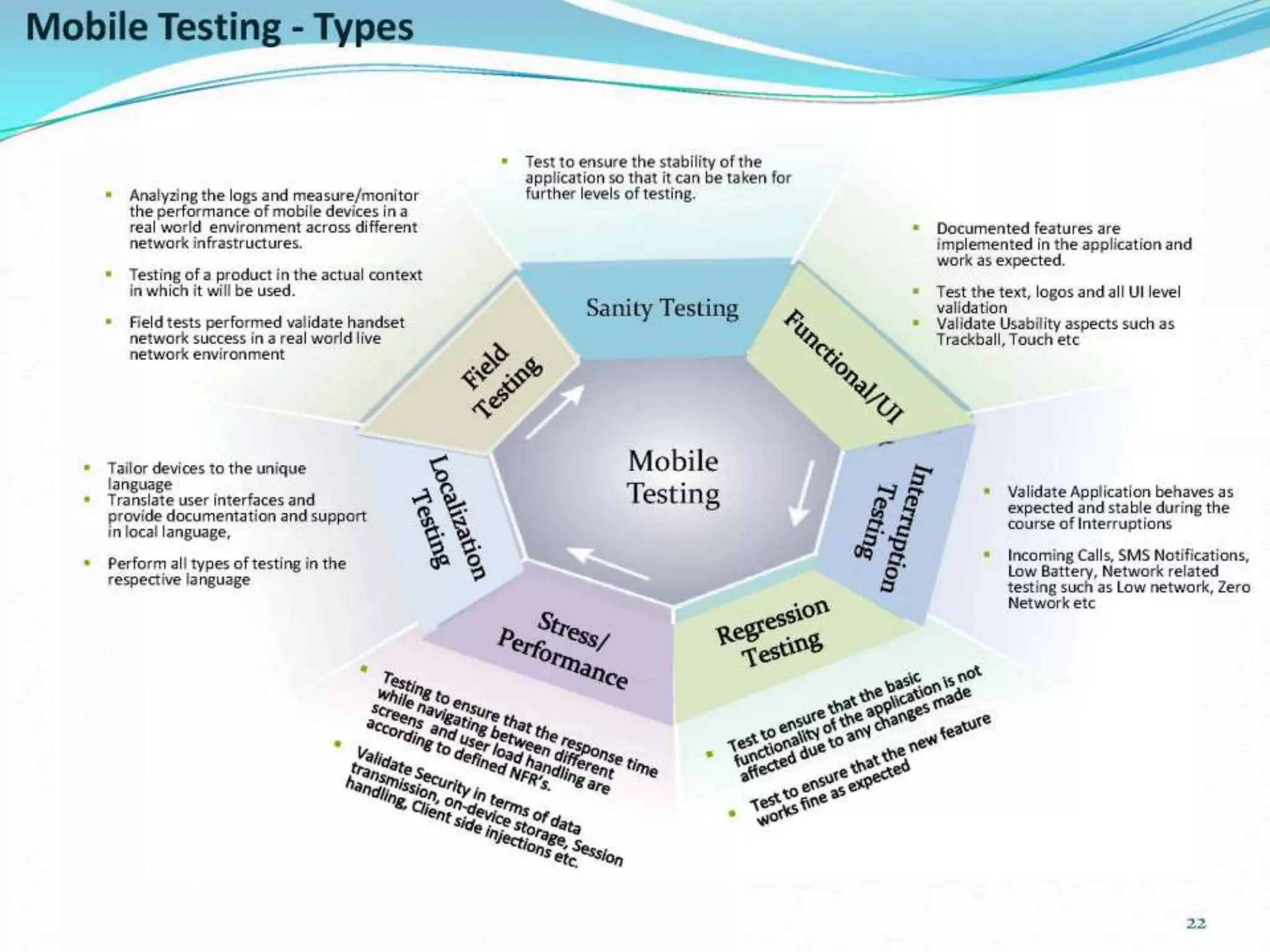
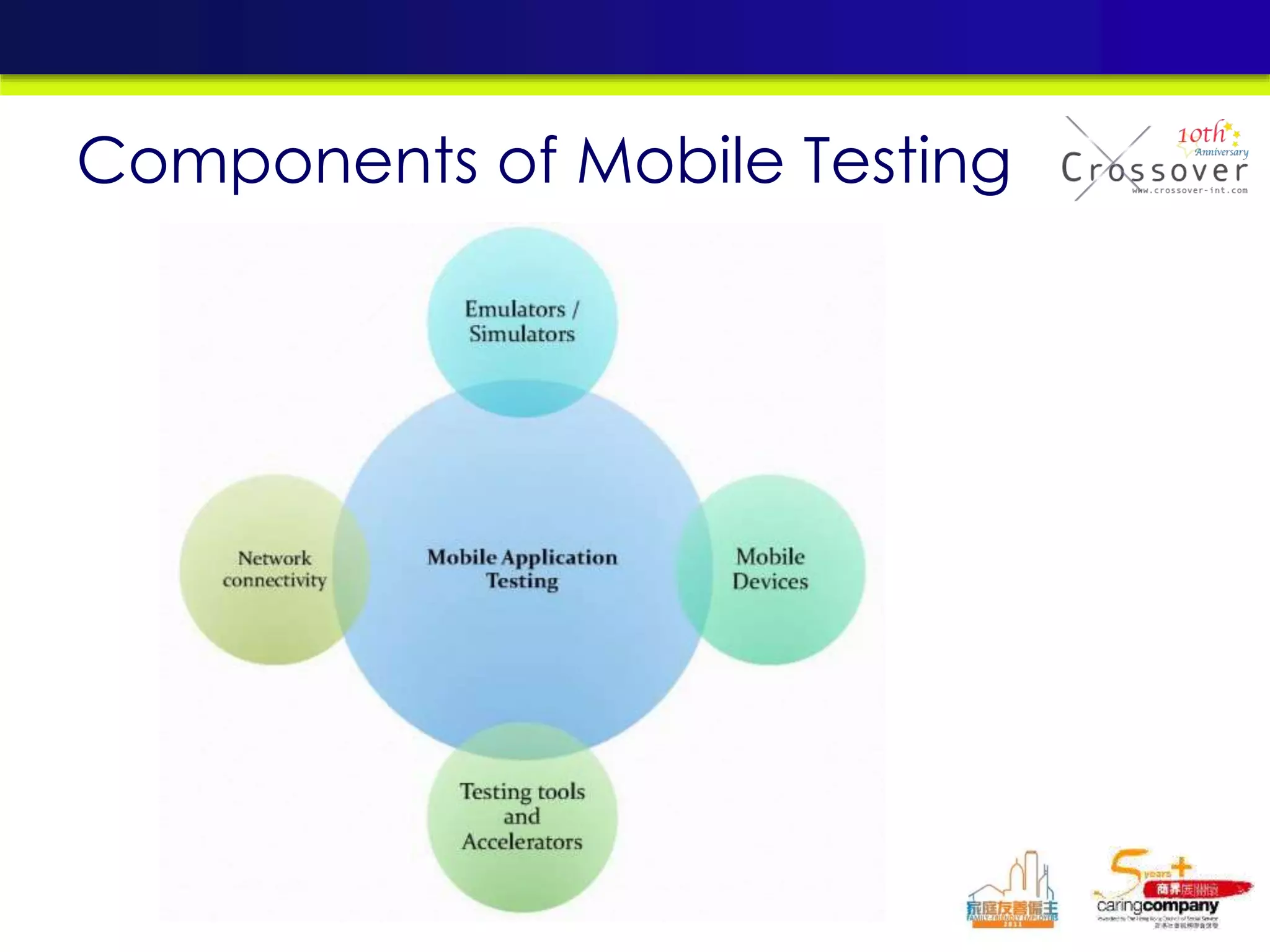
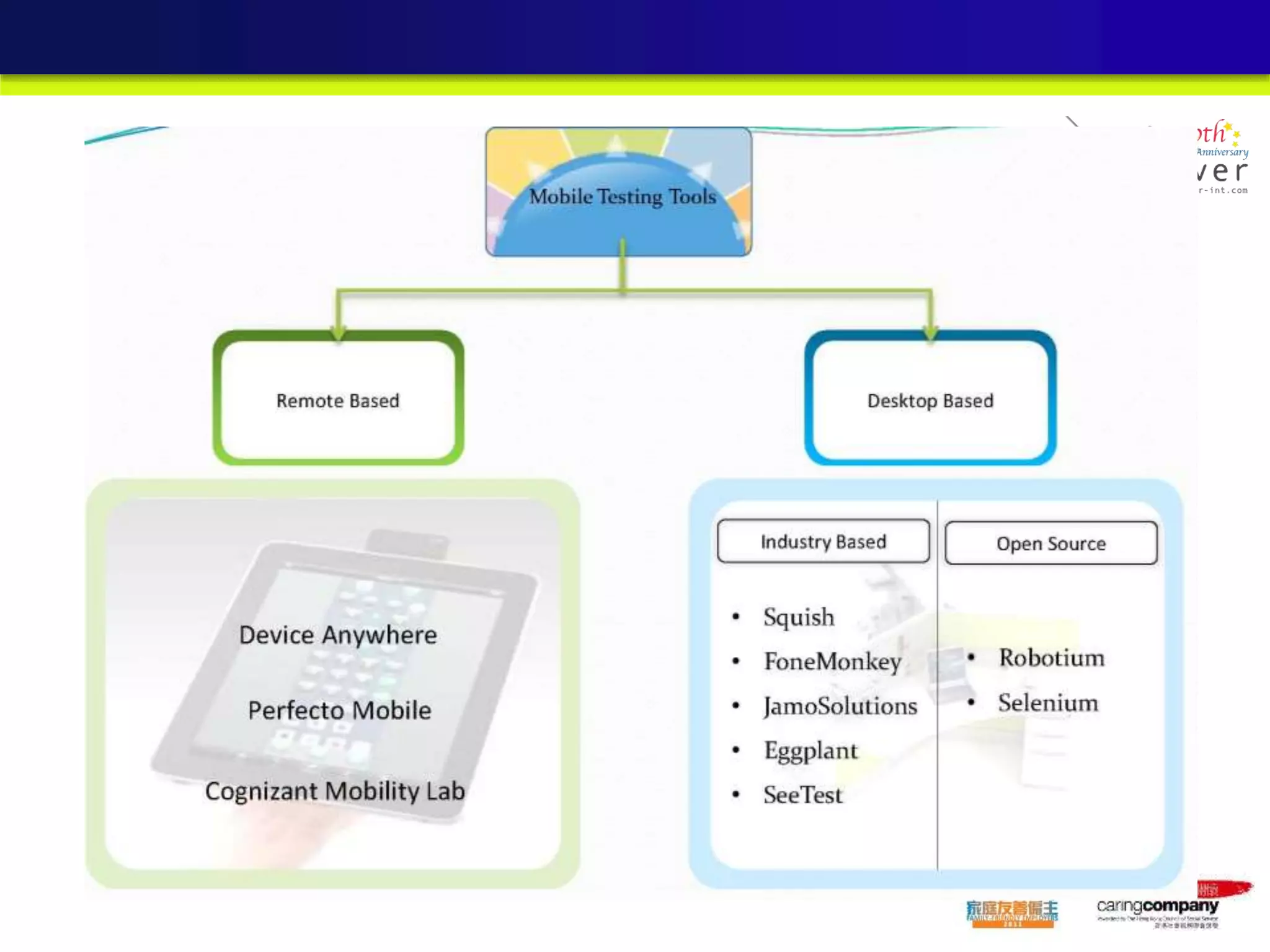
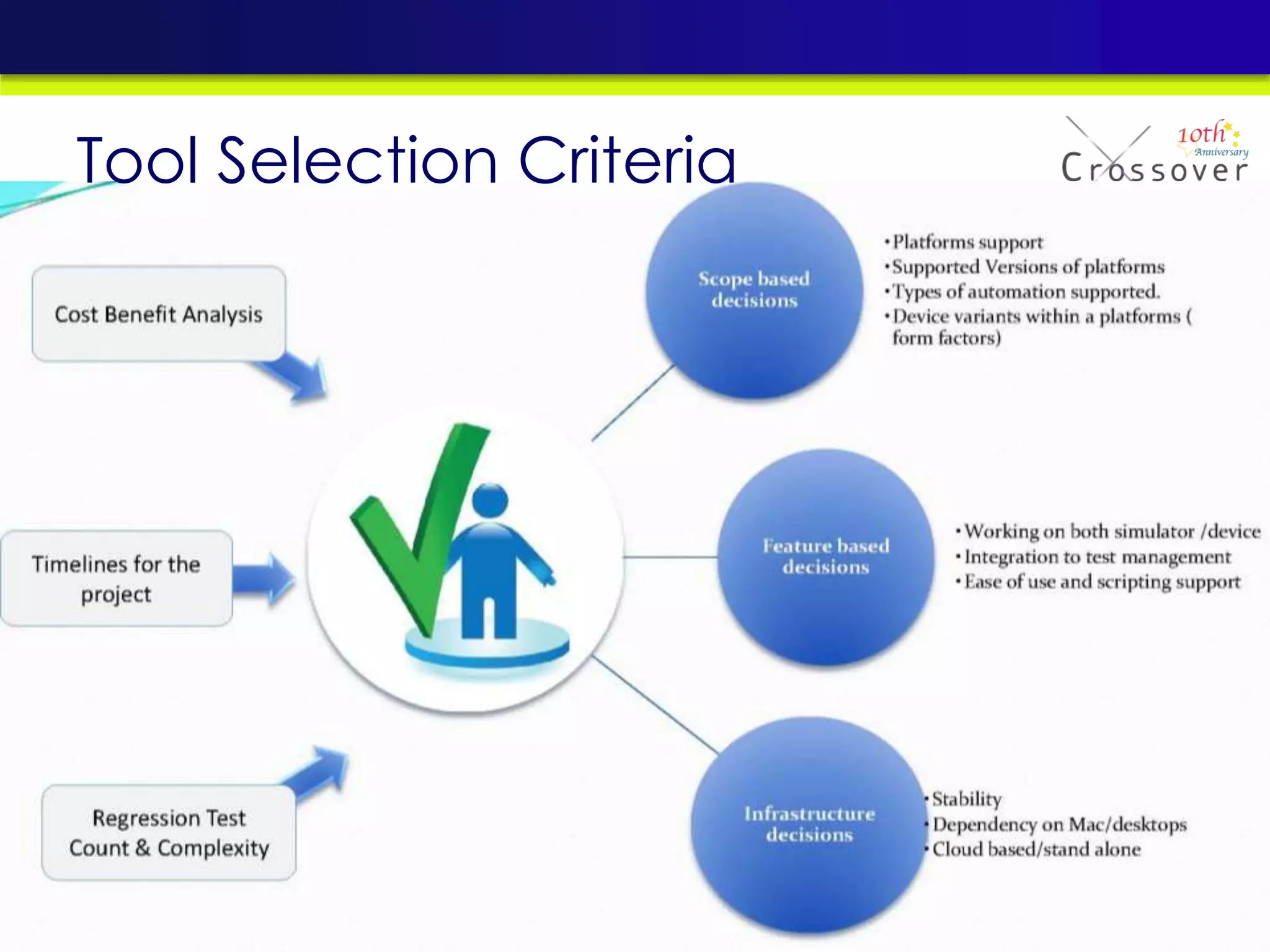
