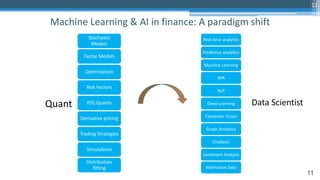
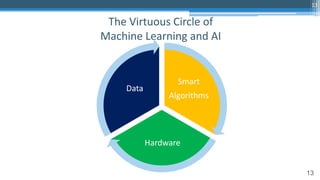
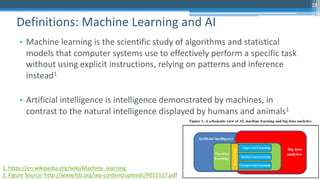
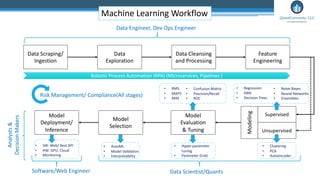
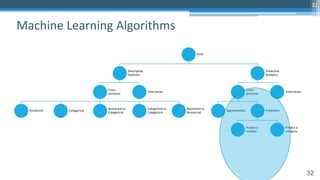
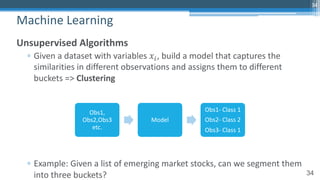
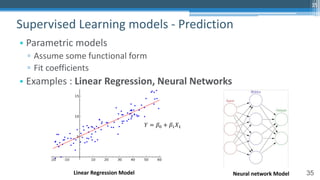
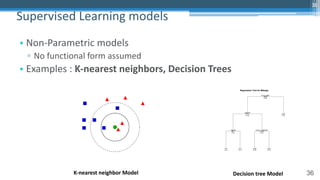
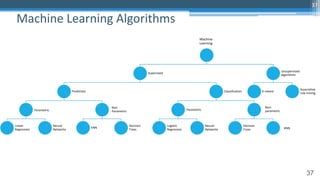
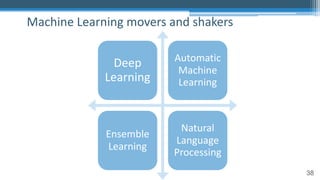
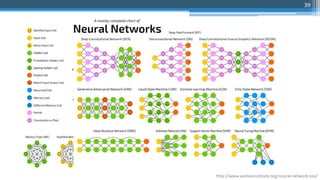
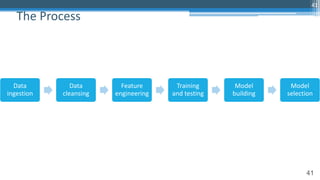
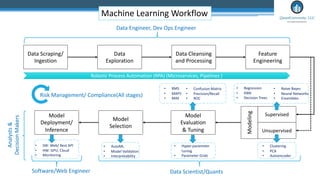
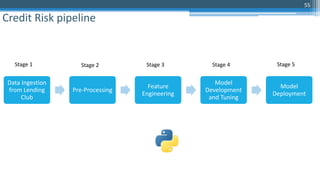
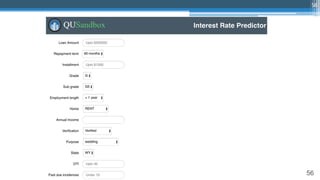
This document outlines an agenda for a master class on AI and machine learning for financial professionals presented by Sri Krishnamurthy. The speaker bio introduces Sri as an experienced financial analyst and consultant who has taught at several universities. The agenda includes an overview of key trends in AI and machine learning, a machine learning primer, and case studies. The document provides background on QuantUniversity and concludes by thanking attendees.