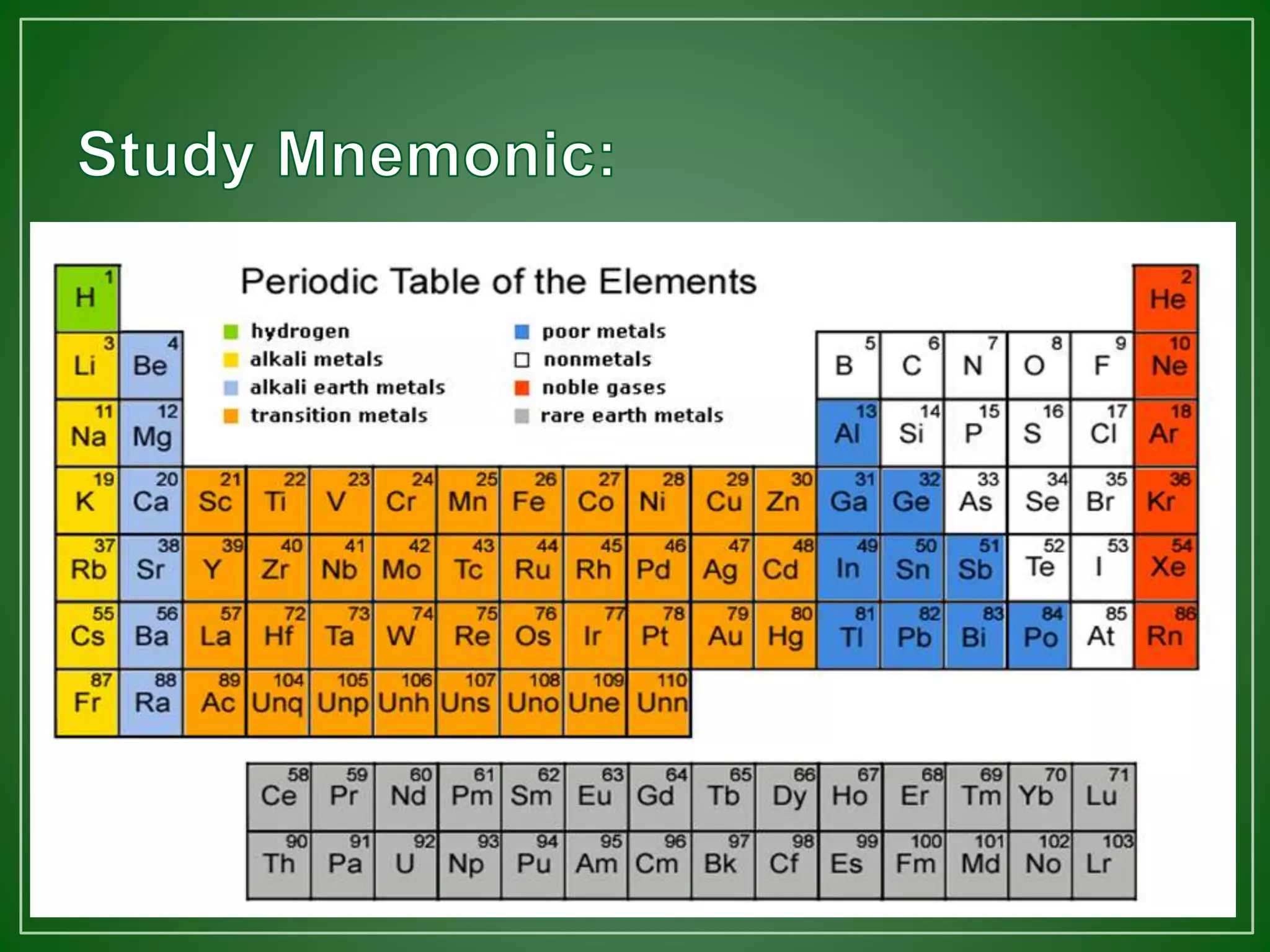
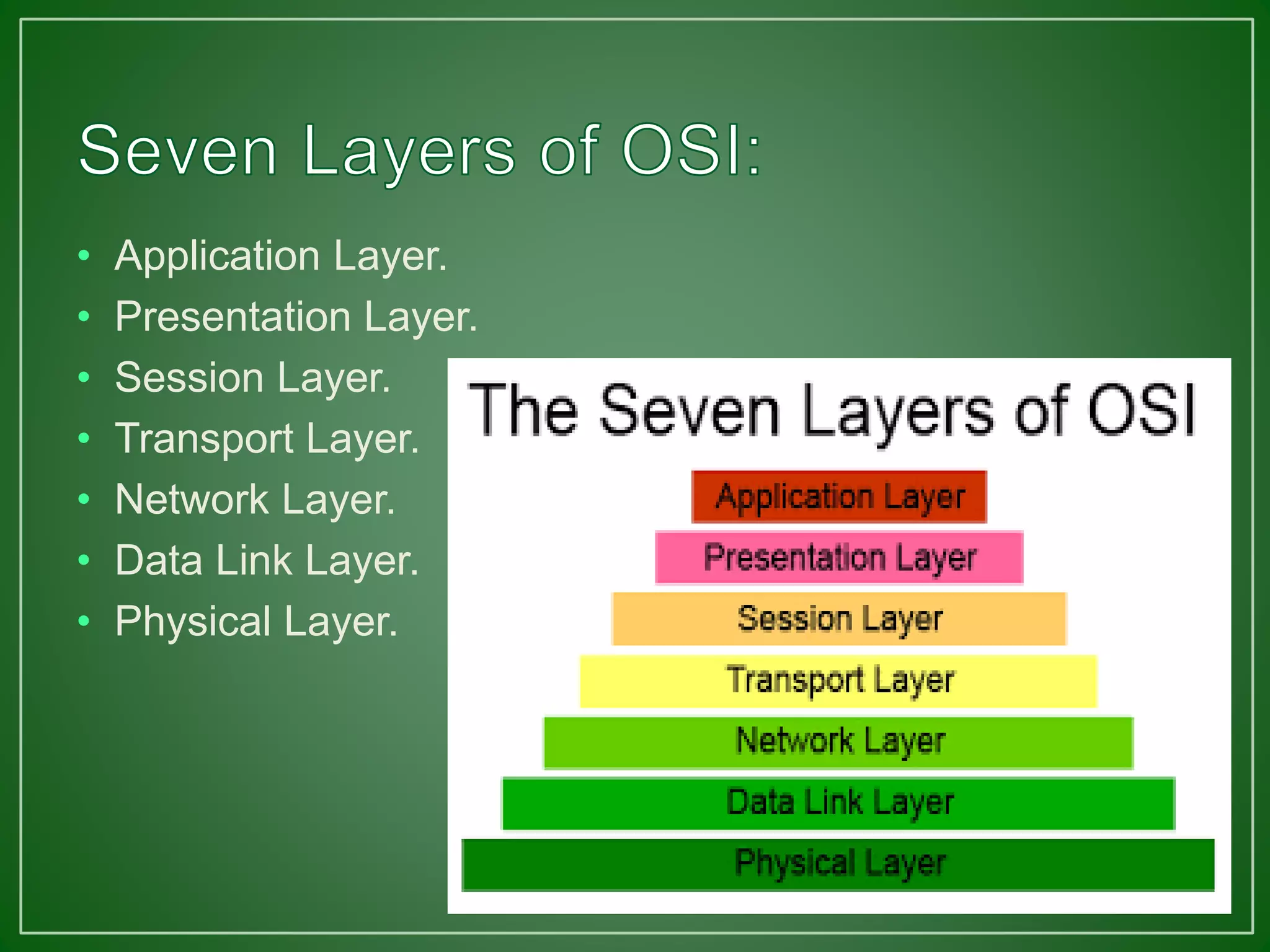
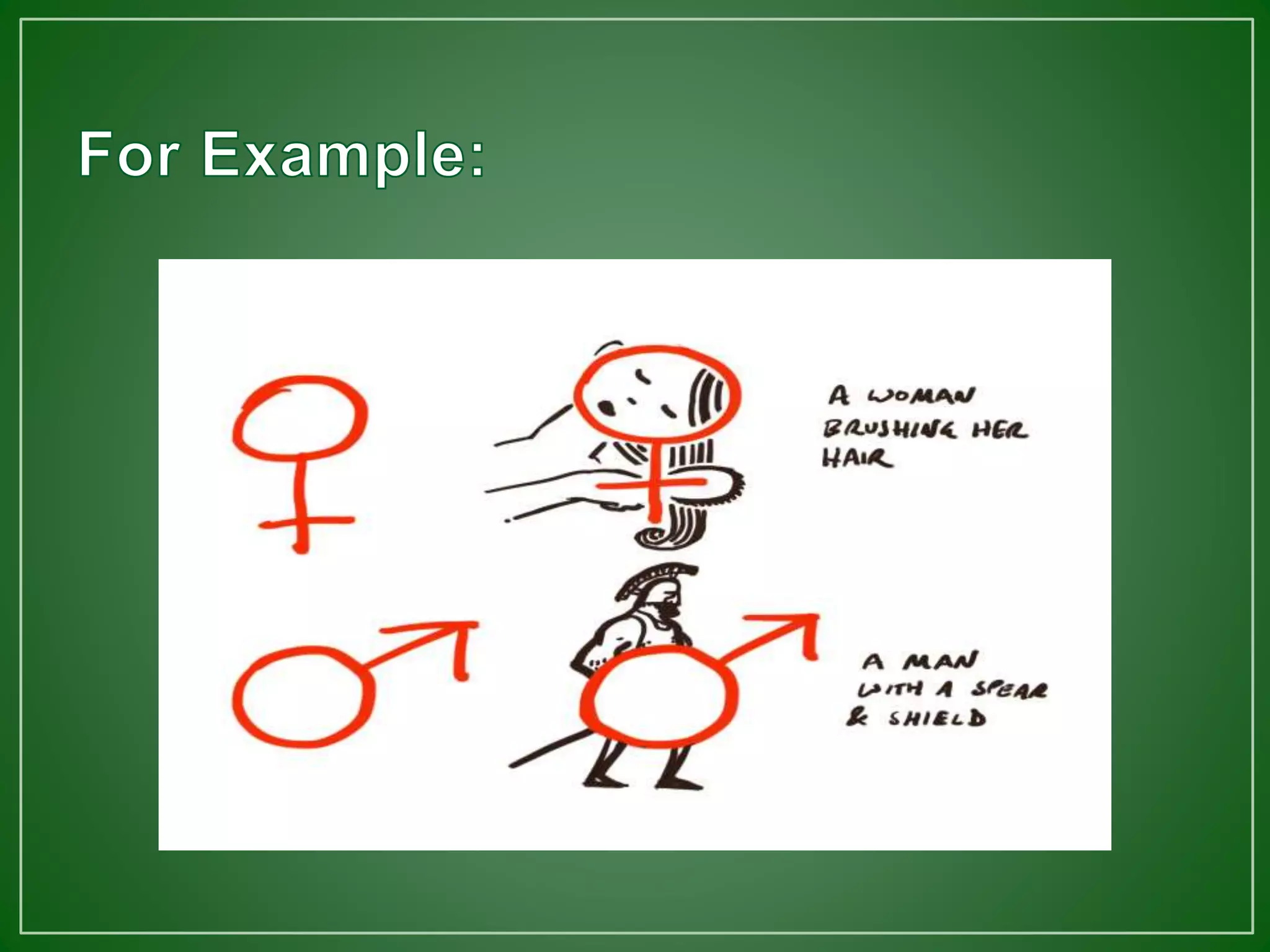
The document discusses mnemonic devices, which are techniques to enhance memory and recall by breaking down complex information into manageable chunks. It describes various types of mnemonics, such as music mnemonics, name mnemonics, expression mnemonics, and others, and provides examples for each type. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of note organization and using creative imagery to aid memorization.