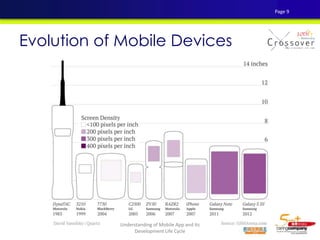
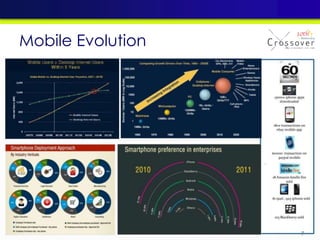
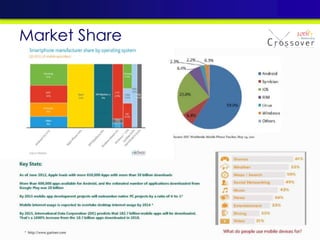
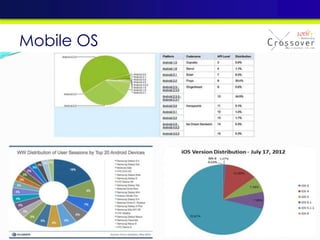
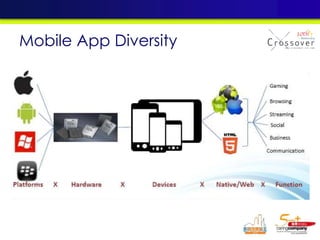
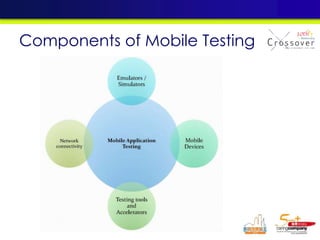
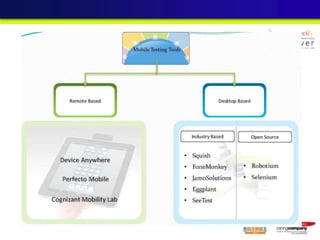
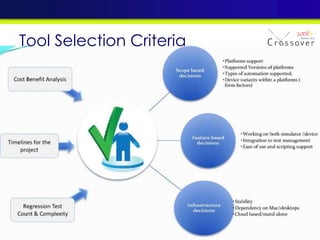
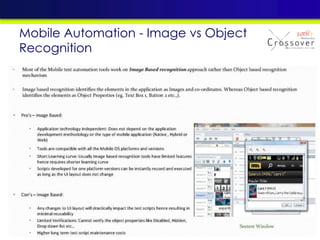
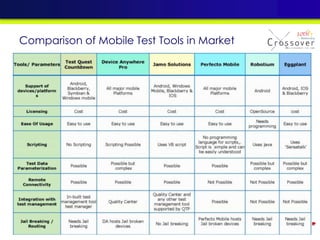
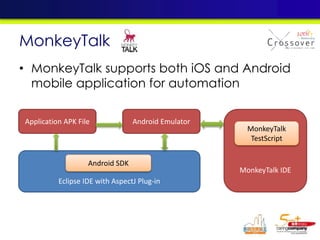
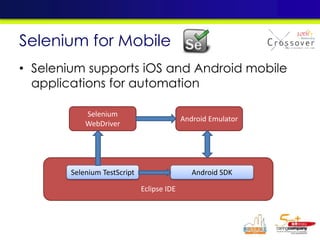
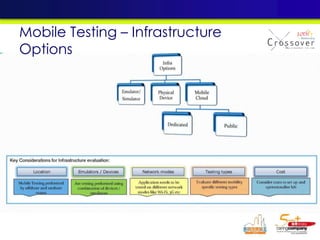
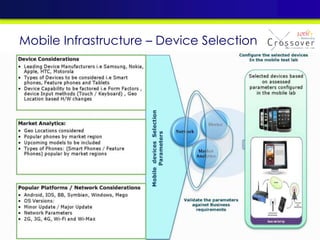
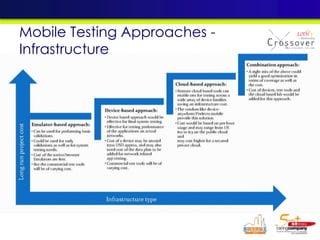
The document discusses mobile testing trends and provides information about:
1) The differences between feature phones and smartphones, including that smartphones can run third-party apps while feature phones have a fixed set of functions.
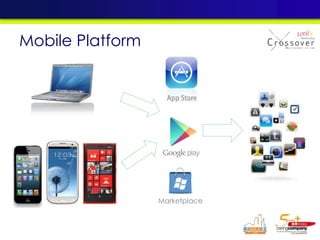
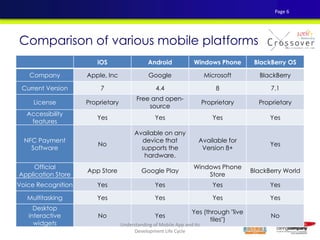
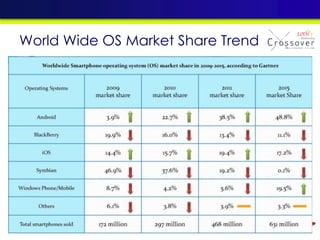
2) An overview of different mobile platforms like iOS, Android, Windows Phone and BlackBerry and their key features.
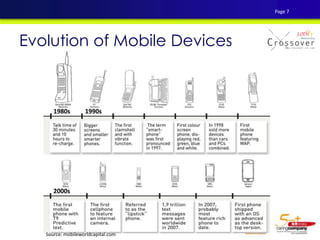
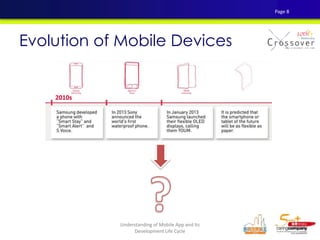
3) The evolution of mobile applications and different types of apps available on app stores.
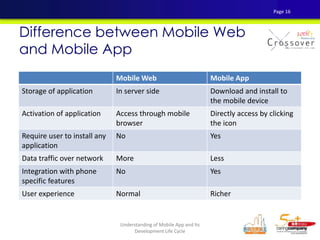
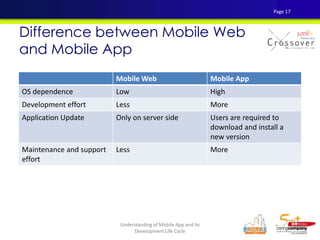
4) The differences between mobile web apps and native mobile apps and their development approaches.