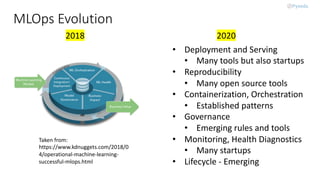
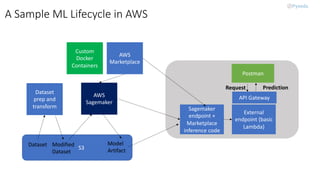
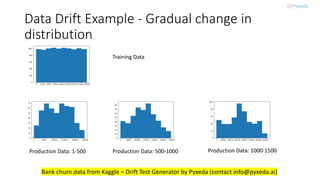
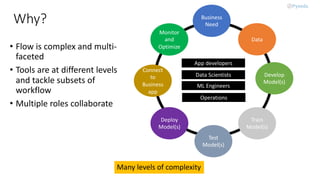
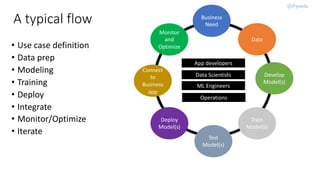
MLOps, a practice combining machine learning and operations, focuses on collaboration to manage the production ML lifecycle, evolving from simple best practices into a comprehensive approach. Despite the availability of sophisticated AI technologies and cloud services, adoption remains minimal due to the complexity of integration among multiple roles and tools. The future of MLOps will likely expand to include aspects like validation, security, adaptability, and scalability.




![MLOps – the term
• Production ML has been done
for many years in large web
companies and others
• First MLOps Platform for
enterprises – from ParallelM in
2018
• Inspired by Database practices
and DBAs, Software lifecycle
• Focus on full lifecycle tooling
combined with Best Practices
• https://www.kdnuggets.com/2
018/04/operational-machine-
learning-successful-mlops.html
MLOps (a compound of “machine learning” and
“operations”) is a practice for collaboration and
communication between data scientists and operations
professionals to help manage production ML (or deep
learning) lifecycle.[1] Similar to
the DevOps or DataOps approaches, MLOps looks to
increase automation and improve the quality of production
ML while also focusing on business and regulatory
requirements. While MLOps also started as a set of best
practices, it is slowly evolving into an independent
approach to ML lifecycle management. MLOps applies to
the entire lifecycle - from integrating with model
generation (software development lifecycle, continuous
integration/continuous delivery), orchestration, and
deployment, to health, diagnostics, governance, and
business metrics.
https://www.kdnuggets.com/2018/04/operational-machine-
learning-successful-mlops.html](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mlopspastpresentfuture-200824234353/85/Ml-ops-past_present_future-7-320.jpg)