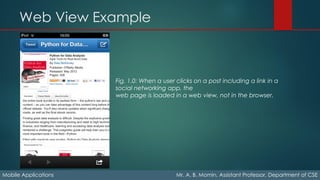
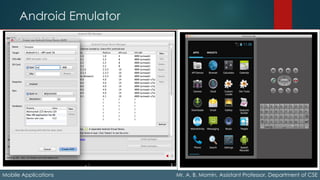
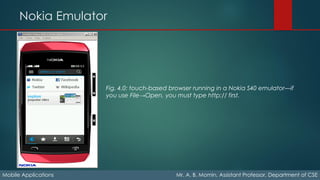
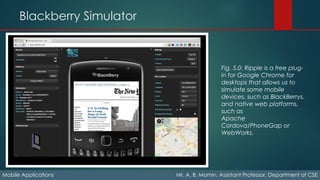
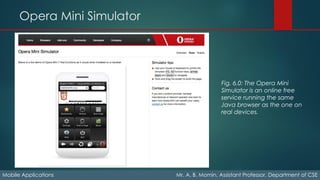
The document details the fundamentals of mobile applications, emphasizing the Wireless Application Protocol (WAP), its key features like push content and GPRS. It explores various input methods, device capabilities (like geolocation and sensors), and web platforms for mobile development, including native, packaged, and hybrid applications. Additionally, it discusses tools and environments for mobile web development, emulators, and simulators used for testing applications across different devices.