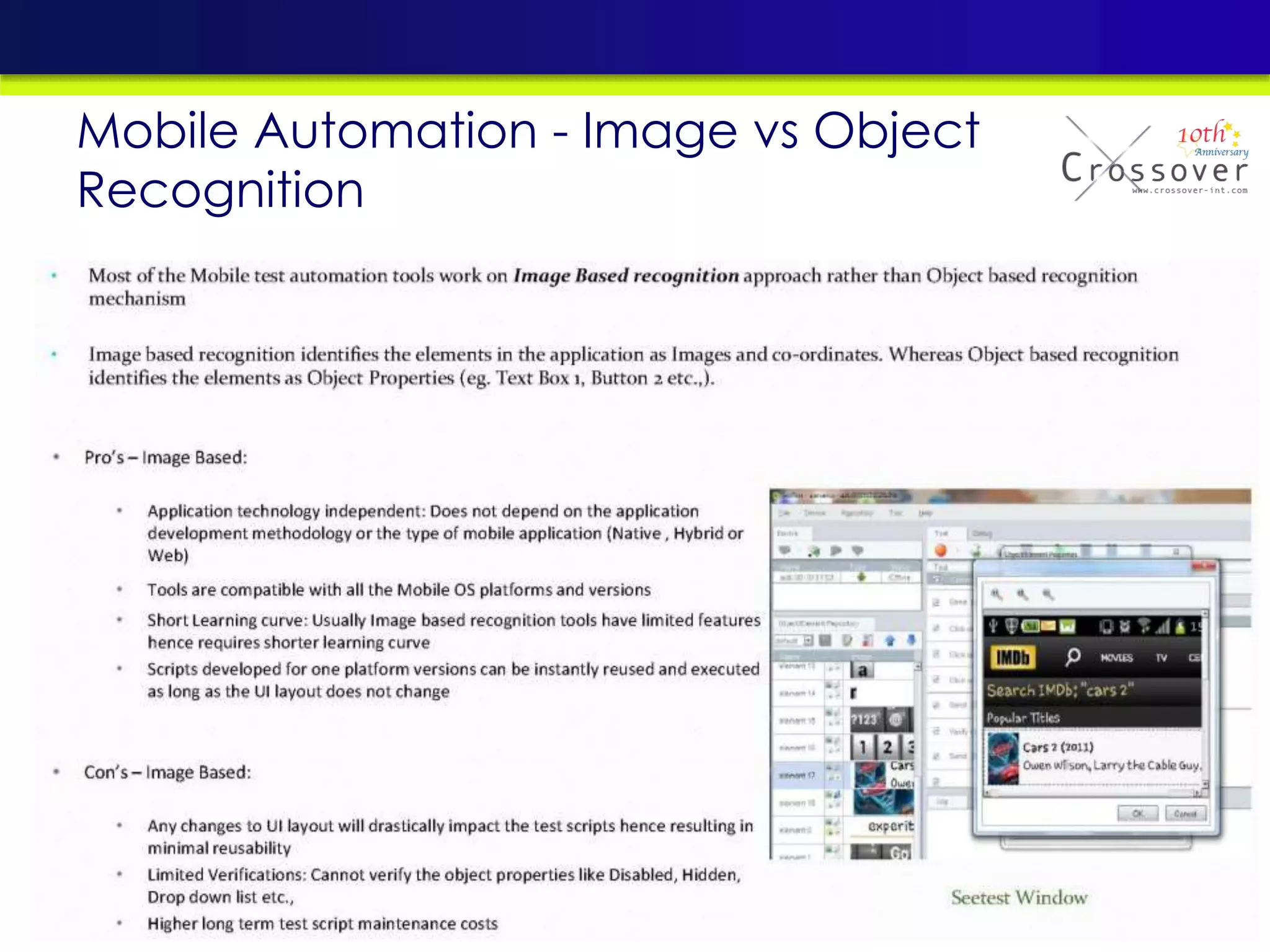
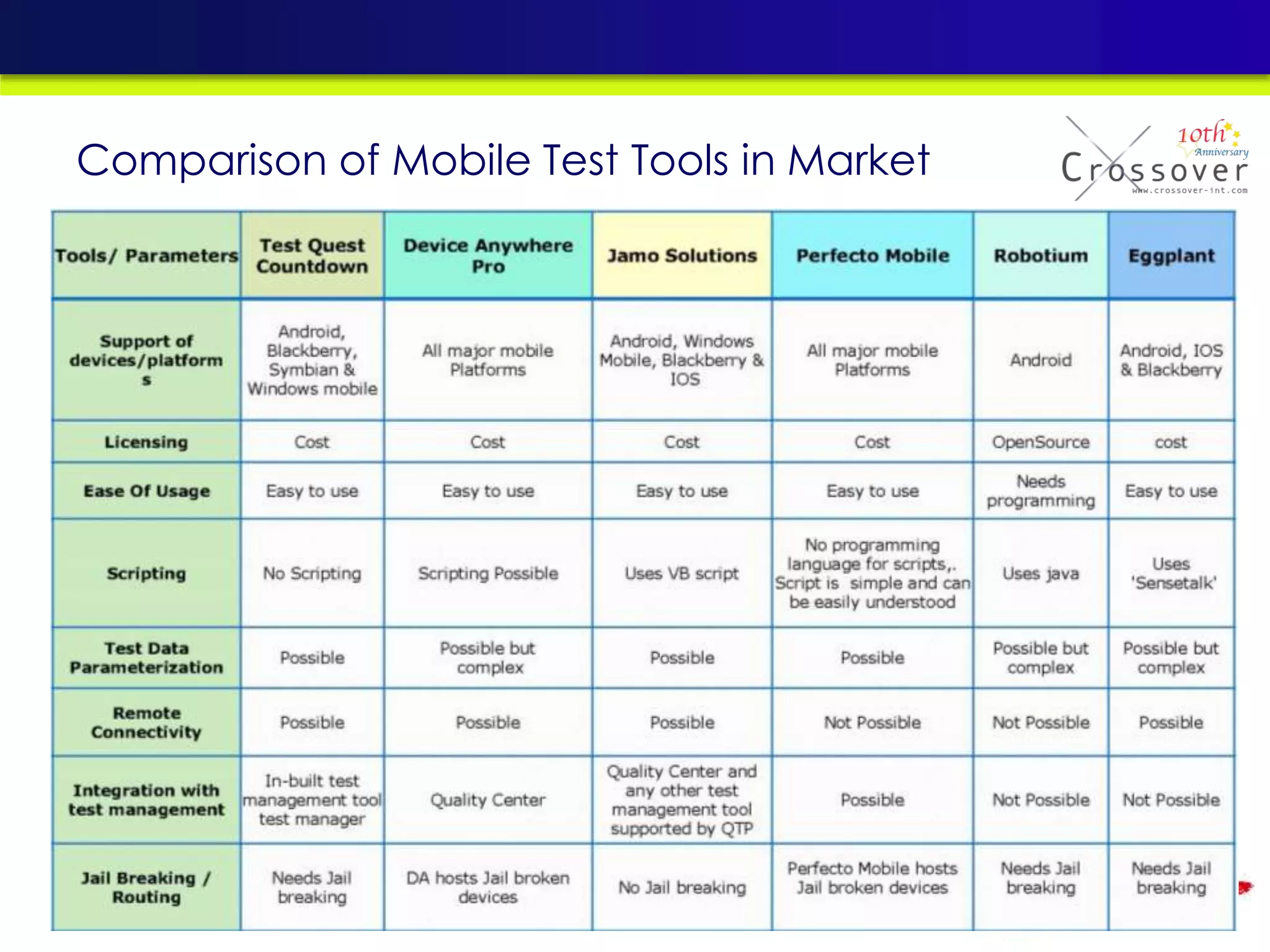
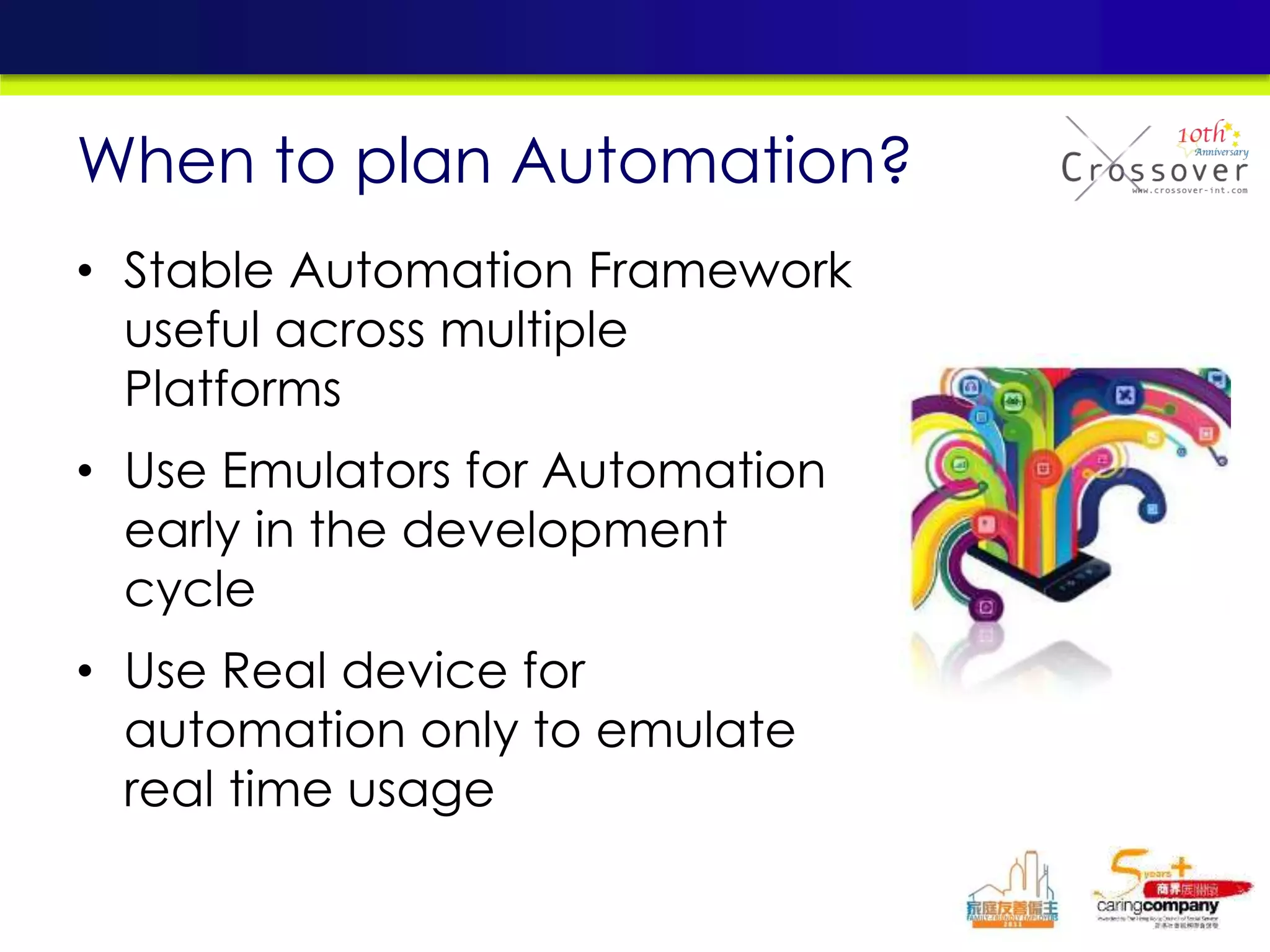
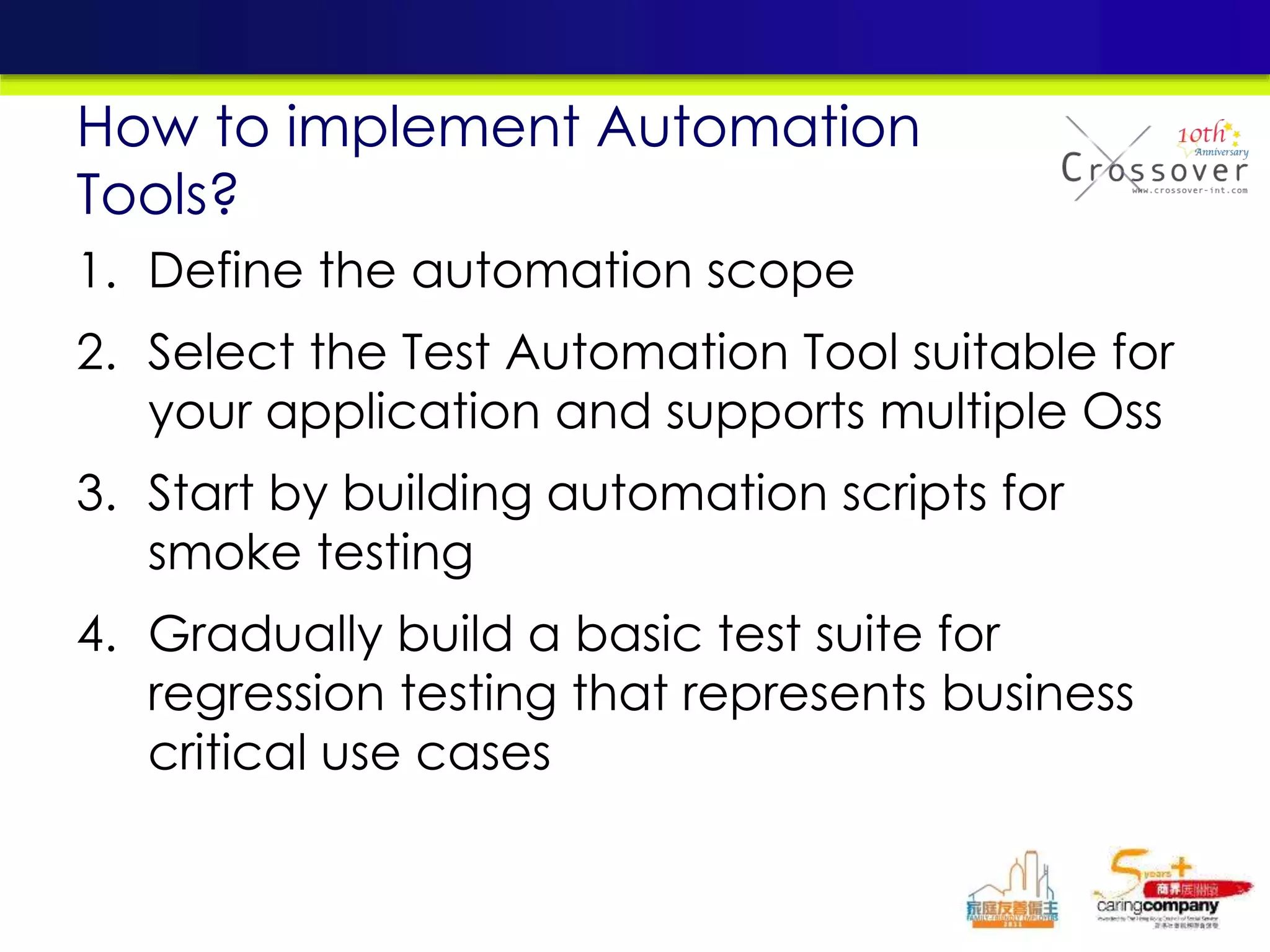
