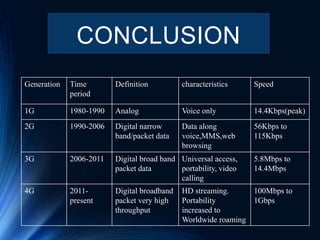
This document summarizes the evolution of mobile communication technologies from 1G to 5G. It provides an overview of each generation including key features and technologies. 1G introduced the first wireless telephone networks in the 1980s allowing for voice calls with poor quality. 2G launched in 1991 and used digital signals, enabling text messages and multimedia. 3G began in 2006 and increased speeds up to 2 Mbps for web and media. 4G started in 2011 and reached speeds from 100 Mbps to 1 Gbps for video calling and customized services. 5G is expected to provide even faster wireless communication with almost no limitations to support interactive multimedia applications.