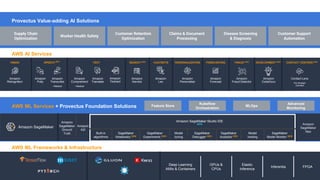
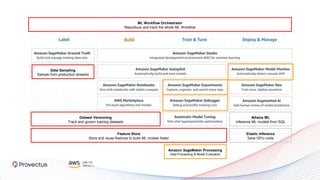
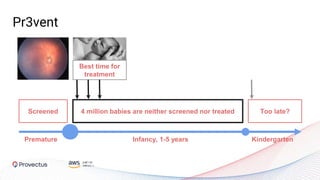
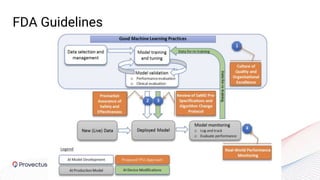
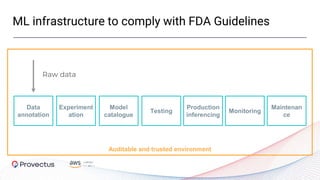
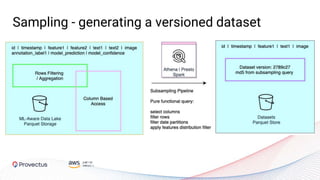
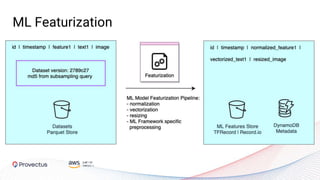
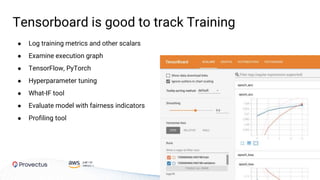
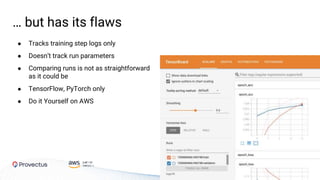
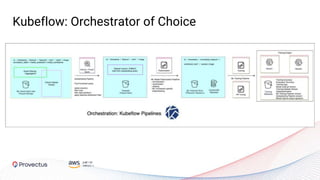
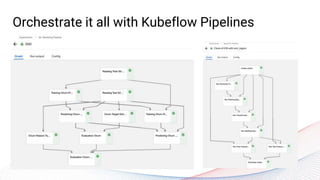
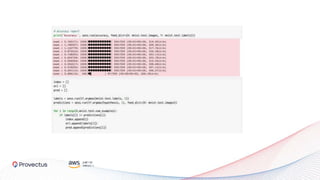
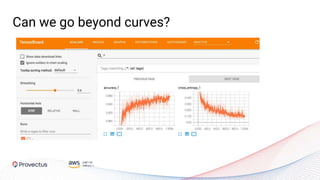
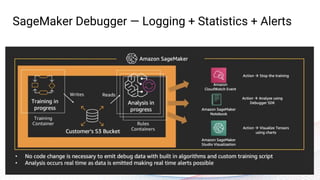
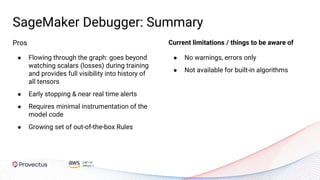
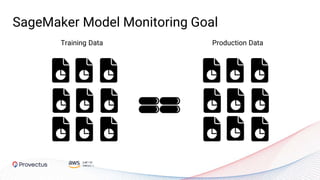
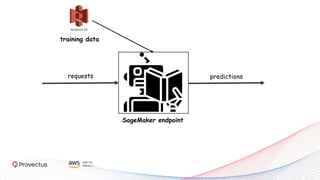
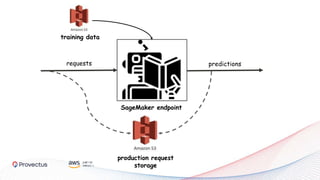
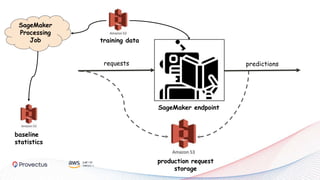
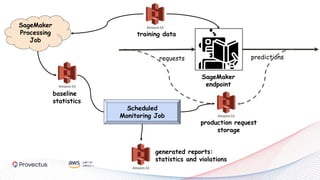
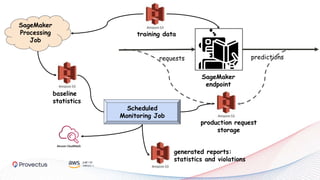
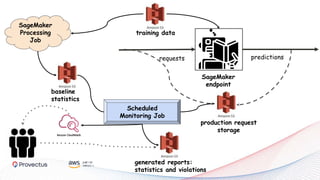
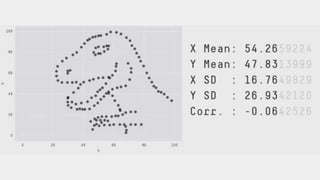
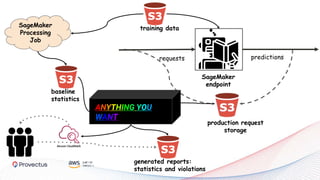
The webinar, presented by Provectus and AWS experts, discusses leveraging Amazon SageMaker for AI and machine learning solutions, emphasizing the importance of understanding its capabilities and best practices. Key topics include using SageMaker for various applications like disease screening and customer support automation, as well as integrating it with AWS infrastructure and tools. The session highlights the significance of data management and ML workflow orchestration to optimize model training and deployment.