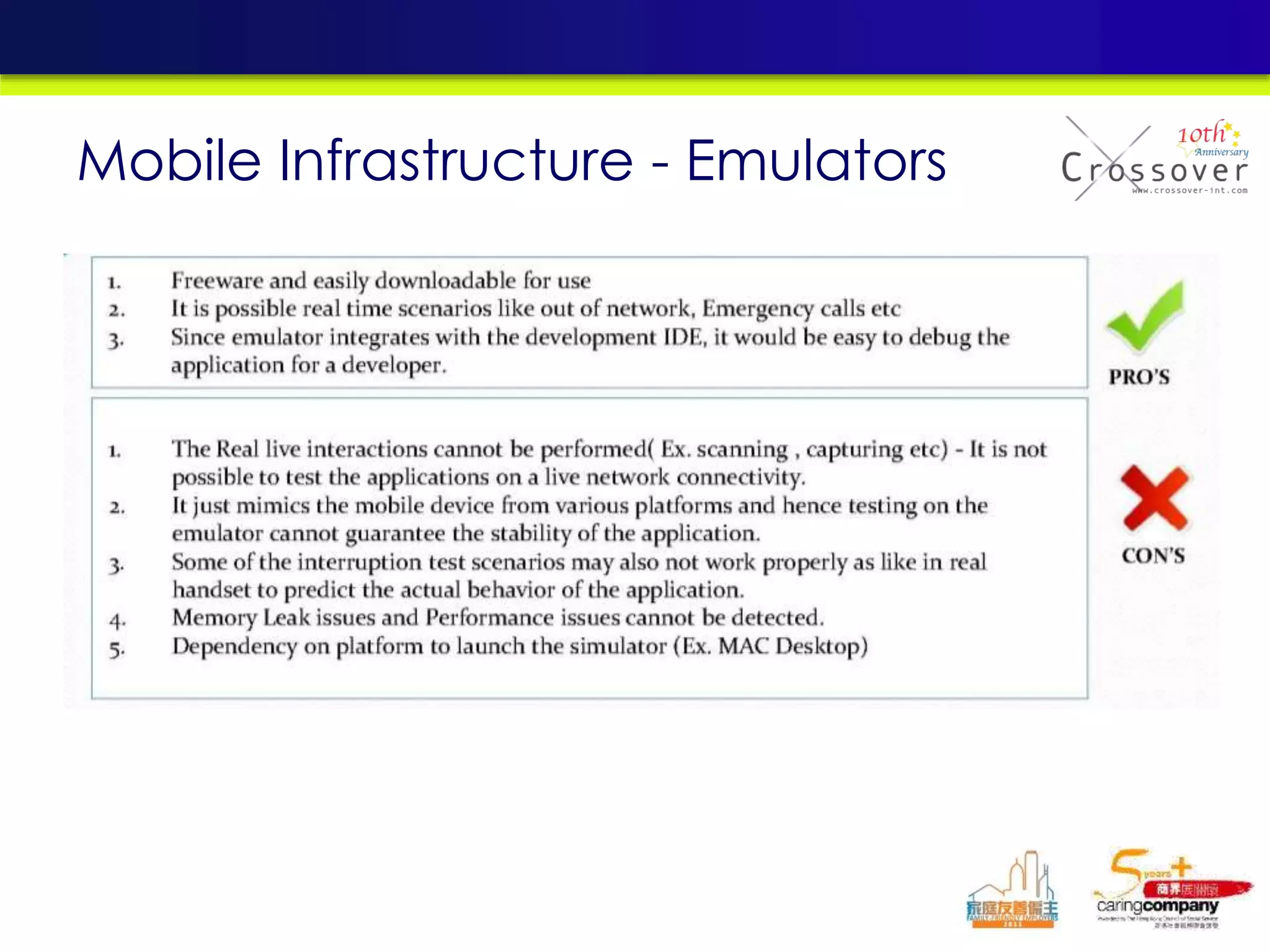
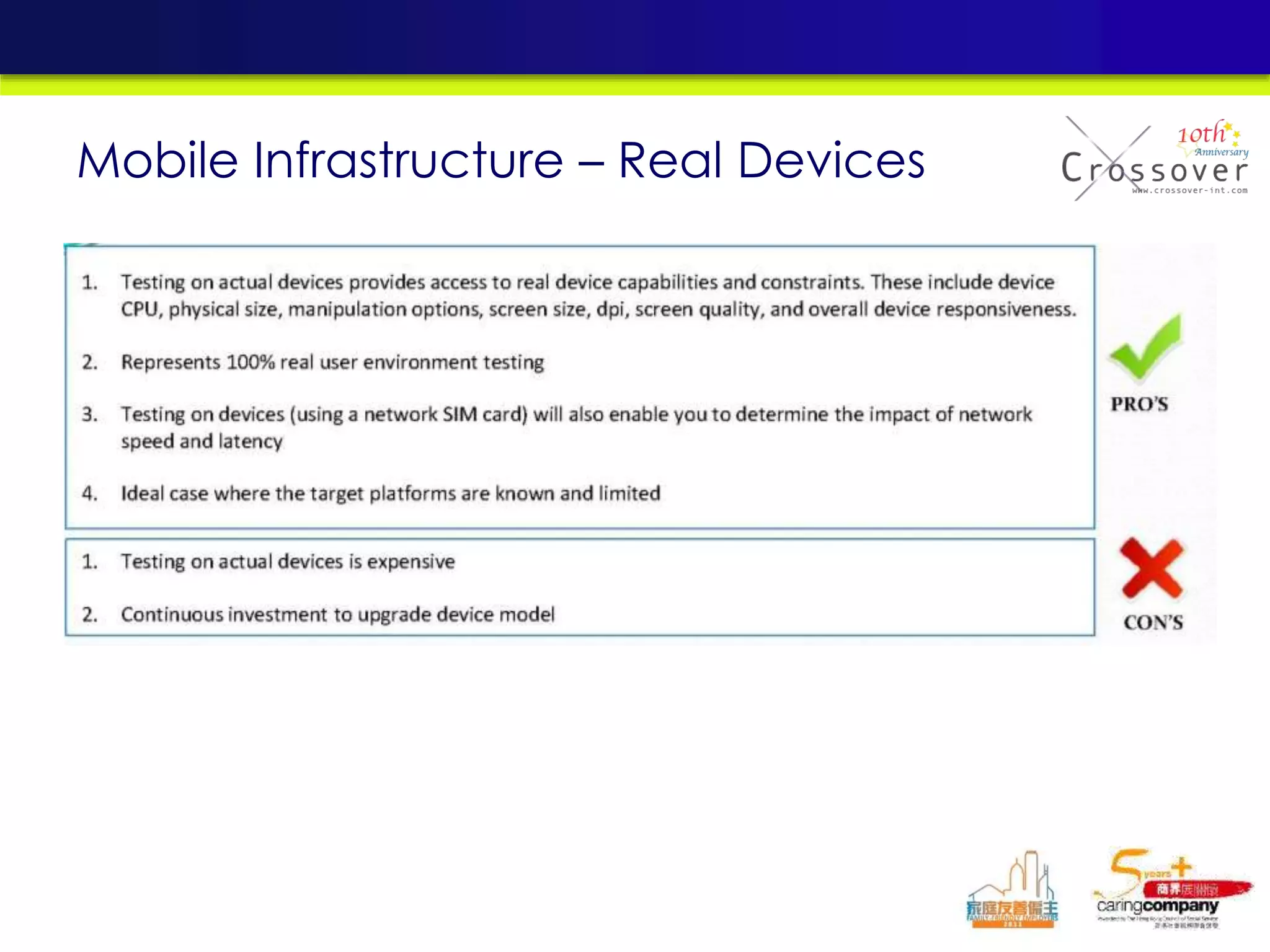
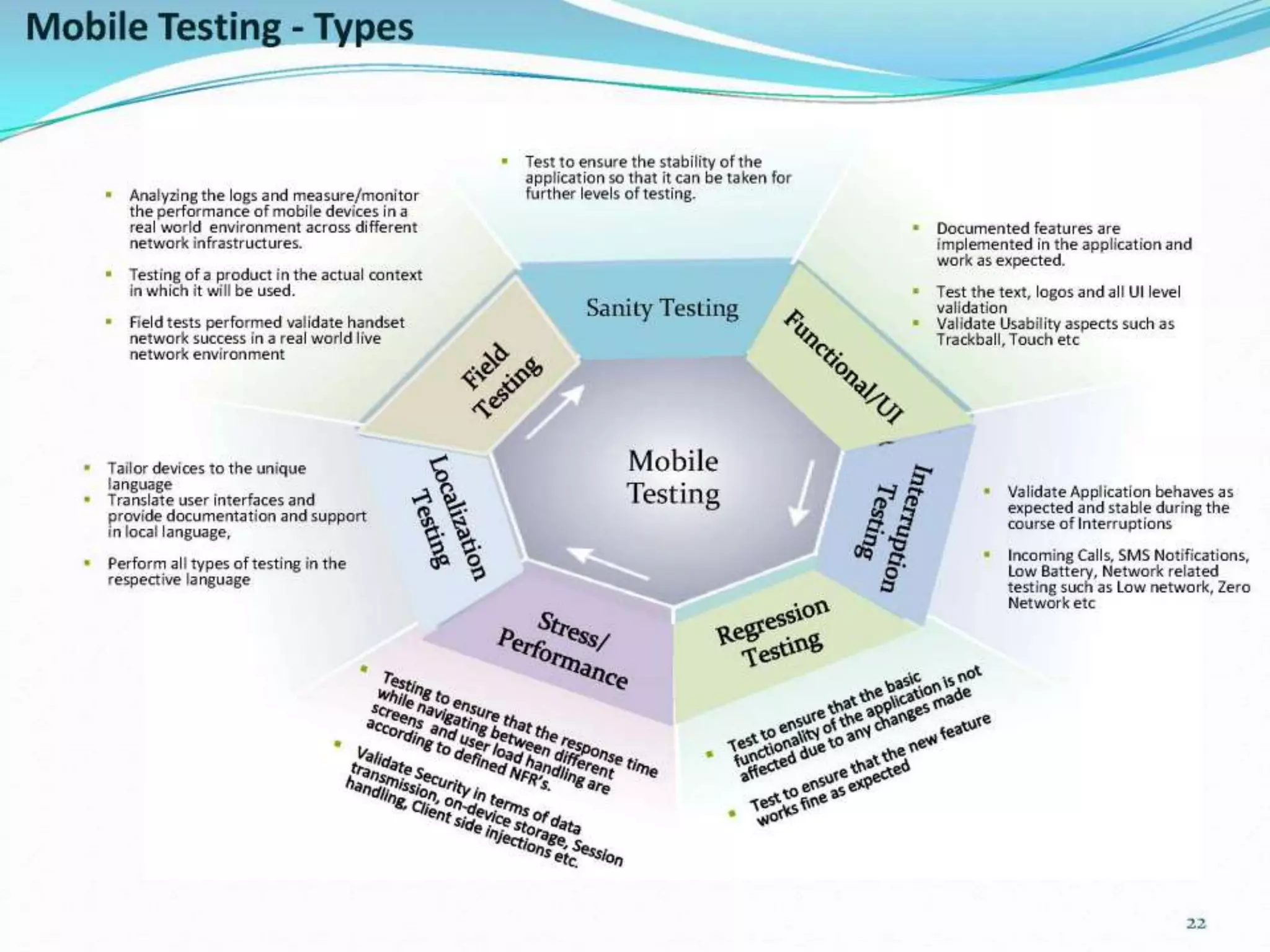
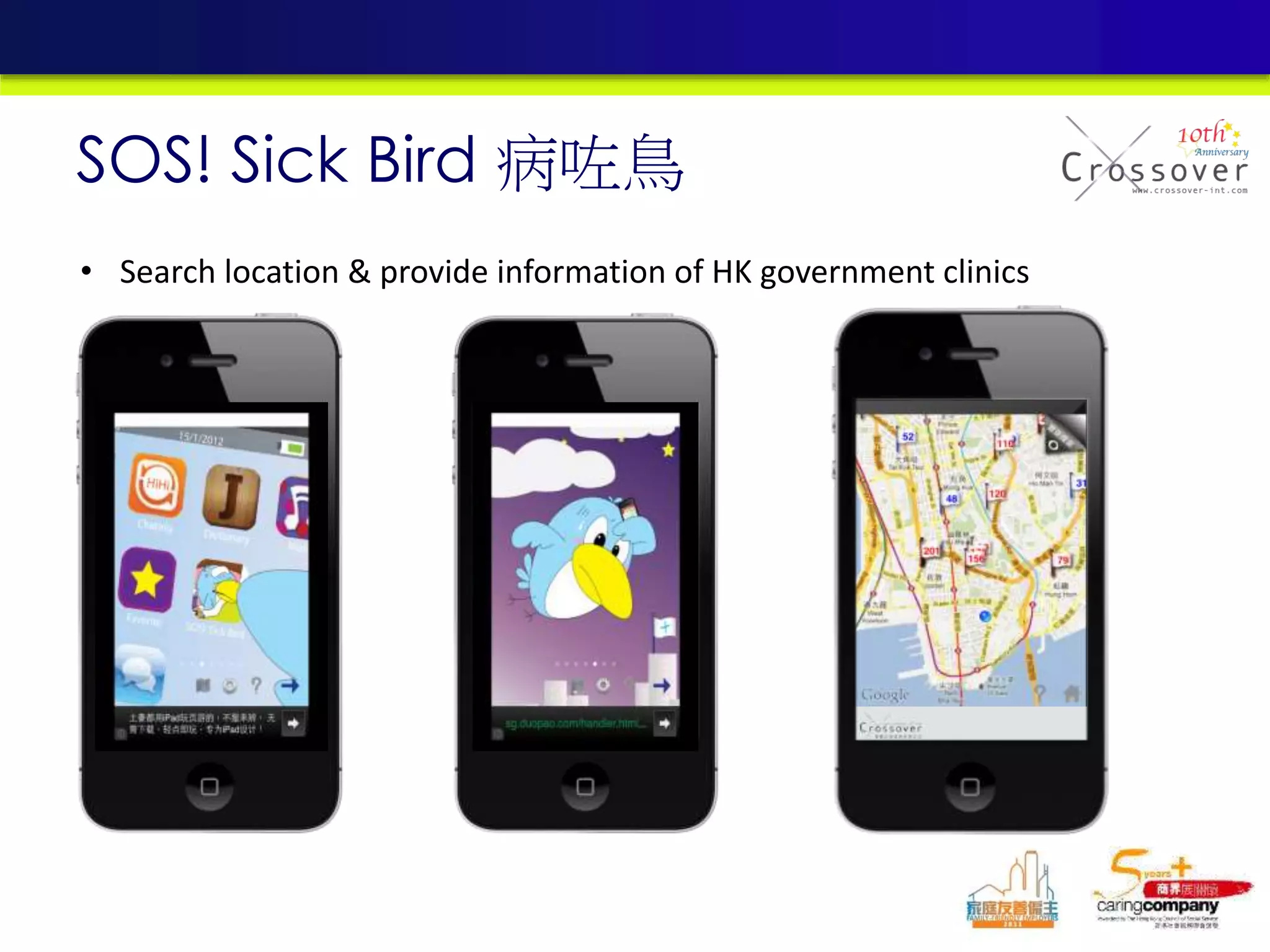
