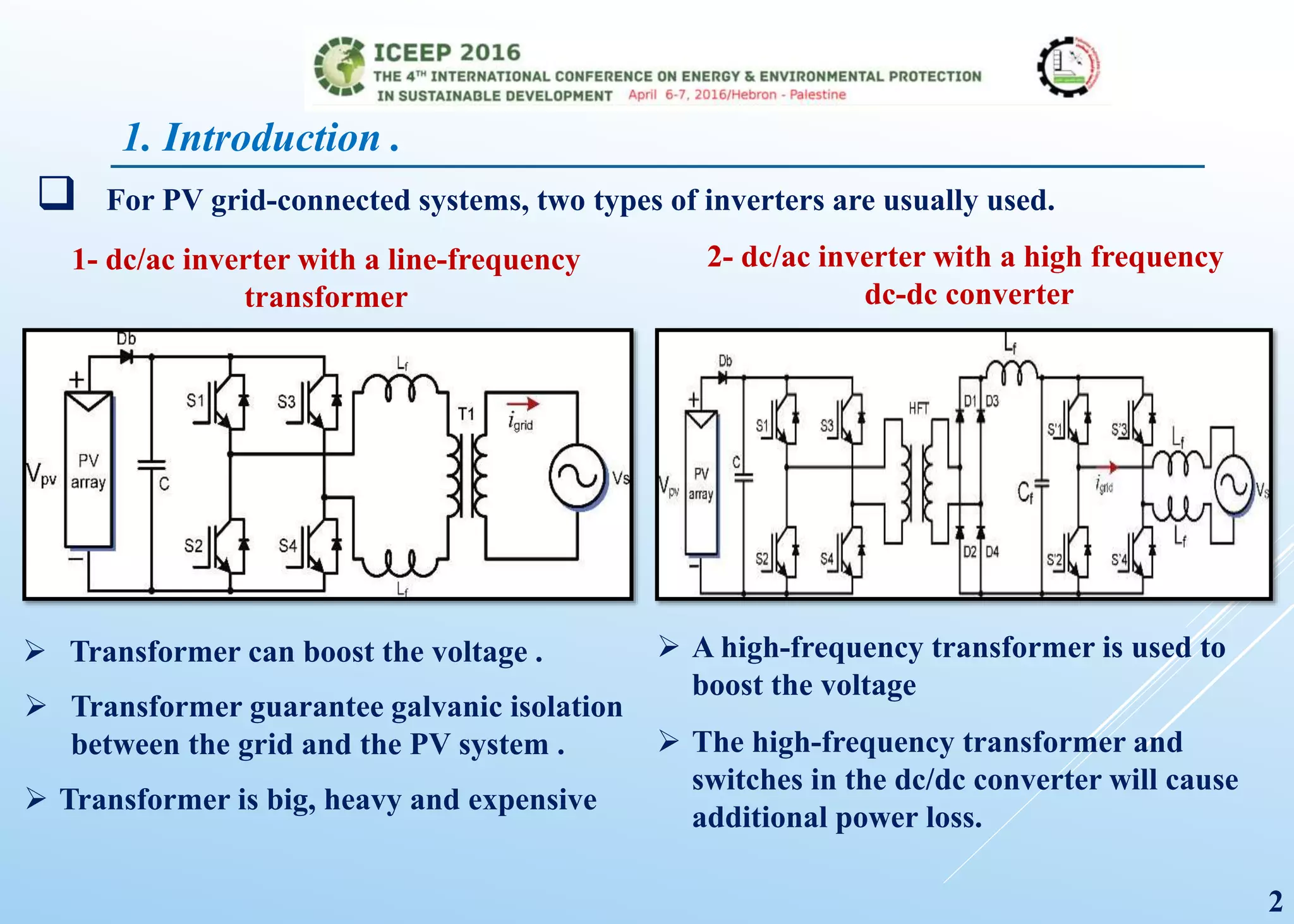
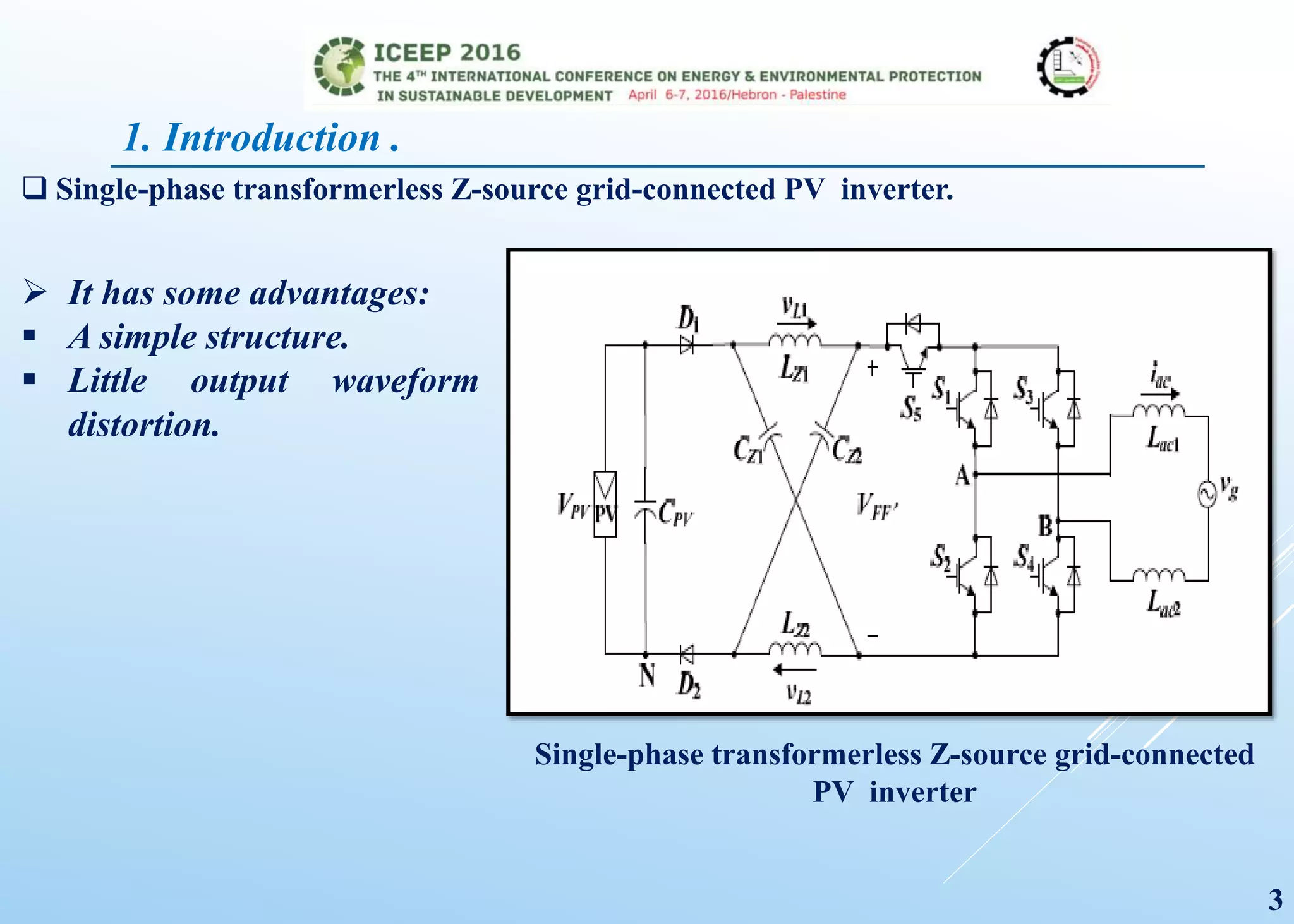
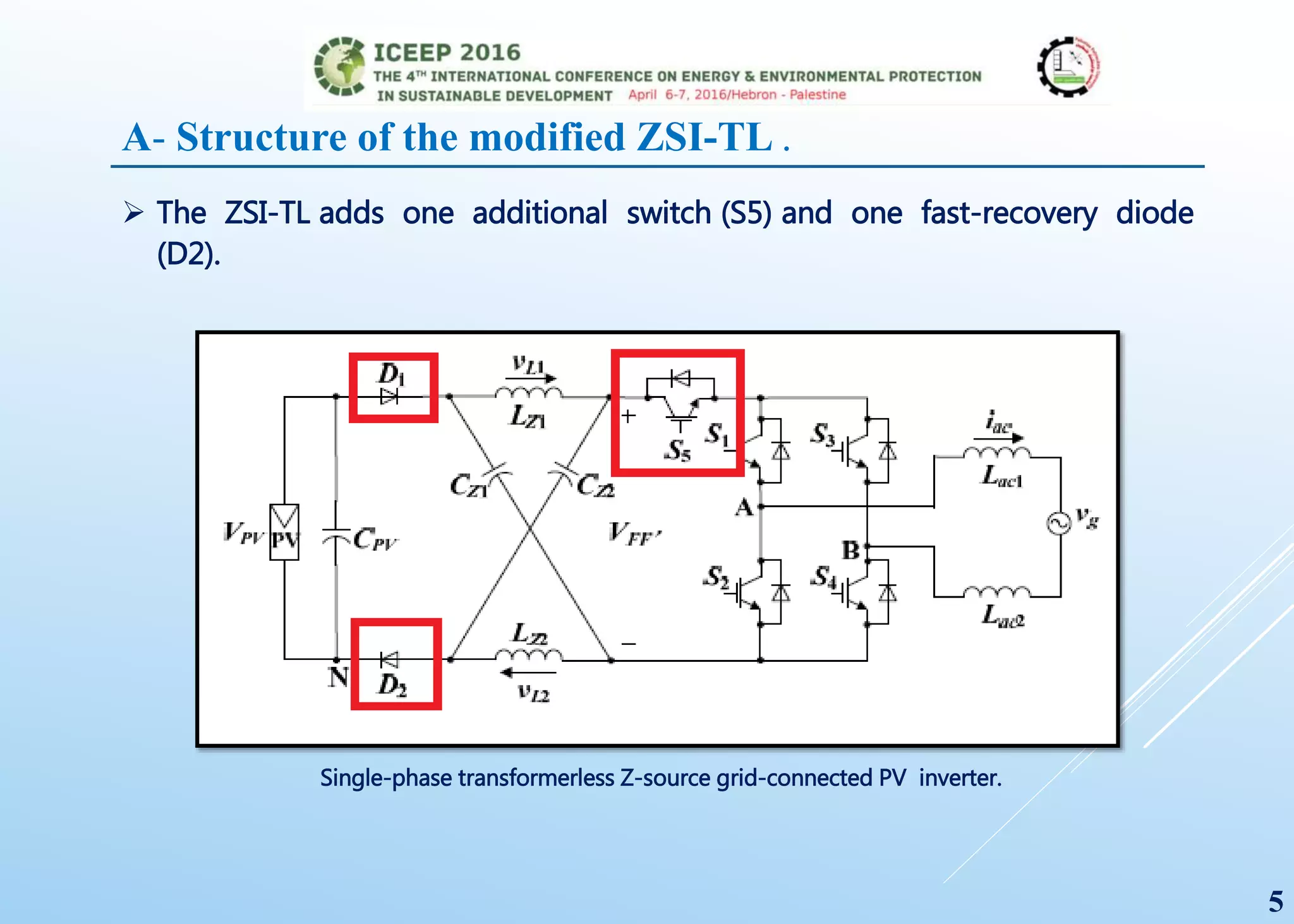
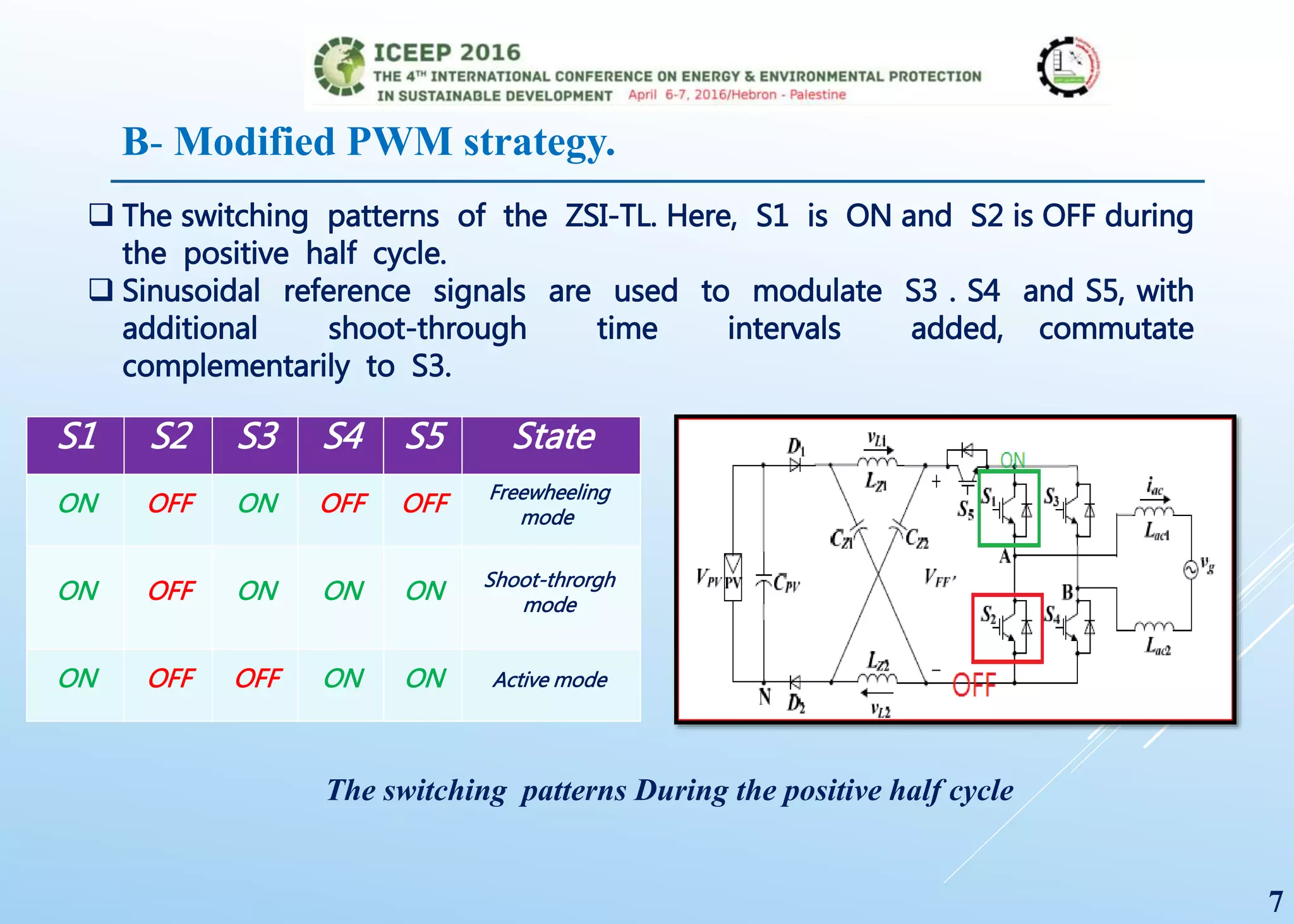
