Embed presentation
Downloaded 46 times

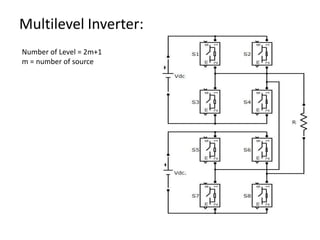

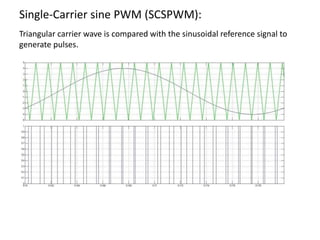
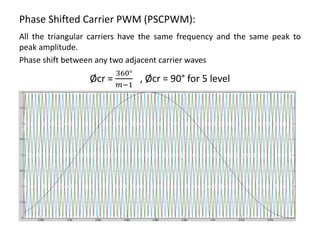
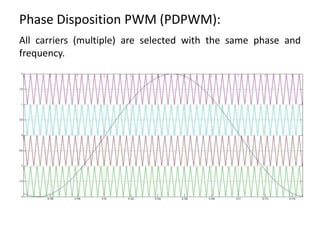
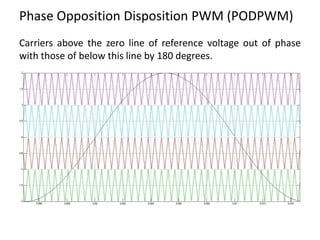
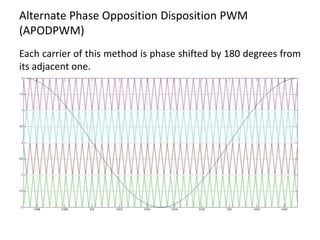
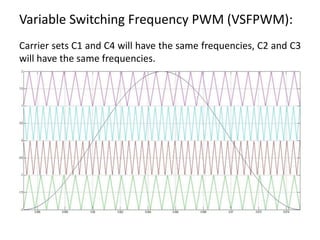
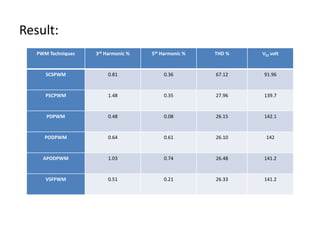

The document discusses various PWM techniques used in multilevel inverters, categorizing them into single-carrier and multi-carrier methods. It provides detailed descriptions of techniques like single-carrier sine PWM, phase shifted carrier PWM, and variable switching frequency PWM, alongside their performance metrics. Results indicate specific harmonic percentages and total harmonic distortion for each PWM technique, highlighting their effectiveness in inverter applications.