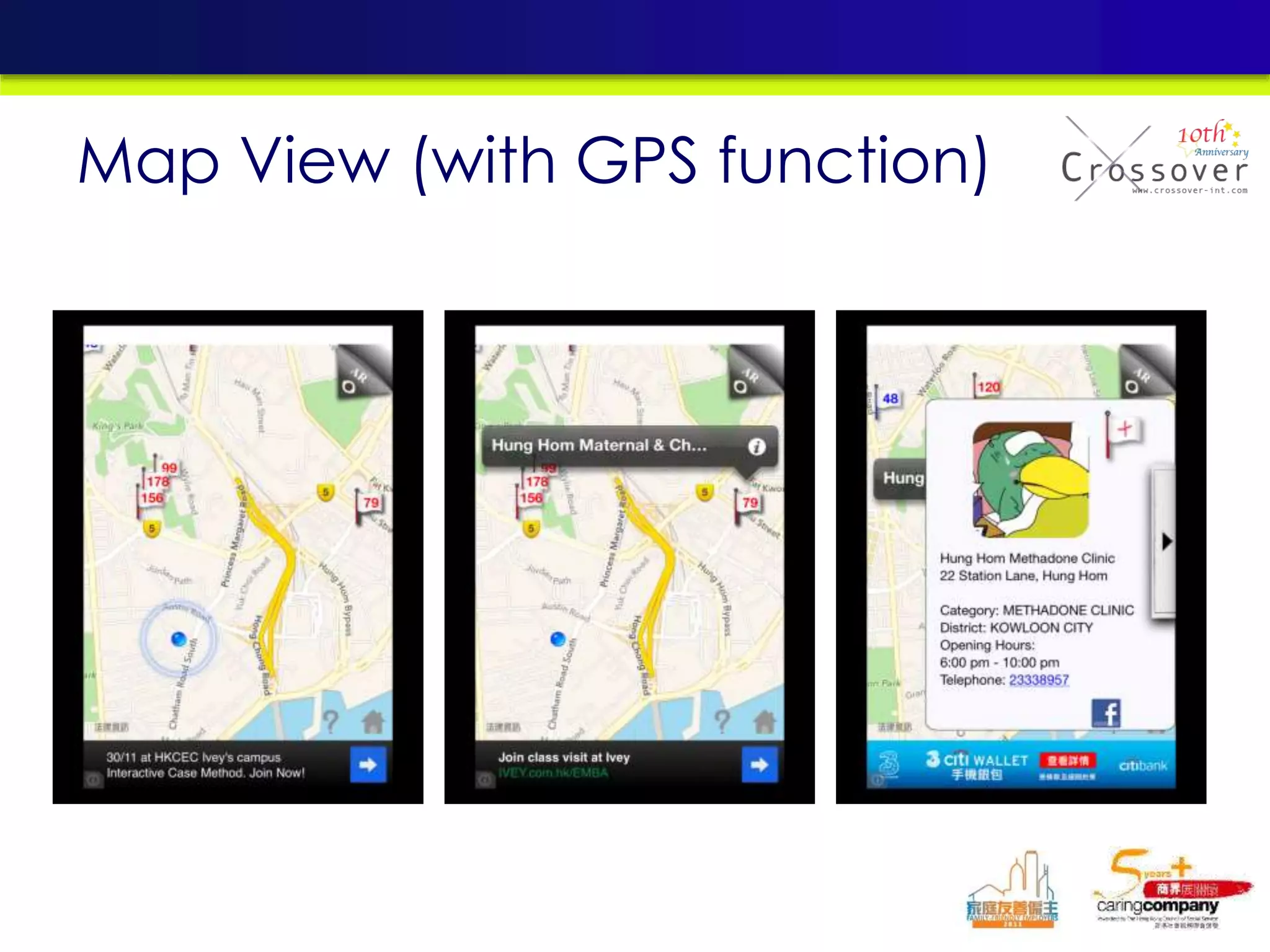
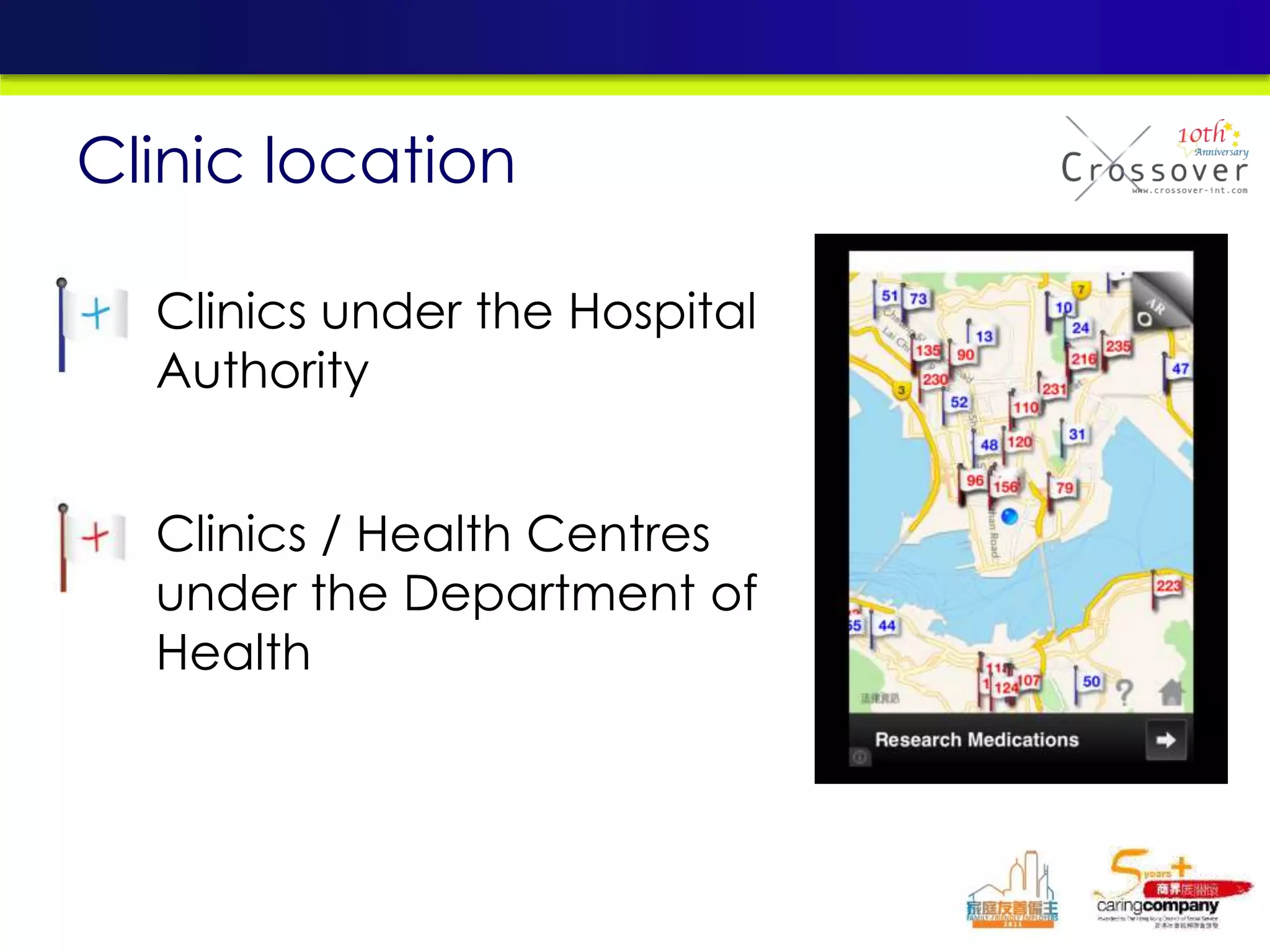
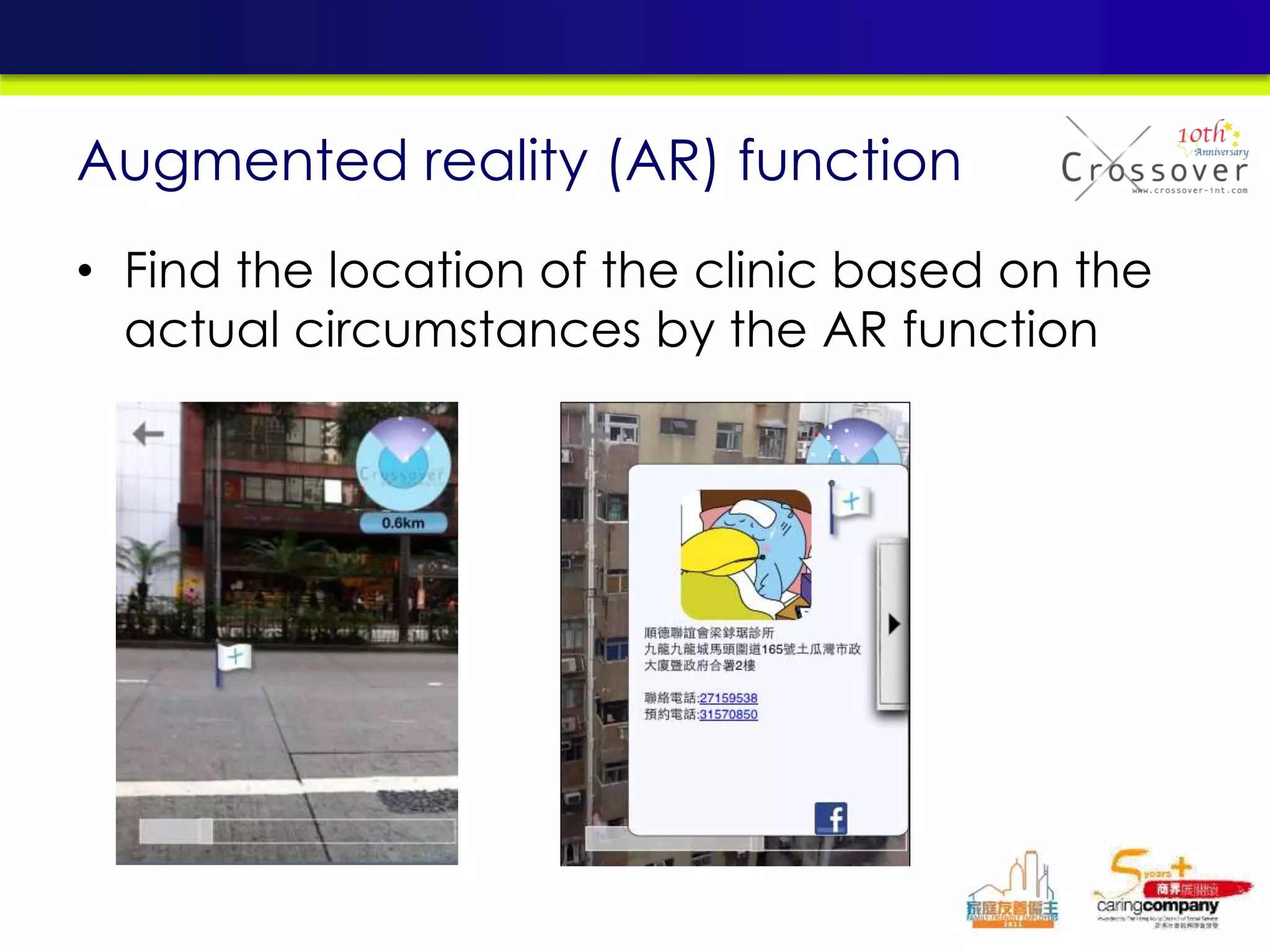