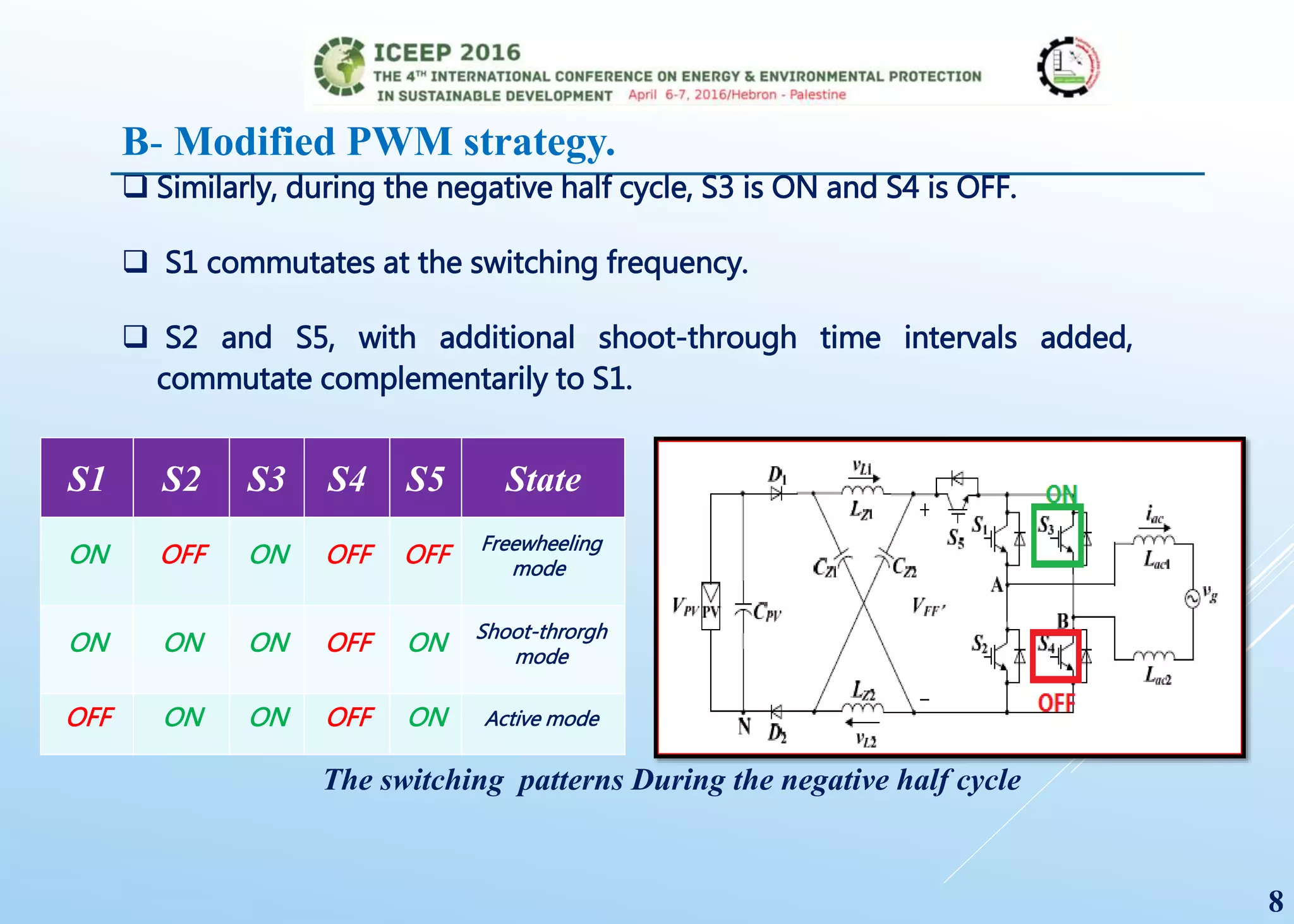
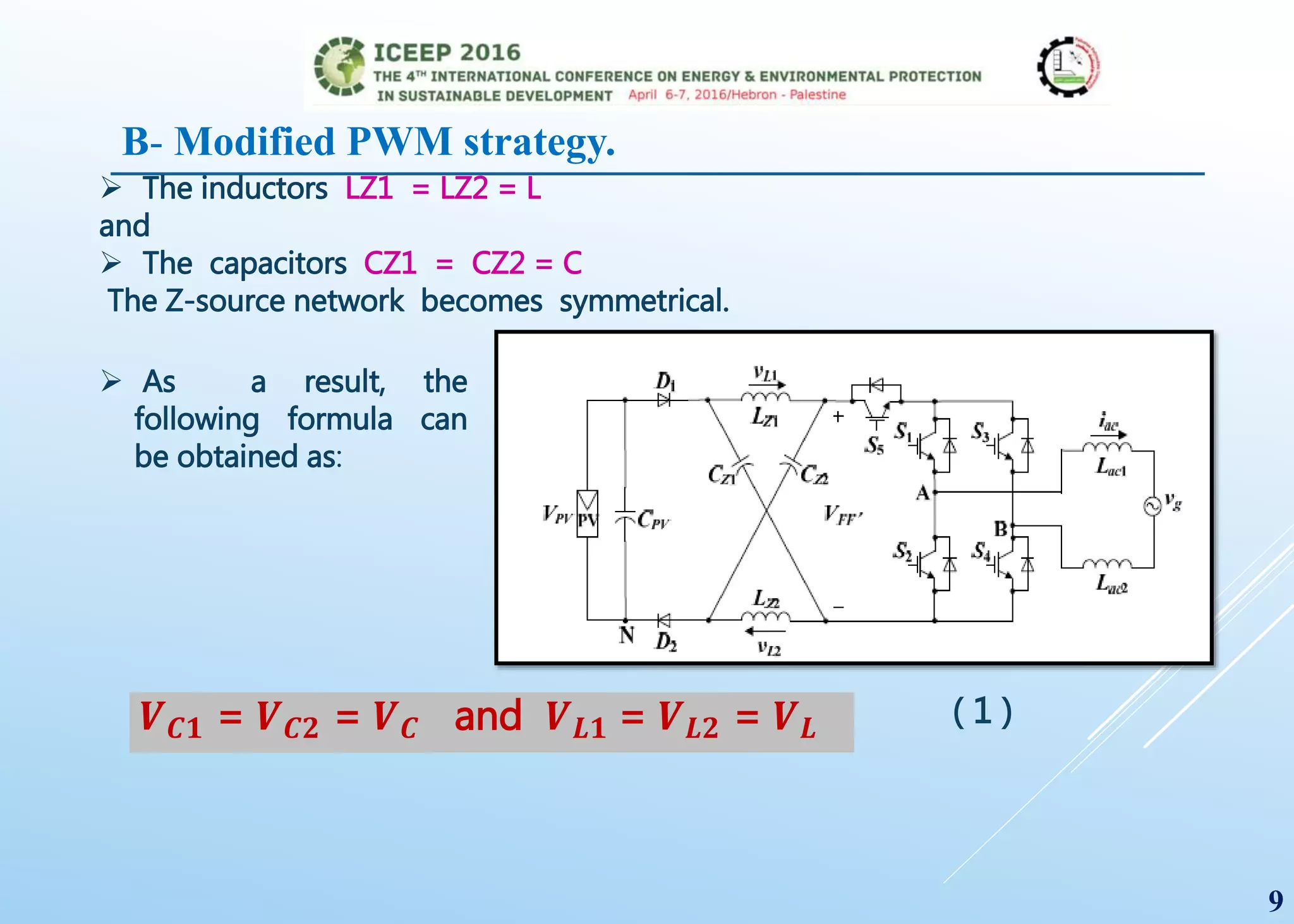
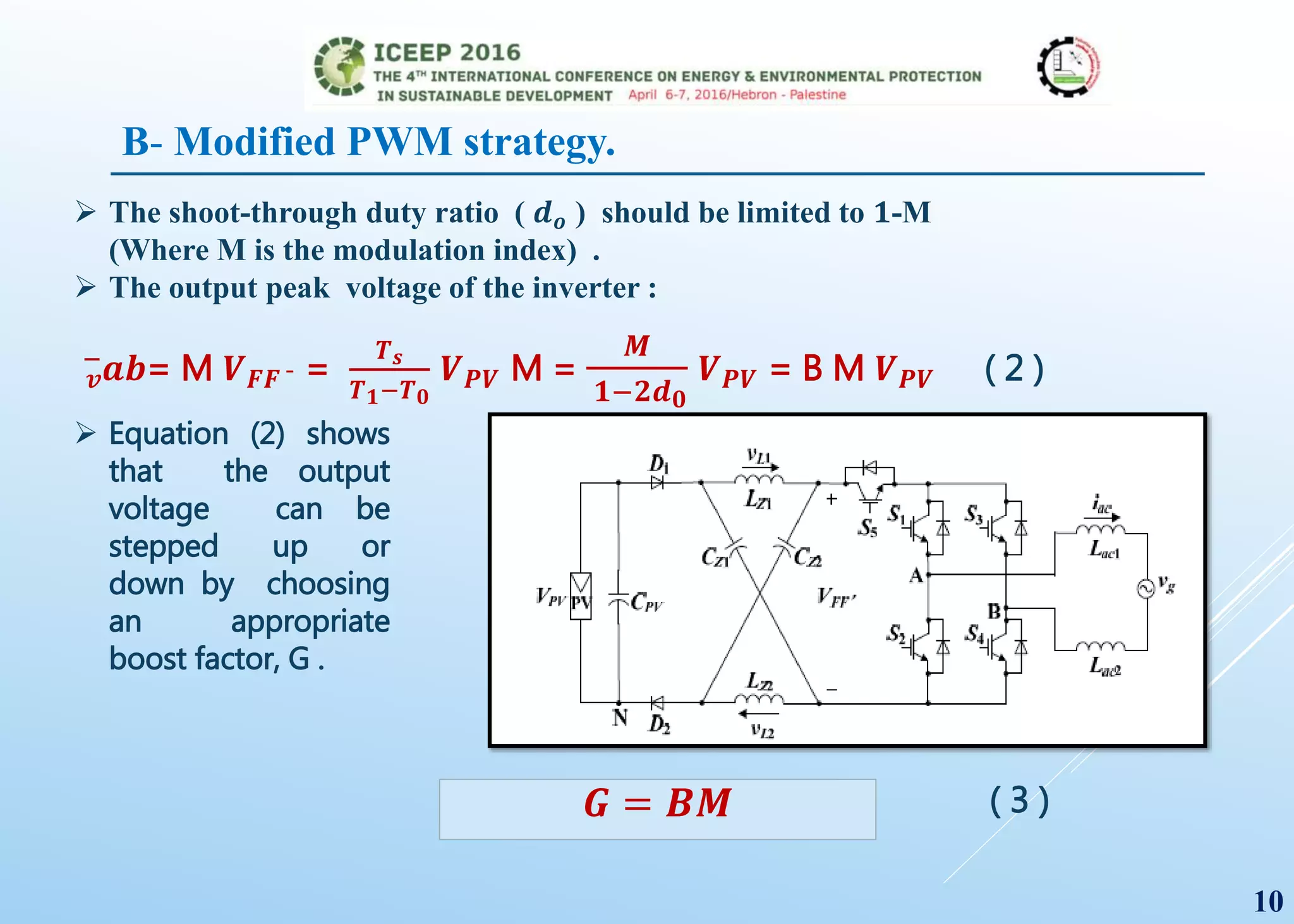
