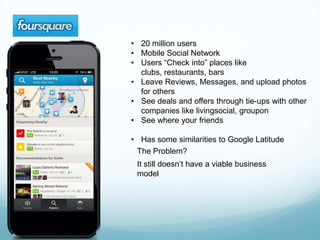
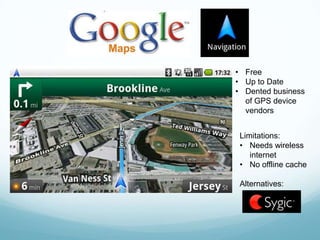
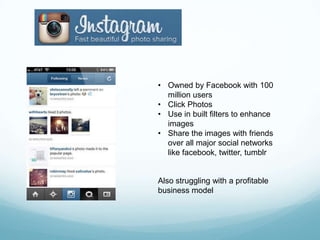
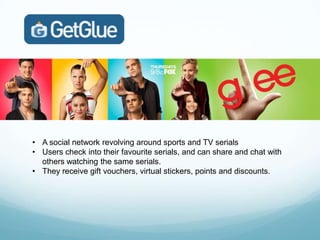
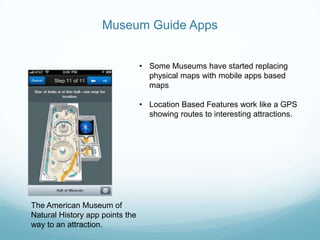
The document discusses mobile computing, describing the components of mobile devices including CPUs, storage, wireless connectivity, and mobile operating systems. It also covers types of mobile applications such as native apps and browser-based apps, considerations for developing mobile apps, and examples of popular mobile apps including Spotify, Foursquare, Instagram, and check-in rewards apps. Mobile apps offer opportunities for economic growth by providing services that desktop software cannot through the mobility and connectivity of smartphones.