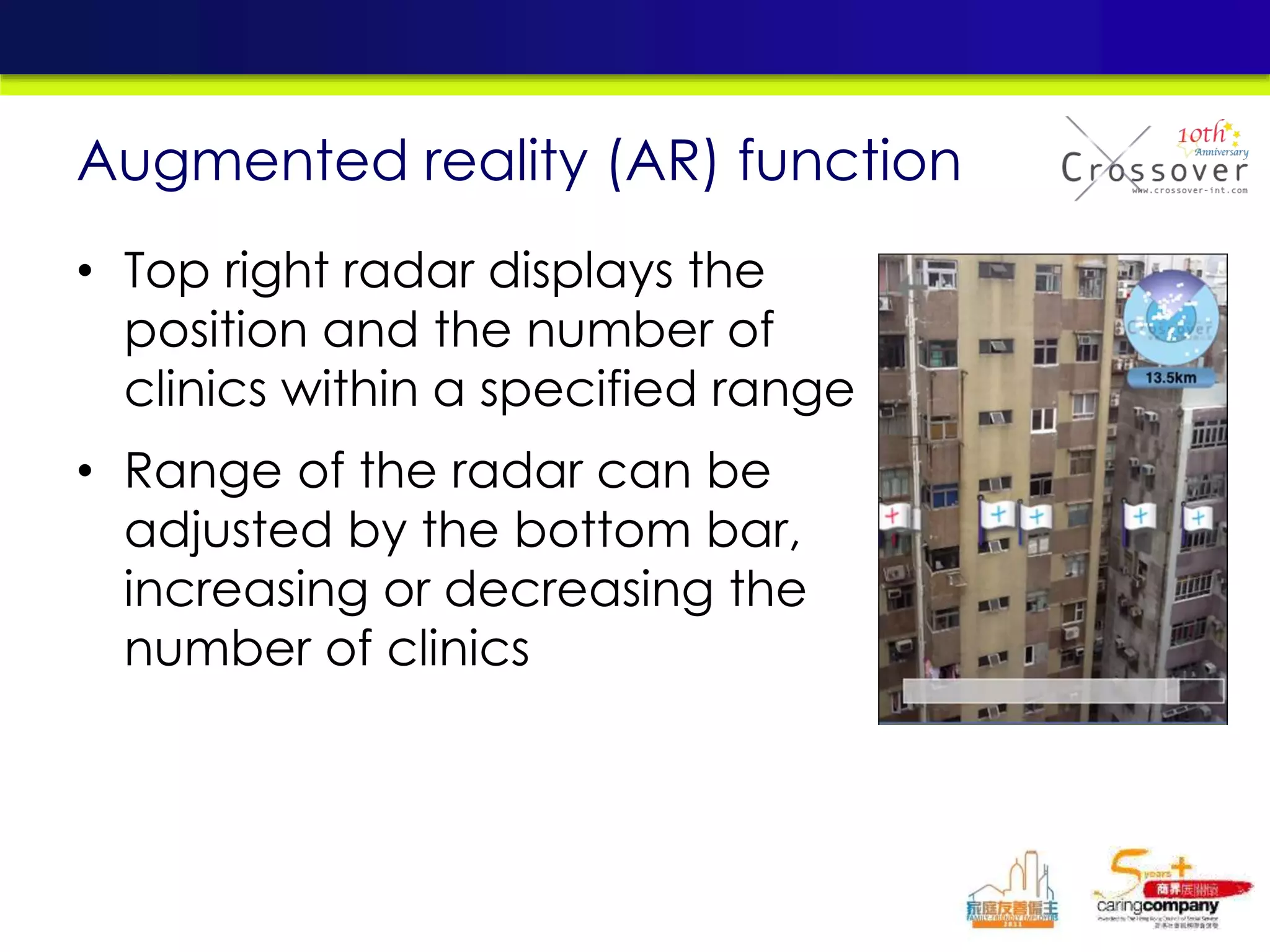
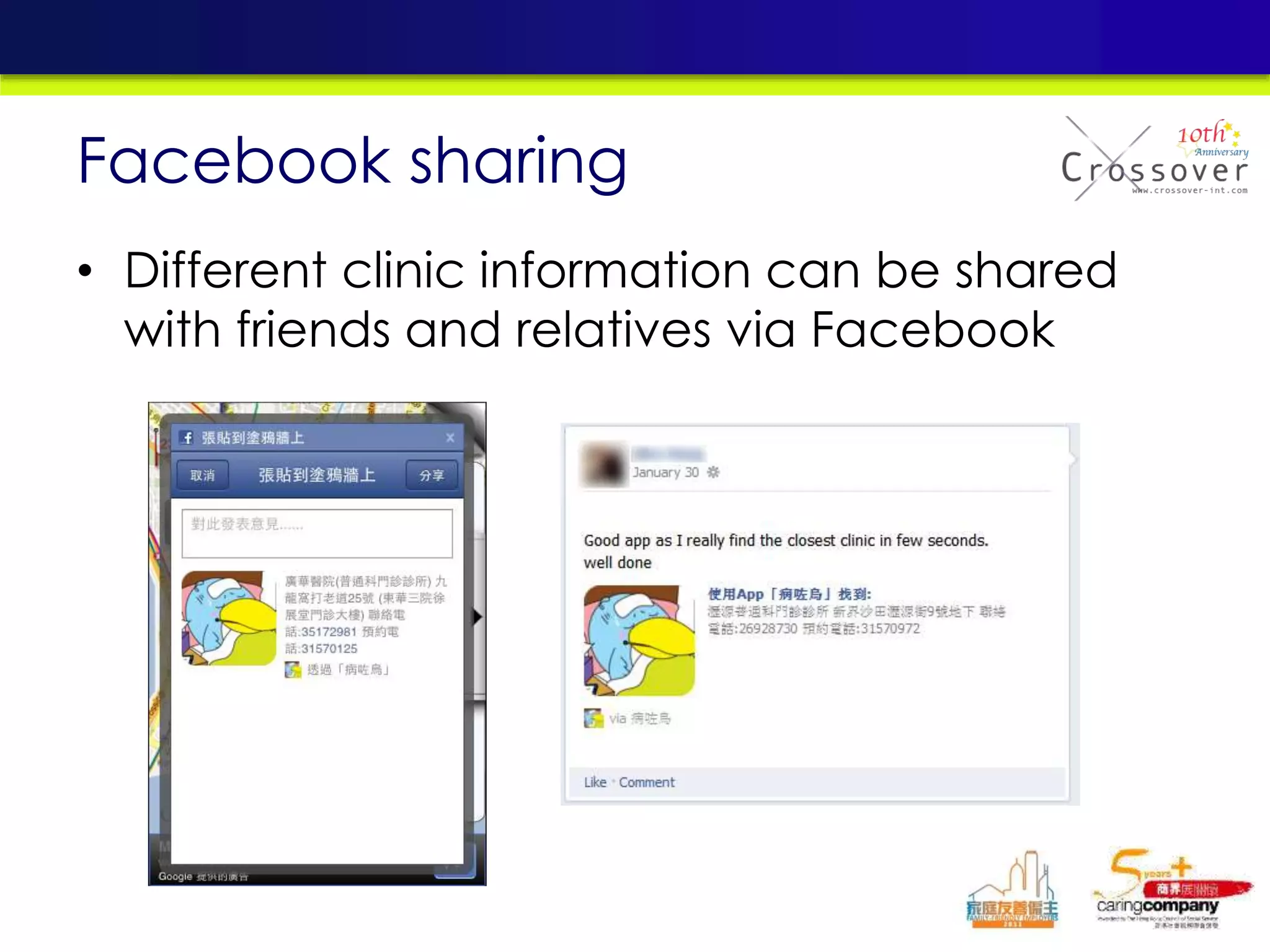
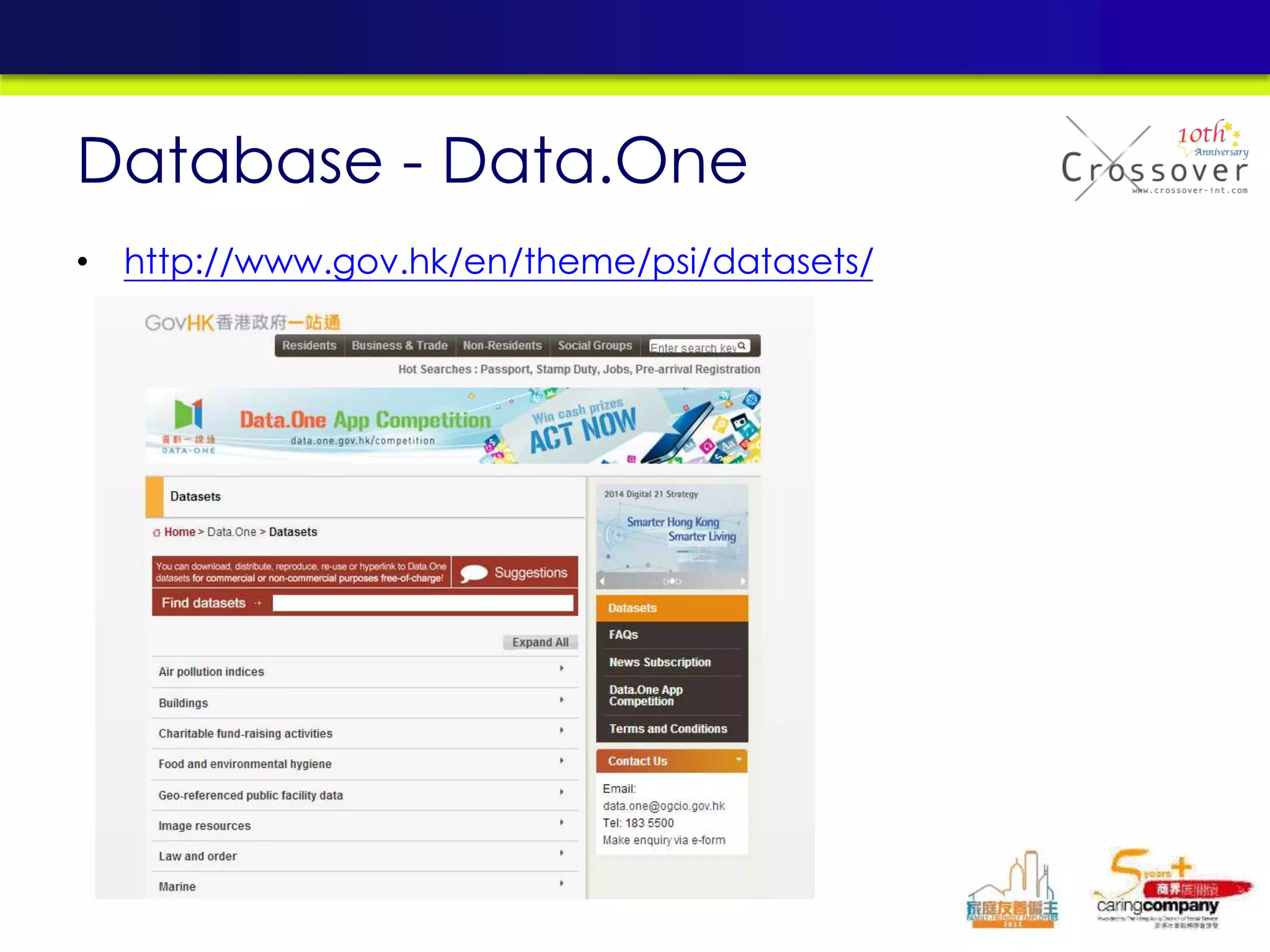
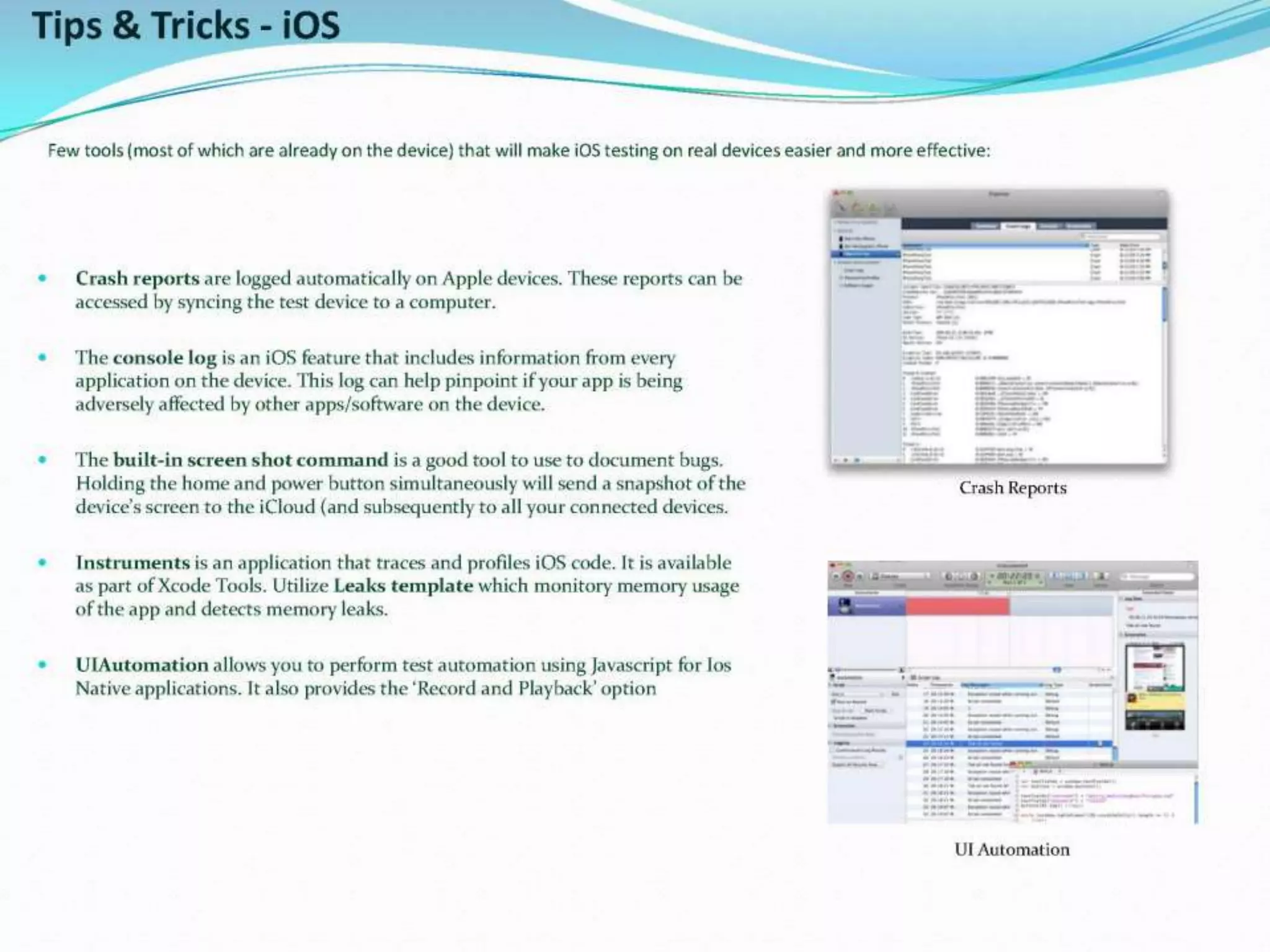