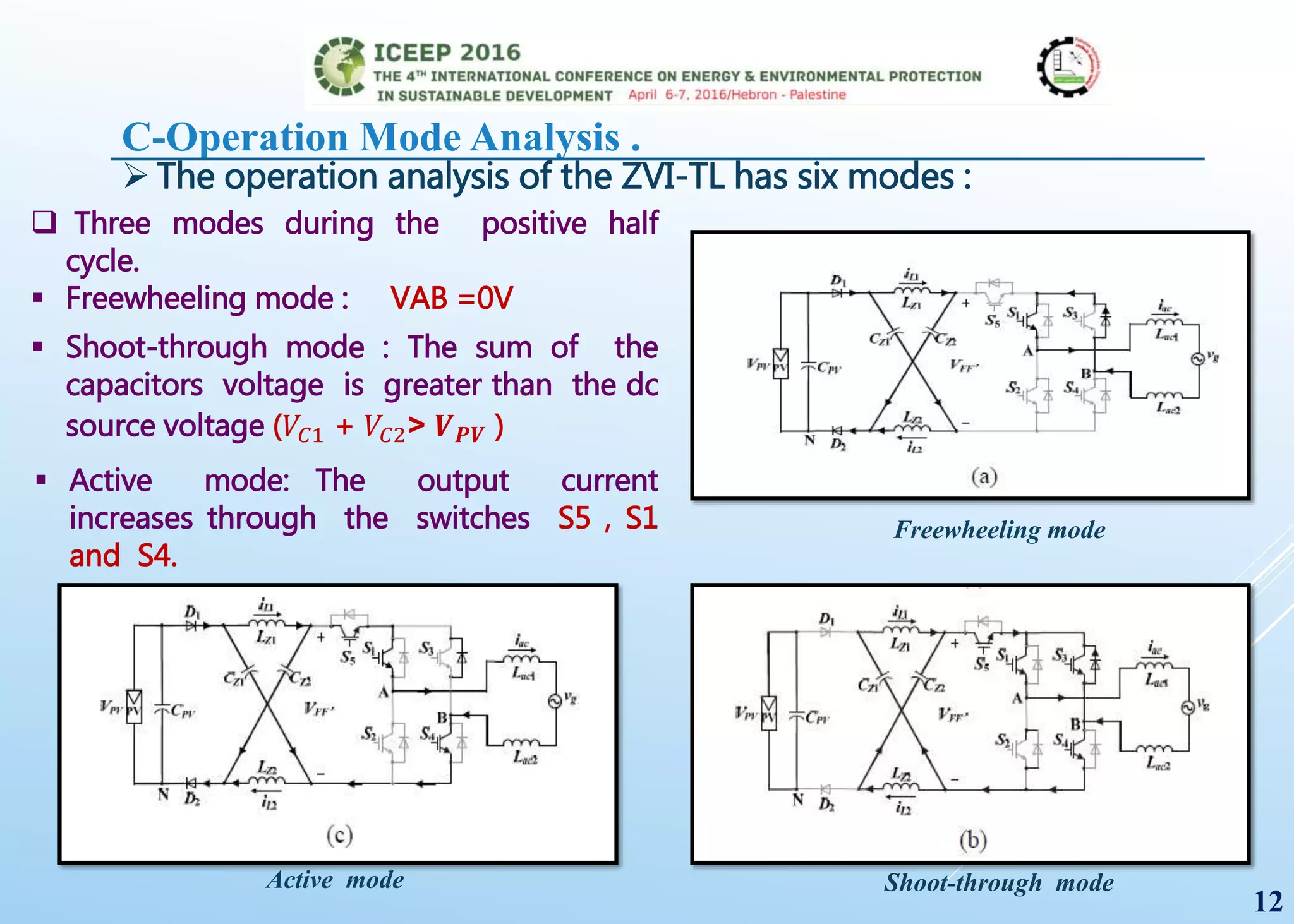
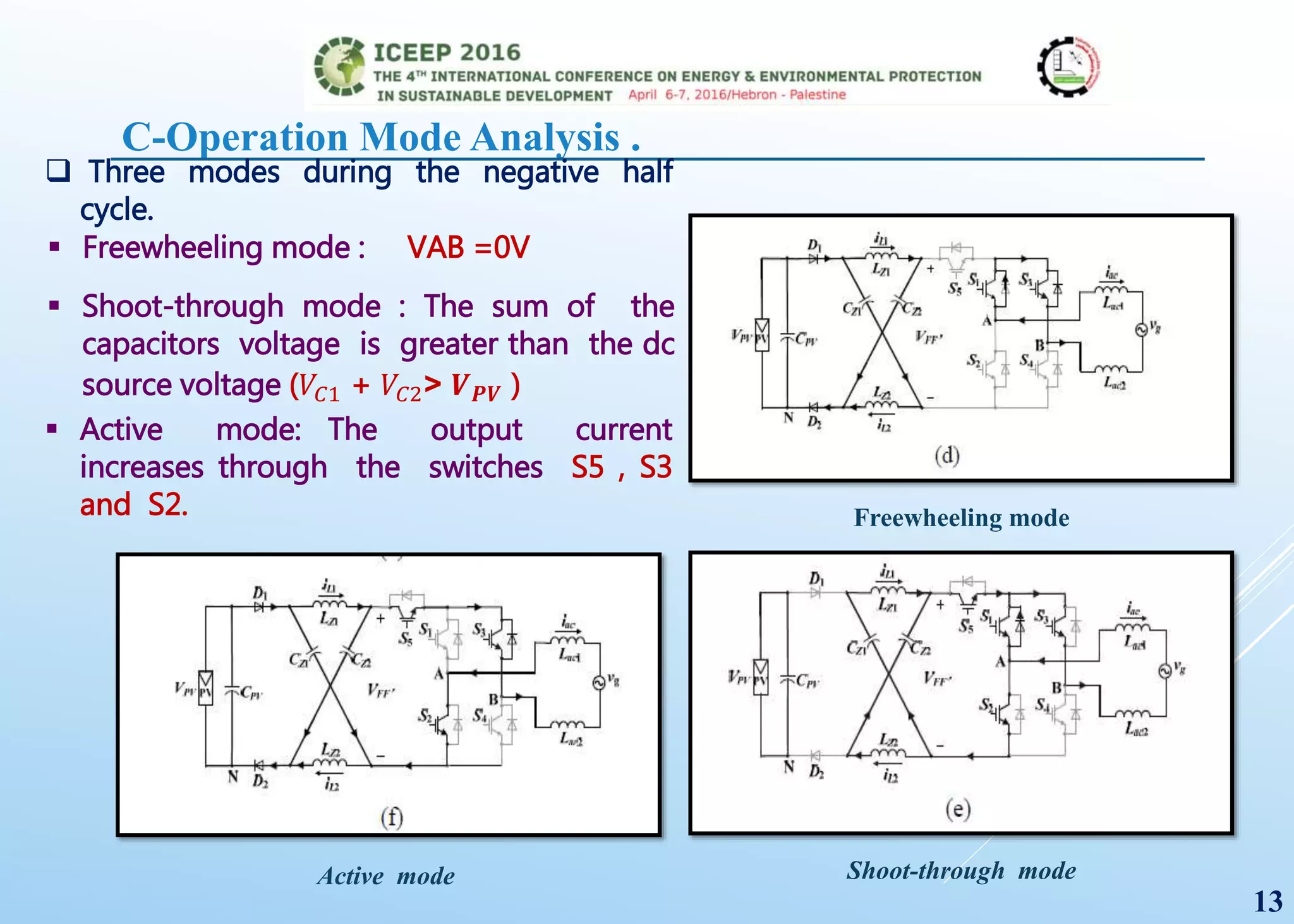
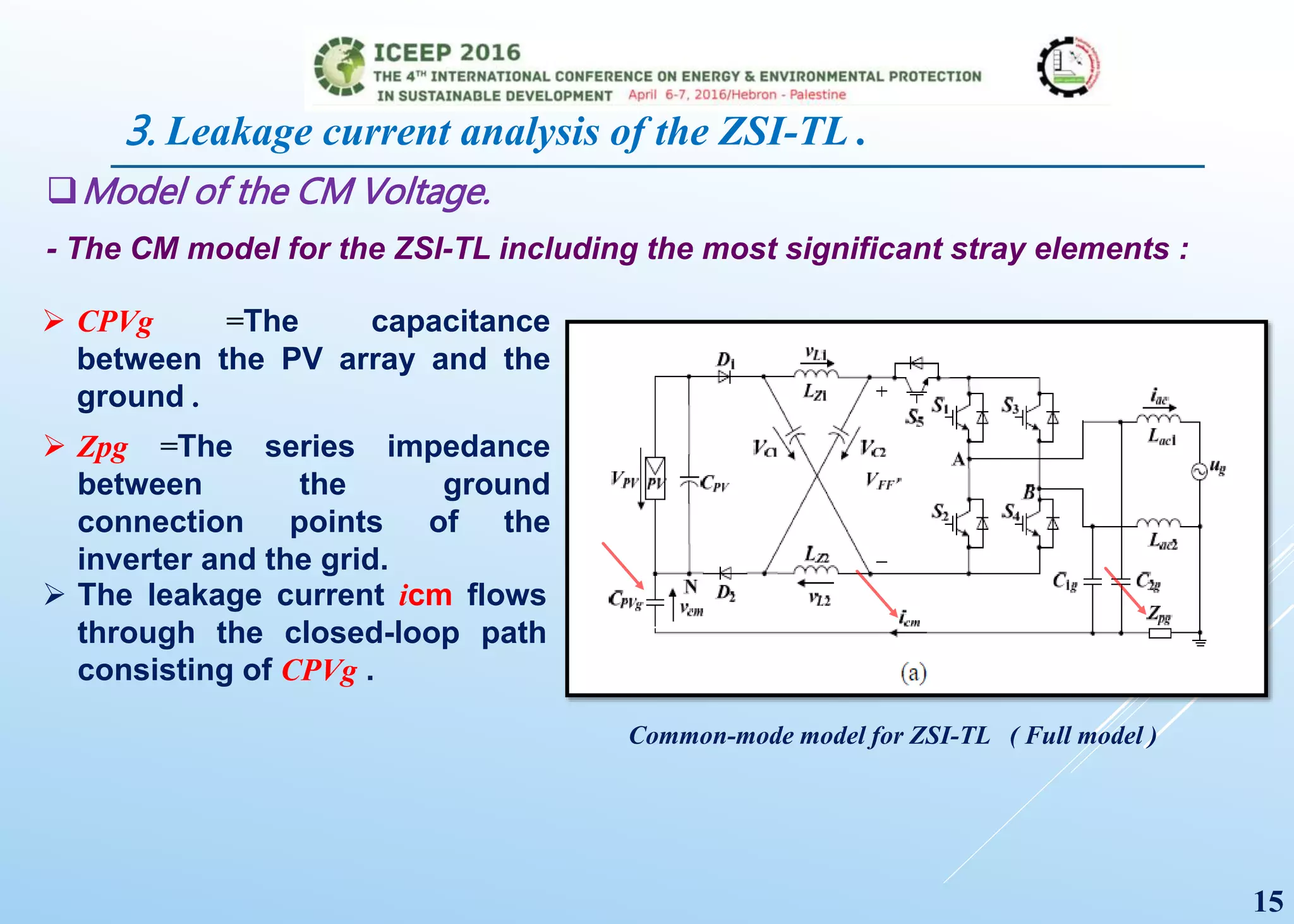
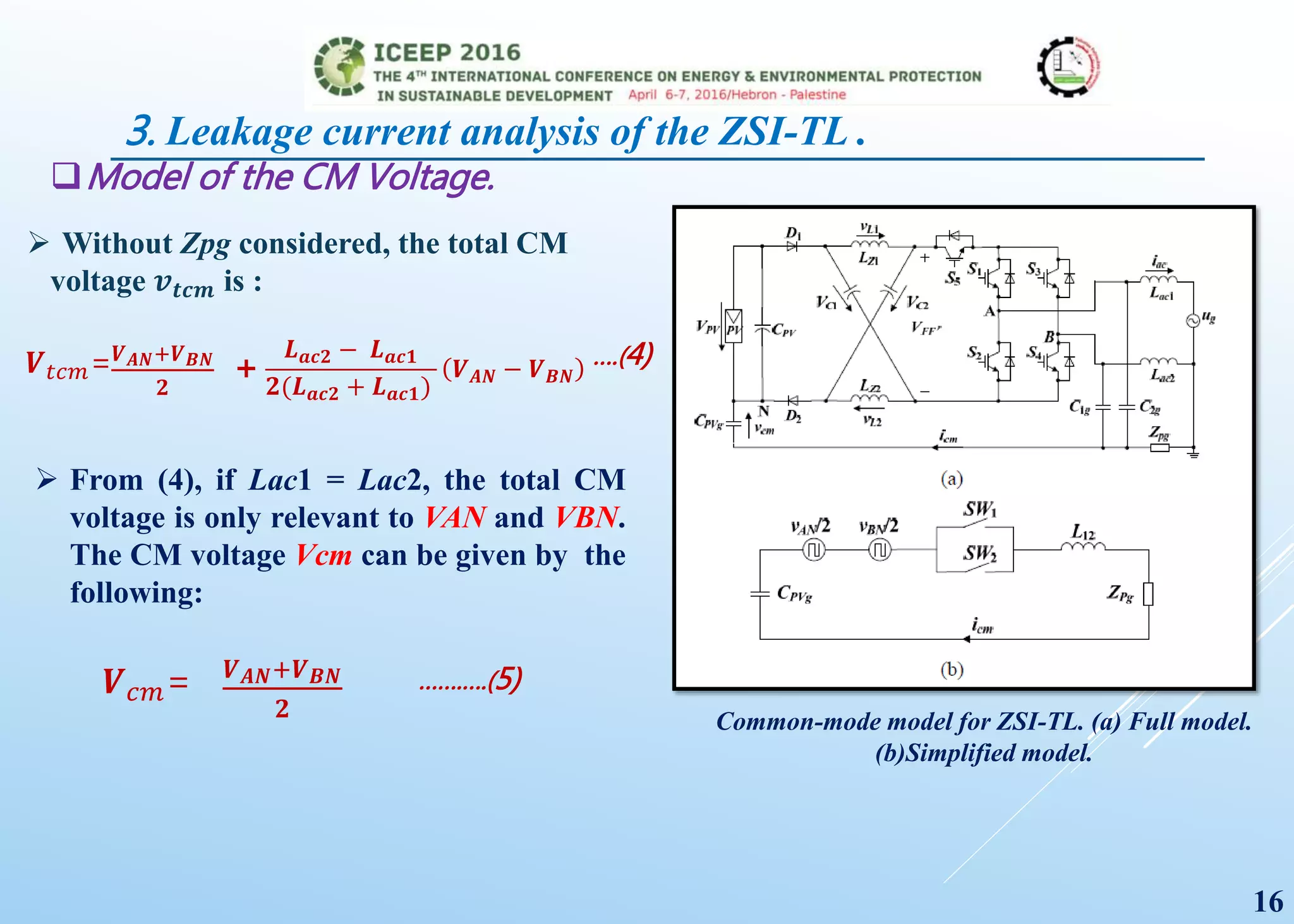
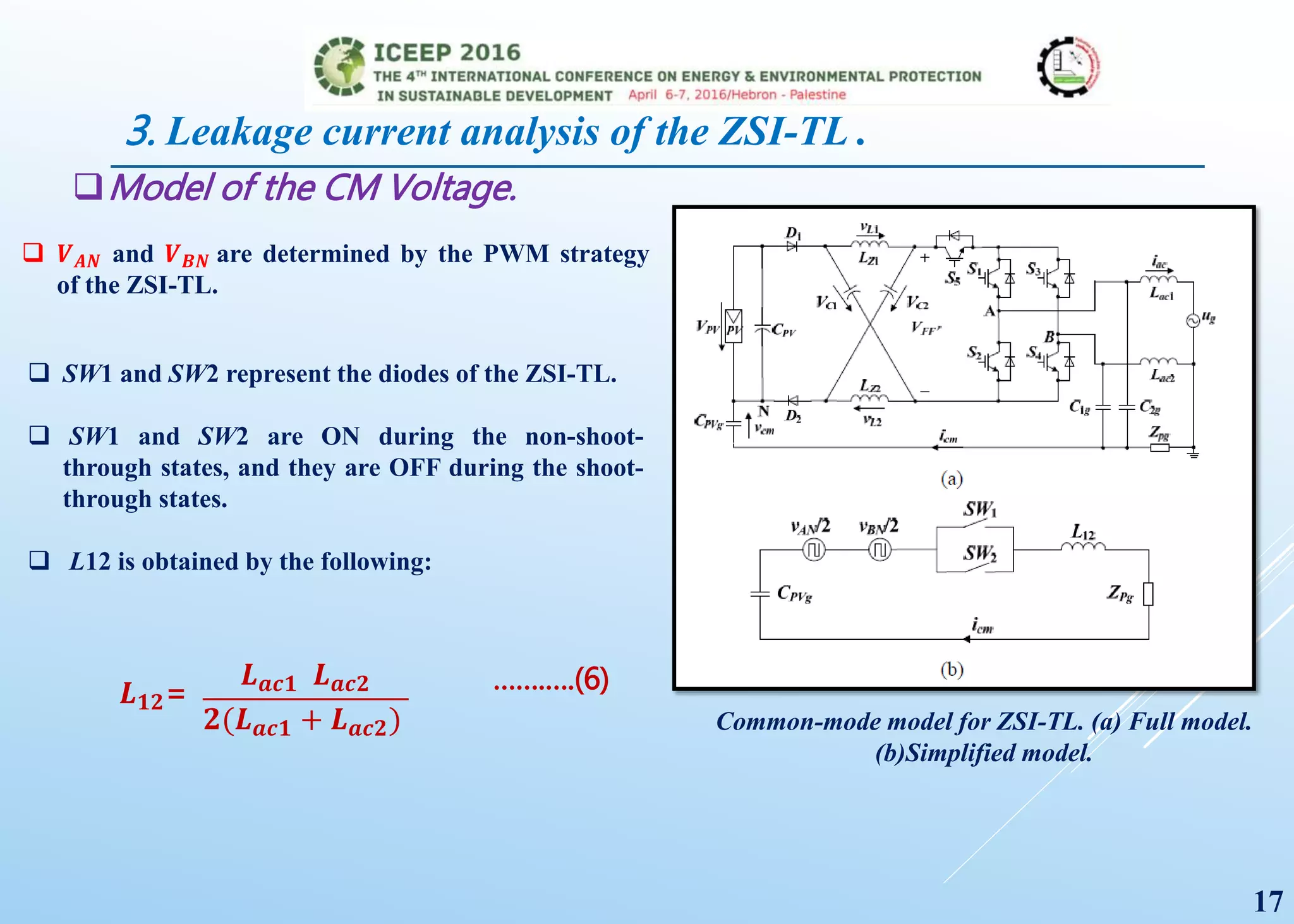
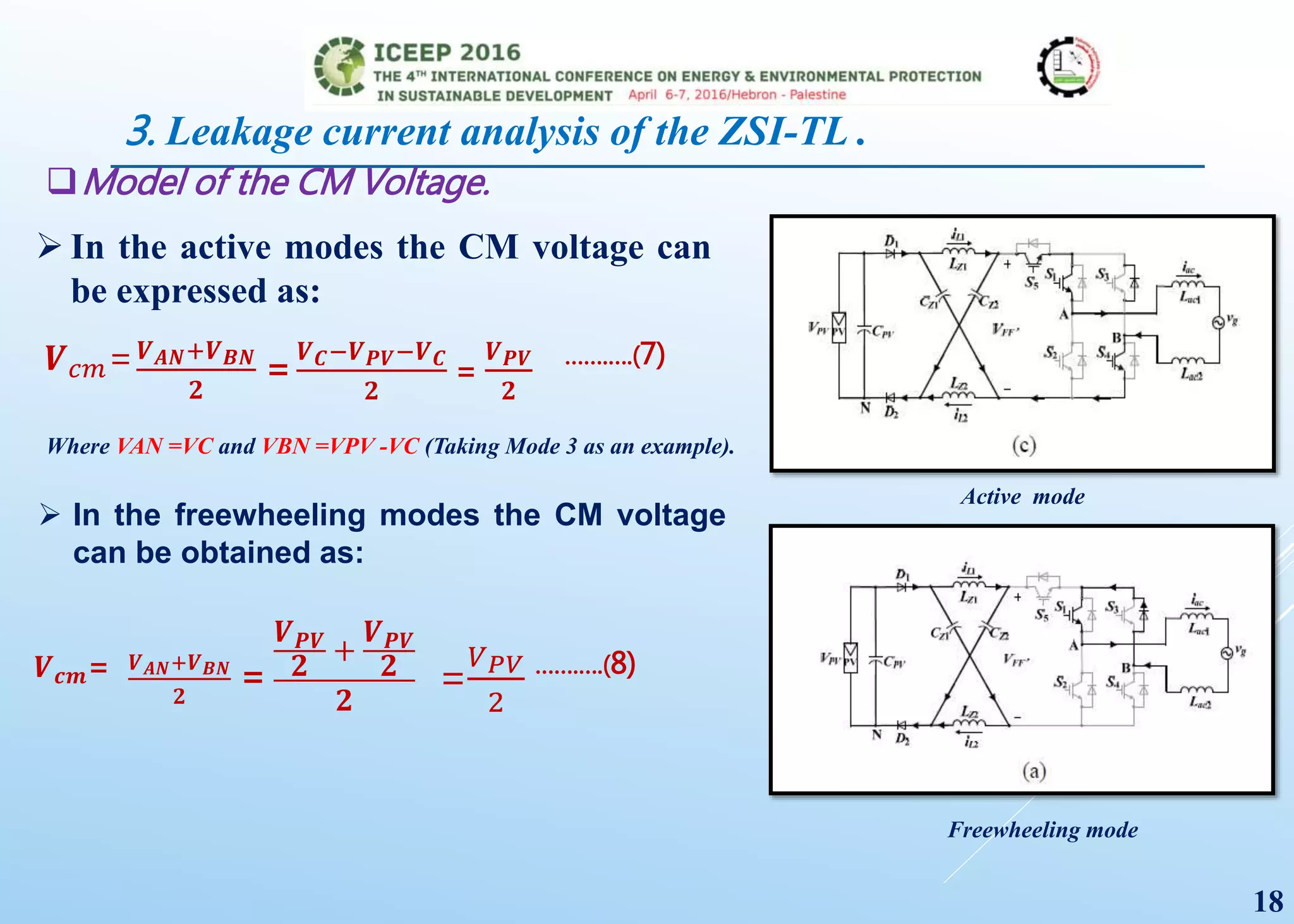
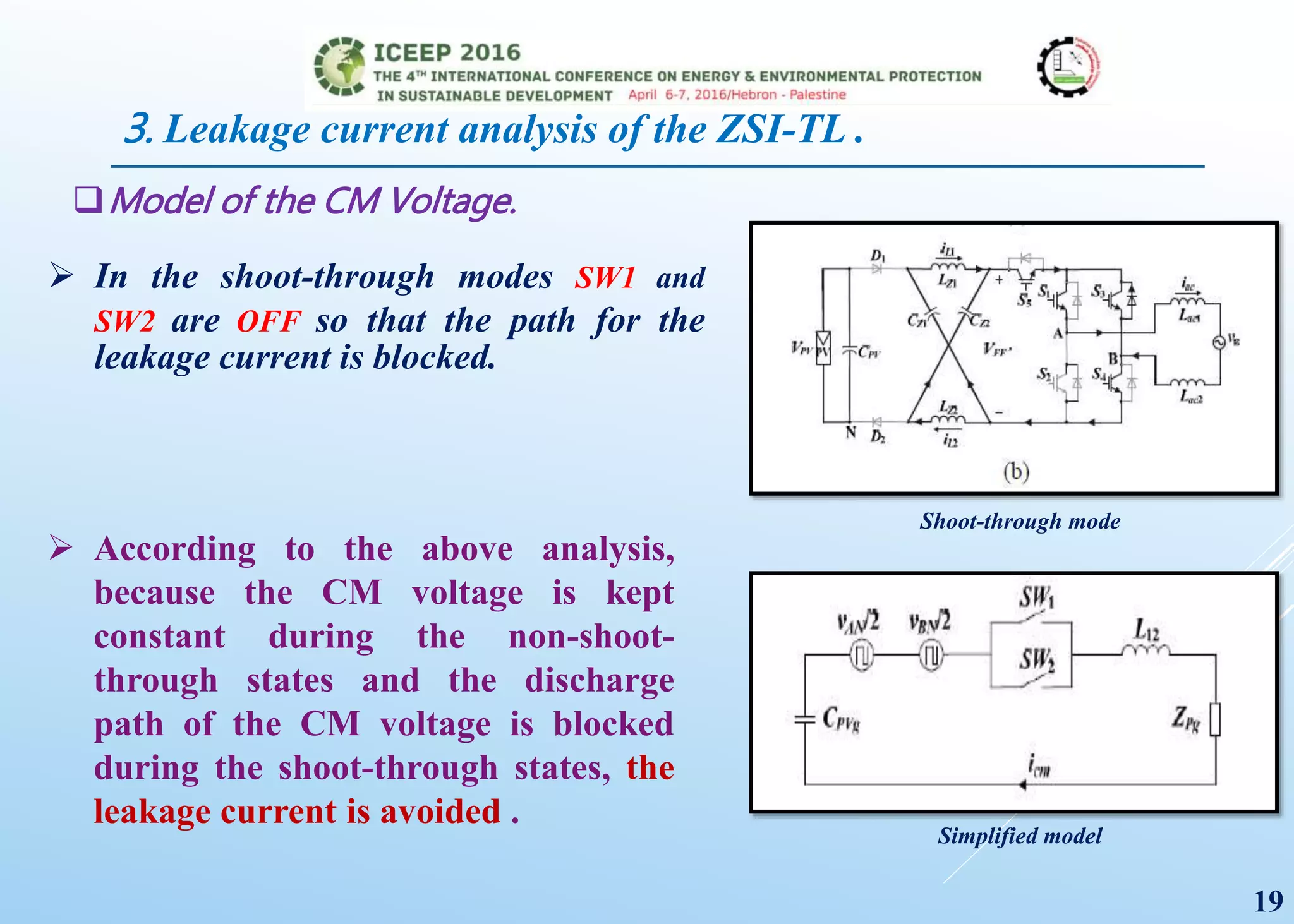
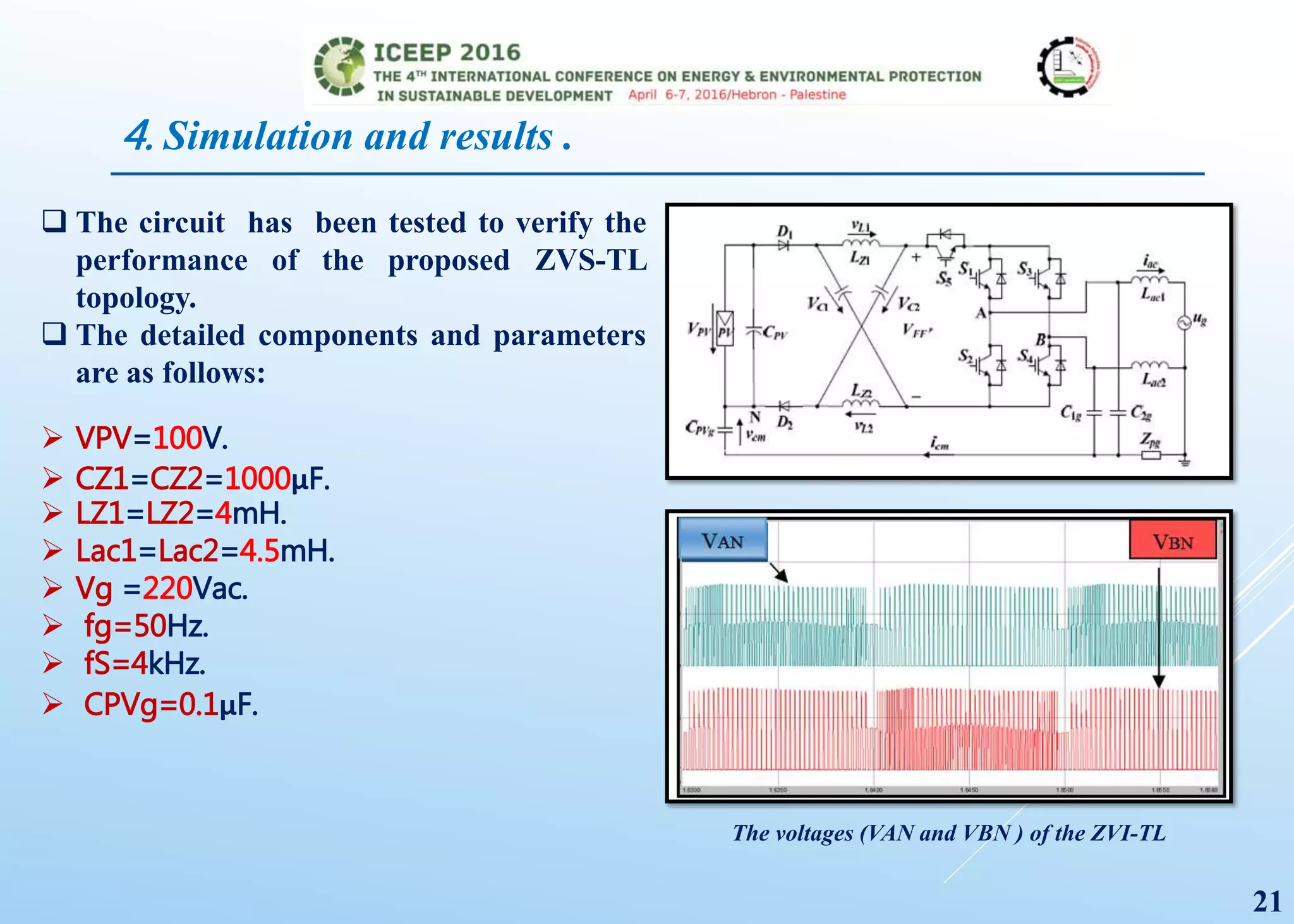