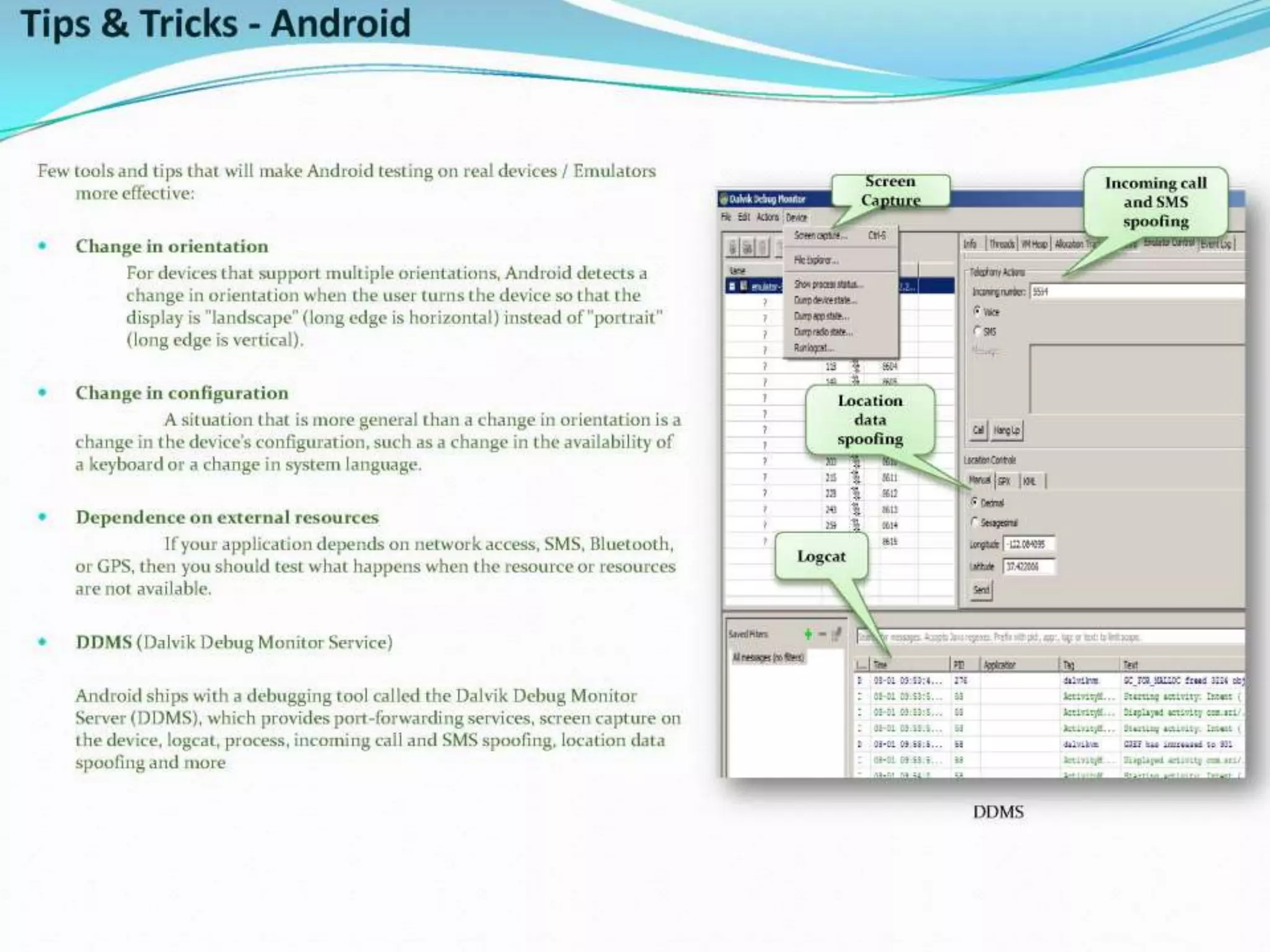
This document provides an overview and agenda for a presentation on practical mobile app testing. It discusses trends in mobile devices and platforms, differences between mobile web and apps, platforms for mobile development, challenges in mobile app testing, and strategies and best practices for testing. It also presents a case study of a mobile app called "SOS! Sick Bird" that helps users in Hong Kong locate nearby government clinics.