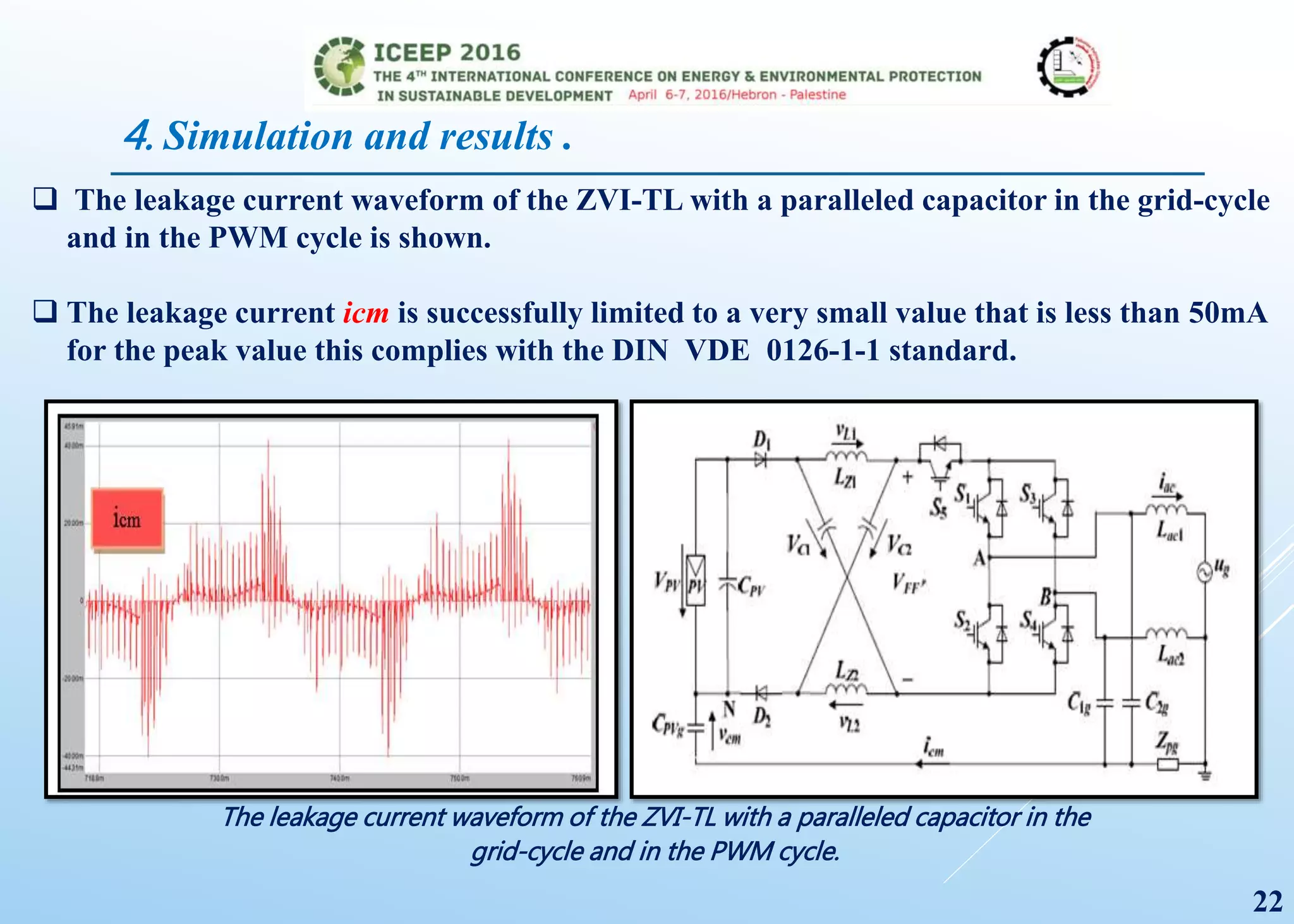
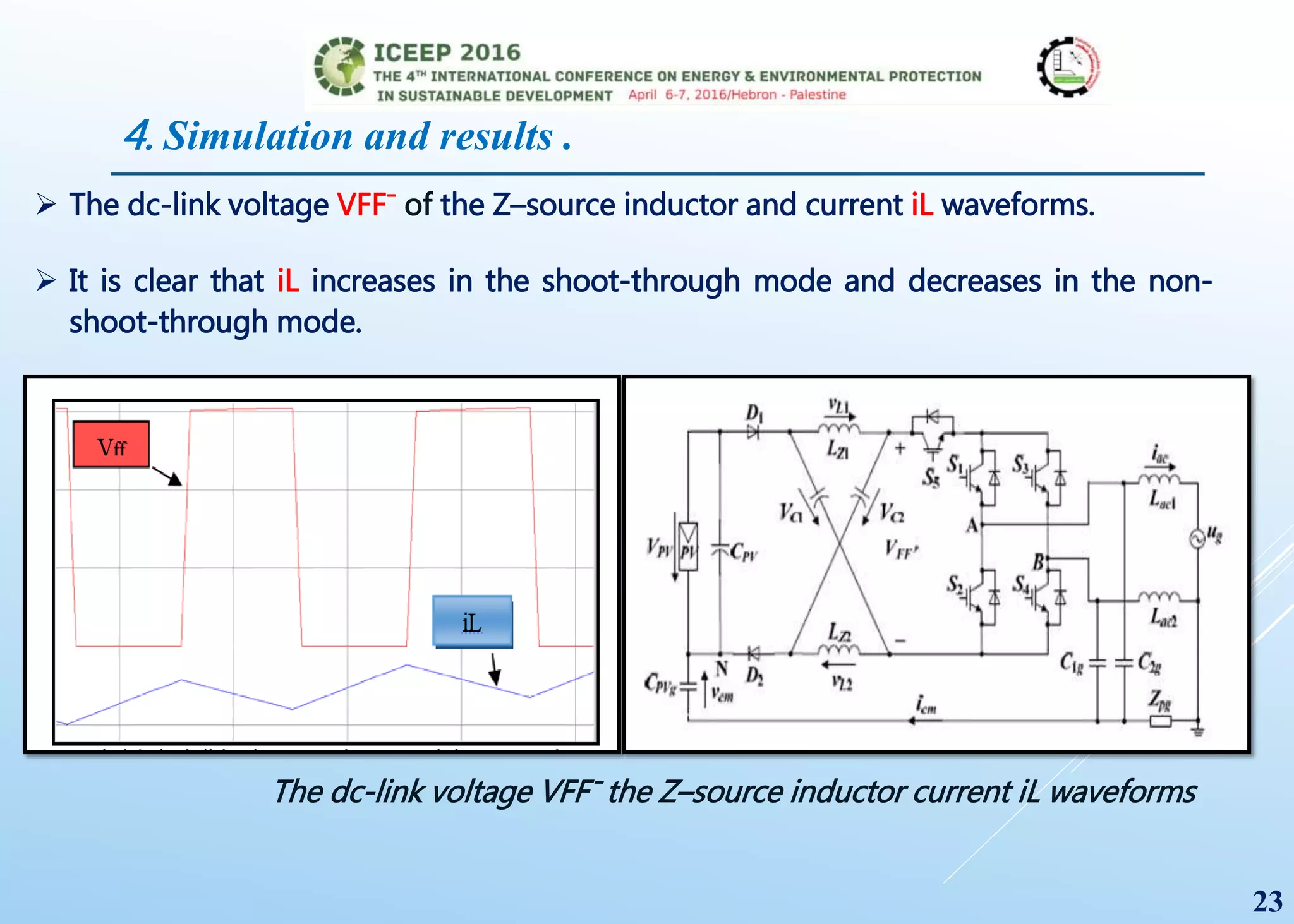
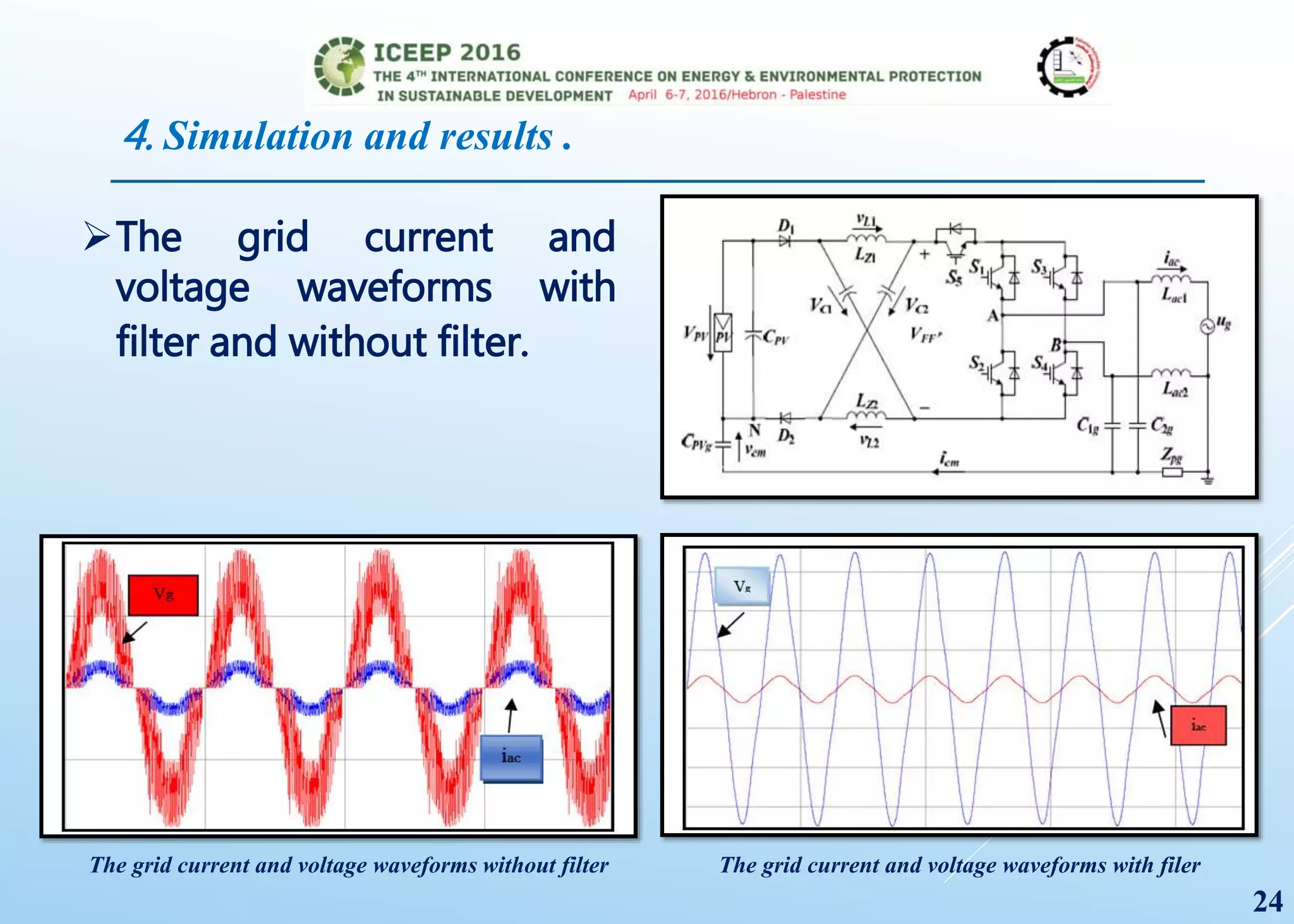
The document presents a detailed study on a modified transformerless z-source inverter topology for photovoltaic grid-connected systems. It discusses the operational principles, modified PWM strategy, and leakage current analysis, demonstrating improvements in efficiency and reduced leakage current. Simulation results validate the performance of the proposed inverter design, highlighting its advantages in terms of reliability and reduced distortion.